Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Connective Tissues: Structure and Functions
Uploaded by
PenelopeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Connective Tissues: Structure and Functions
Uploaded by
PenelopeCopyright:
Available Formats
-CONNECTIVE TISSUES- that invade the body.
Specialized fluid
connective tissues, such as blood and
- From the name itself, one of the major
lymph, ensure the transfer of fluid,
functions of connective tissues is to
nutrients, waste, and chemical
support and connect each tissue and
messengers.
organs.
- Connective Tissues are also dispersed in EMBRYONIC CONNECTIVE TISSUE
a matrix unlike epithelial tissues which
- All connective tissues derive from the
are closely packed together.
mesodermal layer of the embryo
MATRIX
- Mesenchyme: is the first connective
- Typically, the matrix contains a tissue to develop in the embryo.
significant amount of extracellular Mesenchyme is the stem cell line from
material formed by the cells of the which all connective tissues are later
connective tissue that are embedded in it. derived.
In the functioning of this tissue, the
- Clusters of mesenchymal cells are
matrix plays a major role. The main
scattered throughout adult tissue and
component of the matrix is a ground
supply the cells needed for replacement
substance frequently crisscrossed by
and repair after a connective tissue injury.
protein fibers. Normally, this ground
material is a fluid, but, as in bones, it can - Mucous Connective Tissue: also called
also be mineralized and solid. Connective as Wharton’s jelly. It’s a second type of
tissues come in a wide range of forms, yet embryonic connective tissue that are
they typically have three characteristics formed in the umbilical cord. This tissue
in common. is no longer present after birth, leaving
THREE CHARACTERISTIC only scattered mesenchymal cells
COMPONENTS throughout the body.
1. Cells
CLASSIFICATION OF CONNECTIVE
2. Large amounts of amorphous ground
TISSUES
substance
3. Protein Fibers 1. Connective Tissue Proper
FUNCTIONS OF CONNECTIVE TISSUE 2. Supportive Connective Tissue
- The Connective Tissues perform many 3. Fluid Connective Tissue
functions in our body and one of which is
supporting and connecting other tissues.
- These three broad categories of
- Another major function of connective connective tissue are classified according
tissue, is protection, in the form of fibrous to the characteristics of their ground
capsules and bones that protect delicate substance and the types of fibers found
organs and the skeletal system. within the matrix
- In connective tissue, specialized cells
protect the body from microorganisms
Connective Tissue Examples Adipocytes
- These are the cells that store lipids as
C.T.P. S.C.T. F.C.T.
droplets that fill most of the cytoplasm
LOOSE CARTILAGE
- Areolar - Hyaline BLOOD Two Types of Adipocytes: White and
- Adipose - Brown
Fibrocartilage - Brown Adipocytes store lipids as
- Reticular - Elastic many droplets, and have high metabolic
activity.
DENSE BONES - White Adipocytes store lipids as a
- Regular - Compact LYMPH single large drop and are metabolically
Elastic Bone less active.
- Irregular - Cancellous
Elastic Bone Mesenchymal Cell
- The mesenchymal cell is a multipotent
adult stem cell. These cells can
1. CONNECTIVE TISSUE PROPER
differentiate into any type of connective
- In all connective tissue, the fibroblasts tissue cells required for damaged tissue
are properly present. The fixed cells are to be repaired and healed.
fibrocytes, adipocytes, and mesenchymal
Macrophage Cell
cells, indicating that they reside inside the
- This is a large cell derived from a type
connective tissue. In response to chemical
of blood cell, called monocyte which
signals, other cells move in and out of the
enters the connective tissue matrix from
connective tissue. Macrophages, mast
the blood vessels. The macrophage cells
cells, lymphocytes, plasma cells, and
are an essential component of the
phagocytic cells are properly located in
immune system. When stimulated,
connective tissue, but are primarily part
macrophages release cytokines, small
of the body's protective immune system.
proteins that act as chemical messengers.
CELL TYPES - Cytokines recruit other cells of the
immune system to contaminated sites and
Fibroblast
stimulate their activities. Roaming, or
- This is the most abundant cell in
free, macrophages move quickly through
connective tissue proper. It secretes
the movement of amoeboid, swallowing
polysaccharides and proteins that
infectious agents and cellular debris.
combines extra-cellular fluids to produce
Fixed macrophages, in contrast, are
a viscous ground substance that, with
permanent residents of their tissues.
embedded fibrous proteins, forms the
extra-cellular matrix. Mast Cell
- Fibrocyte, a less active form of - Found in connective tissue proper, the
fibroblast, is the second most common mast cell has cytoplasmic granules. These
cell type in connective tissue proper. granules contain the chemical signals
histamine and heparin.
- Mast cells release histamine, an
inflammatory mediator, when irritated or - Have the ability to return to their
damaged, which causes vasodilation and original shape after being stretched, a
increased blood flow at an injury or property called elasticity.
infection site, along with itching, swelling, - Prominent in elastic tissues found in
and redness that you recognize as an skin and the elastic ligaments of the
allergic reaction. vertebral column.
CONNECTIVE TISSUE FIBERS AND 3. Reticular Fibers
GROUND SUBSTANCES - Formed from the same protein subunits
as collagen fibers.
GROUND SUBSTANCE
- Fibers are narrow and are arrayed in a
- Connective tissue’s component
branching network.
between the cells and fibers.
- Provide support and strength.
- Mostly fluid.
- Most abundant in the reticular tissue of
- Supports the cell, binds, stores water
soft organs, such as liver and spleen.
and provides a medium for exchange of
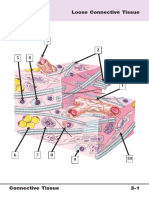
substances. LOOSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE
- is found between many organs where it
FIBERS
acts both to absorb shock and bind tissues
- Three main types of fibers are secreted
together.
by fibroblasts: collagen fibers, elastic
- allows water, salts, and various
fibers, and reticular fibers.
nutrients to diffuse through to adjacent or
- They function together to strengthen
imbedded cells and tissues.
and support connective tissue.
Adipose tissue
Three Types of Fiber
- consists mostly of fat storage cells, with
1. Collagen Fiber little extracellular matrix
- Made from fibrous protein subunits I. White Adipose Tissue
linked together to form a long and - Is the most abundant
straight fiber. - It can appear yellow because of the
- Hold connective tissues together. carotene and related pigments from plant
- Consist of collagen, the most abundant foods
protein in the body, representing about - Can be found protecting the kidneys and
25%. cushioning the back of the eye
- Found in most types of connective - White fat: contributes mostly to lipid
tissues, especially bone, cartilage, storage and can serve as insulation from
tendons, and ligaments. cold temperatures and mechanical
injuries
2. Elastic Fibers
- Contains the protein elastin along with II. Brown Adipose Tissue
lesser amounts of other proteins and - is thermogenic, meaning that as it
glycoproteins. breaks down fats, it releases metabolic
- Can be stretched up to 150% of their heat, rather than producing ATP
relaxed length without breaking. - is more common in infants, thus the
term “baby fat” Two Major Categories of Dense
- in adults, there is a reduced amount of Connective Tissue
brown fat. Found mainly in the in the Regular Dense Connective Tissue -
neck and clavicular regions of the body. parallel to each other, enhancing tensile
- the many mitochondria in the cytoplasm strength and resistance to stretching in
of this tissue explains its efficiency at the direction of the fiber orientations.
metabolizing stored fat - It contains elastin fibers allowing the
ligament to return to its original length
Areolar Tissue
after stretching
- it contains all the cell types and fibers - The ligaments in the vocal folds and
previously described and is distributed in between the vertebrae in the vertebral
a random, web-like fashion column are elastic.
- it fills the spaces between muscle fibers,
surrounds blood and lymph vessels, and Examples:
- Ligaments (Take note, NOT ALL
supports organs in the abdominal cavity
ligaments are parallel)
- it also underlies most epithelia and
- Tendons
represents the connective tissue
component of epithelial membranes Irregular Dense Connective Tissue - the
direction of the fibers is RANDOM.
Reticular Tissue - The tissue gives greater strength in all
- is a mesh-like, supportive framework for directions and less strength in one
soft organs such as lymphatic tissue, the particular direction
spleen, and the liver - In some tissues, fibers crisscross and
- Reticular cells: produce the reticular form a mesh.
fibers that form the network onto which - In other tissues, stretching in several
other cells attach. directions is achieved by alternating
layers where fibers run in the same
DENSE CONNECTIVE TISSUE orientation in each layer, and it is the
- It contains more collagen fibers than layers themselves that are stacked at an
does loose connective tissue. angle.
- As a consequence, it displays greater - The Dermis of the skin is an example of
resistance to stretching irregular dense connective tissue in
- Provides tensile strength, elasticity, and collagen fibers.
protection. - Dense irregular elastic tissues give
arterial walls the strength and the ability
Dense Connective Tissue Bones
to regain the original shape after
Regular Elastic stretching
Irregular Elastic
Compact bone
Cancellous bone
Lymph
2. SUPPORTIVE CONNECTIVE TISSUE - The external ear contains elastic
cartilage
- Provide structure and strength to the
body and protect soft tissues. Bone
- Allow the body to maintain its posture - is the hardest connective tissue.
and protect internal organs. - A highly vascularized tissue
- A few distinct cell types and densely - Bone tissue can recover from injuries in
packed fibers in a matrix characterize a relatively short time
these tissues. - It provides protection to internal organs
- In bone, the matrix is rigid and and supports the body.
described as calcified because of the - Bone’s rigid extracellular matrix
deposited calcium salts. contains mostly collagen fibers embedded
in a mineralized ground substance
Two Major forms of Supportive containing hydroxyapatite, a form of
Connective tissue
calcium phosphate
Cartilage - Both components of the matrix, organic
Bone and inorganic, contribute to the unusual
properties of bone.
Cartilage - Without collagen, bones would be brittle
- Distinctive appearance of cartilage is and shatter easily.
due to polysaccharides called chondroitin - Without mineral crystals, bones would
sulfates, which bind with ground flex and provide little support.
substance proteins to form proteoglycans.
- Embedded within the cartilage matrix Osteocytes - are bone cells like
are chondrocytes or cartilage cells, and chondrocytes and are located within
the space they occupy is called lacunae lacunae.
- A layer of dense irregular connective Cancellous bone - a sponge-like
tissue, the perichondrium, encapsulates structure under the microscope
the cartilage. - Cartilaginous tissue is containing empty spaces between
avascular, thus all nutrients need to trabeculae, or arches of bone proper. It is
diffuse through the matrix to reach the lighter than compact bone and found in
chondrocytes. the interior of some bones and at the end
Three Main Types of Cartilage Tissue of long bones. It shows that a transverse
tissue from long bone pictures a typical
1. Hyaline Cartilage - the most common arrangement of osteocytes in concentric
type of cartilage in the body, consists of circles around a central canal.
short and dispersed collagen fibers and
contains large amounts of proteoglycans. Compact bone - is solid and has greater
structural strength.
2. Fibrocartilage - is tough because it has
thick bundles of collagen fibers dispersed
through its matrix.
3. Elastic Cartilage - contains elastic
fibers as well as collagen and
proteoglycans
- Gives rigid support as well as elasticity
3. FLUID CONNECTIVE TISSUE REFERENCES:
Blood Tissue OpenStax College. (2013).
- Blood has an extracellular matrix called Anatomy &
blood plasma and formed elements. physiology.OpenStax.http://cnx.or
Blood plasma g/contents/14fb4ad7-39a1-4eee-
- Pale yellow fluid consists of ab6e-3ef2482e3e22@8.24
water and other dissolved OpenStax College (2013). 25 4.3.
substances nutrients, wastes, Connective Tissue Supports And
enzymes, etc. Protects. Anatomy and Physiology.
Formed elements Retrieved from
- Red Blood Cell (erythrocytes) - https://opentextbc.ca/anatomyan
Delivers oxygen to body cells and dphysiology/chapter/4-3-
removes carbon dioxide from connective-tissue-supports-and-
them. protects/?
- White Blood Cell (leukocytes) - fbclid=IwAR2HdS92jCy6QWFlYPH
Involves in phagocytosis, _Ljaf1MZWnOag0kMCS__Uu2j05Jd
immunity, and allergic reactions. 9Em_T9PqQ-wA
- Platelets (thrombocytes) - Tortora, G. J. & Derrickson, B.
Participates in blood clotting. (2017). Principle of anatomy and
physiology.Wiley Global Education.
Lymph https://b-
- Extracellular fluid that flows in the ok.asia/book/2956327/dba9b7
lymphatic vessels.
- Clear liquid extracellular matrix, similar
to blood plasma but with much less
protein.
You might also like
- HISTOLOGY-TRANSES-MIDTERMDocument13 pagesHISTOLOGY-TRANSES-MIDTERMblessganzoncandariNo ratings yet
- HISTOLOGY NOTES by Red (Connective)Document2 pagesHISTOLOGY NOTES by Red (Connective)Edzeal Bruan JrNo ratings yet
- Week 3 Module 3 Organization of The Human Body - Tissue (B)Document21 pagesWeek 3 Module 3 Organization of The Human Body - Tissue (B)Kishie Jeyds LaycoNo ratings yet
- The Connective Tissue ReviewerDocument4 pagesThe Connective Tissue ReviewerSasukeNo ratings yet
- Conn. Tissue HemopoiesisDocument14 pagesConn. Tissue HemopoiesischennielafleurNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue Functions and TypesDocument13 pagesConnective Tissue Functions and TypesFitra Aini FirmanNo ratings yet
- Wenmarie D. Co BSMT 3A, Histology: MatrixDocument5 pagesWenmarie D. Co BSMT 3A, Histology: MatrixSayonara WatashinoaiNo ratings yet
- Veta 65. Module 3Document24 pagesVeta 65. Module 3Melon MelonNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2Document18 pagesGeneral Biology 2ayah eliviaNo ratings yet
- Tissues & Membranes: The Relationship Between Structure and Function of Epithelial TissuesDocument3 pagesTissues & Membranes: The Relationship Between Structure and Function of Epithelial Tissueskyla columnaNo ratings yet
- Connective TissuesDocument11 pagesConnective TissuesCamille Ann Faigao FamisanNo ratings yet
- Mc1 Types of Tissues 2 4Document5 pagesMc1 Types of Tissues 2 4Karl Devin CorderoNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue Bone and Joint PhysiologyDocument5 pagesConnective Tissue Bone and Joint PhysiologySairelle Sordilla ObangNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue NotesDocument6 pagesConnective Tissue Notesferdinand padillaNo ratings yet
- Epithelium & Connective Tissue Review (Histology Block 1Document8 pagesEpithelium & Connective Tissue Review (Histology Block 1Miguel Mansilla100% (1)
- 25 4.3 Connective Tissue Supports and ProtectsDocument17 pages25 4.3 Connective Tissue Supports and ProtectsJimmy Jamarolin JacaNo ratings yet
- The Four Primary Tissue TypesDocument33 pagesThe Four Primary Tissue TypesDASH100% (2)
- LO 1 (Week 2) Cell Structure and Organisation (Cheng)Document4 pagesLO 1 (Week 2) Cell Structure and Organisation (Cheng)nit33vNo ratings yet
- Dimaculangan, Yumie F. M4Document4 pagesDimaculangan, Yumie F. M4yumie dimaculanganNo ratings yet
- The Connective Tissue: Functions, Structures and ClassificationsDocument5 pagesThe Connective Tissue: Functions, Structures and ClassificationsPia AbilaNo ratings yet
- ConnectiveDocument12 pagesConnectiveGwyneth NovesterasNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissues 2Document71 pagesConnective Tissues 2Asma Aijaz100% (1)
- Connective tissue cells and fibers explainedDocument4 pagesConnective tissue cells and fibers explainedneil100% (1)
- Tissues - Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument4 pagesTissues - Anatomy and PhysiologyHan CallejaNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument5 pagesConnective TissueAyessah MandanganNo ratings yet
- Histology - Assignment 3Document4 pagesHistology - Assignment 3Shreyasi DongreNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument202 pagesConnective TissuePeter ThompsonNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Connective TissueDocument5 pagesLesson 5 Connective Tissueshairene PiaNo ratings yet
- CH 7 - Structural Organisation in AnimalsDocument8 pagesCH 7 - Structural Organisation in AnimalsLaxmiNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument11 pagesConnective TissueTricia BaborNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue, VnaDocument78 pagesConnective Tissue, Vnavaryvira6677No ratings yet
- CH 7Document9 pagesCH 7Ruchika Kumari, VIII-A, 3956100% (1)
- 7 Structural Organisation in Animals - Notes - SampleDocument2 pages7 Structural Organisation in Animals - Notes - SampleManish KumarNo ratings yet
- connective tissueDocument88 pagesconnective tissueDeniz asmazNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue NotesDocument6 pagesConnective Tissue NotesNand PrakashNo ratings yet
- Histoooooo!!! 345Document5 pagesHistoooooo!!! 345OtencianoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5: Connective TissueDocument5 pagesChapter 5: Connective TissueAALIYAH REIGN MAPUSAONo ratings yet
- Cell Structures and Their FunctionsDocument4 pagesCell Structures and Their FunctionsRaeson Amir ReyesNo ratings yet
- All About Animal Cells: Presentation byDocument32 pagesAll About Animal Cells: Presentation byMarifer Dapat100% (1)
- Connective Tissues: Support, Anchor and Connect the BodyDocument7 pagesConnective Tissues: Support, Anchor and Connect the BodyTom Anthony TonguiaNo ratings yet
- Vet Histo Notes Chap 3Document15 pagesVet Histo Notes Chap 3Mia Kristhyn Calinawagan SabanalNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument20 pagesConnective TissueWadabi100% (1)
- Tissues: Tissue: A Tissue Is A Collection of Cells Having Similar Origin, Structure, and FunctionDocument13 pagesTissues: Tissue: A Tissue Is A Collection of Cells Having Similar Origin, Structure, and FunctionnagahushanamNo ratings yet
- Cells and Tissues & Integumentary SystemDocument21 pagesCells and Tissues & Integumentary SystemTaehyung KimNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue Histology GuideDocument35 pagesConnective Tissue Histology Guide121 FK Johnson KannadyNo ratings yet
- Connective TissueDocument4 pagesConnective TissueLANGWAEMILLNo ratings yet
- Connective Tissue Functions and Components ExplainedDocument56 pagesConnective Tissue Functions and Components ExplainedLAVKESH KUMARNo ratings yet
- Tissues - Human: Tissues Group of Similar Cells and Cell SecretionsDocument7 pagesTissues - Human: Tissues Group of Similar Cells and Cell SecretionsABHINABA GUPTANo ratings yet
- ANIMAL CELL PARTS AND FUNCTIONSDocument5 pagesANIMAL CELL PARTS AND FUNCTIONSNan Fen Jin Sabolarce100% (1)
- CTDocument84 pagesCTNigusu SolomonNo ratings yet
- Histology: Connective Tissue: Dr. Douglas Hamilton DSB 0071 - Dhamil2@uwo - CaDocument11 pagesHistology: Connective Tissue: Dr. Douglas Hamilton DSB 0071 - Dhamil2@uwo - Caray774432No ratings yet
- Connective Tissue: THREE BASIC STRUCTURAL COMPONENTS: Ground Substance, Fibers, CellsDocument6 pagesConnective Tissue: THREE BASIC STRUCTURAL COMPONENTS: Ground Substance, Fibers, CellsKaren Langca-agNo ratings yet
- Anaphy ReviewerDocument13 pagesAnaphy ReviewerChriza Mae Dela Pe�aNo ratings yet
- Tissues and the Four Primary TypesDocument9 pagesTissues and the Four Primary TypesMax Delvalle100% (1)
- Directions For This Reading ActivityDocument5 pagesDirections For This Reading ActivityMariam RuizNo ratings yet
- L6.1-Connective Tissues-Dr.Ghazal,3rd March 2024 ok_11a16c7a783a8a64fee12418d69adb29Document32 pagesL6.1-Connective Tissues-Dr.Ghazal,3rd March 2024 ok_11a16c7a783a8a64fee12418d69adb29LT DRAGONXNo ratings yet
- CH 7 Structural Organisation of AnimalsDocument16 pagesCH 7 Structural Organisation of AnimalsREENA GULERIANo ratings yet
- Plant and Animal Tissues - ObjectivesDocument7 pagesPlant and Animal Tissues - ObjectivesSyedrijal AkberNo ratings yet
- Contributory Factors To The Evolution of The ConceDocument29 pagesContributory Factors To The Evolution of The ConcePenelopeNo ratings yet
- Ethical Consideration in Leadership & ManagementDocument25 pagesEthical Consideration in Leadership & ManagementPenelopeNo ratings yet
- What Should You Do in Case of A Disaster?Document11 pagesWhat Should You Do in Case of A Disaster?PenelopeNo ratings yet
- Practical Research 2 (Reviewer)Document2 pagesPractical Research 2 (Reviewer)PenelopeNo ratings yet
- Water Quality Guide PDFDocument22 pagesWater Quality Guide PDFcontinentalflossNo ratings yet
- Adrenergic Agonists Classification and EffectsDocument15 pagesAdrenergic Agonists Classification and EffectsSeema YadavNo ratings yet
- Enderal Book CollectionDocument266 pagesEnderal Book CollectionMagazyn BotNo ratings yet
- Nipple Discharge 3Document3 pagesNipple Discharge 3Dima PathNo ratings yet
- Paper For Enzyme ActivityDocument7 pagesPaper For Enzyme ActivityFar hatNo ratings yet
- Antecedent Defined: Module 1 Section 2: HISTORICAL ANTECEDENTDocument4 pagesAntecedent Defined: Module 1 Section 2: HISTORICAL ANTECEDENTJudy CruzNo ratings yet
- Chronic Fatigue Syndrome PDFDocument22 pagesChronic Fatigue Syndrome PDFsteffiecruz06No ratings yet
- Pyloric Stenosis: DR Behrang AminiDocument9 pagesPyloric Stenosis: DR Behrang AminivitaNo ratings yet
- Heat Shock Proteins in Veterinary Medicine and SciencesDocument396 pagesHeat Shock Proteins in Veterinary Medicine and SciencesИгор ГалоскиNo ratings yet
- Wei Zheng, 2018Document8 pagesWei Zheng, 2018Hananya ManroeNo ratings yet
- Card 2 Sensible and Insensible Fluid LossDocument1 pageCard 2 Sensible and Insensible Fluid LossCaitlin MenziesNo ratings yet
- Frame Denture - Metal Frame BenefitsDocument8 pagesFrame Denture - Metal Frame BenefitsJennieNo ratings yet
- Master Plan to Achieve Zero Workplace AccidentsDocument38 pagesMaster Plan to Achieve Zero Workplace AccidentsgilbertwildNo ratings yet
- Parents of Episcopal School of Jacksonville Students File Lawsuit Over Mask MandateDocument32 pagesParents of Episcopal School of Jacksonville Students File Lawsuit Over Mask MandateActionNewsJaxNo ratings yet
- Gardasil VAERS ReportsDocument1,637 pagesGardasil VAERS ReportsJudicial Watch, Inc.50% (2)
- Peritoneum 2022Document86 pagesPeritoneum 2022Tayyib KhanNo ratings yet
- Special South Carolina Pecan Festival Section InsideDocument14 pagesSpecial South Carolina Pecan Festival Section Insidenriddick03No ratings yet
- لحل مشكلة كتابة الروشتات للأطفال PDFDocument253 pagesلحل مشكلة كتابة الروشتات للأطفال PDFOmarAly100% (4)
- CMI ZentelDocument3 pagesCMI Zentelreggy kusumaaNo ratings yet
- Novi Lestari 1911304150 B3Document3 pagesNovi Lestari 1911304150 B3FarahNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan On Prevention of MalnutritionDocument7 pagesLesson Plan On Prevention of MalnutritionPriyanka NilewarNo ratings yet
- CPE328 Lecture Notes 1Document5 pagesCPE328 Lecture Notes 1Study SmartNo ratings yet
- 21 Top Orthopedic Tests PDFDocument27 pages21 Top Orthopedic Tests PDFLaraib Mirza100% (1)
- Safety and Efficacy of Vinyl Bags in Prevention of Hypothermia of Preterm Neonates at BirthDocument3 pagesSafety and Efficacy of Vinyl Bags in Prevention of Hypothermia of Preterm Neonates at BirthArgadia YuniriyadiNo ratings yet
- 2.0 Classification of Mental DisordersDocument3 pages2.0 Classification of Mental DisordersJohnBenedictRazNo ratings yet
- EmbryologyDocument26 pagesEmbryologyMeer BabanNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Livelihoods For Smallholders Farmers in Andhra Pradesh and Uttar PradeshDocument39 pagesSustainable Livelihoods For Smallholders Farmers in Andhra Pradesh and Uttar Pradeshchandra DiveshNo ratings yet
- Patient Ratio1:4Nurse:Patient Ratio1:6Intensive Care UnitNurse:Patient Ratio1:2Operating Room Nurse:Patient Ratio1:1Emergency RoomNurse:Patient Ratio1:3General Medical-SurgicalDocument53 pagesPatient Ratio1:4Nurse:Patient Ratio1:6Intensive Care UnitNurse:Patient Ratio1:2Operating Room Nurse:Patient Ratio1:1Emergency RoomNurse:Patient Ratio1:3General Medical-SurgicalDarren FloresNo ratings yet
- Aemses Sof Be LCP 2021 2022Document16 pagesAemses Sof Be LCP 2021 2022ROMEO SANTILLANNo ratings yet
- Fibromyalgia: Annals of Internal MedicineDocument16 pagesFibromyalgia: Annals of Internal MedicineTeofanes PonceNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Infections in ChildrenDocument8 pagesUrinary Tract Infections in ChildrenLorelie AsisNo ratings yet
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (17)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (3)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (78)
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (4)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (403)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- 12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosFrom Everand12 Rules for Life by Jordan B. Peterson - Book Summary: An Antidote to ChaosRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (207)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeNo ratings yet
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (169)
- The Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesFrom EverandThe Ultimate Guide To Memory Improvement TechniquesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (34)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (44)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Techniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementFrom EverandTechniques Exercises And Tricks For Memory ImprovementRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (40)
- The Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingFrom EverandThe Happiness Trap: How to Stop Struggling and Start LivingRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Algorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsFrom EverandAlgorithms to Live By: The Computer Science of Human DecisionsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (722)
- Summary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: How to Be an Adult in Relationships: The Five Keys to Mindful Loving by David Richo: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (11)
- Gut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerFrom EverandGut: the new and revised Sunday Times bestsellerRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (392)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)