Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The TOYO Urea Granulation Technology
The TOYO Urea Granulation Technology
Uploaded by
Shamsudeen Abubakar SodangiCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
The TOYO Urea Granulation Technology
The TOYO Urea Granulation Technology
Uploaded by
Shamsudeen Abubakar SodangiCopyright:
Available Formats
20th AFA International Annual Technical Conference
19-21 June 2007 – Tunisia
Fertilizers Industry : Technology Development & Environmental Protection
The TOYO Urea Granulation Technology
- The Challenges and Achievements
in Producing Urea Granules -
SHUHEI NAKAMURA
Toyo Engineering Corporation
8-1, Akanehama 2-chome, Narashino-shi, Chiba 275-0024, Japan
INTRODUCTION
Since established in 1961, Toyo Engineering Corporation (TOYO), a global
leading engineering contractor and urea process licensor, has licensed its
technologies for over 100 urea plants including granulation units, sharing
1/4 of world urea production capacity as of May 2007.
In late 1970's, TOYO established a urea granulation process based on a
Spouting Bed type urea granulator and expanded its own technical range to
provide a variety of urea fertilizer products in addition to conventional Urea
Prill Product and Urea Solution Product.
In late 1980's, TOYO further improved its design of the granulator by
applying the Spout-Fluid Bed for the granulator, which is a combination of
the spouting beds and fluidized beds and reduces energy requirements
and improves the quality of the
product granules.
The features of TOYO Urea
Granulation Process are given
below:
(1) High Energy Efficiency
(2) High Product Quality
(3) Low Emission
Photo.1: PIM2, Indonesia 1,725 MTPD with ACES Plant
1 © 2007 TOYO ENGINEERING CORP.
20th AFA International Annual Technical Conference
19-21 June 2007 – Tunisia
Fertilizers Industry : Technology Development & Environmental Protection
Now, TOYO is known as the license owner of
the Spout-Fluid Bed Urea Granulation Process
to produce the high quality product which has
been applied for 16 urea plants as of the
middle of 2007 from 50 MT/D to 3,250
MT/D production capacities in single train.
(Refer to Table-1).
In 2007 TOYO has completed basic
engineering for a new 2,640 MTP Urea
Granulation project and license its
Spout-Fluid Bed Granulation technology for
PetroChina Tarim Petrochemical Company.
To meet increasing demand for large
Photo.2: Lutianhua, China
scale urea units, TOYO has started
(2,000 MTPD)
licensing technologies for so-called
“Jumbo Urea Plant” over 3,000 MTPD capacities. Design and engineering
up to 4,500 MTPD have completed and a number of proposals of 3,000 –
3,500 MTPD single train plants have been carried out. In early 2007, TOYO
was awarded an epoch-making contract to supply license and to perform
basic engineering to build a 3,250 MTPD Urea Plant in Iran. TOYO
ACES21® and Spout-Fluid Bed Granulation technologies are being applied
to the project.
Photo.3: SKW, Germany
No.1 Plant (1,200 MTPD) and No2 Plant (500 MTPD)
2 © 2007 TOYO ENGINEERING CORP.
20th AFA International Annual Technical Conference
19-21 June 2007 – Tunisia
Fertilizers Industry : Technology Development & Environmental Protection
This paper reviews the advancement in TOYO Granulation technology in
the aspect of product quality improvement, energy saving, environmental
protection, and approach to Jumbo Granulation Plants.
Table 1
List of TOYO Urea Granulation Plants
Owner Location Capacity On
(MTPD) Stream
1. Mitsui Toatsu Chemicals, Chiba, Japan 50 1975
Inc.
2. Petrochem Ltd. Kapuni, New 470 1983
Zealand
3. Mitsui Toatsu Chemicals, Osaka, Japan 100 1983
Inc.
4. SKW Piesteritz GmbH Piesteritz, Germany 1,200 1995
5. Petrochem Ltd. Kapuni, New 750 1997
Zealand
6. SKW Piesteritz GmbH Piesteritz, Germany 500 1998
7. Ningxia Chemical Works of Ningxia, China 1,740 1999
CNPC
8. PT. Pupuk Iskandar Muda Aceh, Indonesia 1,725 2005
(PIM-2)
9. Lutianhua Group Inc. Sichuan, China 2,000 2000
(CNTIC)
10. Zhanyi Fertilizer Plant Yunnan, China 600 2002
11. Ningxia Petrochemical Co. Ningxia, China 870 2006
12. Shanxi Lanhua Sci-Tech Shanxi, China 1,000 (2007)
Vent
13. Petroleo Brasileiro S.A Laranjeiras, Brazil 600 (2007)
(PetroBras)
14. Confidential CIS 2,000 (2007)
15 PetroChina Tarim Xinjiang, China 2,640 (2009)
Petrochemical Co.
16 National Petrochemical Shiraz, Iran 3,250 (2010)
Company
3 © 2007 TOYO ENGINEERING CORP.
20th AFA International Annual Technical Conference
19-21 June 2007 – Tunisia
Fertilizers Industry : Technology Development & Environmental Protection
Photo.4: Ningxia PetroChina
Photo.5: Ballance, New Zealand (750 MTPD)
No.1 Plant (1,740 MTPD)
and No.2 Plant (870 MTPD)
PROCESS FEATURES
1. Efficient Granulation Mechanism
TOYO’s urea granulation technology adopts Spout-Fluid Bed Granulator.
In the Spout-Fluid Bed Granulator, spouting bed is formed by an upward
stream of air introduced into the bottom of the granulator and fluidized bed is
formed surrounding the spouting beds.
The air introduced into the spouting bed maintains that the particles remain
in suspension. The droplets of urea solution fed to the bed through the
spray nozzles are deposited on the surfaces of suspended seed particles.
Thus the particles gradually grow up in layer-upon-layer.
Since air introduced to the granulator not only forms spouting bed and
fluidized bed but also promotes cooling and drying the granules. 96%
concentrated feed solution can be fed to the granulator to obtain a product
with a moisture content of 0.3% or less. Thus biuret formation and steam
consumption can be minimized.
4 © 2007 TOYO ENGINEERING CORP.
20th AFA International Annual Technical Conference
19-21 June 2007 – Tunisia
Fertilizers Industry : Technology Development & Environmental Protection
Recycle Seed
Urea Solution
Fluidizing Air
Spouting Air Product
Optimal Arrangement of Multi-stage Spouted Bed
– Round and Uniform Product
– High Drying Efficiency
Fig.1: Illustration for Spout-Fluid Bed Granulator
2. High Energy Efficiency
TOYO Urea Granulation Process consumes less utility.
Most of the energy for Granulation Process is consumed by fans, pumps
and solid transportation equipment as electric power. Fig.2 shows the
breakdown of power consumption for each user in Urea Granulation Plant.
80% of total power is consumed by fans. Therefore, the reduction of the
power consumption by fans is essential for energy saving.
Fig.2: Power Consumption of Spout-Fluid Bed Granulation
5 © 2007 TOYO ENGINEERING CORP.
20th AFA International Annual Technical Conference
19-21 June 2007 – Tunisia
Fertilizers Industry : Technology Development & Environmental Protection
TOYO has succeeded to minimize power consumption of fans by
introducing the following features:
(1) No compressed air for atomization
TOYO’s Urea Granulation Process utilizes single (liquid) phase
spray nozzle combined with spouting air, eliminating the need
of atomizing air compressor.
(2) Optimal bed depth in the granulator
The combination of spouting bed and fluidized bed is the feature
of TOYO’s Urea granulation Process. It does not need to keep
high bed depth in granulator, resulting in significant saving of
electric power for fluidizing air fan.
(3) Smaller pressure drop in dust scrubber (See Fig. 3)
Packed bed type dust scrubber proprietarily designed by TOYO
realizes both low pressure drop and high efficiency, reducing
power for the induced fan considerably.
Following table shows the typical energy consumption of TOYO’s Urea
Granulation Process.
Table-2 Utility Consumption (typical)
Steam 0.01 MT/MT
Power 23 kWh/MT
Cooling Water Nil
In case Bulk Flow Cooler is applied instead of fluidized bed cooler for
product cooling, the power consumption can be reduced by 4-5 kWh/T as
shown in Fig.2.
6 © 2007 TOYO ENGINEERING CORP.
20th AFA International Annual Technical Conference
19-21 June 2007 – Tunisia
Fertilizers Industry : Technology Development & Environmental Protection
3. High Product Quality
TOYO Spout-Fluid Bed Granulation Process produces the excellent quality
product by the following functions:
(1) Cooling – low biuret formation
As the granulator rapidly cools the urea melt sprayed onto the
granules, biuret formation is negligibly small.
(2) Drying – low moisture and high hardness
The granulator dries the granules so that the moisture content in
the product become low enough to have sufficient hardness.
(3) Suspending – round and uniform product
Round and uniform product is obtained because the seed particles
are suspended in the spouting bed during the granulating process.
As a result, the granular urea product is quite resistant against fracture and
caking during storage and transportation.
Table-3 shows the typical product specification of TOYO’s Urea Granulation
Process.
Table-3 Product Qualities (typical)
Total Nitrogen 46.3 wt.%
Biuret 0.8 wt.%
Moisture 0.2 wt.%
Formaldehyde 0.45 wt.%
Size 2 - 4 mm 95 wt.%
Hardness 3.5kg/granule for 3 mm
7 © 2007 TOYO ENGINEERING CORP.
20th AFA International Annual Technical Conference
19-21 June 2007 – Tunisia
Fertilizers Industry : Technology Development & Environmental Protection
4. Production of Various Sized Granule
Various sizes of granular urea product can be produced in accordance with
market demand and applications, simply by changing the screen mesh sizes
as shown in Fig. 3.
Fig.3: Flexibility of Product Size
5. Environmental Protection
Urea dust in the exhaust air from the granulator is a major concern of air
pollution in a urea granulation plant. Optimal air velocity for spouting bed
and through free board area of granulator minimizes the dust formation in
8 © 2007 TOYO ENGINEERING CORP.
20th AFA International Annual Technical Conference
19-21 June 2007 – Tunisia
Fertilizers Industry : Technology Development & Environmental Protection
the granulator. And the uniquely designed (Packed Bed type) low
pressure-loss dust scrubber reduces urea dust to less than 30 mg/Nm3.
Dust scrubber is normally located on the ground level as shown in Photo.6. In case
there is the limitation for available area, dust scrubber can be installed above the
Granulator as shown in Photo.1 and 2.
Fig.4: Dust Scrubber
Photo.6: Zhanyi, China (600 MTPD),
Dust Scrubber on Ground
Process Description
Fig.5 shows a typical process flow sheet for TOYO Urea Granulation
Process.
The urea solution concentrated in the evaporator is supplied into the
spouting bed through the single fluid spray nozzles to enlarge the recycle
particles (seeds) in the granulator. The water content in the feed urea
solution is evaporated in the spouting beds in the granulator to produce the
9 © 2007 TOYO ENGINEERING CORP.
20th AFA International Annual Technical Conference
19-21 June 2007 – Tunisia
Fertilizers Industry : Technology Development & Environmental Protection
urea granules with 0.2 - 0.3 wt.% of moisture content. The enlarged
granules are cooled in fluidized beds in the granulator.
Fig.5: Process Flow Diagram
Photo.8: Crusher
Photo.7: Screen
Coarse granules produced in the granulator are screened to separate the
product size granules from over and under size granules through the double
deck screen (See Photo.7). Under size granules are recycled to the
granulator as seeds and over size granules are crushed through the double
roller type crusher (See Photo.8) and recycled to the granulator together
with the under size granules as the seeds.
10 © 2007 TOYO ENGINEERING CORP.
20th AFA International Annual Technical Conference
19-21 June 2007 – Tunisia
Fertilizers Industry : Technology Development & Environmental Protection
Exhaust air from the granulator and cooler is scrubbed in the wet type dust
scrubber to recover the urea dusts as urea solution. Recovered urea
solution is recycled to the urea plant for recovery.
LARGE SCALE PLANT APPLICATION
Nowadays the capacity of ammonia plant becomes larger and larger to be
2,000 MTPD as standard capacity. The required capacity of Urea Plant
also becomes larger (more than 3,000 MTPD) to meet the increasing
capacity of ammonia plant.
Since 1975, TOYO has scaled-up Granulation Plant successfully from 50
MTPD to 3,250 MTPD as shown Fig.6.
Fig.6: Granulator Scale-up History
Following design philosophy has been applied for former scale up of plant
and it should be applied for the further scale-up of the plant (e.g. 3,500
MTPD or larger) in the same way, utilizing the state-of-the-art granulation
process simulator, full knowledge and know-how on solid handling
11 © 2007 TOYO ENGINEERING CORP.
20th AFA International Annual Technical Conference
19-21 June 2007 – Tunisia
Fertilizers Industry : Technology Development & Environmental Protection
equipment and machinery, and incorporating the latest experience of the
3,250 MTPD at the same time.
(1) Increasing the number of spouting bed in proportion to the
production capacity. (See Fig.7)
The capacity of Granulator is increased simply by adding required
number of spouting bed under same condition. The sprayed
capacity and air flow rate for one spouting bed is maintained for any
plant capacity.
Therefore, large scale granulator is designed based on proven unit
of spouting bed, extending the length of granulator from
experienced size of granulator, considering following aspects:
- uniform transversal particle distribution
- avoiding back mixing
- uniform air distribution
- transportability of granulator
Fig.7 : Granulator Scale-up Philosophy
12 © 2007 TOYO ENGINEERING CORP.
20th AFA International Annual Technical Conference
19-21 June 2007 – Tunisia
Fertilizers Industry : Technology Development & Environmental Protection
(2) Increasing Number of Screen, Crusher and Bucket Elevator
The capacity of solid handling section is also increased simply by
adding required number of screens and crushers considering
available capacity of machine.
Table 4: Required Number of Screen and Crusher
Fig.8: 3D Model of 3,250MTPD Urea Granulation Plant
13 © 2007 TOYO ENGINEERING CORP.
20th AFA International Annual Technical Conference
19-21 June 2007 – Tunisia
Fertilizers Industry : Technology Development & Environmental Protection
Other transportation equipment such as bucket elevators and belt
conveyors will not be the bottleneck even for the large scale plant e.g.
3,500 MTPD, in terms of their availability. Therefore, the number of
trains of transportation equipment should be determined considering
equipment layout and operability.
Above mentioned approach eliminates bottlenecks and risks due to
large capacity Granulation plant. In fact, basic design for a 2,640
MTPD Urea Granulation Plant in china has been completed, and a
3,250 MTPD Urea Granulation Plant including synthesis section in
Iran is now in basic design stage.
Further Improvements
TOYO continues R&D to improve its own Urea Granulation Technology.
The improvements are:
- new spray nozzle design for granulator enhancing drying efficiency
- improved configuration of granulator enhancing high quality of
granular urea product
The fruits of the above R&D are being incorporated in the granulator
design of the latest projects.
CONCLUSION
TOYO’s Spout-Fluid Bed Granulation Technology has been applied to 16
urea granulation plants in 8 countries, including the latest two Jumbo
units; 2,640 MTPD unit for PetroChina Tarim and 3,250 MTPD unit for
NPC (Shiraz Petrochemical) Iran.
Now, 3,500 MTPD of larger units are ready for implementation, and it is no
longer “challenging” project for TOYO.
References
1. G. Nishikawa T. Yanagawa, H. Morikawa, E. Sakata and Y. Kojima, “Large
Scale Urea Granulation Plants based on TEC Technology”, Nitrogen 2001,
Tampa, USA
14 © 2007 TOYO ENGINEERING CORP.
You might also like
- TrangenesisVs SelectiveBreedingDocument11 pagesTrangenesisVs SelectiveBreedingTomasLiefferingNo ratings yet
- Tropical Plant GuideDocument15 pagesTropical Plant GuideDerrick Yson (Mangga Han)No ratings yet
- Toensmeier Perennial Vegetables HandoutDocument5 pagesToensmeier Perennial Vegetables HandoutjacquesjzaNo ratings yet
- Cost Estimating SimplifiedDocument14 pagesCost Estimating SimplifiedsuperjerixNo ratings yet
- Livestock Feeding PracticesDocument12 pagesLivestock Feeding Practicesbaskar100% (1)
- Nutrafin Aquatic News NR 3 USADocument16 pagesNutrafin Aquatic News NR 3 USAcornerstone2100% (1)
- Reactor Kinetics of Urea Formation: November 2015Document21 pagesReactor Kinetics of Urea Formation: November 2015Javiera MellaNo ratings yet
- General Motors Diet Plan PDFDocument2 pagesGeneral Motors Diet Plan PDFJoan Urminita100% (1)
- Sulphur - Magazine July-Aug - 2021 - CompressedDocument48 pagesSulphur - Magazine July-Aug - 2021 - CompressedGuillaumea Foucault100% (1)
- Ammonia PresentationDocument142 pagesAmmonia PresentationM Hamza Nadeem AnjumNo ratings yet
- Advanced Distillation Technologies: Design, Control and ApplicationsFrom EverandAdvanced Distillation Technologies: Design, Control and ApplicationsNo ratings yet
- Nitric Acid Manufacturing ProcessDocument7 pagesNitric Acid Manufacturing ProcessLenin PrabhuNo ratings yet
- Gas Holders Risk AssessmentDocument48 pagesGas Holders Risk AssessmentRonak MotaNo ratings yet
- Dammonium PhosphateDocument17 pagesDammonium PhosphateMary Jane Cañete100% (1)
- Tropical RainforestDocument20 pagesTropical RainforestDebbie Eclarino100% (1)
- NFL Final ReportDocument74 pagesNFL Final Reportaman11750No ratings yet
- Brief Description of Urea ProcessDocument7 pagesBrief Description of Urea ProcessGaurav Mishra100% (1)
- Vacuum TheoryDocument79 pagesVacuum TheoryrusyadNo ratings yet
- Avant-Garde Mr. K Mohan KumarDocument46 pagesAvant-Garde Mr. K Mohan KumarSivakumar SelvarajNo ratings yet
- ESP To Bag FilterDocument1 pageESP To Bag FiltersolquihaNo ratings yet
- 2000 Development of The ACES 21 ProcessDocument17 pages2000 Development of The ACES 21 ProcessTTaddictNo ratings yet
- AMT-SR Brochure - CatalystDocument7 pagesAMT-SR Brochure - Catalystviki_vignesNo ratings yet
- Hydrogenation of Nitrobenzene: To AnilineDocument7 pagesHydrogenation of Nitrobenzene: To Anilinesuzie annNo ratings yet
- Brochure BriquettingDocument24 pagesBrochure Briquettingssmith2007No ratings yet
- Haber Bosch Process, Revision of The Revised Edition 2017, 2017Document20 pagesHaber Bosch Process, Revision of The Revised Edition 2017, 2017Mark Anthony HenryNo ratings yet
- Organic Fertilizer Quality Norms IndiaDocument68 pagesOrganic Fertilizer Quality Norms IndiaSridhar IyerNo ratings yet
- Iffco PhulpurDocument55 pagesIffco PhulpurTarun Mishra100% (1)
- Process Flow Diagram - Nitric AcidDocument1 pageProcess Flow Diagram - Nitric AcidAsma NasserNo ratings yet
- Centrifugal Pumps For Molten Sulphur Amp H2so4 ProductionDocument6 pagesCentrifugal Pumps For Molten Sulphur Amp H2so4 ProductionDavid Camilo Guerrero GonzalezNo ratings yet
- Prilling and GranulationDocument56 pagesPrilling and GranulationMuhammad SaddamNo ratings yet
- Screw CompressorDocument23 pagesScrew CompressorvaibhavNo ratings yet
- 3-Energy Efficiency Gains in Indian Ammonia Plants Retrospects and ProspectsDocument14 pages3-Energy Efficiency Gains in Indian Ammonia Plants Retrospects and ProspectsMuhammad Naeem100% (1)
- 400kW Geothermal Power Plant at Chena Hot Springs, AlaskaDocument38 pages400kW Geothermal Power Plant at Chena Hot Springs, AlaskaKenneth TanNo ratings yet
- Failure of LP Flash Drum Packing Bed Support: Geoff BlewettDocument10 pagesFailure of LP Flash Drum Packing Bed Support: Geoff BlewettDheeraj DheeruNo ratings yet
- P Psa S G E P: Olybed Ystems FOR AS Xtraction and UrificationDocument2 pagesP Psa S G E P: Olybed Ystems FOR AS Xtraction and UrificationVivi OktaviantiNo ratings yet
- Ud He TechnologyDocument16 pagesUd He TechnologyBejavada Suresh100% (1)
- 2008 Morikawa TEC IFA ACES21 Advanced Urea Production Technology - 2Document15 pages2008 Morikawa TEC IFA ACES21 Advanced Urea Production Technology - 2MubasharNo ratings yet
- Urea Fertilizer: Lecture By: Engr. Mina ArshadDocument26 pagesUrea Fertilizer: Lecture By: Engr. Mina ArshadDanish BaigNo ratings yet
- Coal For AmmoniaDocument10 pagesCoal For AmmoniaH.J.Prabhu100% (1)
- Ku Reprint Ps April2007Document2 pagesKu Reprint Ps April2007keyur1109No ratings yet
- Olmi Urea Stripper & Carbamate Condenser LeafletDocument6 pagesOlmi Urea Stripper & Carbamate Condenser LeafletHamzaNoumanNo ratings yet
- Influence of The Nature of The Roots Blower On Pressure Fluctuations in A Fluidized BedDocument13 pagesInfluence of The Nature of The Roots Blower On Pressure Fluctuations in A Fluidized BedcoolcupidguyNo ratings yet
- Basaroof ReactionDocument14 pagesBasaroof ReactiontreyzzztylerNo ratings yet
- Biuret in Urea Fertilizers - R.L MikellsenDocument2 pagesBiuret in Urea Fertilizers - R.L MikellsenRizka MaharanaNo ratings yet
- UreaDocument40 pagesUreaBrigette Pavillar100% (1)
- Heat Integration of An Aniline Production Process To Optimize CosDocument224 pagesHeat Integration of An Aniline Production Process To Optimize CosCastillo Catalan LeonardoNo ratings yet
- Urea ProductionDocument2 pagesUrea Productiongaur1234No ratings yet
- OTS Ammonia Urea Profertil ArgentinaDocument16 pagesOTS Ammonia Urea Profertil ArgentinaGeorge Van BommelNo ratings yet
- Broschure Schiele Ventilatoren enDocument6 pagesBroschure Schiele Ventilatoren enbbmokshNo ratings yet
- Muhammad Nasir KhanDocument4 pagesMuhammad Nasir KhanMohammad Sameer KhanNo ratings yet
- AMACS Mist Eliminator BrochureDocument16 pagesAMACS Mist Eliminator BrochureAainaTheMirror100% (1)
- Prilling TechnologyDocument33 pagesPrilling TechnologySaptarshi BoralNo ratings yet
- Meyer Coal 2014Document23 pagesMeyer Coal 2014Molote Erwin MalieheNo ratings yet
- KSFL ReportDocument56 pagesKSFL ReportAbhishek KumarNo ratings yet
- PlantDocument8 pagesPlantpf06No ratings yet
- Chemical Reactor DesigningDocument32 pagesChemical Reactor DesigningAkhtar Hockey RotrianNo ratings yet
- KVTBrochure 19122012 PDFDocument12 pagesKVTBrochure 19122012 PDFvb_pol@yahooNo ratings yet
- CASE STUDY On Phosphoric Acid Plant ProcessDocument3 pagesCASE STUDY On Phosphoric Acid Plant ProcessIsrael NarvastaNo ratings yet
- Co2 Compressor NewDocument6 pagesCo2 Compressor NewUzair AshrafNo ratings yet
- Aiche 36 012problematic Low Temperature ShiftDocument10 pagesAiche 36 012problematic Low Temperature ShiftHsein WangNo ratings yet
- CASALE-GROUP Melamine HP TechnologyDocument5 pagesCASALE-GROUP Melamine HP TechnologyRudy Mamani CuellarNo ratings yet
- Drum Granulator 30000TDocument4 pagesDrum Granulator 30000TShahid LatifNo ratings yet
- Shrink and SwellDocument3 pagesShrink and SwellAkshay SetlurNo ratings yet
- BM15-17 UdaanDocument105 pagesBM15-17 UdaanAnonymous HzljLSMcNo ratings yet
- Graphite Heat ExchangersDocument9 pagesGraphite Heat ExchangersRehinaNo ratings yet
- Air Filter For TurbineDocument8 pagesAir Filter For TurbineAnonymous Q9i062VNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Thermal Conductivity, Volume 3: Organic Compounds C8 to C28From EverandHandbook of Thermal Conductivity, Volume 3: Organic Compounds C8 to C28No ratings yet
- Sugarcane Biorefinery, Technology and PerspectivesFrom EverandSugarcane Biorefinery, Technology and PerspectivesFernando SantosNo ratings yet
- Econs 0 59 1 67 2 74 3 80 85 5 89 6 92Document6 pagesEcons 0 59 1 67 2 74 3 80 85 5 89 6 92aaa206No ratings yet
- Handout 2Document22 pagesHandout 2aaa206No ratings yet
- Publicacao 565 Epolicy2005Document10 pagesPublicacao 565 Epolicy2005aaa206No ratings yet
- 475 Using Asme Performance Test Codes in TheDocument18 pages475 Using Asme Performance Test Codes in Theaaa206No ratings yet
- Air PDFDocument10 pagesAir PDFAbednego ZanoNo ratings yet
- 01 F70 D 01Document69 pages01 F70 D 01dhyantiNo ratings yet
- TISSUES - SA 1 Question PaperDocument3 pagesTISSUES - SA 1 Question PaperSatheesh KarunakaranNo ratings yet
- MS PT101Document2 pagesMS PT101Pandiya RajanNo ratings yet
- Week 4Document8 pagesWeek 4NoMu OmNomNo ratings yet
- 2017 Rindasu Ciceoi Agro Homeopatie CraiovaDocument8 pages2017 Rindasu Ciceoi Agro Homeopatie CraiovaNipurn ChandraNo ratings yet
- Diagram 19 Shows A Part of A Stem of A Plant Where The Phloem Tissues That Has Been Removed. How Will It Affect The Plant?Document6 pagesDiagram 19 Shows A Part of A Stem of A Plant Where The Phloem Tissues That Has Been Removed. How Will It Affect The Plant?Sahida ShafieNo ratings yet
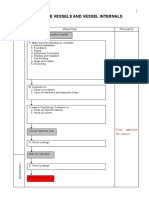
- Pressure Vessels and Vessel Internals: (1) Columns/DrumsDocument11 pagesPressure Vessels and Vessel Internals: (1) Columns/DrumsKNo ratings yet
- Senior Neet Weekly Test QP (03-10-2021)Document20 pagesSenior Neet Weekly Test QP (03-10-2021)Tanzeela HashmiNo ratings yet
- Typical Inspection Plan (TIP) Index: Project Inspection Division / IAGDocument5 pagesTypical Inspection Plan (TIP) Index: Project Inspection Division / IAGvajidqcNo ratings yet
- Arts and Crafts in Philippines13Document18 pagesArts and Crafts in Philippines13EleoNo ratings yet
- MB1A, B, C - SerialDocument2 pagesMB1A, B, C - SerialVarunNo ratings yet
- NuHemp Brand Information Package - Web PresentationDocument23 pagesNuHemp Brand Information Package - Web PresentationNuHemp100% (2)
- MICAT Sample PaperDocument107 pagesMICAT Sample PaperSHIVAM MAHENDRUNo ratings yet
- PDF-6.2 The Pressurized Water ReactorDocument35 pagesPDF-6.2 The Pressurized Water ReactorJohn W HollandNo ratings yet
- Stock Pointer: Ador Welding LTDDocument16 pagesStock Pointer: Ador Welding LTDgiridesh3No ratings yet
- Nuclear Power in China.Document48 pagesNuclear Power in China.wgtacagNo ratings yet
- Jurnal TPPHP Ekstrusi 2 PDFDocument115 pagesJurnal TPPHP Ekstrusi 2 PDFNadNo ratings yet
- Mulberry Production - Lead MagnetDocument7 pagesMulberry Production - Lead MagnetValiant Dominic D. VelardeNo ratings yet
- Efficient Automation of Concrete Batching Plant Using PLC & Scada Project Reference No: 38S0193Document4 pagesEfficient Automation of Concrete Batching Plant Using PLC & Scada Project Reference No: 38S0193Gangadhar PradhanNo ratings yet
- Conservation Status of Plant Species in Tehsil Takht-eNasrati, District Karak, Khyber Pakhtun KhawaDocument7 pagesConservation Status of Plant Species in Tehsil Takht-eNasrati, District Karak, Khyber Pakhtun KhawaAna JohnyNo ratings yet
- GYMNOSPERMS (A)Document4 pagesGYMNOSPERMS (A)Aprille CastroNo ratings yet
- Production Technology of LucerneDocument14 pagesProduction Technology of LucerneAnonymous x7gqMPvZIwNo ratings yet
- Prac 1Document2 pagesPrac 1Athira ThyraNo ratings yet