Professional Documents
Culture Documents
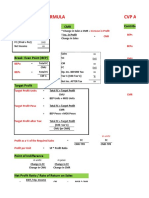
Contribution Margin Income Statement
Uploaded by
Meghan Kaye LiwenOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Contribution Margin Income Statement
Uploaded by
Meghan Kaye LiwenCopyright:
Available Formats
CONTRIBUTION MARGIN INCOME STATEMENT
Sales-Variable Cost= CM
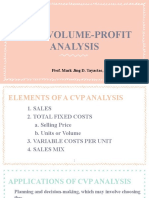
KEY ASSUMPTION OF CVP ANALYSIS
1. All costs are classifiable as either variable or fixed
2. Cost and revenue relationships are predictable and linear over a relevant range of activity and a
specified period of time.
3. Total variable costs change directly with the cost driver, but variable costs per unit are constant
over the relevant range
4. Total fixed costs are constant over the relevant range, but fixed costs per unit vary inversely with
the cost driver
5. Selling prices per unit and market condition remain unchanged
6. Production equal sales (when there is no change in inventory)
7. The time value of money is ignored.
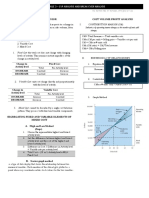
BREAK-EVEN ANALYSIS
Break-even point- neither profit nor loss
A. Single-Product
FC
1. BEP ( Pesos ) =
CMR
FC
2. BEP ( Units )=
CMu
B. Multiple Products
FC
1. BEP ( Pesos ) =
WaCMR
Total CM
a. WaCMR=
Total Sales
b. WaCMR=∑ of [ ( CMR∗Sales Mix Ratio ) per product ]
Sales∈Pesos
* Sales Mix Ratio=
Total Sales∈Pesos
FC
2. BEP ( Units )=
WaCMu
Total CM
a. WaCMu=
Total Units
b. WaCMu=∑ of [ ( CMu∗Sales Mix Ratio ) per product ]
Sales∈Units
* Sales Mix Ratio=
Total Sales∈Units
MARGIN OF SAFETY
- Amount of peso-sales/ number of units by which actual or budgeted sales may be decreased without
resulting into a loss
1. MOS ( Pesos ) =Sales∈Pesos−BEP ∈Pesos
2. MOS ( Units )=Sales∈Units−BEP ∈Units
MOS ( Pesos )
MOS ( Units )=
Selling Price
MOS ( Pesos )
3. MOS Ratio=
Sales∈ Pesos
MGMT GOALS Required Sales Required Sales (PESOS)
(QUANTITY)
To earn desired profit FC + DP FC + DP
before tax (DP) CMU CMR
To earn desired profit
before tax (DP) MOS ( Units )∗CMU MOS ( Pesos )∗CMR
To earn Desired Profit DP DP
after Tax [ (
FC +
1−tax rate )] [ (
FC+
1−tax rate )]
CMU CMR
To earn desired profit FC + DP FC+ DP
ratio (Profit as % of CMU−PU CMR−PR
sales)
OPERATING LEVERAGE
-extent to which a company uses fixed cost in its cost structure
- used to calculate a company’s break-even point and help set appropriate selling prices to cover all
costs and generate a profit.
OPERATING LEVERAGE FACTOR (OLF) or DEGREE OF OPERATING LEVERAGE (DOL)
-used to measure the extent of the change in EBIT resulting from the change in sales
Total CM
1. DOL∨OLF =
EBIT
% ∆∈EBIT
2. DOL∨OLF =
% ∆∈Sales
3. % ∆∈Profit=% ∆∈Sales∗DOL
You might also like
- Schedule and FormulasDocument55 pagesSchedule and FormulasRodmae VersonNo ratings yet
- CVP Analysis and Marginal CostingDocument5 pagesCVP Analysis and Marginal CostingKJKSZPJ LXGIWYLNo ratings yet
- Mas: CVP and Break-Even Analysis Concept Summary: Period of TimeDocument3 pagesMas: CVP and Break-Even Analysis Concept Summary: Period of TimeClyde RamosNo ratings yet
- CVP FormulasDocument4 pagesCVP FormulasMelanie Daclan AntepasadoNo ratings yet
- Cost-Volume Profit AnalysisDocument3 pagesCost-Volume Profit AnalysisVianca MaquilanNo ratings yet
- Cost Volume Profit Analysis Review NotesDocument10 pagesCost Volume Profit Analysis Review NotesAlexis Kaye DayagNo ratings yet
- CVP AnalysisDocument4 pagesCVP AnalysisAngela Miles DizonNo ratings yet
- Profit Sales VC + FC CM FC Can Be Computed In: UnitsDocument2 pagesProfit Sales VC + FC CM FC Can Be Computed In: UnitsHiraya ManawariNo ratings yet
- Cost Volume Profit AnalysisDocument2 pagesCost Volume Profit AnalysisBloodyapplesNo ratings yet
- Mas 06-03 Cost Volume Profit (CVP)Document7 pagesMas 06-03 Cost Volume Profit (CVP)xernathanNo ratings yet
- Cost Volume Profit AnalysisDocument4 pagesCost Volume Profit AnalysisMd. Abu NaserNo ratings yet
- StratCost CVP 1Document65 pagesStratCost CVP 1Vrix Ace MangilitNo ratings yet
- Management Advisory ServicesDocument16 pagesManagement Advisory ServicesJohn Carlos WeeNo ratings yet
- SC Class 2Document54 pagesSC Class 2rodrigo.felix17012002No ratings yet
- 678MAC4 Cost Volume ProfitDocument18 pages678MAC4 Cost Volume ProfitMaria Christina CandelarioNo ratings yet
- CVP Copy 4Document2 pagesCVP Copy 4BloodyapplesNo ratings yet
- MS - Until WCM HeyheiDocument16 pagesMS - Until WCM Heyheimisonim.eNo ratings yet
- Chapter - One Cost-Volume-Profit AnalysisDocument10 pagesChapter - One Cost-Volume-Profit Analysisabateneh sintayehuNo ratings yet
- CVP LectureDocument9 pagesCVP Lecturejohanna mapilotNo ratings yet
- Sensitivity % Change in OutputDocument22 pagesSensitivity % Change in OutputPrincessNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Lesson 3 CVP AnalysisDocument6 pagesWeek 3 - Lesson 3 CVP AnalysisReynold Raquiño AdonisNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 CVP AnalysisDocument8 pagesChapter 1 CVP AnalysisBenol MekonnenNo ratings yet
- Cost Acc Chapter 4Document5 pagesCost Acc Chapter 4ElleNo ratings yet
- Công TH CDocument19 pagesCông TH Ckim oanhNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - CVP AnalysisDocument2 pagesModule 3 - CVP AnalysisJoshua CabinasNo ratings yet
- Cost Accounting A Break Even AnalysisDocument23 pagesCost Accounting A Break Even AnalysisMy wifeNo ratings yet
- Mas-02: Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis: If There Is An Increase in Then Profit Tends ToDocument3 pagesMas-02: Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis: If There Is An Increase in Then Profit Tends ToClint AbenojaNo ratings yet
- CVP AnalysisDocument48 pagesCVP AnalysisTonie NascentNo ratings yet
- Cost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis: Cmu SPDocument3 pagesCost-Volume-Profit (CVP) Analysis: Cmu SPKuya ANo ratings yet
- 9003 CVP AnalysisDocument7 pages9003 CVP AnalysisSirNo ratings yet
- Break-Even Point and Cost-Volume-Profit AnalysisDocument44 pagesBreak-Even Point and Cost-Volume-Profit AnalysisKhánh Đoan NgôNo ratings yet
- M5 Cost-Volume Profit Analysis As Managerial Planing ToolDocument6 pagesM5 Cost-Volume Profit Analysis As Managerial Planing Toolwingsenigma 00No ratings yet
- CVP StudentsDocument21 pagesCVP StudentsrbnbalachandranNo ratings yet
- ACAUD 3139 Strategic ManagementDocument31 pagesACAUD 3139 Strategic ManagementchxrlttxNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 - Cost-Volume-Profit AnalysisDocument3 pagesLesson 2 - Cost-Volume-Profit AnalysisVanesa Calimag ClementeNo ratings yet
- Strat Cost Handout 02 CVP Analysis Updated 0212 - CompressDocument17 pagesStrat Cost Handout 02 CVP Analysis Updated 0212 - CompressAerwyna AfarinNo ratings yet
- CVP AnalysisDocument2 pagesCVP Analysissakura harunoNo ratings yet
- CVP AnalysisDocument5 pagesCVP AnalysisAzumi RaeNo ratings yet
- Cost Volume Profit Analysis Review NotesDocument17 pagesCost Volume Profit Analysis Review NotesAlexis Kaye DayagNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4Document2 pagesChapter 4Lawliet RyuzakiNo ratings yet
- Module 3 Cost Volume Profit Analysis Notes PDFDocument3 pagesModule 3 Cost Volume Profit Analysis Notes PDFMadielyn Santarin MirandaNo ratings yet
- Marginal Costing 07Document10 pagesMarginal Costing 07Suraj JoseNo ratings yet
- Lesson 2 ProblemsDocument1 pageLesson 2 Problemshaech jaemNo ratings yet
- Chapter - One Cost-Volume-Profit AnalysisDocument13 pagesChapter - One Cost-Volume-Profit Analysisliyneh mebrahituNo ratings yet
- Types of Cost BehaviourDocument9 pagesTypes of Cost BehaviourmeseleNo ratings yet
- CVP AnalysisDocument37 pagesCVP Analysis20B81A1235cvr.ac.in G RUSHI BHARGAVNo ratings yet
- Cost-Volume-Profit AnalysisDocument51 pagesCost-Volume-Profit AnalysisKalash SinghalNo ratings yet
- Breakeven AnalysisDocument21 pagesBreakeven AnalysisrdksjNo ratings yet
- COSTMAN - MidtermDocument23 pagesCOSTMAN - MidtermHoney MuliNo ratings yet
- MSCI111 - CVP ModelsDocument22 pagesMSCI111 - CVP ModelsViviene Seth Alvarez LigonNo ratings yet
- Strat CostDocument6 pagesStrat CostrylNo ratings yet
- Module 3 CVP and Breakeven AnalysisDocument4 pagesModule 3 CVP and Breakeven Analysiskhaireyah hashimNo ratings yet
- Formulas of Managerial Accounting Chapter 5Document2 pagesFormulas of Managerial Accounting Chapter 5Shahinul KabirNo ratings yet
- Mas 02 - CVPDocument24 pagesMas 02 - CVPAlexis RiveraNo ratings yet
- Topic 4Document32 pagesTopic 4Razique RezaNo ratings yet
- Bingcang & Tamon (CVP, Module 5)Document67 pagesBingcang & Tamon (CVP, Module 5)FayehAmantilloBingcangNo ratings yet
- CVP AnalysisDocument35 pagesCVP AnalysisAbby MendozaNo ratings yet
- Cost Volume Profit AnalysisDocument40 pagesCost Volume Profit AnalysisRajguru JavalagaddiNo ratings yet
- CPA Review Notes 2019 - BEC (Business Environment Concepts)From EverandCPA Review Notes 2019 - BEC (Business Environment Concepts)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (9)
- Responsibility For VariancesDocument3 pagesResponsibility For VariancesMeghan Kaye LiwenNo ratings yet
- Factory Overhead Variances: Flexible Budget ApproachDocument4 pagesFactory Overhead Variances: Flexible Budget ApproachMeghan Kaye LiwenNo ratings yet
- Factory Overhead Cost StandardsDocument3 pagesFactory Overhead Cost StandardsMeghan Kaye LiwenNo ratings yet
- Labor VariancesDocument4 pagesLabor VariancesMeghan Kaye LiwenNo ratings yet
- A. Four-Variance MethodDocument3 pagesA. Four-Variance MethodMeghan Kaye LiwenNo ratings yet
- Mix and Yield VariancesDocument4 pagesMix and Yield VariancesMeghan Kaye LiwenNo ratings yet
- Materials Purchase Price VarianceDocument3 pagesMaterials Purchase Price VarianceMeghan Kaye LiwenNo ratings yet
- For Questions 6Document3 pagesFor Questions 6Meghan Kaye LiwenNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in PartnershipDocument3 pagesReviewer in PartnershipMeghan Kaye LiwenNo ratings yet
- Mix and Yield VariancesDocument4 pagesMix and Yield VariancesMeghan Kaye LiwenNo ratings yet
- Standard Cost Under Absorption and Variable CostingDocument4 pagesStandard Cost Under Absorption and Variable CostingMeghan Kaye LiwenNo ratings yet
- Computation and Analysis of VariancesDocument3 pagesComputation and Analysis of VariancesMeghan Kaye LiwenNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1-5Document30 pagesChapter 1-5Leonardo R. Aldovino, Jr.No ratings yet
- Materi Amb CH 8Document73 pagesMateri Amb CH 8Sri HaryantiNo ratings yet
- Knifeedge Business-Model-CanvasDocument2 pagesKnifeedge Business-Model-CanvasIke NnajidemmaNo ratings yet
- CRM FlipkartDocument17 pagesCRM FlipkartHarish Krishnan80% (5)
- Get Started Go Live Communication and Adoption GuideDocument12 pagesGet Started Go Live Communication and Adoption GuideJodeeNo ratings yet
- Milo MaterialsDocument17 pagesMilo MaterialsNwabuisi PamelaNo ratings yet
- Indian Advertising CompaniesDocument4 pagesIndian Advertising Companiesyogesh vermaNo ratings yet
- Employee BrandingDocument12 pagesEmployee BrandingZeinabAlaweihNo ratings yet
- Get-As International PLCDocument55 pagesGet-As International PLCTesfaye Degefa100% (1)
- Summer Training Project ReportDocument64 pagesSummer Training Project ReportSaim aliNo ratings yet
- Module 1 Introduction To Business PolicyDocument54 pagesModule 1 Introduction To Business Policycha11100% (1)
- 6-Types of Cost-23-08-2021 (23-Aug-2021) Material - I - 23-Aug-2021 - MEE1014 - Elements - of - Cost - NewDocument67 pages6-Types of Cost-23-08-2021 (23-Aug-2021) Material - I - 23-Aug-2021 - MEE1014 - Elements - of - Cost - NewSahil KumarNo ratings yet
- Technology Management - UGDocument167 pagesTechnology Management - UGjeezcn100% (1)
- MBA691 Final ProjectDocument39 pagesMBA691 Final ProjectIam TwinStorms80% (5)
- "A Study On Sales and Marketing Strategy of Hero Motocorp": Summer Training Report OnDocument91 pages"A Study On Sales and Marketing Strategy of Hero Motocorp": Summer Training Report Onravi singhNo ratings yet
- Social Enterprise ReportDocument40 pagesSocial Enterprise Reportupadhyay.tanishqaNo ratings yet
- Business Plan Done On Juice ProcessingDocument25 pagesBusiness Plan Done On Juice Processingbernabas92% (48)
- Chapter 01 Intro To Production and Operations ManagementDocument43 pagesChapter 01 Intro To Production and Operations ManagementDuga RennabelleNo ratings yet
- Sas#3-Mkt 007Document8 pagesSas#3-Mkt 007Cyrill Paghangaan VitorNo ratings yet
- It Implementations and Strategic Alignment of Air AsiaDocument5 pagesIt Implementations and Strategic Alignment of Air AsiaManish SharmaNo ratings yet
- Understanding The Supply ChainDocument28 pagesUnderstanding The Supply ChainAakanksha Anand BediNo ratings yet
- Term PaperDocument9 pagesTerm Paperapi-252903965No ratings yet
- Digital Trends 2023 by WmaDocument87 pagesDigital Trends 2023 by WmaJabuke U SlafrokuNo ratings yet
- Draft Conceptual PaperDocument5 pagesDraft Conceptual PaperIqlima HanifizzulfaNo ratings yet
- The Rebirth of Online Shopping: A Quantitative Research of Online Shopping and Its EffectsDocument5 pagesThe Rebirth of Online Shopping: A Quantitative Research of Online Shopping and Its EffectsKen MateyowNo ratings yet
- Segmentation, Targeting, Positioning and Strategy of Radio Company in Kendari, Southeast SulawesiDocument8 pagesSegmentation, Targeting, Positioning and Strategy of Radio Company in Kendari, Southeast SulawesiinventionjournalsNo ratings yet
- 22 Imutable LawsDocument2 pages22 Imutable LawsWahid T. YahyahNo ratings yet
- TDU Research Proposal 2Document9 pagesTDU Research Proposal 2ushe100% (1)
- P&G Japan-The SK-II Project PDFDocument6 pagesP&G Japan-The SK-II Project PDFJojo Javier100% (1)
- Week 2 - Health Communication (Autosaved)Document30 pagesWeek 2 - Health Communication (Autosaved)Alvin De lunaNo ratings yet