Professional Documents
Culture Documents
HIV/AIDS Concept Map
Uploaded by
Aira AgolongOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
HIV/AIDS Concept Map
Uploaded by
Aira AgolongCopyright:
Available Formats
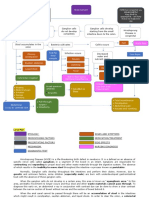
HIV/AIDS CONCEPT MAP
RISK FACTORS
Laboratory Test for HIV Age
HIV stands for human immunodeficiency Race
ELISA test virus. It harms the immune system by Sex
Western Blot test Have an unprotected sex
destroying a type of white blood cell that
Saliva test Have an STI ( sexually
helps your body fight infection. If left
Viral load test transmitted disease)
untreated, HIV can lead to a disease called
Home test Used IV drugs
AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency disease
syndrome).
SIGNS AND SYMPTOMS
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY Recuring fever or profuse
PREVENTION night sweats
Exposure to infected body fluids Extreme and unexplained
Use treatment as tiredness
prevention Rapid weight loss
Use a clean needle Infection w/ HIV retrovirus Fungal infections of the
If you’re pregnant get mouth, fingernails, anus
medical care right away HIV invades nucleus of Helper T and toes
Use post-exposure lymphocytes (CD4 surface antigen) Diarrhea that lasts for
prophylaxis (PEP) if you’ve more than a week
been expose to HIV Swollen glands in armpits
Use condom every timw Destruction of T lymphocytes Helper T cell Immune suprresion AIDS neck or groin
you have sex
Tell your sexual partners if COMPLICATIONS
you have HIV Nursing Management
Kidney disease
Wasting syndrome
Independent Nursing Management Dependent Nursing Management Liver disease
Neurological complications
>Improve skin integrity > Improve Airway Clearance >Non-nucleoside Reverse Transcriptase Inhibitors Lymphoma
>Improve activity intolerance >Relieve pain and discomfort >Protease inhibitors (Pis) >Integrase Inhibitors Candidiasis (thrush)
>Promote skin integrity >Prevent infection >Fusion Inhibitors >gp120 Attachment Inhibitor
Cytomegalovirus
> Promote usual bowel patterns >CCR5 Antagonist
You might also like
- Comcogtable 3 Summary All TestsDocument17 pagesComcogtable 3 Summary All TestsanamariapobleteNo ratings yet
- Medical Record FormDocument4 pagesMedical Record FormДария КоваленкоNo ratings yet
- National HIV Prevention Program ExplainedDocument39 pagesNational HIV Prevention Program ExplainedR'mon Ian Castro SantosNo ratings yet
- Concept Mapping - Liver CirrhosisDocument3 pagesConcept Mapping - Liver CirrhosisJoanna Mae MovidoNo ratings yet
- Vascular Surgery MedCosmos Surgery - MCQDocument34 pagesVascular Surgery MedCosmos Surgery - MCQMike GNo ratings yet
- History of Past IllnessDocument4 pagesHistory of Past IllnesspachichoyNo ratings yet
- Hirschsprung Disease: A Congenital Birth Defect of the IntestinesDocument3 pagesHirschsprung Disease: A Congenital Birth Defect of the IntestinesJan Rae Barnatia AtienzaNo ratings yet
- PA Jennifer PaglingayenDocument27 pagesPA Jennifer PaglingayenJm PecadizoNo ratings yet
- Performing An A-G Patient Assessment: A Step-By-Step GuideDocument3 pagesPerforming An A-G Patient Assessment: A Step-By-Step GuidenasimhsNo ratings yet
- NCP Imapired Skin IntegrityDocument5 pagesNCP Imapired Skin IntegrityAno BaItoNo ratings yet
- 2017 April Exam CompilationDocument8 pages2017 April Exam CompilationabbasyaqobiNo ratings yet
- Mental Health Week 4, Cognition Performance Exit Final ScoreDocument100 pagesMental Health Week 4, Cognition Performance Exit Final ScoreNadia LoveNo ratings yet
- Cellular AberrationsDocument94 pagesCellular AberrationsKatherineCentenoIlaganRNNo ratings yet
- 2.1 Medical Surgical Nursing - I Papers QPDocument15 pages2.1 Medical Surgical Nursing - I Papers QPAnju KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 2Document2 pagesNursing Care Plan 2Isabel Barredo Del MundoNo ratings yet
- The Effectiveness of Muntingia calabura Leaves as a Natural Mosquito RepellentDocument8 pagesThe Effectiveness of Muntingia calabura Leaves as a Natural Mosquito RepellentAira Agolong100% (2)
- Pediatric Rashes GuideDocument33 pagesPediatric Rashes GuideEskilda LucildaNo ratings yet
- MMMHMC-N-QP-022-FORM 1 REV.0 Intravenous Fluid Flow Sheet Template < 40 charsDocument1 pageMMMHMC-N-QP-022-FORM 1 REV.0 Intravenous Fluid Flow Sheet Template < 40 charsWyn AgustinNo ratings yet
- Ovarian Cyst Case StudyDocument18 pagesOvarian Cyst Case Studyrobertson_qt18100% (2)
- Ovarian Cyst Case StudyDocument18 pagesOvarian Cyst Case Studyrobertson_qt18100% (2)
- Ineffective Health MaintenanceDocument6 pagesIneffective Health MaintenanceRYAN SAPLADNo ratings yet
- NCP Infection NewDocument3 pagesNCP Infection NewXerxes DejitoNo ratings yet
- Nursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis A PDFDocument2 pagesNursingcrib Com NURSING CARE PLAN Hepatitis A PDFswapnilazarusNo ratings yet
- Hizon 2 NCP 1 Npi I Am SamDocument5 pagesHizon 2 NCP 1 Npi I Am SamDan HizonNo ratings yet
- Ncp-Impaired Verbal CommunicationDocument4 pagesNcp-Impaired Verbal CommunicationEzra TuanNo ratings yet
- Aaa Gastrectomy NCP FinalDocument13 pagesAaa Gastrectomy NCP Finallexzaf100% (1)
- Goboy - Risk For Infection NCPDocument3 pagesGoboy - Risk For Infection NCPLouise GermaineNo ratings yet
- Tarasoff CaseDocument2 pagesTarasoff Casealyssa marie salcedo100% (1)
- Chest Tube Reflective EssayDocument2 pagesChest Tube Reflective EssayAnjae GariandoNo ratings yet
- NCP FoodDocument1 pageNCP FoodAdrian ArdamilNo ratings yet
- Post Open Reduction Internal Fixation PathophysiologyDocument3 pagesPost Open Reduction Internal Fixation PathophysiologyRizalyn QuindipanNo ratings yet
- NURSING CARE PLAN Dog Bite InjuryDocument3 pagesNURSING CARE PLAN Dog Bite Injurykarrey danielNo ratings yet
- Hemophilia N C P BY BHERU LALDocument1 pageHemophilia N C P BY BHERU LALBheru LalNo ratings yet
- NCP Readiness RevisionDocument3 pagesNCP Readiness RevisionimnasNo ratings yet
- Melinda Jaffe Is A 28Document1 pageMelinda Jaffe Is A 28coosa liquorsNo ratings yet
- Assessment Dianosis Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Dianosis Planning Intervention Rationale Evaluationkyaw100% (1)
- Impaired Tissue Integrity BurnDocument1 pageImpaired Tissue Integrity BurntabaloveNo ratings yet
- Improve Home Ventilation for Family HealthDocument2 pagesImprove Home Ventilation for Family HealthNathanyel Leigh MongosoNo ratings yet
- Risk For Disproportionate GrowthDocument8 pagesRisk For Disproportionate GrowthRahajeng Intan HandayaniNo ratings yet
- N P I Sa M PleDocument1 pageN P I Sa M PleSkyeNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care Plan - Cough and ColdsDocument1 pageFamily Nursing Care Plan - Cough and ColdsArnx QuilonNo ratings yet
- NCP Blurred VisionDocument3 pagesNCP Blurred Visionناديه المعمريNo ratings yet
- NCP Self Care DeficitDocument3 pagesNCP Self Care DeficitLeizel ApolonioNo ratings yet
- FNCPDocument3 pagesFNCPDarcey NicholeNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan for Breast CancerDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan for Breast CancerMaina BarmanNo ratings yet
- NCP - Impaired Urinary EliminationDocument3 pagesNCP - Impaired Urinary EliminationFretzgine Lou ManuelNo ratings yet
- Moral Principles ExerciseDocument1 pageMoral Principles ExerciseGerome Isaiah RabangNo ratings yet
- FNCPDocument6 pagesFNCPCheska YsabelleNo ratings yet
- Cefipime HCL (AXERA)Document2 pagesCefipime HCL (AXERA)Kristine YoungNo ratings yet
- 10 Herbal Medicines Approved by DOH for Various AilmentsDocument10 pages10 Herbal Medicines Approved by DOH for Various AilmentsMark Cruze100% (1)
- Prenatal Care Common Discomforts During PregnancyDocument5 pagesPrenatal Care Common Discomforts During PregnancyKarina MadriagaNo ratings yet
- Cutaneous Anthrax Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesCutaneous Anthrax Nursing Care PlanYayin Pestaño100% (1)
- NCP Ch31 p991-992Document2 pagesNCP Ch31 p991-992Ala'a Abd Mansor100% (2)
- Interview Guide For Nursing Health HistoryDocument3 pagesInterview Guide For Nursing Health HistoryDersly LaneNo ratings yet
- Family NCPDocument3 pagesFamily NCPmarohunk50% (2)
- Deficient KnowledgeDocument3 pagesDeficient KnowledgeCamilleAnneRoseRabinoNo ratings yet
- Planning: NCP #1 Chronic Pain Related To Compression of Spinal Nerves As Evidenced byDocument10 pagesPlanning: NCP #1 Chronic Pain Related To Compression of Spinal Nerves As Evidenced byNicole Anne TungolNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Airway Clearance - PTBDocument2 pagesIneffective Airway Clearance - PTBIrish Eunice FelixNo ratings yet
- Balance Skeletal TractionDocument5 pagesBalance Skeletal TractionRachel Ann JimenezNo ratings yet
- HEALTH-TEACHING (Safety)Document3 pagesHEALTH-TEACHING (Safety)Asterlyn ConiendoNo ratings yet
- Health-Perception-Health-Management PatternDocument3 pagesHealth-Perception-Health-Management PatternBela MillenaNo ratings yet
- NCP Leptospirosis - NewDocument5 pagesNCP Leptospirosis - Newglaiza_requintoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationlaehaaaNo ratings yet
- Novilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNovilyn C. Pataray BSN - Ii: Assessment Diagnosi S Pathophysiolog Y Planning Interevention Rationale EvaluationCharina AubreyNo ratings yet
- Reflective Essay-Rexson A. DalanginDocument3 pagesReflective Essay-Rexson A. DalanginRexson Alcantara DalanginNo ratings yet
- HIV and Aids: HIV Is A Virus That InfectsDocument1 pageHIV and Aids: HIV Is A Virus That InfectsryanNo ratings yet
- Medical Technology and Bioethics Exploring HIV and AIDSDocument2 pagesMedical Technology and Bioethics Exploring HIV and AIDSEmman QuiopaNo ratings yet
- How To Know The Signs & Symptoms of Aids?: How Is HIV Transmitted??Document2 pagesHow To Know The Signs & Symptoms of Aids?: How Is HIV Transmitted??Santika WidyaNo ratings yet
- Hiv Aids: Human Immunodeficiency Virus H Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome ADocument6 pagesHiv Aids: Human Immunodeficiency Virus H Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome AMaryGraceVelascoFuentesNo ratings yet
- HIV/AIDs Biology Fact SheetDocument4 pagesHIV/AIDs Biology Fact Sheetraahmed2020ahNo ratings yet
- What Is HIV?Document10 pagesWhat Is HIV?MarryRose Dela Torre FerrancoNo ratings yet
- The Problem and Its ScopeDocument51 pagesThe Problem and Its ScopeAira AgolongNo ratings yet
- REQ - PneumoniaDocument6 pagesREQ - PneumoniaAira AgolongNo ratings yet
- February 23Document2 pagesFebruary 23Aira AgolongNo ratings yet
- February 23Document2 pagesFebruary 23Aira AgolongNo ratings yet
- Sleep Quality & Academic Performance Among Nursing StudentsDocument2 pagesSleep Quality & Academic Performance Among Nursing StudentsAira AgolongNo ratings yet
- Enrollment FormDocument1 pageEnrollment FormAira AgolongNo ratings yet
- Certification From The AdviserDocument4 pagesCertification From The AdviserAira AgolongNo ratings yet
- The Problem and Its ScopeDocument51 pagesThe Problem and Its ScopeAira AgolongNo ratings yet
- DirectionsDocument3 pagesDirectionsAira AgolongNo ratings yet
- ReferencesDocument4 pagesReferencesAira AgolongNo ratings yet
- AnnotatedDocument10 pagesAnnotatedAira AgolongNo ratings yet
- ImmuneDocument1 pageImmuneAira AgolongNo ratings yet
- Activity 1: Enumerate and Discuss The Phases in Community OrganizationDocument1 pageActivity 1: Enumerate and Discuss The Phases in Community OrganizationAira AgolongNo ratings yet
- Parameter Result Unit Reference Range: WBC Neu% Lym% Mon% Eos% Bas% RBC% HGB HCT MCV MCH MCHC RDW-CVDocument2 pagesParameter Result Unit Reference Range: WBC Neu% Lym% Mon% Eos% Bas% RBC% HGB HCT MCV MCH MCHC RDW-CVAira AgolongNo ratings yet
- Closetmaid 6105440 Spacecreations 50"-121" Classic Closet KitDocument3 pagesClosetmaid 6105440 Spacecreations 50"-121" Classic Closet KitAira AgolongNo ratings yet
- 1Document1 page1Aira AgolongNo ratings yet
- Closetmaid 6105440 Spacecreations 50"-121" Classic Closet KitDocument3 pagesClosetmaid 6105440 Spacecreations 50"-121" Classic Closet KitAira AgolongNo ratings yet
- DirectionsDocument3 pagesDirectionsAira AgolongNo ratings yet
- Attention !!: Missing Puppies Dark Brown and Black Nawala 2 Ka Itoy (Dark Brown and Black)Document1 pageAttention !!: Missing Puppies Dark Brown and Black Nawala 2 Ka Itoy (Dark Brown and Black)Aira AgolongNo ratings yet
- Republic of The Philippines: Jose Rizal Memorial State UniversityDocument39 pagesRepublic of The Philippines: Jose Rizal Memorial State UniversityAira AgolongNo ratings yet
- Pathway, Show The Major Pathway of CSF Flow. Beginning in The Lateral Ventricles, CSF FlowsDocument2 pagesPathway, Show The Major Pathway of CSF Flow. Beginning in The Lateral Ventricles, CSF FlowsMary Scarlette CenaNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Commercially Available Anti–Dengue Virus IgM TestsDocument5 pagesEvaluation of Commercially Available Anti–Dengue Virus IgM TestsAndri YansyahNo ratings yet
- An Update On The Pathogenesis of Hashimoto's Thyroiditis: A. P. WeetmanDocument8 pagesAn Update On The Pathogenesis of Hashimoto's Thyroiditis: A. P. WeetmanMauricio VidalNo ratings yet
- Dafus AgasDocument2 pagesDafus AgasHerawati YustikasariNo ratings yet
- Clinical Management of Injured Birds-of-PreyDocument9 pagesClinical Management of Injured Birds-of-PreyLjón BjörnNo ratings yet
- History Taking in DermatologyDocument2 pagesHistory Taking in DermatologyMizrab NadeemNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Catheter RelatedDocument3 pagesPrevention of Catheter Relatednoviyanti christiana100% (1)
- 77.18 Shen Guan and Three Emperors - Master Kidney PointDocument3 pages77.18 Shen Guan and Three Emperors - Master Kidney Pointalbar ismuNo ratings yet
- Personal Hygiene and Health Care - Social and PreventiveDocument37 pagesPersonal Hygiene and Health Care - Social and Preventiveanubhav thakurNo ratings yet
- CARDIOVASCULAR EXAMINATION Human DiseaseDocument4 pagesCARDIOVASCULAR EXAMINATION Human DiseaseVictoria MedfordNo ratings yet
- Staphylococcus Aureus PhisiologyDocument21 pagesStaphylococcus Aureus PhisiologyJohann MuñozNo ratings yet
- Social Medicine Topic 1Document4 pagesSocial Medicine Topic 1SheikhNo ratings yet
- Indian Gooseberry Collyrium Effective for Ulcerative BlepharitisDocument13 pagesIndian Gooseberry Collyrium Effective for Ulcerative Blepharitissitiatikah65No ratings yet
- Fang-Cinnarizine DSDocument2 pagesFang-Cinnarizine DSlowell cerezoNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Disease-Specific and Generic Diagnostic Pitfalls A Qualitative StudyDocument11 pagesCharacteristics of Disease-Specific and Generic Diagnostic Pitfalls A Qualitative StudyMahmoud AbouelsoudNo ratings yet
- Legg Calvé Perthes DiseaseDocument19 pagesLegg Calvé Perthes DiseaseFranklin Pito JellaNo ratings yet
- Epidemiology: Chapter 1: IntroductionDocument134 pagesEpidemiology: Chapter 1: IntroductionLoai Mohammed IssaNo ratings yet
- PBL Tutor - (Student) GuideDocument6 pagesPBL Tutor - (Student) GuidedellangelaNo ratings yet
- The de Ritis Ratio: The Test of TimeDocument14 pagesThe de Ritis Ratio: The Test of TimeMike NundweNo ratings yet
- Prelim Examination MaternalDocument23 pagesPrelim Examination MaternalAaron ConstantinoNo ratings yet
- Demncia Frontotemporal ContinumDocument25 pagesDemncia Frontotemporal ContinumcositaamorNo ratings yet
- The Minamata Incident: by Tom CunninghamDocument16 pagesThe Minamata Incident: by Tom CunninghamTom CunninghamNo ratings yet