Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Festo Manipuladorses DHSL-6 - en
Uploaded by
Flávio leme da SilvaOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Festo Manipuladorses DHSL-6 - en
Uploaded by
Flávio leme da SilvaCopyright:
Available Formats
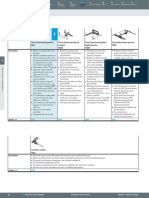
Linear gantries
Movements in 2D:
a linear gantry consists of a
gantry axis and a yoke drive.
• High mechanical rigidity and
sturdy design
• Pneumatic and electrical com-
ponents – freely combinable
• As electrical solution – variable
positioning/any desired inter-
mediate positions
Range of application:
• Ideal for long gantry strokes
• Often used for feeding
applications
• Workpiece masses up to 5 kg
(effective load up to 10 kg)
• Long gantry strokes up to 3 m
and heavy loads up to 10 kg
• High requirements on system
resistance to torsion
Example: construction materials Requirements
industry • High dynamic response
Handling, palletising and • Gentle acceleration and
packing of ceramic tiles braking
• Jerk-free movement
• Good positioning flexibility
Solution
• Linear gantry with toothed belt
axes and cantilever axis
• Complete solution, including
vacuum gripper
12 Handling system overview – Subject to change – 2009/09
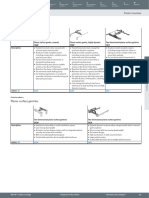
Type Important characteristics Axis design Effective load Max. effective strokes Components
• Linear gantry • High process reliability thanks Y: Mono: Y: Y:
as mono axis to installation integration Gantry axes 0 to 6 kg Up to 5000 mm DGC/EGC
• Free movement • Pneumatic and electric drives Z:
of the Z-axis (with freely programmable Slide Z: Z:
in the vertical positions) Cantilever axis Up to 300 mm DGSL
plane (2D) • Repetition-accurate, cen- EGSA
tralised direct axis connections
• Mini slide on the Z-axis for
maximum precision
• See above • See above, points 1 – 3 Y: Mono: Y: Y:
Gantry axes 0 to 5 kg Up to 5000 mm DGC/EGC
• Pneumatic cantilever axis on Z:
the Z-axis with high repetition Handling axis Z: Z:
accuracy, high dynamic Up to 200 mm HMPL
response and intermediate
positions
• See above • See above, points 1 – 3 Y: Mono: Y: Y:
Gantry axes 0 to 10 kg* Up to 5000 mm DGC/EGC
• Pneumatic handling axis on the Z:
Z-axis with high rigidity and Handling axis Z: Z:
intermediate positions Up to 400 mm HMP
• Linear gantry • See above, points 1 – 3 Y: Mono: Y: Y:
as mono or Gantry axes 0 to 15 kg Up to 5000 mm DGC/EGC
duo axis • Electric cantilever axis on the Z:
• Free movement Z-axis for large strokes, high Cantilever axis Duo: Z: Z:
of the Z-axis in dynamic response and low 0 ... 25 kg Up to 900 mm DGEA
the vertical moving dead weight
plane (2D)
Higher effective loads of up to 50 kg on request * With the pneumatic drive DGC, can be used as duo axis
2009/09 – Subject to change – Handling system overview 13
Standard linear gantry LP 6
Effective load up to 6 kg
Motor controller package on
electric axes
Servo motor: EMMS-AS
Controller: CMMS/P-AS (CMMD)
Technical data
Stroke/mm Intermed. position Repetition accuracy/mm
Z-axis End position Intermediate
position
ZR DGEA-25 0 … 800 Any ± 0.05 ± 0.05
SP EGC-70-BS-KF 0 … 1000 Any ± 0.02 ± 0.02
SP EGSA-60 0 … 300 Any ± 0.01 ± 0.01
SP DNCE-32 with FENG 0 … 400 Any ± 0.02 ± 0.02
ES EGSL-75 0 … 300 Any ± 0.015 ± 0.015
P DGSL-20 0 … 250 – ± 0.01 –
P DFM-25 0 … 400 – Max. 0.05 –
P DNC-32 with FENG 0 … 500 – ± 0.2 –
PS DNCI-32 with FENG 0 … 500 2/any ** <± 0.5 <± 0.5/± 2**
Y-axis
ZR EGC-120-TB-KF *** 0 … 8500 Any ± 0.08 ± 0.08
SP EGC-120-BS-KF *** 0 … 2500 Any ± 0.02 ± 0.02
ZR EGC-HD-160 0 … 5000 Any ± 0.08 ± 0.08
SP EGC-HD-160 0 … 2500 Any ± 0.02 ± 0.02
P DGC-40 **** 0 … 8500 1* ± 0.02 ****** ± 0.02 ******
PS DGCI-40 **** 0 … 2000 2/any** Max. ± 0.4 Max. ± 0.4/± 2
P DGC-25 + FA 0 … 8500 1* ± 0.02 ± 0.02/± 0.1
PS DGCI-25 + FA 0 … 2000 2/any** Max. ± 0.4 Max. ± 0.4/± 2
* More than 1 on request
** 2 with SPC11/CMPX, any with SPC200/CMAX; <± 0.5 mm with SPC11/CMPX/± 2 mm with SPC200/CMAX
*** Max. Z-stroke 600 mm
**** Max. Z-stroke 200 mm
***** With cushioning P1/Y3
****** With shock absorber YSR/YSRW
Grey shading: drive components in the illustration
EGC-HD: available end of 2011
22 Handling Guide – Subject to change – 2010/2011
Reference for cycle times
Note
Z-axis
2,5 Selection matrix
DGEA-25 Types of handling units
2 Pages 6 to 9
Cycle time [s]
EGSA-60
1,5 DNCE-32/FENG
Handling components
EGC-70-BS
1 Page 95
DGSL-20
0,5 DFM-25
Gripping/rotating
DNC-32/FENG Adaptation options
0 EGSL-75 Page 71
0 200 400 600 800
Stroke [mm] Control cabinets
Page 92
Y-axis Frames
Page 78
4,5
4,0
CAD drawings/
3,5
Cycle time [s]
CAD hotline
3,0
EGC-120 2D and 3D drawings
2,5
DGC-40
2,0
1,5 DGCI-40 Tel. +49 (0)711 347-4667
1,0 DGC-25+FA
0,5 DGCI-25+FA Individual project engi-
0,0 neering and cycle time
0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 calculation
Stroke [mm]
Tel. +49 (0)711 347-4381
Fax enquiry
Form
Page 101
Note
An operating pressure of
6 bar is assumed for all
the pneumatic drives
shown here.
2010/2011 – Subject to change – Handling Guide 23
Overview of Festo control products
FED-CEC CPX terminal
Integrated con- CoDeSys controller Motion con-
troller FED-CEC CPX-CEC-C1 troller
CPX-CEC-M1
FED-CEC FED
CAN-Bus CAN-Bus CAN-Bus
SFC-DC MTR-DCI CMMx CMMx SFC-DC MTR-DCI CMMx
Single axis C1: single axis C1: single axis
(point-to-point asynchronous) M1: interpolation M1: interpolation
Maximum number Recommended: 8 axes Recommended: 8 axes Recommended: 8 axes
of possible axes Note: one axis is treated as a Note: one axis is treated as a Note: one axis is treated as a
CANopen node. CANopen node. CANopen node.
128 nodes are possible (as defined 128 nodes are possible (as defined 128 nodes are possible (as defined
by CANopen specifications). by CANopen specifications). by CANopen specifications).
Motion • Point-to-point asynchronous
• Every axis moves with its own pre-defined parameter
• The axes do not reach their end positions at the same time and the path is not defined
• 2.5D interpolation
• PLC Open
Special features Integrated controller Function integration on the CPX valve platform
in a display screen
• CNC editor
• DXF import
• Cam disk editor
Application • Handling systems Path control, bonding,
examples • Pick & place, palletising cutting, handling,
flying saw, cam disk
Programming CoDeSys CoDeSys CoDeSys + Softmotion
environment
2010/2011 – Subject to change – Handling Guide 81
Modular control
CMXR robotic controller
Modular con- Motion controller CMXR-C1 CMXR-C2
troller CECX-C1 CECX-M1 (Basic) (Advanced)
FED
FED Teach-
Panel
CAN-Bus CAN-Bus CAN-Bus CAN-Bus
SFC-DC MTR-DCI CMMx SFC-DC MTR-DCI CMMx CMMx CMMx
Single axis Interpolation Robotics Robotics
(point-to-point asynchronous) (2.5D) (3D) (3D)
Recommended: 8 axes Max. 6 interpolated axes, of which max. 3 basic axes and 1 orientation axis
Note: one axis is treated as a CANopen node. and max. 3 dependent auxiliary axes that are interpolated together with the
128 nodes are possible (as defined by CANopen specifications). kinematics system.
Additional single axes (not interpolat-
ed together with others) can be con-
trolled via the integrated CoDeSys
PLC. Recommended: 16 axes.
3D contour interpolation with an orientation axis for kinematics systems
with up to 4 degrees of freedom.
E.g. 3D gantry with an axis of rotation on the front end.
• 2.5D interpolation CoDeSys control: point-to-point asyn-
• PLC Open chronous
• Powerful PLC • Economical design and configuration with the Festo Configuration Tool (FCT)
• Encoder interface • Simple programming of motions with Festo Teach Language (FTL),
• Interrupt function no specialist expertise required
• Fast clock pulse inputs • Optional teach pendant with 2-channel permission button
• Profibus master • Reduced speed in manual override mode
• Two Canbus masters • Automatic repositioning when continuing interrupted motions
• RS 232/ RS 485-A/422-A • Simple teaching of positions
• Definition of tools, allowing easy use of multiple grippers
• Real orientation axes on the front end
• Integrated kinematics models e.g. for Cartesian systems, tripod,
H- and T-gantries
• CNC editor • Increased flexibility with the inte-
• DXF import grated CoDeSys PLC, e.g. for the
• Cam disk editor integration of vision systems
• Tracking function for applications
involving selecting items from a
conveyor belt
• Speed-independent path switching
points with time compensation,
e.g. for bonding applications
• Complete automation of a cell is
possible
• Handling systems Path control, bonding, cutting, han- Handling, palletising, bonding, Tracking applications such as pro-
• Pick & place, palletising dling, flying saw, cam disk metered dispensing, painting, cutting cessing of moving parts on a convey-
or belt or synchronised kinematics
movement with up to 6D
CoDeSys CoDeSys + Softmotion Festo Teach Language (FTL) FTL + CoDeSys
82 Handling Guide – Subject to change – 2010/2011
You might also like
- ProductOverview 2023 EN-94Document1 pageProductOverview 2023 EN-94Ismail AliNo ratings yet
- ProductOverview 2023 EN-92Document1 pageProductOverview 2023 EN-92Ismail AliNo ratings yet
- Session12 PDFDocument8 pagesSession12 PDFStar SealNo ratings yet
- ProductOverview 2023 EN-93Document1 pageProductOverview 2023 EN-93Ismail AliNo ratings yet
- Liebherr Cranes For Windpower p401 01 E07 2016Document32 pagesLiebherr Cranes For Windpower p401 01 E07 2016Mohit PandeyNo ratings yet
- Eriez Sl08 Lifting Magnets BrochureDocument24 pagesEriez Sl08 Lifting Magnets Brochuredante224No ratings yet
- Jib Crane IntroductionDocument12 pagesJib Crane IntroductionRameez Ali FaridiNo ratings yet
- Power Transmission Systems: Power Screws: Engineering 1040: Mechanisms & Electric Circuits Fall 2011Document13 pagesPower Transmission Systems: Power Screws: Engineering 1040: Mechanisms & Electric Circuits Fall 2011loveselvan43No ratings yet
- Lattice Crawler - PictureDocument6 pagesLattice Crawler - PictureMohamed FathyNo ratings yet
- RB Flexible Coupling: The Standard Range ComprisesDocument12 pagesRB Flexible Coupling: The Standard Range ComprisesMoamenNo ratings yet
- Brochure Pala CatDocument2 pagesBrochure Pala CatWilder Dianderas MandujanoNo ratings yet
- Konecranes - Hoists, Cranes & WinchesDocument16 pagesKonecranes - Hoists, Cranes & WinchesGogyNo ratings yet
- Electric Reach Truck 48 Volt 1400 / 1600 KG 2800 / 3200 LbsDocument8 pagesElectric Reach Truck 48 Volt 1400 / 1600 KG 2800 / 3200 LbsThanh Ngoc0% (1)
- Anch RS: Material: Performance: RangesDocument8 pagesAnch RS: Material: Performance: RangesInamMuradNo ratings yet
- MP20 Measuring Head: Dimensions & WeightsDocument1 pageMP20 Measuring Head: Dimensions & WeightsJose Sostenes100% (1)
- TRB - 8 Pages - GBDocument5 pagesTRB - 8 Pages - GBСергей ЧетвериковNo ratings yet
- JLG E450ajDocument2 pagesJLG E450ajAnaMariaDavidNo ratings yet
- Edrive Eliminator HD BrochureDocument12 pagesEdrive Eliminator HD BrochureminakirolosNo ratings yet
- Heavy Duty Ball Screw Linear ActuatorsDocument12 pagesHeavy Duty Ball Screw Linear ActuatorsFernando NinoNo ratings yet
- B Chiyoda-1Document16 pagesB Chiyoda-1harisNo ratings yet
- Direct: CNC Machining CentreDocument2 pagesDirect: CNC Machining CentreRivas IsaacNo ratings yet
- Hyundai Warehouse EquipmentDocument15 pagesHyundai Warehouse EquipmentPeterNo ratings yet
- CLARK WPX FeatureBrochureDocument8 pagesCLARK WPX FeatureBrochureThanh NgocNo ratings yet
- Ficha Técnica - DynoMiner Advanced (Inglés)Document2 pagesFicha Técnica - DynoMiner Advanced (Inglés)Pedro Ramos PAchecoNo ratings yet
- Rope BergDocument16 pagesRope BergsmsobhanNo ratings yet
- Contactless Sensor MTS-360: Magnetic Rotary Angle and Position Sensor-ControlDocument5 pagesContactless Sensor MTS-360: Magnetic Rotary Angle and Position Sensor-ControlMuhammed Aboul AzmNo ratings yet
- Economical. Durable. Easy To Operate.: DBR Rope HoistDocument12 pagesEconomical. Durable. Easy To Operate.: DBR Rope HoistsarochimNo ratings yet
- 2 Torsion SMDocument27 pages2 Torsion SMWesam Salah Aloolo100% (1)
- Liebherr RMG Technical DescriptionDocument4 pagesLiebherr RMG Technical DescriptionHua Hidari YangNo ratings yet
- Testing of Bored Pile InclinationDocument5 pagesTesting of Bored Pile InclinationBrian LukeNo ratings yet
- Powerbor DrillsDocument6 pagesPowerbor DrillsalphatoolsNo ratings yet
- GTC-350 LNG en Gen S 202210Document16 pagesGTC-350 LNG en Gen S 202210scroll pageNo ratings yet
- Speed and Accuracy Applications: Linear Drive UnitsDocument31 pagesSpeed and Accuracy Applications: Linear Drive UnitsajaykrishnaaNo ratings yet
- DBR en v15 ScreenDocument12 pagesDBR en v15 ScreenErc Nunez VNo ratings yet
- Crane Types: Tower Cranes: TrolleyDocument1 pageCrane Types: Tower Cranes: Trolleyeplan drawingsNo ratings yet
- Erco Bender 76Document1 pageErco Bender 76Johan SneiderNo ratings yet
- IEC/IEEE Capacitive & Coupling Capacitor Voltage Transformers (CVT & CCVT)Document16 pagesIEC/IEEE Capacitive & Coupling Capacitor Voltage Transformers (CVT & CCVT)Bravery DamanikNo ratings yet
- Week 8 TaskDocument2 pagesWeek 8 TaskNg Yi XuanNo ratings yet
- Ultraplant PortableDocument13 pagesUltraplant PortableFrancisco PerezNo ratings yet
- Eriez-Vibratory Feeders PDFDocument16 pagesEriez-Vibratory Feeders PDFruben quedo salazarNo ratings yet
- RHM 60 - Coriolis Mass Flowmeter For Medium FL Ow Also Suited For High Pressure ApplicationsDocument6 pagesRHM 60 - Coriolis Mass Flowmeter For Medium FL Ow Also Suited For High Pressure ApplicationsTeknik GresikNo ratings yet
- Manual, Electric, and Air Equipment: Quick GuideDocument6 pagesManual, Electric, and Air Equipment: Quick GuideDaniel BotiaNo ratings yet
- RT-160 60T1 PDFDocument8 pagesRT-160 60T1 PDFCollblanc Seatours Srl Jose LahozNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Vibratory Plate: A Trusted CompactorDocument2 pagesHydrostatic Vibratory Plate: A Trusted Compactorhamdi galipNo ratings yet
- Cat 7395Document2 pagesCat 7395Erick Yamir Abril ValdiviaNo ratings yet
- Engineering Design (Marine Engineering)Document7 pagesEngineering Design (Marine Engineering)Abdul MalikNo ratings yet
- Unit 2 - Elements of AutomationDocument48 pagesUnit 2 - Elements of AutomationGautham BVNo ratings yet
- X-Solar Hybrid 4x300w Led - FtuDocument2 pagesX-Solar Hybrid 4x300w Led - FtuAbe BustomiNo ratings yet
- Liebherr All Terrain Cranes Spec 696fb165327Document12 pagesLiebherr All Terrain Cranes Spec 696fb165327Maxin ShihobNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Magnetic Bearings Overview of The PresentationDocument21 pagesIntroduction To Magnetic Bearings Overview of The PresentationAbhijeeth NagarajNo ratings yet
- Topflex Emv Uv 3 Plus 2yslcyk JDocument2 pagesTopflex Emv Uv 3 Plus 2yslcyk JagusNo ratings yet
- Summary of Mecanic DomainDocument13 pagesSummary of Mecanic DomainNelson KemdengNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1.1-Power Transmission (Belt Drive)Document48 pagesChapter 1.1-Power Transmission (Belt Drive)shazwani zamriNo ratings yet
- ProductOverview 2023 EN-38Document1 pageProductOverview 2023 EN-38Ismail AliNo ratings yet
- Modular Jacquard: Electronic JacquardsDocument12 pagesModular Jacquard: Electronic JacquardsMohammad MorassaeiNo ratings yet
- All Position Oxy-Fuel Cutting Machine: Features and BenefitsDocument5 pagesAll Position Oxy-Fuel Cutting Machine: Features and BenefitsDuctoanNo ratings yet
- "Double Articulated System": General FeaturesDocument3 pages"Double Articulated System": General FeaturesANKURNo ratings yet
- 6 3 p0016 0044 Rotary - en PDFDocument29 pages6 3 p0016 0044 Rotary - en PDFmok waneNo ratings yet
- Datasheet MacGregor General Purpose Crane - Original - 33371 - 2Document2 pagesDatasheet MacGregor General Purpose Crane - Original - 33371 - 2Acank NasirNo ratings yet
- Catalog: Movitrac LTE-B+Document72 pagesCatalog: Movitrac LTE-B+Flávio leme da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Simatic Et 200al - For Effortless Installation Anywhere: Engineered With TIA PortalDocument8 pagesSimatic Et 200al - For Effortless Installation Anywhere: Engineered With TIA PortalFlávio leme da SilvaNo ratings yet
- RCS Staubli A100eDocument8 pagesRCS Staubli A100eFlávio leme da SilvaNo ratings yet
- EN CMS50 63 71 Electric Cylinders 07 - 2010Document180 pagesEN CMS50 63 71 Electric Cylinders 07 - 2010Flávio leme da SilvaNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Load, Shear, and MomentDocument17 pagesRelationship Between Load, Shear, and MomentEu AumentadoNo ratings yet
- Project Managers Program: Technical NoteDocument20 pagesProject Managers Program: Technical NotealfreliaNo ratings yet
- Aadhar Xerox Copy 2. Bank Passbook Xerox Copy 3. Passport Size Photo 2nos. 4. Mobile NumberDocument4 pagesAadhar Xerox Copy 2. Bank Passbook Xerox Copy 3. Passport Size Photo 2nos. 4. Mobile NumberBest Movie scenesNo ratings yet
- E-06e-AUF Magnetization Curve and Hysteresis LoopDocument4 pagesE-06e-AUF Magnetization Curve and Hysteresis LoopV. GrigorasNo ratings yet
- RCC 100 Important Questions 39Document33 pagesRCC 100 Important Questions 39Engr Mehdi BugtiNo ratings yet
- BS en 13554-2011Document20 pagesBS en 13554-2011widiantoekoNo ratings yet
- EEE 104 LS 01 MDS March2020Document50 pagesEEE 104 LS 01 MDS March2020Sharmin Rini100% (1)
- Continuous Over Two Equal Spans, Uniform Loads: L, in L, inDocument4 pagesContinuous Over Two Equal Spans, Uniform Loads: L, in L, inAzilan SeyerNo ratings yet
- Electricity MCQ'SDocument131 pagesElectricity MCQ'SSalik SalikNo ratings yet
- Investigating Inertia: Grade Level Quarter/Domain Week & Day No. LC Code S8FE-Ia-17Document32 pagesInvestigating Inertia: Grade Level Quarter/Domain Week & Day No. LC Code S8FE-Ia-17caveNo ratings yet
- College of Engineering, Architecture and Technology: Capiz State UniversityDocument5 pagesCollege of Engineering, Architecture and Technology: Capiz State UniversityCarlo CabanusNo ratings yet
- Bravais Lattices and Miller IndicesDocument17 pagesBravais Lattices and Miller IndicesSabir AliNo ratings yet
- Funktion-One F124 SpecDocument1 pageFunktion-One F124 SpecMuhammad IrvandaNo ratings yet
- G. L. Alexanderson - The William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition. Problems and Solutions - 1965-1984.-Mathematical Association of America (1985) PDFDocument156 pagesG. L. Alexanderson - The William Lowell Putnam Mathematical Competition. Problems and Solutions - 1965-1984.-Mathematical Association of America (1985) PDFahoaseoNo ratings yet
- VBR Neet Academy & Pu College: Kcet Grand Test-5 - PCMBDocument15 pagesVBR Neet Academy & Pu College: Kcet Grand Test-5 - PCMBAmogh PalyamNo ratings yet
- Training Report (NTPC & Bseb) 2010-DhananjayDocument27 pagesTraining Report (NTPC & Bseb) 2010-DhananjayKusum Chaudhary100% (1)
- API 1104 - Sample Quiz - 2012Document42 pagesAPI 1104 - Sample Quiz - 2012장재성No ratings yet
- Fabric Stiffness TestingDocument13 pagesFabric Stiffness TestingFahima RashidNo ratings yet
- Stair Case Pressurization FAN - OmarDocument2 pagesStair Case Pressurization FAN - OmarDesigner Forever100% (1)
- Physics2011 PDFDocument16 pagesPhysics2011 PDFceraNo ratings yet
- CBSE Class 8 Science Worksheet Sound: Get Free Worksheets OnDocument4 pagesCBSE Class 8 Science Worksheet Sound: Get Free Worksheets OnAshish Gambhir0% (1)
- Hyper InverterDocument8 pagesHyper Inverteravik royNo ratings yet
- 2Q PT3 GuevarraDocument6 pages2Q PT3 GuevarraAkeelah EstacioNo ratings yet
- NDE On Threaed ConnectionDocument6 pagesNDE On Threaed ConnectionIvy LiNo ratings yet
- Solenoid Valves 90barDocument31 pagesSolenoid Valves 90baralessandro silvaNo ratings yet
- NMR - Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument71 pagesNMR - Multiple Choice QuestionsOmSilence265171% (31)
- Unit 4 Formula SheetDocument1 pageUnit 4 Formula SheetAporajita HossainNo ratings yet
- Lab 5-Drag Force in Flow Over A BodyDocument21 pagesLab 5-Drag Force in Flow Over A BodyKhairul AimanNo ratings yet
- Improvement of Thermal Insulation and Compressive Performance ofDocument10 pagesImprovement of Thermal Insulation and Compressive Performance ofLin YangNo ratings yet
- Bus Admittance MatrixDocument25 pagesBus Admittance MatrixNor HanarosNo ratings yet