Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Industry Content
Uploaded by
Sarah SaccaOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Industry Content
Uploaded by
Sarah SaccaCopyright:
Available Formats
indirect Human
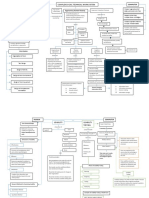
Services Curriculum Framework HSC Content overview INDUSTRY CONTEXT
direct
verbal
bullying and harassment
physical
types
psychological
sexual
principles
intent of legislation antidiscrimination
employers antidiscrimination industry bodies
rights and responsibilities
employees internet
workplace policy and procedures journals
strategies to eliminate bias and harassment sources networks
consequences and legal ramifications professional associations
inappropriate workplace behaviour
recourse available special interest groups
unions
legal sources of information
difference between job description
ethical
role/duty statement
legal and ethical framework
access and use workplace manuals
access and equity
manager/supervisor/team leader
child protection
colleagues
conflict of interest
strategies for understanding and clarifying work instructions
dignity of risk
discrimination
duty of care
human rights issues affecting the industry community services industry
interrelationship between
informed consent health industry
mandatory reporting features of 'service' industries
privacy, confidentiality and disclosure primary function
translation legal and ethical issues services provided
sectors/departments
responsibilities occupational areas
work role boundaries
limitations examples of organisations/businesses/agencies
interrelationship of legal and ethical aspects interrelationship between sectors/departments
obligations for client, worker and industry personcentred
workplace policy and procedures rightsbased
act
Industry context nature of the industry
interdisciplinary
service delivery models
team
regulation difference between multidisciplinary
codes of practice legislative requirements interagency
industry approaches to care and service delivery
purpose and intent for particular sector/department underpinning principles and/or characteristics
application for specific workplace and individual practice models of funding
what constitutes a breach how work is organised and undertaken
legal and ethical obligations role of support services
ramifications
interrelationships with outside services
career pathways and knowledge and skills required industry terminology relating to role and service provision
fulltime
parttime client
casual types compliance and meaning for worker
contract industry
agency industrywide
underpinning values, principles and ethics
award workplace specific
agreement difference and application contemporary issues and implications for provision of care and/or delivery of service
contract value
terms and conditions for specific job role working in the industry expected standards
employee and employer rights and responsibilities work standards consequences of noncompliance
principles for specific job role
intent of legislation seeking opportunities to improve work practices and client outcomes
employers equal employment opportunity (EEO)
employment purpose and requirements
reciprocal rights and responsibilities accreditation
employees consequences of noncompliance
workplace policy and procedures effect of change on client, worker and organisation
employer and employee groups
professional associations primary role/function(s) of key industry bodies
unions
industry
worker purpose and value of code of conduct
client
importance
individual industry currency
strategies to maintain
workplace
You might also like
- Workshops For Iso 45001Document32 pagesWorkshops For Iso 45001AliNo ratings yet
- Complex Social Technical Work System: Computer HumanDocument2 pagesComplex Social Technical Work System: Computer HumanCasas, Jo-an Pauline A.No ratings yet
- Rajasree Rajan OB CIADocument9 pagesRajasree Rajan OB CIAswathiNo ratings yet
- Frame Work of Employee Relation Law, Professional Practices, Lahore Garrison UniversityDocument25 pagesFrame Work of Employee Relation Law, Professional Practices, Lahore Garrison UniversitytouseefaqNo ratings yet
- Organisational Behaviour and Human Resource Management F (1)Document13 pagesOrganisational Behaviour and Human Resource Management F (1)RajiNo ratings yet
- 206HRM Employee Relations and Labour Legislations (SPPU Uni. Sub. Prof. Notes.)Document37 pages206HRM Employee Relations and Labour Legislations (SPPU Uni. Sub. Prof. Notes.)ShrunaliNo ratings yet
- Referente Requerimientos Específicos Parámetros Notas / Observaciones Artículos, Titulos, Libros AplicablesDocument4 pagesReferente Requerimientos Específicos Parámetros Notas / Observaciones Artículos, Titulos, Libros Aplicablesalexander bracamonteNo ratings yet
- Zoghbimanrique de Lara 2007 Investigating The Effects of ProcedDocument15 pagesZoghbimanrique de Lara 2007 Investigating The Effects of ProcedMarko PrpićNo ratings yet
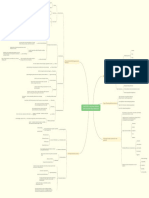
- Mind-Map-Vet-Business-Services-Stage-6-Workplace-Information (A)Document1 pageMind-Map-Vet-Business-Services-Stage-6-Workplace-Information (A)josephineNo ratings yet
- Pluralistic Unitary Marxist: Input Conversion OutputDocument8 pagesPluralistic Unitary Marxist: Input Conversion OutputajayzxNo ratings yet
- Mallick 2014Document12 pagesMallick 2014nhatvpNo ratings yet
- Wang 2010 ImpDocument18 pagesWang 2010 ImpMuhammad Ali BhattiNo ratings yet
- Industrial Relations - An IntroDocument23 pagesIndustrial Relations - An IntroRishabh GoyalNo ratings yet
- Literature Review - 20202126Document10 pagesLiterature Review - 20202126ayushi biswasNo ratings yet
- Employee Performance at Workplace: Conceptual Model and Empirical ValidationDocument17 pagesEmployee Performance at Workplace: Conceptual Model and Empirical ValidationRamkumarNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER5 - Consumer Markets and Consumer Buyer BehaviorDocument1 pageCHAPTER5 - Consumer Markets and Consumer Buyer BehaviorVy TườngNo ratings yet
- Human Factors and ErgonomicDocument23 pagesHuman Factors and ErgonomicMilson AndreanNo ratings yet
- Exploring The Impact of HPWS in Professional Service Firms - CPJP&R 2013Document18 pagesExploring The Impact of HPWS in Professional Service Firms - CPJP&R 2013Victor M. Suarez AvelloNo ratings yet
- Lee 2020Document9 pagesLee 2020Komal YousafNo ratings yet
- The Relationship Between Leader-Member Exchange, Work Engagement and Organizational Citizenship BehaviourDocument24 pagesThe Relationship Between Leader-Member Exchange, Work Engagement and Organizational Citizenship BehaviourIfon NajaNo ratings yet
- Ingles - Sustentación TG Mba Mauricio Betancur y Manuela Lopera MbaDocument1 pageIngles - Sustentación TG Mba Mauricio Betancur y Manuela Lopera MbaTecnica Alfa y OmegaNo ratings yet
- Sarmiento, Nimoel Aron V. Activity-03 - ECQDocument3 pagesSarmiento, Nimoel Aron V. Activity-03 - ECQNimoel Aron SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Lecture 7Document12 pagesLecture 7beenuvadheraNo ratings yet
- Leadership Styles and EmployeeDocument26 pagesLeadership Styles and EmployeeSorin johnNo ratings yet
- Research and DevelopmentDocument35 pagesResearch and DevelopmentPsychopath GuyNo ratings yet
- Human Resource Management and Industrial Relation in India by Pooja Rani & Neha Shri VastavDocument13 pagesHuman Resource Management and Industrial Relation in India by Pooja Rani & Neha Shri Vastavijr_journalNo ratings yet
- Sublist 1: of The Academic Word List - Most Frequent Words in FamiliesDocument1 pageSublist 1: of The Academic Word List - Most Frequent Words in FamiliesX Froggy LeeNo ratings yet
- Sarah - Journal SummaryDocument17 pagesSarah - Journal Summarysiti_sarah146No ratings yet
- RM - 10 Mark ProjectDocument40 pagesRM - 10 Mark ProjectAashutosh RauniyarNo ratings yet
- SSRN Id1508515Document7 pagesSSRN Id1508515killystepNo ratings yet
- Examining Per-Pro Distinction With ApaDocument10 pagesExamining Per-Pro Distinction With Apaapi-683959564No ratings yet
- Ls Quickguide Mi Academic Vocabulary PDFDocument7 pagesLs Quickguide Mi Academic Vocabulary PDFBellucci ResanualtoNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3 TRADE UNIONS Part 1Document23 pagesCHAPTER 3 TRADE UNIONS Part 1Nur Ismaliyana IsmailNo ratings yet
- Lepm 2021 (R)Document4 pagesLepm 2021 (R)Swati PorwalNo ratings yet
- Industrial Relation and Labor LawsDocument8 pagesIndustrial Relation and Labor LawsAyesha SohailNo ratings yet
- HBO Module 1aDocument7 pagesHBO Module 1aPonsica RomeoNo ratings yet
- Local Media7579940144065994400Document16 pagesLocal Media7579940144065994400Leonel James SuraltaNo ratings yet
- ch02 Rev01 Lores StampedDocument13 pagesch02 Rev01 Lores StampedAdelana EmmanuelNo ratings yet
- International Journal of Business and Management Invention (IJBMI)Document11 pagesInternational Journal of Business and Management Invention (IJBMI)inventionjournalsNo ratings yet
- 438-440-Ieteh294 EtsrDocument4 pages438-440-Ieteh294 EtsrSanjay VinceNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document6 pagesWeek 2Abogada JomaryNo ratings yet
- Employee Performance at Workplace Conceptual ModelDocument18 pagesEmployee Performance at Workplace Conceptual ModelNon Htaw MonNo ratings yet
- Effects of Organizational Justice in Terpersonal Communication and Work Discipline On Employee PerformanceDocument6 pagesEffects of Organizational Justice in Terpersonal Communication and Work Discipline On Employee PerformanceFadlan KambarNo ratings yet
- MLS578023 39 4emrkplkjDocument13 pagesMLS578023 39 4emrkplkjRengki RamaNo ratings yet
- Drsania - 3266 - 20398 - 2 - CHAPTER 2 (2020)Document32 pagesDrsania - 3266 - 20398 - 2 - CHAPTER 2 (2020)Bilal MukaddamNo ratings yet
- PPM EN 2007 01 AbbottDocument12 pagesPPM EN 2007 01 Abbott10 Anureet kaurNo ratings yet
- A Three-Component Conceptualization of Organizational CommitmentDocument8 pagesA Three-Component Conceptualization of Organizational CommitmenthudaNo ratings yet
- Promoting OSHADocument1 pagePromoting OSHADayah AlimonNo ratings yet
- HCM Embedded Learning: Enterprise and Workforce StructuresDocument32 pagesHCM Embedded Learning: Enterprise and Workforce Structuresknani9090No ratings yet
- Wa0024.Document7 pagesWa0024.Rohit SinghNo ratings yet
- Empowerment Series The Skills of Helping Individuals Families Groups and Communities Enhanced 8th Edition Ebook PDFDocument62 pagesEmpowerment Series The Skills of Helping Individuals Families Groups and Communities Enhanced 8th Edition Ebook PDFdebra.glisson665100% (39)
- Socio TechnicalDocument21 pagesSocio TechnicalhhaiderNo ratings yet
- Contextualization-of-Basic-Competencies-to-Common RICE MACHINERY OPERATIONS NCIIDocument23 pagesContextualization-of-Basic-Competencies-to-Common RICE MACHINERY OPERATIONS NCIIJanu MaglenteNo ratings yet
- Labor Management RelationsDocument10 pagesLabor Management RelationsKimberly PalmeroNo ratings yet
- 5560-Article Text-10881-1-10-20210115Document18 pages5560-Article Text-10881-1-10-20210115mekdi endaleNo ratings yet
- PendukungDocument16 pagesPendukungMuhammad FikriNo ratings yet
- 21st Contex TemplateDocument8 pages21st Contex TemplateMer IsoyNo ratings yet
- Relations SocialesDocument28 pagesRelations SocialesoussamaNo ratings yet
- Guide-2018stats 2 PDFDocument54 pagesGuide-2018stats 2 PDFscorober87No ratings yet
- SSP PDFDocument2 pagesSSP PDFMujahid PashaNo ratings yet
- Andrada Vs PeopleDocument2 pagesAndrada Vs PeopleCJ FaNo ratings yet
- CMT - II Hyderabad Metro Case StudyDocument18 pagesCMT - II Hyderabad Metro Case StudySenjo SebastianNo ratings yet
- VtM2nded1 Page PDFDocument1 pageVtM2nded1 Page PDFJoseph CortesNo ratings yet
- Chapter-: Recent Marketing Strategies of Commercial Banks in Kerala-It's Impact and ImplicationsDocument62 pagesChapter-: Recent Marketing Strategies of Commercial Banks in Kerala-It's Impact and ImplicationsSir GodwishNo ratings yet
- Budgeting Approaches by DR MpsinghDocument26 pagesBudgeting Approaches by DR MpsinghNishant AnandNo ratings yet
- Strategic ManagementDocument217 pagesStrategic ManagementMurtaza Shaikh100% (1)
- Component of SpeakingDocument3 pagesComponent of SpeakingDian Miranda75% (8)
- Revolutionary Nationalist MovementsDocument2 pagesRevolutionary Nationalist Movementsmuralli_201095No ratings yet
- Women's Metaphor - From Glass Ceiling' To Labyrinth' - Santovec - 2010 - Women in Higher Education - Wiley Online LibraryDocument5 pagesWomen's Metaphor - From Glass Ceiling' To Labyrinth' - Santovec - 2010 - Women in Higher Education - Wiley Online LibraryVERONICA AKOURYNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Development AdministrationDocument17 pagesCurriculum Development AdministrationNAZRUL ISLAM MONDALNo ratings yet
- SANDY1Document3 pagesSANDY1Sankalp RajNo ratings yet
- Yosef A.A. Ben-JochannanDocument14 pagesYosef A.A. Ben-JochannanHaqi Jamison100% (1)
- Nikita Elmadianti - Assignment 3Document2 pagesNikita Elmadianti - Assignment 3NIKITA ELMADIANTINo ratings yet
- 100 000 Worth of The Biggest Money Making Secrets Ever RevealedDocument102 pages100 000 Worth of The Biggest Money Making Secrets Ever Revealedyoosha100% (2)
- Collective Bargaining Agreement - FinalDocument30 pagesCollective Bargaining Agreement - FinalSage Rainelle LingatongNo ratings yet
- A Study On Satisfaction, Perception and Expectation Level of Institutional Consumers Towards Paint Brands in Al-Kharj Region, Kingdom of Saudi ArabiaDocument16 pagesA Study On Satisfaction, Perception and Expectation Level of Institutional Consumers Towards Paint Brands in Al-Kharj Region, Kingdom of Saudi ArabiaShekhar MauryaNo ratings yet
- Changes in PMBOK® Guide 6th Edition08042018 PDFDocument1 pageChanges in PMBOK® Guide 6th Edition08042018 PDFNabil ShaukatNo ratings yet
- Verified Complaint - Ball & Chain Case - 1st Amendment ViolationsDocument48 pagesVerified Complaint - Ball & Chain Case - 1st Amendment ViolationsMichael PancierNo ratings yet
- Taking A Second LookDocument7 pagesTaking A Second LookPeri CyanideNo ratings yet
- NEBOSH HSE Certificate in Process Safety Management - NEBOSHDocument8 pagesNEBOSH HSE Certificate in Process Safety Management - NEBOSHamra_41No ratings yet
- Contemporary ReportingDocument14 pagesContemporary ReportingJomer Navara AltarejosNo ratings yet
- MRRD 2020 LVRRGuidelineandStandards Vol2GeometricDesign AsCAP AFG2155A 200831 CompressedDocument206 pagesMRRD 2020 LVRRGuidelineandStandards Vol2GeometricDesign AsCAP AFG2155A 200831 CompressedMichaelNo ratings yet
- Inventory Management in Supply ChainDocument11 pagesInventory Management in Supply Chainparadise AngelNo ratings yet
- Chair of St. Peter Technical Institute (Cspti) : Student Application FormDocument2 pagesChair of St. Peter Technical Institute (Cspti) : Student Application FormRobin Julius DetrasNo ratings yet
- Reflection ACSDocument3 pagesReflection ACSThemba MdlaloseNo ratings yet
- Retail Management Word Search PuzzleDocument1 pageRetail Management Word Search PuzzleSitiSuharijanSaidNo ratings yet
- College Entrance Testing-SAT & ACTDocument3 pagesCollege Entrance Testing-SAT & ACTVeaceslav PituscanNo ratings yet
- General Conditions of Contract For Construction Works - 2004 & 2010 ClausesDocument18 pagesGeneral Conditions of Contract For Construction Works - 2004 & 2010 ClausesPaul Maposa40% (5)