Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Foam Fire Extinguisher: Types of Fires
Uploaded by
Wasif IrfanOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Foam Fire Extinguisher: Types of Fires
Uploaded by
Wasif IrfanCopyright:
Available Formats
Fire Extinguishers Explained
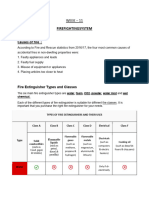
Types of Fires
SSA SSB SSC
A CL A A
CL
CL
Solid material fires that Fires that involve flammable These flames burn on
burn materials such as liquids, including paraffin, flammable gases such as
paper, wood or plastic. petrol and oil. propane, butane and methane.
SSD
ASS E ASS F
A L L
CL
C
C
Are fires that ignite with Caused by electricity, or These fires are
metals such as aluminium, involve electrical equipment ignited with oils or
magnesium or titanium. and apparatus. cooking fat.
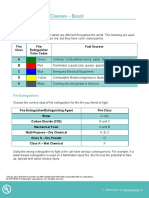
Types of Fire Extinguishers
Foam Fire Extinguisher
Used for : Classes A and B
Dangerous if used for : Class F
How it works: the foam released by this extinguisher
seals the surface of the burning material, preventing
any stray materials from escaping and igniting
elsewhere, as well as ultimately suffocating the fire.
This extinguisher can be used on solid materials and
flammable liquids such as paraffin and petrol (Classes
A and B), but not for chip and pan fires (Class F).
Water Fire Extinguisher
Used for: Class A
Dangerous if used for: Classes E and F
How it works: the water soaks the burning materials,
such as paper, wood or fabric (Class A) and cools them
down, completely putting out the fire. However, these
extinguishers are very dangerous to use on oil and fat
fires as well as electrical fires (Classes E and F).
Carbon Dioxide
Fire Extinguisher
Used for : Classes B and E
Dangerous if used for : Class A and C
How it works: the carbon dioxide cuts off the oxygen
supply to the fire, which smothers the blaze and puts it
out. They are ideal for electrical fires and flammable
liquids such as petrol and paraffin (Classes B and E),
but are dangerous for use on solid materials and
flammable gases including methane, propane or butane
(Classes A and C).
Powder Fire Extinguisher
Used for: Classes A, B, C, and E.
Specialist types available for Class D.
Dangerous if used for: Class F
How it works: a powder is released and acts as a blanket
which suffocates and cools the flames. The powder also
prevents the flames from spreading, making it effective
for most fire types including solid materials, flammable
liquids, gases and electrical equipment (Classes A, B, C
and E), however it’s not suitable for oil or pan fat fires
(Class F). Specialist mixtures of powder extinguishers
are available for fires involving metals (Class D).
Automatic Fire Extinguisher
Used for: Classes A, B, C and E
Dangerous if used for: Class F
How it works: automatic fire extinguishers are ideal for
locations where manual operation is not possible, or
immediate activation is of utmost priority. They release an
extinguishing agent when fire is detected, making them
ideal for blazes involving solid materials, flammable
liquids and gases as well as electrical fires (Classes A, B,
C and E). However, they can’t be used in areas with a high
risk of fire ignited by oils or fats (Class F).
Wet Chemical
Fire Extinguisher
Used for: Class F
Dangerous if used for: Classes B, C, D and E
How it works: these extinguishers are specially formulated
to tackle blazes involving oils and fats, with the chemicals
reacting to create a fine film, suffocating the blaze. These
extinguishers are perfect for use in kitchens with a high
risk of fires involving cooking oils or fats (Class F),
however they should not be used for any liquid, gas,
metal or electrical fires (Classes B through to E).
City Fire Protection are leading providers of fire safety equipment and training
for businesses around the country. For more information, please get in touch
with us today and we’ll be more than happy to help you.
City Fire Protection, 172a Selsdon Road, South Croydon, Surrey CR2 6PJ
Email: admin@cityfire.co.uk
020 3432 8918
You might also like
- Fire Extinguishing AgentsDocument3 pagesFire Extinguishing AgentsTsangngat ChaokasNo ratings yet
- Report in AMT 219: By: Michael Ken O. Estrada Amt - 2 Year Fire Protection Safety in The Shop and On The Flight LineDocument25 pagesReport in AMT 219: By: Michael Ken O. Estrada Amt - 2 Year Fire Protection Safety in The Shop and On The Flight LineAndy AlmineNo ratings yet
- Choosing Fire ExtinguishersDocument1 pageChoosing Fire ExtinguishersJehannah Dayanara HayudiniNo ratings yet
- Fire Extinguishers: A Health and Safety Guideline For Your WorkplaceDocument8 pagesFire Extinguishers: A Health and Safety Guideline For Your WorkplaceAkhtar QuddusNo ratings yet
- Fighting Different Types of FiresDocument3 pagesFighting Different Types of FiresNini JimbuuNo ratings yet
- Choosing Fire Extinguishers: Class A: Class B: Class C: Class D: Class E: Class FDocument2 pagesChoosing Fire Extinguishers: Class A: Class B: Class C: Class D: Class E: Class FsubhoNo ratings yet
- POWDER Fire Extinguishers: Model: Fire Rate Clean Agent (FX)Document1 pagePOWDER Fire Extinguishers: Model: Fire Rate Clean Agent (FX)Angga WisudiantoNo ratings yet
- Fire Extinguishers: Class ADocument5 pagesFire Extinguishers: Class ASunitha LaskarNo ratings yet
- Types of Fire ExtinguishersDocument2 pagesTypes of Fire Extinguishersfaisalhotline9500No ratings yet
- Water Fire ExtinguisherDocument5 pagesWater Fire ExtinguisherMaejie GellesNo ratings yet
- 1Document2 pages1georgel.ghitaNo ratings yet
- Fire Extinguisher ClassesDocument3 pagesFire Extinguisher ClassesshivabhaNo ratings yet
- Fire Extinguishers PDFDocument5 pagesFire Extinguishers PDFabujar gaffari mollaNo ratings yet
- Fire Extinguishers TypesDocument1 pageFire Extinguishers TypesDrGajanan VaishnavNo ratings yet
- Fire/Smoke: There Are 6 Classes of FiresDocument2 pagesFire/Smoke: There Are 6 Classes of FiresRémi WatineNo ratings yet
- Classes of Fire AND Methods To Fight It: Universiti Teknologi Mara Fakulti Kejuruteraan Kimia Process Safety (CPE615)Document4 pagesClasses of Fire AND Methods To Fight It: Universiti Teknologi Mara Fakulti Kejuruteraan Kimia Process Safety (CPE615)sfycNo ratings yet
- Gantt ChartDocument9 pagesGantt ChartHibryFathiNo ratings yet
- Fire Load - Mod 2Document4 pagesFire Load - Mod 2Ebin EldhoNo ratings yet
- Types of Fire ExtinguisherDocument3 pagesTypes of Fire ExtinguisherJessica B. AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 WEEK 5 8 Fire Fighting Onboard ShipsDocument27 pagesTopic 2 WEEK 5 8 Fire Fighting Onboard Shipslawrence christian dragidoNo ratings yet
- Fire Extinguisher Classes - CanadaDocument2 pagesFire Extinguisher Classes - CanadamuruganandamdesinghNo ratings yet
- Classes of FireDocument4 pagesClasses of FireDaniel OnyukaNo ratings yet
- 12.CMDF (Fire Safety)Document32 pages12.CMDF (Fire Safety)macky02 sorenatsacNo ratings yet
- Pamphlet On Classification of Fires & Types of Fire ExtinguishersDocument12 pagesPamphlet On Classification of Fires & Types of Fire ExtinguishersHariharan MuthukrishananNo ratings yet
- Definisi KebakaranDocument7 pagesDefinisi KebakaranV HipsterNo ratings yet
- Fire Extinguishers Type 124Document8 pagesFire Extinguishers Type 124pruthviNo ratings yet
- Week 11 NotesDocument27 pagesWeek 11 Notescharusri74No ratings yet
- Fire Extinguishers GeneralDocument1 pageFire Extinguishers GeneralrscseNo ratings yet
- All You Ever Wanted To Know About Fire Extinguishers - .Document6 pagesAll You Ever Wanted To Know About Fire Extinguishers - .Rahul RamachandranNo ratings yet
- All You Ever Wanted To Know About Fire Extinguishers - .Document6 pagesAll You Ever Wanted To Know About Fire Extinguishers - .Rahul RamachandranNo ratings yet
- Xyzklm 6789 JKJKJKDocument1 pageXyzklm 6789 JKJKJKnguyenthinhvinhkhaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5.4 Fire Fighting TriangleDocument35 pagesChapter 5.4 Fire Fighting Triangleektas30998No ratings yet
- Fires 2Document16 pagesFires 2Jairah AngueNo ratings yet
- TMS Fire Extinguisher TrainingDocument31 pagesTMS Fire Extinguisher TrainingChilaNo ratings yet
- Fire Extenquizer PresentationDocument1 pageFire Extenquizer PresentationmuruganandamdesinghNo ratings yet
- CHPTR 2 BuildingDocument8 pagesCHPTR 2 BuildingLebya UminNo ratings yet
- Fire SafetyDocument24 pagesFire SafetyazelNo ratings yet
- Clasificación de ExtintoresDocument2 pagesClasificación de ExtintoresSharyk PachecoNo ratings yet
- Fire LectureDocument26 pagesFire LectureCamille AndreaNo ratings yet
- WRAESNO052Document4 pagesWRAESNO052Alona DelacruzNo ratings yet
- Estimation of Fire Load and Its Risk Assessment in WarehouseDocument4 pagesEstimation of Fire Load and Its Risk Assessment in WarehouseNational Institute of Safety EngineersNo ratings yet
- Apar TypesDocument2 pagesApar Typesnamasayafredie6752No ratings yet
- Fire Extinguisher Training: Firestop EngineersDocument37 pagesFire Extinguisher Training: Firestop Engineersganesha2011No ratings yet
- Fire Watch Complete Training Course Gti HseDocument50 pagesFire Watch Complete Training Course Gti HseScor PioNo ratings yet
- Topic 2Document27 pagesTopic 2jerwin custacioNo ratings yet
- Fire TriangleDocument3 pagesFire TriangleJieceryl GoliasNo ratings yet
- Cara2 Menggunakan Fire ExtinguisherDocument12 pagesCara2 Menggunakan Fire ExtinguisherMax's MelesNo ratings yet
- Fire Extinguisher Classes - AsiaDocument1 pageFire Extinguisher Classes - AsiamuruganandamdesinghNo ratings yet
- Fire ManagementDocument5 pagesFire ManagementJim RojanNo ratings yet
- Safety Talk (Alaa Almilad) Fire Extinguishers and Their ApplicationsDocument13 pagesSafety Talk (Alaa Almilad) Fire Extinguishers and Their ApplicationsAamir AhmedNo ratings yet
- Fire Extinguisher Classes - CanadaDocument1 pageFire Extinguisher Classes - CanadamuruganandamdesinghNo ratings yet
- Fire Extinguisher Classes - (A, B, C, D, F)Document10 pagesFire Extinguisher Classes - (A, B, C, D, F)SAFEER ABDUL KHARIMNo ratings yet
- All You Ever Wanted To Know About Fire ExtinguishersDocument6 pagesAll You Ever Wanted To Know About Fire ExtinguishersAndrés RobattoNo ratings yet
- What Are The Different Classes of Fires?Document12 pagesWhat Are The Different Classes of Fires?Геннадий ОльховскийNo ratings yet
- Name:Ya Meng Wan Class:10 Tvet School:Diamond Secondary School Topic:Fire Teacher:Mr. Aravind MohanlallDocument13 pagesName:Ya Meng Wan Class:10 Tvet School:Diamond Secondary School Topic:Fire Teacher:Mr. Aravind MohanlallMeng WanNo ratings yet
- Classes of Fire and Fire ExtinguishersDocument14 pagesClasses of Fire and Fire ExtinguishersAdebayo O. Johnson100% (2)
- BFT - Grade 9-10 (Part II) Docx PDFDocument10 pagesBFT - Grade 9-10 (Part II) Docx PDFGuyan GordonNo ratings yet
- Types of Fires: Class ADocument3 pagesTypes of Fires: Class ARichard Jay OyalesNo ratings yet
- Project Hse PlanDocument21 pagesProject Hse PlanSK JAHANGIR ALAMNo ratings yet
- Cat Buchholtz 2015Document42 pagesCat Buchholtz 2015pawan kumar raiNo ratings yet
- Exercise 1.1 (Solutions) : Merging Man and MathsDocument9 pagesExercise 1.1 (Solutions) : Merging Man and MathsWasif IrfanNo ratings yet
- TRX Oil Test PropertiesDocument48 pagesTRX Oil Test PropertiesbibhooNo ratings yet
- A Guide To Transformer Oil Analysis: BY I.A.R. GRAY Transformer Chemistry ServicesDocument12 pagesA Guide To Transformer Oil Analysis: BY I.A.R. GRAY Transformer Chemistry ServicesAnonymous OCDJg17Z100% (1)
- Tranformer Oil Sampling MethodsDocument68 pagesTranformer Oil Sampling MethodsMohammed NouzalNo ratings yet
- Cat Buchholtz 2015Document42 pagesCat Buchholtz 2015pawan kumar raiNo ratings yet
- The Testing ofDocument337 pagesThe Testing ofWasif IrfanNo ratings yet
- The Testing ofDocument337 pagesThe Testing ofWasif IrfanNo ratings yet
- 1ZCL000006TSG Test Report PDFDocument15 pages1ZCL000006TSG Test Report PDFAkshay GatkalNo ratings yet
- Fire Extinguisher Safety and Handling InstructionsDocument20 pagesFire Extinguisher Safety and Handling InstructionsWasif IrfanNo ratings yet
- Testing TransformerDocument83 pagesTesting Transformercharleselitb92100% (1)
- 4008TAG1A TAG2A 1000 Kva For 50HzDocument15 pages4008TAG1A TAG2A 1000 Kva For 50HzWasif IrfanNo ratings yet
- IA Pricelist 2021Document144 pagesIA Pricelist 2021Wasif IrfanNo ratings yet
- IA Pricelist 2021Document144 pagesIA Pricelist 2021Wasif IrfanNo ratings yet
- 4006-23tag2a - Tag3aDocument14 pages4006-23tag2a - Tag3aImran MazharNo ratings yet
- VAMP40 Course - Feeder - 5. Current Circuits Supervision, 2nd Harmonic Blocking Function, Free Programable Current Curve - Prime KitDocument20 pagesVAMP40 Course - Feeder - 5. Current Circuits Supervision, 2nd Harmonic Blocking Function, Free Programable Current Curve - Prime KitWasif IrfanNo ratings yet
- Is There Life After DeathDocument4 pagesIs There Life After DeathWasif IrfanNo ratings yet
- Preparing A Case StudyDocument16 pagesPreparing A Case StudyWasif IrfanNo ratings yet
- Maxwells EquationsDocument11 pagesMaxwells EquationsWasif IrfanNo ratings yet
- Tad722ge PDFDocument2 pagesTad722ge PDFWasif Irfan100% (1)
- BasicsOfElectricalDrives4thEditionbyPillai 1Document245 pagesBasicsOfElectricalDrives4thEditionbyPillai 1Anonymous lV8E5mEONo ratings yet
- Brown Stove Works Gas - ManualDocument32 pagesBrown Stove Works Gas - ManualChuck StoneNo ratings yet
- ModuSec-Secure Modular Construction SystemDocument49 pagesModuSec-Secure Modular Construction SystemBrendan LynchNo ratings yet
- The ImmolatorDocument2 pagesThe ImmolatorAlfonsoNo ratings yet
- Guidance - BS EN 13565-2 Foam System Standard PDFDocument8 pagesGuidance - BS EN 13565-2 Foam System Standard PDFsondk2No ratings yet
- CAT Prime Application Grease SDSDocument9 pagesCAT Prime Application Grease SDSKuhnNo ratings yet
- Solid Fuels Report CDI6Document21 pagesSolid Fuels Report CDI6Mark Jared TanNo ratings yet
- Project Hse PlanDocument21 pagesProject Hse PlanSK JAHANGIR ALAMNo ratings yet
- Light A Fire With Water: Step 1: Components and Tools NeededDocument4 pagesLight A Fire With Water: Step 1: Components and Tools NeededEyong Tambe KelvinNo ratings yet
- 948 (r00)Document176 pages948 (r00)Julio Harold Urquizo Rojas100% (1)
- 1000XP User Manual Fuel CellDocument53 pages1000XP User Manual Fuel CellRaka SaripiantoNo ratings yet
- Bionlov Fuel For Bio Fireplaces: Dangerous Preparation Charakteristics CardDocument11 pagesBionlov Fuel For Bio Fireplaces: Dangerous Preparation Charakteristics CardJHUPEL ABARIALNo ratings yet
- Criminology Reviewer Ngani: Jhay A. TicoyDocument14 pagesCriminology Reviewer Ngani: Jhay A. TicoyHanz Albrech AbellaNo ratings yet
- Iso TS 29761-2015Document32 pagesIso TS 29761-2015Farhad British WingsNo ratings yet
- MSDS INOX MX3 Original - AerosolDocument5 pagesMSDS INOX MX3 Original - AerosolvokNo ratings yet
- Fire and Earthquake Preparedness SeminarDocument45 pagesFire and Earthquake Preparedness SeminarOcseum Noisap YojNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Hazard AwarenessDocument21 pagesUnit 8 Hazard AwarenessEina Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Omm D375a-5 Tier 3 Ten00140-00Document334 pagesOmm D375a-5 Tier 3 Ten00140-00Syahrir KobarNo ratings yet
- FPM-DC-5091 - Fireproofing Spec (Chevron)Document20 pagesFPM-DC-5091 - Fireproofing Spec (Chevron)theunknown076100% (1)
- 2605A-En Case Study Credit Valley HospitalDocument2 pages2605A-En Case Study Credit Valley HospitalAdvenser GroupNo ratings yet
- OSHA Module 3Document17 pagesOSHA Module 3Varsha GNo ratings yet
- Dioxins and Polyvinylchloride in Combustion and Fires: July 2015Document15 pagesDioxins and Polyvinylchloride in Combustion and Fires: July 2015fefeauliaNo ratings yet
- Fire Protection Policy, Safy 2021Document3 pagesFire Protection Policy, Safy 2021Walid El WahshNo ratings yet
- 01 Quotation - Nippon Paint Philippines - Ajssent Inc - Rev6-1Document17 pages01 Quotation - Nippon Paint Philippines - Ajssent Inc - Rev6-1Jade PutisNo ratings yet
- Azadirachtin 10% MSDSDocument6 pagesAzadirachtin 10% MSDS缪忠琴No ratings yet
- Living Things and AirDocument13 pagesLiving Things and Airxena100% (1)
- Fire Prevention On Construction Sites - Joint Code of Practice 10th EditionDocument36 pagesFire Prevention On Construction Sites - Joint Code of Practice 10th EditionMamoon AlyahNo ratings yet
- Bom Chan KhongDocument78 pagesBom Chan KhongKhổng C. PhongNo ratings yet
- Topic 4Document16 pagesTopic 4Kiven M. GeonzonNo ratings yet
- Fire Safety of Non Domestic Furniture bs7176 PDFDocument4 pagesFire Safety of Non Domestic Furniture bs7176 PDFaffashNo ratings yet
- Manual: Assembly and Operation of Hospital Waste Incinerator For Disaster Relief and Rural Hospitals (HWI-4)Document27 pagesManual: Assembly and Operation of Hospital Waste Incinerator For Disaster Relief and Rural Hospitals (HWI-4)sambadeeNo ratings yet