Professional Documents
Culture Documents
09 Carbohydrate Metabolism
Uploaded by
scuderia ferrari0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 pageiasm
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Documentiasm
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
14 views1 page09 Carbohydrate Metabolism
Uploaded by
scuderia ferrariiasm
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
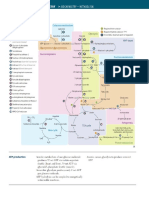
CHK L09 TCA + Carbohydrate Metabolism
上學習 quizlet.com/_5f61kz
1. Five uses of glucose Metabolism
Fat synthesis (storage)
Amino acid synthesis
Glycoconjugate
Pentose phosphate pathway
2. Four pathways where G6P is the common molecule Glycolysis
Gluconeogenesis
Glycogenesis
Pentose phosphate pathway
3. Citrate (6C) Isocitrate (6C)
4. Isocitrate (6C) ∝-ketogluturate (5C)
5. ∝-ketoglutarate (5C) Succinyl CoA (4C)
6. Succinyl CoA (4C) Succinate (4C)
7. Succinate (4C) Fumarate (4C)
8. Fumarate (4C) Malate (4C)
9. Malate (4C) Oxaloacetate (4C)
10. Oxaloacetate (4C) Citrate (6C)
11. Link reaction: enzyme Pyruvate dehydrogenase
12. Pentose Phosphate Pathway (PPP): products - NADPH
- Pentose Phosphate
- ATP
13. PPP: two main enzymes (in the nonoxidative - Transketolase
reactions) - Transaldolase
14. NADPH: function Reducing agent to prevent oxidative species damage
15. Pentose phosphate: example Ribose 5' phosphate
16. Pentose phosphate: function Precursor for nucleotides
17. Intermediate for glucose entering PPP G6P
18. Outline synthesis of amino acids and fats from Glucose --> citrate (in mitochondria) --> transported out --> cleaved to form
glucose acetyl group + oxaloacetate
19. Glucoconjugates (3) UDP-glucose
UDP-glucuronate
UDP-galactose
20. UDP-glucose: function Glycogen synthesis
21. Give examples of things that UDP- Glycoproteins
glucuronate/galactose is used to make Proteoglycans
Glycolipids
Glucuronides (glucuronate)
You might also like
- BIOCHEMISTRY - Summary of PathwaysDocument8 pagesBIOCHEMISTRY - Summary of PathwaysWendy Mae100% (9)
- PLE 2019 - Biochem Questions and Answer KeyDocument21 pagesPLE 2019 - Biochem Questions and Answer Keydickson65% (17)
- Uric Acid MetabolismDocument3 pagesUric Acid MetabolismAlifah SyarafinaNo ratings yet
- 1M. 2 - Biochemistry - Glycolysis and KrebsDocument4 pages1M. 2 - Biochemistry - Glycolysis and KrebsKate Lynne Camonayan100% (1)
- Group 5 - Aerobic Cellular RespirationDocument5 pagesGroup 5 - Aerobic Cellular Respirationditucalan.ha2003No ratings yet
- Summary of Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationDocument1 pageSummary of Photosynthesis and Cellular RespirationMariser ReyesNo ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis + Evaluations 4/23/2003Document30 pagesGluconeogenesis + Evaluations 4/23/2003Ajay Pal NattNo ratings yet
- BIOCHEM (Glucogeniosis)Document30 pagesBIOCHEM (Glucogeniosis)Kara Kristine Tuano NarismaNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism Catabolism Blok 7 2018Document136 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism Catabolism Blok 7 2018N A Anggriani WulandariNo ratings yet
- ' Biochemistry ' Biochemistry-Metabolism Section Ii: Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative PhosphorylationDocument10 pages' Biochemistry ' Biochemistry-Metabolism Section Ii: Electron Transport Chain and Oxidative Phosphorylationgksah711No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism 1Document22 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism 1Affie SaikolNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis 3MDDocument48 pagesGlycolysis 3MDgostrider0093sNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Complete Notes (B.pharm 2nd Sem)Document25 pagesCarbohydrate Complete Notes (B.pharm 2nd Sem)DIPENDRA KUMAR KUSHAWAHANo ratings yet
- Asy GlycolysisDocument69 pagesAsy GlycolysisErdem AltunNo ratings yet
- Pathway Glycolysis TCA Cycle Gluconeogenesis What Is It For?Document2 pagesPathway Glycolysis TCA Cycle Gluconeogenesis What Is It For?Rosel Ann BontiaNo ratings yet
- Purines Pyrimidines: de Novo Pyrimidine and Purine SynthesisDocument44 pagesPurines Pyrimidines: de Novo Pyrimidine and Purine SynthesisKimber ManiulitNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis GluconeogenesisDocument66 pagesGlycolysis GluconeogenesisRahmad AllulNo ratings yet
- Lect # 3 GluconeogenesisDocument40 pagesLect # 3 GluconeogenesisUbaid ur Rahman100% (1)
- Major Metabolic PathwaysDocument23 pagesMajor Metabolic PathwaysgianelleNo ratings yet
- 11 - Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument68 pages11 - Carbohydrate MetabolismcheckmateNo ratings yet
- 7 HMP Shunt Pathway RO PDF v1Document9 pages7 HMP Shunt Pathway RO PDF v1Radwa MohamedNo ratings yet
- 2 GlycolysisDocument41 pages2 Glycolysislou765500No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism: By:-Dr - Priyanka Sharma 1 Year MDS Dept. of Public Health DentistryDocument93 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism: By:-Dr - Priyanka Sharma 1 Year MDS Dept. of Public Health DentistrySimham Venu0% (1)
- (ENDOCRINE) Tugas Biochemistry Week 2 Jeremy Evans Darmawan 01071180101Document4 pages(ENDOCRINE) Tugas Biochemistry Week 2 Jeremy Evans Darmawan 01071180101Jeremy EvansNo ratings yet
- Curs GluconeogenesisDocument25 pagesCurs GluconeogenesisOnofrei MariaNo ratings yet
- 10 Cell MetabolismDocument11 pages10 Cell Metabolismecon finaNo ratings yet
- Substrates&EnzymesDocument15 pagesSubstrates&EnzymesTanyaTouchéNo ratings yet
- CarbohydrateDocument30 pagesCarbohydrateisma rizkyNo ratings yet
- Microbial MetabolismDocument49 pagesMicrobial MetabolismOmelNo ratings yet
- Gluconeogenesis 2Document2 pagesGluconeogenesis 2Nikhitha NunnaNo ratings yet
- Summary of PathwaysDocument1 pageSummary of Pathwaysayan100% (1)
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument7 pagesCarbohydrate MetabolismGianneCarloGomedNo ratings yet
- Metabolism Poster AssignmentDocument6 pagesMetabolism Poster AssignmentMuhammad Najam AbbasNo ratings yet
- Metabolism Poster AssignmentDocument6 pagesMetabolism Poster AssignmentMuhammad Najam AbbasNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Metabolism: NotesDocument15 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism: Notesarmin509No ratings yet
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument8 pagesCarbohydrate MetabolismMakilan CharleneNo ratings yet
- 10 GluconeogenesisDocument18 pages10 GluconeogenesiskulturewearzmNo ratings yet
- Harpers 20Document9 pagesHarpers 20Dewi RatnasariNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis and Gluconeogenesis: Instructor-RclDocument33 pagesGlycolysis and Gluconeogenesis: Instructor-RclPrince Kyle R. DolosoNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis J FermentationDocument14 pagesGlycolysis J FermentationBONAVENTURA ALVINO DESMONDANo ratings yet
- Return To The Medical Biochemistry Page: SearchDocument13 pagesReturn To The Medical Biochemistry Page: SearchMUHAMMAD RIDONo ratings yet
- GluconeogenesisDocument31 pagesGluconeogenesisRajakannanNo ratings yet
- Colegio de San Juan de LetranDocument9 pagesColegio de San Juan de Letranking untalanNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument19 pagesBiochemistry: Carbohydrate MetabolismALINo ratings yet
- 8 Vias Utilizacion GlucosDocument35 pages8 Vias Utilizacion GlucosHéctor GalvánNo ratings yet
- Bioc192 2018 s2Document30 pagesBioc192 2018 s2Joel CatlettNo ratings yet
- Carbohydratemetabolism 140214034339 Phpapp01Document93 pagesCarbohydratemetabolism 140214034339 Phpapp01yixecix709No ratings yet
- Bio LectureDocument38 pagesBio LectureDaniel ZederNo ratings yet
- Irreversible Steps (1, 3, 10) With 3 As Rate-Limiting/committed StepDocument1 pageIrreversible Steps (1, 3, 10) With 3 As Rate-Limiting/committed StepMiaoNo ratings yet
- 1st Half of Glycolysis To Kreb CycleDocument2 pages1st Half of Glycolysis To Kreb CycleDoreen Shane CabigonNo ratings yet
- Slides GlicóliseDocument10 pagesSlides GlicóliseTãhsìn Ãhsäñ SãrkãrNo ratings yet
- Glycolysis-Gluconeogenesis-Pentose Phosphate-Krebs Cycle Cristhian Camilo Lozano FernandezDocument4 pagesGlycolysis-Gluconeogenesis-Pentose Phosphate-Krebs Cycle Cristhian Camilo Lozano FernandezCristhian LozanoNo ratings yet
- METABOLISMDocument11 pagesMETABOLISMking untalanNo ratings yet
- Carbo ChemDocument123 pagesCarbo ChemHan MichelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18 - Nucleotide Metabolism: Nucleotides Are Composed of Three ComponentsDocument5 pagesChapter 18 - Nucleotide Metabolism: Nucleotides Are Composed of Three ComponentsSaiful IslamNo ratings yet
- Define GlycolysisDocument3 pagesDefine GlycolysisjhanensuarezNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate MetabolismDocument72 pagesCarbohydrate MetabolismJeffson BalmoresNo ratings yet
- GlycolysisDocument29 pagesGlycolysisAtif Amin BaigNo ratings yet
- Rate Limiting Step PDFDocument1 pageRate Limiting Step PDFCoy NuñezNo ratings yet
- Vías Centrales Del Metabolismo de Los CarbohidratosDocument35 pagesVías Centrales Del Metabolismo de Los CarbohidratosfreddyNo ratings yet
- Hexose Monophosphate ShuntDocument38 pagesHexose Monophosphate ShuntKausik SenNo ratings yet
- Enzymes Involved in Glycolysis, Fatty Acid and Amino Acid Biosynthesis: Active Site Mechanisms and InhibitionFrom EverandEnzymes Involved in Glycolysis, Fatty Acid and Amino Acid Biosynthesis: Active Site Mechanisms and InhibitionNo ratings yet
- 06 LipidsDocument1 page06 Lipidsscuderia ferrariNo ratings yet
- 04 From Protein Structure To Protein FunctionDocument1 page04 From Protein Structure To Protein Functionscuderia ferrariNo ratings yet
- 07 Structure of CellDocument1 page07 Structure of Cellscuderia ferrariNo ratings yet
- 05 EnzymesDocument1 page05 Enzymesscuderia ferrariNo ratings yet
- 02 From DNA To ProteinDocument1 page02 From DNA To Proteinscuderia ferrariNo ratings yet
- Biomolecules: Pre-Medical: Biology AllenDocument12 pagesBiomolecules: Pre-Medical: Biology AllenAnupamNo ratings yet
- Nucleotide Metabolism PPDocument65 pagesNucleotide Metabolism PPCLEMENTNo ratings yet
- მიტოქონდრიის ფუნქცია და კიბოDocument1 pageმიტოქონდრიის ფუნქცია და კიბოEMD GROUPNo ratings yet
- Glutamic Acid Application For Enhancement of GrowtDocument8 pagesGlutamic Acid Application For Enhancement of GrowtJhe Hann BurcaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry MCQ PDFDocument11 pagesBiochemistry MCQ PDFjfjfjfNo ratings yet
- A Review On The Improvement of SteviaDocument27 pagesA Review On The Improvement of SteviaGeorge ChoisNo ratings yet
- Nutritional Requirements of BacteriaDocument25 pagesNutritional Requirements of BacteriaAira MiyaNo ratings yet
- Biochem Task 9 BocalanbethinnaDocument4 pagesBiochem Task 9 BocalanbethinnaANA MARIA BETHINNA BOCALANNo ratings yet
- MCQS On Protein Metabolism BY Siraj Ul IslamDocument12 pagesMCQS On Protein Metabolism BY Siraj Ul Islamsirajkhan93100% (2)
- XL S8 2016 P (Gate2016.info)Document28 pagesXL S8 2016 P (Gate2016.info)jaya2504No ratings yet
- Genetic Control of Cell Function PDFDocument14 pagesGenetic Control of Cell Function PDFEDGAR A. SERVINNo ratings yet
- Smith Ch27 Lecture Edit-AMINOACIDOS 6TADocument85 pagesSmith Ch27 Lecture Edit-AMINOACIDOS 6TAfabiana perez ruizNo ratings yet
- SericultureDocument39 pagesSericultureAKSHATA PATILNo ratings yet
- Science Reviewer Q3 G10Document4 pagesScience Reviewer Q3 G10Jenny Ann SantosNo ratings yet
- SOPs For AdmissionDocument19 pagesSOPs For AdmissionHafiza AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Fiza Ribosome PPT Zoology 1 SemDocument21 pagesFiza Ribosome PPT Zoology 1 SemSiddharth BirlaNo ratings yet
- Q Bank Biochemistry: Every Chapter Every Important Question Marks DistributionDocument25 pagesQ Bank Biochemistry: Every Chapter Every Important Question Marks DistributionHK Nova Chiu100% (1)
- Proteins and Amino Acids: Function Follows FormDocument23 pagesProteins and Amino Acids: Function Follows FormbobNo ratings yet
- A World That Stay Normally Hidden From Our Eyes But Matter A Lot To UsDocument11 pagesA World That Stay Normally Hidden From Our Eyes But Matter A Lot To UsVîñàý PãtêlNo ratings yet
- Pancreatic Cancer MetabolismDocument36 pagesPancreatic Cancer MetabolismShivaprakash Jagalur MuttNo ratings yet
- Academic Handbook 0Document386 pagesAcademic Handbook 0Steven BatuboNo ratings yet
- Test Bank For Molecular Diagnostics Fundamentals Methods and Clinical Applications 1st Edition BuckinghamDocument36 pagesTest Bank For Molecular Diagnostics Fundamentals Methods and Clinical Applications 1st Edition Buckinghambullfrog.cayman.z05o100% (33)
- Central DogmaDocument35 pagesCentral Dogmatariqul13017No ratings yet
- Respiration and Lipid Metabolism - SummaryDocument3 pagesRespiration and Lipid Metabolism - SummaryxprakashNo ratings yet
- Inorg Biochem RandomnotesDocument20 pagesInorg Biochem RandomnotesDianne VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- General Genetics Notes With DR ChandleeDocument36 pagesGeneral Genetics Notes With DR ChandleeVenice CariñoNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid MetabolismDocument23 pagesAmino Acid MetabolismZ ZNo ratings yet