Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Review Article: Concepts of Complete Denture Occlusion: An Imperative Review of Literature
Review Article: Concepts of Complete Denture Occlusion: An Imperative Review of Literature
Uploaded by
HujarOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Review Article: Concepts of Complete Denture Occlusion: An Imperative Review of Literature
Review Article: Concepts of Complete Denture Occlusion: An Imperative Review of Literature
Uploaded by
HujarCopyright:
Available Formats
(e) ISSN Online: 2321-9599
Kaur M et al. Concepts of Complete Denture Occlusion. (p) ISSN Print: 2348-6805
SJIF (Impact factor) 2017= 6.261
Review Article Index Copernicus value = 80.90
Concepts of Complete Denture Occlusion: An Imperative Review of Literature
1
Manpreet Kaur, 2Renu Bala Pachar
1,2
PG Student, Department of Prosthodontics, Maharaja Ganga Singh Dental College & Research Centre, Sri
Ganganagar, Rajasthan, India
ABSTRACT:
Occlusion encompasses a wide section in dentistry and has been described as the most important subject in all the disciplines of dentistry. Occlusion
is the meeting ground of all phases and all specialties of dentistry. Since then, several balanced and nonbalanced occlusion concepts were proposed in
the literature. It is necessary for clinician to have knowledge about occlusion-related issues for good clinical practice in all dental disciplines.
Occlusion has attained its current role as ‘the medium of dentistry’. Successfully treated patients has the capability to fundamentally change static
and dynamic relationships of occlusion, while aiming for achieving as near ‘‘ideal’’ occlusion as possible. Occlusal surfaces of the teeth should
essentially replaced either by restorations in natural teeth, or replacement of some or all of the teeth which is required for the routine functioning of
teeth. The masticating mechanism of successfully treated patients carry out its normal physiologic functions while the TMJ, the neuromuscular
mechanism, the teeth, and their supporting structures remain in a good state of health. The concepts of occlusion involve not only the static
relationship of teeth but also their functional interrelationships and all components of the masticatory system. Studies have been done to investigate
the occlusal relationship of maxillary and mandibular teeth during protrusion and lateral excursion movements. Based on these studies, there are
various occlusal concepts of balanced occlusion, group function cuspid protection and mutually protected occlusion. A balanced occlusion appears to
be most appropriate because of tooth contacts observed during nonfunctional activities of patients. This article discusses about different concepts of
occlusion in complete denture.
Keywords: Denture, Mastication, Occlusion.
Correspondence: Dr Manpreet Kaur, PG Student, Department of Prosthodontics, Maharaja Ganga Singh Dental
College & Research Centre, Sri Ganganagar, Rajasthan, India
This article may be cited as: Kaur M, Pachar RB. Concepts of Complete Denture Occlusion: An Imperative Review
of Literature. J Adv Med Dent Scie Res 2017;5(12):96-99.
Access this article online
Quick Response Code
Website: www.jamdsr.com
DOI:
10.21276/jamdsr.2017.5.12.27
I
NTRODUCTION:
Dentate status of a person can affect diet, nutritional DYNAMIC CONCEPT1,8
status, and general health. Achieving predictable The dynamic concept of occlusion is primarily concerned
functional working and beauty of smile design is with jaw movements involved in mastication. As the teeth
dependent on incorporation of sound occlusal principal.1-2 of one jaw glide over the teeth of the opposing jaw, the
Dental occlusion plays a central and important role in jaw movements and occlusion are made.
clinical dentistry and is essential for physiologic function. Four occlusal concepts of occlusal rehabilitation in
The role of the dental occlusion becomes more important complete denture are :
when teeth are missing. Edentulous, occlusion-free jaws Unbalanced articulation
are subjected to a variety of functional, aesthetic, Balanced articulation
psychological and social impairments.3-6 Establishing Linear or monoplane articulation
occlusion that permits normal and efficient masticatory Lingualized articulation.
function is basic to dentistry and survival.7
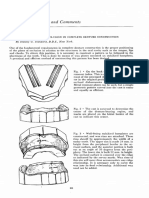
UNBALANCED ARTICULATION 9
STATIC CONCEPT 1: Pound’s concept
The static concepts of occlusion include centric Sharp palatal cusps of maxillary posterior teeth should
occlusion, protrusive occlusion, right and left lateral occlude with opposing widened central fossae of the
occlusion which must be balanced with the simultaneous mandibular posterior teeth. In the right lateral position,
contacts at their very first contact of all the teeth on both the occlusal contact forces are directed toward the lingual
sides of the arch. side of the lower ridge and the buccal cusps on the
working side are out of occlusion. (Fig 1a, 1b)
Journal of Advanced Medical and Dental Sciences Research |Vol. 5|Issue 12| December 2017 96
You might also like
- 8 Finishing DetailingDocument171 pages8 Finishing Detailingsanjeed sanjuNo ratings yet
- Cincinnati Sobering Center Business Plan Final DraftDocument26 pagesCincinnati Sobering Center Business Plan Final DraftWVXU News75% (4)
- Panch KarmaDocument59 pagesPanch KarmavkushwahaNo ratings yet
- Case FormulationDocument22 pagesCase FormulationELvine Gunawan100% (5)
- The Importance of OcclusionDocument7 pagesThe Importance of OcclusionZahra ZaNo ratings yet
- Concept of OcclusionDocument81 pagesConcept of Occlusionchawalito27100% (1)
- Orthodontic in Mixed DentitionDocument8 pagesOrthodontic in Mixed Dentitionagnesia tiaraNo ratings yet
- FMR OcclusionDocument10 pagesFMR OcclusionSkAliHassanNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Cervical LymphadenopathyDocument13 pagesPediatric Cervical LymphadenopathyShaira Aquino VerzosaNo ratings yet
- Treatment Planning Single Maxillary Anterior Implants for DentistsFrom EverandTreatment Planning Single Maxillary Anterior Implants for DentistsNo ratings yet
- QSP 04 Procedure For Referral of PatientDocument6 pagesQSP 04 Procedure For Referral of PatientAniruddha ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- 7 RetainerinorthodonticsDocument6 pages7 RetainerinorthodonticsSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Various Concepts of Occlusion in Full MouthDocument5 pagesVarious Concepts of Occlusion in Full Mouthdea swastika100% (1)
- Group Function Occlusion I JosDocument6 pagesGroup Function Occlusion I JosAnonymous gVCIYF6dFNo ratings yet
- Concepts of Arrangement of Artifical Teeth, SelectiveDocument7 pagesConcepts of Arrangement of Artifical Teeth, SelectiveAmar BhochhibhoyaNo ratings yet
- Positioning & DrapingDocument27 pagesPositioning & DrapingJennifer Solano Cruel100% (5)
- 3D Printing Industry Roadmap - India (Aerospace) Summit DocumentDocument19 pages3D Printing Industry Roadmap - India (Aerospace) Summit DocumentSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Mandibular MovementDocument56 pagesMandibular MovementSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Pathophysiology of PneumoniaDocument4 pagesPathophysiology of PneumoniaShermane Criszen F. Sallan100% (4)
- 6.clinical Case ReportMultidisciplinary Approach For Rehabilitation of Debilitated Anterior ToothDocument6 pages6.clinical Case ReportMultidisciplinary Approach For Rehabilitation of Debilitated Anterior ToothSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Support in Complete DentureDocument30 pagesSupport in Complete DentureSahana Rangarajan100% (2)
- Different Types of Tooth PreparationDocument56 pagesDifferent Types of Tooth PreparationSahana Rangarajan100% (1)
- Health10 (Las#4)Document6 pagesHealth10 (Las#4)cheri elaineNo ratings yet
- Occlusion, Malocclusion and Method of Measurements - An OverviewDocument7 pagesOcclusion, Malocclusion and Method of Measurements - An OverviewDiana BernardNo ratings yet
- Review: Types of Finish Lines or Gingival Margins Intooth PreparationDocument6 pagesReview: Types of Finish Lines or Gingival Margins Intooth PreparationSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Occlusal Concepts in Complete Denture Prosthodontics: A Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesOcclusal Concepts in Complete Denture Prosthodontics: A Literature ReviewSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Case Study 1 0 - Pancreatic Cancer FinalDocument23 pagesCase Study 1 0 - Pancreatic Cancer Finalapi-270737306No ratings yet
- Occlusal Principles and Considerations For Implants: An OverviewDocument5 pagesOcclusal Principles and Considerations For Implants: An OverviewKrupali JainNo ratings yet
- Coronoplasty 2Document4 pagesCoronoplasty 2Befalia Aisarahmadani100% (1)
- Esthetic - Considerations - in - Orthodontics - An - Overview SECOND YEAR JC (FIRST)Document6 pagesEsthetic - Considerations - in - Orthodontics - An - Overview SECOND YEAR JC (FIRST)VEENA k.aNo ratings yet
- Occlusal Forms and Philosophies in Full Mouth Rehabilitation: A Literature ReviewDocument5 pagesOcclusal Forms and Philosophies in Full Mouth Rehabilitation: A Literature ReviewSkAliHassanNo ratings yet
- Occlusion and Occlusal Considerations in Implantology: I J D ADocument6 pagesOcclusion and Occlusal Considerations in Implantology: I J D AJASPREETKAUR0410No ratings yet
- Concepts of Arrangement of Artifical Teeth, Selective Grinding and Balanced Occlusion in Complete Denture ProsthodonticsDocument7 pagesConcepts of Arrangement of Artifical Teeth, Selective Grinding and Balanced Occlusion in Complete Denture ProsthodonticsHujarNo ratings yet
- An Appraisal On Occlusal Philosophies in Full-Mouth Rehabilitation A Literature ReviewDocument4 pagesAn Appraisal On Occlusal Philosophies in Full-Mouth Rehabilitation A Literature ReviewaggrolNo ratings yet
- Complete Denture Remounting: Acta Stomatol Croat, Vol. 35, Br. 3, 2001. 381Document7 pagesComplete Denture Remounting: Acta Stomatol Croat, Vol. 35, Br. 3, 2001. 381Dentist HereNo ratings yet
- Enhancing Stability: A Review of Various Occlusal Schemes in Complete Denture ProsthesisDocument8 pagesEnhancing Stability: A Review of Various Occlusal Schemes in Complete Denture ProsthesisPriyanka GandhiNo ratings yet
- Functional Occlusion in Orthodontics: ClinicalDocument11 pagesFunctional Occlusion in Orthodontics: ClinicalNaeem MoollaNo ratings yet
- ISSN: 0975-833X: Case StudyDocument3 pagesISSN: 0975-833X: Case StudyDeya rahmadhanyNo ratings yet
- 29.D17 384 Muhammad Harun Achmad4 PDFDocument7 pages29.D17 384 Muhammad Harun Achmad4 PDFDeviNo ratings yet
- To Open or To Close Space - That Is The Missing Lateral Incisor QuestionDocument9 pagesTo Open or To Close Space - That Is The Missing Lateral Incisor QuestionmeghaNo ratings yet
- Occlusion As Reked To Co Prosthodontics Refrtow E: Complete DenturesDocument11 pagesOcclusion As Reked To Co Prosthodontics Refrtow E: Complete DenturesKrupali JainNo ratings yet
- Occlusion For StabilityDocument8 pagesOcclusion For StabilitydrsmritiNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Treatment: The Soft Tissue Paradigm: ASE EportDocument4 pagesOrthodontic Treatment: The Soft Tissue Paradigm: ASE EportDrAshish KalawatNo ratings yet
- Anterior Guidance Hand OutDocument37 pagesAnterior Guidance Hand OutAswathi RaghuthamanNo ratings yet
- Ijhs 14575+2768 2785Document18 pagesIjhs 14575+2768 2785ambersNo ratings yet
- SDA - ImplicationsDocument10 pagesSDA - ImplicationsVivek ShankarNo ratings yet
- Aesthetics in Complete Denture - A REVIEWDocument2 pagesAesthetics in Complete Denture - A REVIEWInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Management of A Growing Skeletal Class II Case With Functional ApplianceDocument6 pagesOrthodontic Management of A Growing Skeletal Class II Case With Functional ApplianceLidya DiandraNo ratings yet
- ABO Grading SystemDocument82 pagesABO Grading Systemsanjeed sanjuNo ratings yet
- Timm 1976Document8 pagesTimm 1976SwathiLingannagariNo ratings yet
- An Evidence-Based Evaluation of The Concept of Centric Relation in The 21st CenturyDocument6 pagesAn Evidence-Based Evaluation of The Concept of Centric Relation in The 21st Centuryilich sevilla100% (1)
- Group Function OcclusionDocument6 pagesGroup Function OcclusionHamad KayaniNo ratings yet
- Incisal GuidanceDocument5 pagesIncisal Guidancejinny1_0No ratings yet
- Aos Occlusal OverviewDocument8 pagesAos Occlusal OverviewnadiaNo ratings yet
- Minimally Invasive Endodontics A Promising Future Concept A Review Article - 2017Document7 pagesMinimally Invasive Endodontics A Promising Future Concept A Review Article - 2017izeldien5870No ratings yet
- Concepts of Occlusion in Prosthodontics: A Literature ReviewDocument6 pagesConcepts of Occlusion in Prosthodontics: A Literature ReviewNadya RaudillahNo ratings yet
- Implant Esthetics: Review ArticleDocument6 pagesImplant Esthetics: Review ArticleSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- 1,2-Prosthodontic - Docx (1,2) Fifth ClassDocument6 pages1,2-Prosthodontic - Docx (1,2) Fifth Classjbkw2hcnfpNo ratings yet
- The Importance of Treating Functional Cross Bite A Clinical ViewpointDocument7 pagesThe Importance of Treating Functional Cross Bite A Clinical ViewpointAna María ReyesNo ratings yet
- Space Regainers in Pediatric DentistryDocument6 pagesSpace Regainers in Pediatric DentistryDiba Eka DiputriNo ratings yet
- Space Regainers in Pediatric Dentistry: January 2015Document6 pagesSpace Regainers in Pediatric Dentistry: January 2015Fajar Kusuma Dwi KurniawanNo ratings yet
- EBSCO FullText 2023 11 07Document8 pagesEBSCO FullText 2023 11 07Gianna LirianoNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Management of Occlusal Wear: A Case ReportDocument7 pagesDiagnosis and Management of Occlusal Wear: A Case ReportAya KassemNo ratings yet
- Occlusion Concepts in DentistryDocument81 pagesOcclusion Concepts in Dentistrydorasani99No ratings yet
- Pankey-Mann-Schuyler Philosophy-Critical AnalysisDocument5 pagesPankey-Mann-Schuyler Philosophy-Critical Analysisvishwas madaanNo ratings yet
- OCCLUSIONDocument14 pagesOCCLUSIONzainNo ratings yet
- Fox 1983Document9 pagesFox 1983avi pahwaNo ratings yet
- Occlusion in CD - Aniket MoneDocument188 pagesOcclusion in CD - Aniket MoneAniket MoneNo ratings yet
- JCDP 19 624Document4 pagesJCDP 19 624Priyanka GandhiNo ratings yet
- CantileverrrrDocument8 pagesCantileverrrrAYU WULANDARNo ratings yet
- Etm 14 6 6027 PDFDocument7 pagesEtm 14 6 6027 PDFmalekan2005No ratings yet
- ANTERIORPOINTOFREFERENCEDocument6 pagesANTERIORPOINTOFREFERENCEwaf51No ratings yet
- 09 - Splinting - A Healing Touch For An Ailing PeriodontiumDocument5 pages09 - Splinting - A Healing Touch For An Ailing PeriodontiumStefana NanuNo ratings yet
- Planos de OclusiónDocument1 pagePlanos de OclusiónSofi MoralesNo ratings yet
- Fundatia Stomatologiei - OCLUZOLOGIADocument7 pagesFundatia Stomatologiei - OCLUZOLOGIAHornea AndreeaNo ratings yet
- Management and Sequelae of Intruded Anterior Primary Teeth: A Systematic ReviewDocument12 pagesManagement and Sequelae of Intruded Anterior Primary Teeth: A Systematic ReviewwaydergNo ratings yet
- Support in Complete DentureDocument16 pagesSupport in Complete DentureSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Navigation in Dental Implantology: The Influence of Surgical Experience On Implant Placement Accuracy and Operating Time. An in Vitro StudyDocument9 pagesDynamic Navigation in Dental Implantology: The Influence of Surgical Experience On Implant Placement Accuracy and Operating Time. An in Vitro StudySahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Frankel Appliance Certified Fixed Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument76 pagesFrankel Appliance Certified Fixed Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademySahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Clinical Report Rehabilitation of Maxillary Surgical Defect With A Cast Partial Denture ObturatorDocument4 pagesClinical Report Rehabilitation of Maxillary Surgical Defect With A Cast Partial Denture ObturatorSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Finishing and Polishing Agents: - Presented by DR Arpita DuttaDocument89 pagesFinishing and Polishing Agents: - Presented by DR Arpita DuttaSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Factors Affecting Shade of All Ceramic Restorations - A Literature ReviewDocument8 pagesFactors Affecting Shade of All Ceramic Restorations - A Literature ReviewSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- A Hollow Bulb Obturator For Maxillary Resection in A Completely Edentulous PatientDocument6 pagesA Hollow Bulb Obturator For Maxillary Resection in A Completely Edentulous PatientSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Fulltext - Jda v5 Id1107Document3 pagesFulltext - Jda v5 Id1107Sahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Significance of Facebow For Dental RestorationsDocument5 pagesSignificance of Facebow For Dental RestorationsSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- 7 Shreeprada Dash IJPHRDDecember 2018 IssueDocument7 pages7 Shreeprada Dash IJPHRDDecember 2018 IssueSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Mouth Guards in Dentistry-A Review: September 2018Document6 pagesMouth Guards in Dentistry-A Review: September 2018Sahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Cases and Comments: by Stanley G. Standard, D.D.S., New YorkDocument3 pagesCases and Comments: by Stanley G. Standard, D.D.S., New YorkSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Long-Term Follow-Up of Maxillary Fixed Retention: Survival Rate and Periodontal HealthDocument7 pagesLong-Term Follow-Up of Maxillary Fixed Retention: Survival Rate and Periodontal HealthSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Gothic Arch TrachingDocument7 pagesGothic Arch TrachingSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Elegant Galaxy Background Breakthrough by SlidesgoDocument48 pagesElegant Galaxy Background Breakthrough by SlidesgoSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Prosthodontics Horizontal Jaw Relation: Dr. Firas AbdulameerDocument6 pagesProsthodontics Horizontal Jaw Relation: Dr. Firas AbdulameerSahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Sauser 1957Document9 pagesSauser 1957Sahana RangarajanNo ratings yet
- Acls ScoreDocument3 pagesAcls ScoreaveekumbharNo ratings yet
- Complications in The Use of The Mandibular Body, Ramus and Symphysis As Donor Sites in Bone Graft Surgery. A Systematic ReviewDocument9 pagesComplications in The Use of The Mandibular Body, Ramus and Symphysis As Donor Sites in Bone Graft Surgery. A Systematic ReviewBrenda Carolina Pattigno ForeroNo ratings yet
- Ward Dec 7-8Document18 pagesWard Dec 7-8Gio PinedaNo ratings yet
- PPHDocument21 pagesPPHDhananjaya ShivalingappaNo ratings yet
- Asnic Table of BenefitsDocument5 pagesAsnic Table of BenefitsmohamedNo ratings yet
- LST 2009 Surgical Safety Check List (Australia and New Zealand) PDFDocument1 pageLST 2009 Surgical Safety Check List (Australia and New Zealand) PDFaskjhwiuehNo ratings yet
- Andocor BrochureDocument19 pagesAndocor BrochureAffan AhmadNo ratings yet
- Pressure Flow Urodynamic Studies: The Gold Standard For Diagnosing Bladder Outlet ObstructionDocument8 pagesPressure Flow Urodynamic Studies: The Gold Standard For Diagnosing Bladder Outlet ObstructionmarcelloNo ratings yet
- Nongenital WartsDocument13 pagesNongenital WartsPreisy G. I. TampiNo ratings yet
- Application of Suchman TheoryDocument5 pagesApplication of Suchman TheoryAnusha VergheseNo ratings yet
- Lidocaine Spray On An Endoscope Immediately Before Gi-5-067Document5 pagesLidocaine Spray On An Endoscope Immediately Before Gi-5-067Byung ChaNo ratings yet
- 224 Closed Manipulation Casting of Distal Radius Fractures Fernandez DL 2005 Hand Clin p307-316 PDFDocument10 pages224 Closed Manipulation Casting of Distal Radius Fractures Fernandez DL 2005 Hand Clin p307-316 PDFanindyadputriNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmology: World Journal ofDocument5 pagesOphthalmology: World Journal ofRohamonangan TheresiaNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 COVID-19 Safety ProtocolsDocument2 pagesActivity 1 COVID-19 Safety ProtocolsErica Z. AdugNo ratings yet
- The Audit Process and How To Ensure A Successful AuditDocument19 pagesThe Audit Process and How To Ensure A Successful AuditRudy surya 08No ratings yet
- The Circulatory System PDFDocument4 pagesThe Circulatory System PDFPerry SinNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Tablet PDFDocument2 pagesEvaluation of Tablet PDFKim50% (2)
- Trauma UretraDocument3 pagesTrauma UretraTita FadiahNo ratings yet
- PBLDocument22 pagesPBLOmar AhmedNo ratings yet
- Impaired Skin Integrity For NCP Oct. 212020Document2 pagesImpaired Skin Integrity For NCP Oct. 212020Benjie DimayacyacNo ratings yet
- Our Lady of Fatima UniversityDocument3 pagesOur Lady of Fatima UniversityMICHAEL M. ISIDRONo ratings yet