Professional Documents
Culture Documents
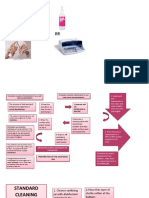
Critical Items: Cleaning
Uploaded by
Krishnendra MulgundOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Critical Items: Cleaning
Uploaded by
Krishnendra MulgundCopyright:
Available Formats
Involves washing with cool water and detergent (<45ᵒ).
Can be
done by automated machine (including ultrasound cleaners) or Cleaning Items that enter sterile tissue eg surgical
manually. It lowers the bioburden before disinfection/sterilisation Critical items instruments, cardiac catheters, implants,
needles
Contact mucous membranes eg
Done using gluteraldehyde, hydrogen Spaulding classification
Chemical Semi-critical items laryngoscopes, fibre-optic endoscopes. They
peroxide, peracetic acid, alcohol. require high level disinfection
Hot water at 77ᵒ for 30 mins. Spores not killed. Pasteurisation
Come in contact with healthy skin eg BP cuff,
Non-critical items
pulse oximetry
Pseudomonas, klebsiella and mycobacterium
Disinfection
can be transmitted. The external surface is
washed and rinsed, internal channels are
CEACCP
brushed and flushed with detergent. Cleaning Physical removal of foreign material
Detachable parts are removed and soaked in Endoscopes
detergent. They are pressure tested to Decontamination
determin integrity of seals before immersion to A process destroying contamination such that
reduce the risk of damage to the head of the they cannot reach a susceptible site in sufficient
scope Decontamination
quantities to initiate a harmful response. It is
followed by disinfection or decontamination.
A process that eliminates many or all
Steam at 121 or 134ᵒ for 15 or 3 mins respectively Steam Terminology Disinfection
pathogens except bacterial spores.
Ethylene oxide 29-65ᵒ for 5-12 hrs Chemical which kills bacteria, viruses and
High-level disinfection spores. Only sporicidal under certain
Sterilisation conditions
Gluteraldehyde 2% for >10 hrs
Chemical
Renders an object completely free of all viable
Gas plasma has ionised gas and free radicals Sterilisation
microbial life
capable of inactivating microbes in 75 mins
/Decontamination/CEACCP
http://ceaccp.oxfordjournals.org/content/4/4/103.full.pdf
You might also like
- Rationale For Surgical HandwashingDocument2 pagesRationale For Surgical HandwashingPhil Pasaol100% (1)
- Wound ManagementDocument25 pagesWound ManagementAlwin RaisNo ratings yet
- General Principles in Clinical Microbiology Supplemental NotesDocument13 pagesGeneral Principles in Clinical Microbiology Supplemental NotesAhnorrei PavlaskaNo ratings yet
- Sterilization and DisinfectionDocument67 pagesSterilization and DisinfectionBhoomika Sikri100% (1)
- Standard Cleaning Procedures of Nail Care ToolsDocument3 pagesStandard Cleaning Procedures of Nail Care ToolsIrish Nicole PacionNo ratings yet
- Save Time and Money. Deliver High Quality Water.: Stay in Control of Your Drinking Water Treatment ProcessDocument1 pageSave Time and Money. Deliver High Quality Water.: Stay in Control of Your Drinking Water Treatment ProcessleonardseniorNo ratings yet
- General Surgery Notes For Dental StudentsDocument128 pagesGeneral Surgery Notes For Dental StudentsMustafa SaßerNo ratings yet
- Cleaning and Disinfection IPC SGNHCDocument74 pagesCleaning and Disinfection IPC SGNHCRoshani sharmaNo ratings yet
- FPa 003Document6 pagesFPa 003stepuptoblockNo ratings yet
- Tanzania Checklist 08 05Document17 pagesTanzania Checklist 08 05amanuel waleluNo ratings yet
- Aseptic and Sterilization TechniquesDocument5 pagesAseptic and Sterilization TechniquesSister RislyNo ratings yet
- Procedures For Using Steam Autoclaves: QUESTIONS: Contact DRS, 217-333-2755, For Additional InformationDocument1 pageProcedures For Using Steam Autoclaves: QUESTIONS: Contact DRS, 217-333-2755, For Additional InformationZafirahAhmadFauziNo ratings yet
- Operating Room Techniques: Presented By: Leonardo C. Matunding, RN, MNDocument82 pagesOperating Room Techniques: Presented By: Leonardo C. Matunding, RN, MNKurt RoseteNo ratings yet
- Environmental Sampling in Food Facilities: by Gabriela Martinez, Scientific Director, Labplas, Quebec, CanadaDocument2 pagesEnvironmental Sampling in Food Facilities: by Gabriela Martinez, Scientific Director, Labplas, Quebec, CanadamaritaNo ratings yet
- FM - HSE COSHH Assessment-2Document3 pagesFM - HSE COSHH Assessment-2anisaanNo ratings yet
- MicrobiologyDocument3 pagesMicrobiologyJedrilyn CanopinNo ratings yet
- CSSDDocument32 pagesCSSDRAHUL100% (1)
- Workplace Readiness 2nd Infographics 0Document1 pageWorkplace Readiness 2nd Infographics 0onahiatusNo ratings yet
- L4 - Sterilization and DisinfectionDocument23 pagesL4 - Sterilization and DisinfectionArshad AbbasNo ratings yet
- Sterilisation TechniquesDocument4 pagesSterilisation TechniquesmehekNo ratings yet
- Sterlization AsepsisDocument30 pagesSterlization AsepsisVinod BharatiNo ratings yet
- Rochester InstituteDocument4 pagesRochester InstituteDCG CandyNo ratings yet
- Ginetex: Textile Care SymbolsDocument15 pagesGinetex: Textile Care SymbolsananthiNo ratings yet
- Hazard: Types of Safety Hazard Types Source Possible InjuryDocument2 pagesHazard: Types of Safety Hazard Types Source Possible InjuryRicardo Lorenzo AlasNo ratings yet
- Expertip 1 Cleaning and Conditioning of Dryer FabricsDocument4 pagesExpertip 1 Cleaning and Conditioning of Dryer FabricsnotengofffNo ratings yet
- Medical Vs Surgical AsepsisDocument2 pagesMedical Vs Surgical AsepsisRikaria. CurryNo ratings yet
- Wound Care: Types of DressingDocument5 pagesWound Care: Types of DressingAmit MartinNo ratings yet
- CH 7Document9 pagesCH 7sajahassan004No ratings yet
- Celitron - Medical Waste Solution - IsS AC-575 Brochure - BookletDocument5 pagesCelitron - Medical Waste Solution - IsS AC-575 Brochure - BookletBladimir CamposNo ratings yet
- Sterilisation & DisinfectionDocument57 pagesSterilisation & DisinfectionmiziezuraNo ratings yet
- Germ Shield - Battlecard - July2020Document1 pageGerm Shield - Battlecard - July2020Shweta SharmaNo ratings yet
- Risk Assessment For Water Proofing BerryDocument4 pagesRisk Assessment For Water Proofing BerryjeyesbelmenNo ratings yet
- Verde de Malaquita - Sigma Aldrich-115942-EnDocument2 pagesVerde de Malaquita - Sigma Aldrich-115942-EnDiegoNo ratings yet
- EVS Standard Cart TemplateDocument1 pageEVS Standard Cart Templatesilvia_guerra_1No ratings yet
- Control of Microbial GrowthDocument4 pagesControl of Microbial GrowthJerreca DasasNo ratings yet
- Bacoban TDSDocument2 pagesBacoban TDSscribdNo ratings yet
- Poster Irrigation System in EndodonticDocument2 pagesPoster Irrigation System in EndodonticMonika LohakpureNo ratings yet
- BeautyCare Week34Document3 pagesBeautyCare Week34jewelpandinooNo ratings yet
- 04 LEC DecontaminationDocument1 page04 LEC Decontaminationericka abasNo ratings yet
- Nading, A. Local Biologies, Leaky Things, and The Chemical Infrastructure of Global Health PDFDocument16 pagesNading, A. Local Biologies, Leaky Things, and The Chemical Infrastructure of Global Health PDFWagner AlvesNo ratings yet
- Sterilisation and DisinfectionDocument61 pagesSterilisation and Disinfectionbhoomika kharviNo ratings yet
- Cleaning and Disinfecting Beauty Salon EquipmentDocument11 pagesCleaning and Disinfecting Beauty Salon EquipmentChandan SinghNo ratings yet
- Week3 Main-Evidence RevisedDocument7 pagesWeek3 Main-Evidence RevisedaywankolanghoNo ratings yet
- Sterilization and AsepsisDocument48 pagesSterilization and AsepsissevattapillaiNo ratings yet
- ParticleDocument1 pageParticleS DasNo ratings yet
- Combs TeachingplanDocument5 pagesCombs Teachingplanapi-539369902No ratings yet
- Bio204 Principles of Biochemical EngineeringDocument32 pagesBio204 Principles of Biochemical EngineeringHanifullah JanNo ratings yet
- ASPIRO TechnologyDocument19 pagesASPIRO Technologysehyong0419No ratings yet
- Laparoscopic AppendectomyDocument4 pagesLaparoscopic AppendectomyBrandy JaffarNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan FormDocument2 pagesHealth Teaching Plan FormChadd Vyllmorr VillarinNo ratings yet
- Health Teaching Plan FormDocument2 pagesHealth Teaching Plan FormChadd Vyllmorr VillarinNo ratings yet
- Term Methods Actions Level of Activity Uses: PhenolsDocument5 pagesTerm Methods Actions Level of Activity Uses: PhenolsJuliana ViteNo ratings yet
- Principle, Advantages, Disadvantages, Application S of Different Sterilisation Methods and in Process ControlDocument50 pagesPrinciple, Advantages, Disadvantages, Application S of Different Sterilisation Methods and in Process ControlAhmed ImranNo ratings yet
- Bacillocid Extra PharmaDocument1 pageBacillocid Extra PharmaPabhat KumarNo ratings yet
- Reliable Sars-Cov-2 Detection For Safety in The Food IndustryDocument4 pagesReliable Sars-Cov-2 Detection For Safety in The Food IndustryElviraNo ratings yet
- Business Model Canvas: Existing Alternative SolutionDocument2 pagesBusiness Model Canvas: Existing Alternative SolutionPRINCESS DIANNE DUG-ANo ratings yet
- Rinoplastia Não CirúrgicaDocument12 pagesRinoplastia Não CirúrgicadrlucasfaveroNo ratings yet
- 1.6.5 Preliminary Hazard Analysis - Rev0Document22 pages1.6.5 Preliminary Hazard Analysis - Rev0singla.nishant1245No ratings yet
- School Under 12 Team 58Document1 pageSchool Under 12 Team 58Krishnendra MulgundNo ratings yet
- FullDocument6 pagesFullKrishnendra MulgundNo ratings yet
- Sicilian Classical 6.Bc4 Velimirovic Attack (Games)Document4 pagesSicilian Classical 6.Bc4 Velimirovic Attack (Games)Krishnendra MulgundNo ratings yet
- IndexDocument522 pagesIndexKrishnendra MulgundNo ratings yet
- Sicilian Classical 6.Bc4 Velimirovic AttackDocument4 pagesSicilian Classical 6.Bc4 Velimirovic AttackKrishnendra MulgundNo ratings yet
- Patient Factors: General AnaesthesiaDocument2 pagesPatient Factors: General AnaesthesiaKrishnendra MulgundNo ratings yet
- Delayed RecoveryDocument2 pagesDelayed RecoveryKrishnendra MulgundNo ratings yet
- Acute Disturbance in Cognitive Function DiagnosisDocument3 pagesAcute Disturbance in Cognitive Function DiagnosisKrishnendra MulgundNo ratings yet
- 2018 Summer Edition - FINALDocument21 pages2018 Summer Edition - FINALKrishnendra MulgundNo ratings yet
- (Osborn) Chapter 20: Learning Outcomes (Number and Title)Document26 pages(Osborn) Chapter 20: Learning Outcomes (Number and Title)KittiesNo ratings yet
- Pathogen Safety Data Sheet: Candida AlbicansDocument1 pagePathogen Safety Data Sheet: Candida AlbicansDila AngelikaNo ratings yet
- Iap Immunisation ScheduleDocument6 pagesIap Immunisation ScheduleG VenkateshNo ratings yet
- ClostridumDocument30 pagesClostridumFrancesca VargasNo ratings yet
- Pertimbangan Terapi Kortikosteroid Pada Stomatitis Herpetik RekurenDocument8 pagesPertimbangan Terapi Kortikosteroid Pada Stomatitis Herpetik RekurenPutri AmaliaNo ratings yet
- Daftar Pustaka ParasitDocument11 pagesDaftar Pustaka Parasitresnha419No ratings yet
- Staphylococcus AureusDocument19 pagesStaphylococcus AureusLucas0% (1)
- Vaccination CertificateDocument1 pageVaccination CertificateXyrene Del RosarioNo ratings yet
- Abstrak Dr. IKA CspADocument2 pagesAbstrak Dr. IKA CspAfauzanNo ratings yet
- Bakteri Anaerob: Morfologi, Fisiologi, Epidemiologi, Diagnosis, Pemeriksaan Sy. Miftahul El J.TDocument46 pagesBakteri Anaerob: Morfologi, Fisiologi, Epidemiologi, Diagnosis, Pemeriksaan Sy. Miftahul El J.TResti Zulvanita DeviNo ratings yet
- Dodi Daftar PustakaDocument3 pagesDodi Daftar PustakaToni PinemNo ratings yet
- Pag-Oring Nuevo National High School: All Students of PNNHS Teachers Other StakeholdersDocument1 pagePag-Oring Nuevo National High School: All Students of PNNHS Teachers Other StakeholdersAlmiraMayAlvarezMarquezNo ratings yet
- SOP For Procurement of CultureDocument5 pagesSOP For Procurement of Culturegreen solution100% (2)
- Difference Between Spore and Cyst in Bacteria - Definition, Features, FunctionDocument7 pagesDifference Between Spore and Cyst in Bacteria - Definition, Features, FunctionMuhammad Junaid KhanNo ratings yet
- Micro Not in SketchyDocument4 pagesMicro Not in Sketchyrpascua123No ratings yet
- Price List HNA - All Share - Updated - 100123Document1 pagePrice List HNA - All Share - Updated - 100123nurul kusumaNo ratings yet
- IFN - Instructions For UseDocument5 pagesIFN - Instructions For UseMike SanchezNo ratings yet
- Nursing Education 2006Document292 pagesNursing Education 2006War SxaNo ratings yet
- Malaria Leaflet PDFDocument2 pagesMalaria Leaflet PDFPrimus moneNo ratings yet
- The Conquest of Infectious DiseaseDocument8 pagesThe Conquest of Infectious DiseaseericaNo ratings yet
- PlagueDocument20 pagesPlagueHemanth G.No ratings yet
- Kitajima 2020 BrasilDocument101 pagesKitajima 2020 BrasilFrancisca Beltrán GuzmánNo ratings yet
- Valacyclovir in The Treatment of Herpes Simplex HeDocument11 pagesValacyclovir in The Treatment of Herpes Simplex HeGrnitrv 22No ratings yet
- Oet Granular FeverDocument7 pagesOet Granular FeverSajal ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Textbook of Medical Parasitology Protozoology HelmDocument2 pagesTextbook of Medical Parasitology Protozoology HelmRomelu MartialNo ratings yet
- Stenotrophomonas. Maltophilia - A Rare Cause of Bacteremia in A Patient of End Stage Renal Disease On Maintenance HemodialysisDocument3 pagesStenotrophomonas. Maltophilia - A Rare Cause of Bacteremia in A Patient of End Stage Renal Disease On Maintenance HemodialysisInternational Organization of Scientific Research (IOSR)No ratings yet
- Treatment of Bacterial InfectionDocument5 pagesTreatment of Bacterial InfectionKarla Barria MansillaNo ratings yet
- Women and HIVDocument217 pagesWomen and HIVMuhammad Ricky RamadhianNo ratings yet
- Covid-19 Ag Card Home Test Kit: Do Not Open Items Until Instructed To Do SoDocument32 pagesCovid-19 Ag Card Home Test Kit: Do Not Open Items Until Instructed To Do SoRevNo ratings yet
- HepaviewDocument2 pagesHepaviewFelic NaitiliNo ratings yet