Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2015 AHA Physio PALS Poster
2015 AHA Physio PALS Poster
Uploaded by
Denny IntanCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2015 AHA Physio PALS Poster
2015 AHA Physio PALS Poster
Uploaded by
Denny IntanCopyright:
Available Formats
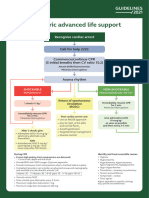
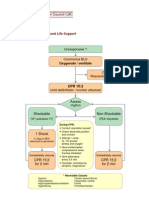
Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Algorithm
AHA 2015 Update
Pediatric Cardiac Arrest Algorithm—2015 Update
1
CPR QUALITY
Start CPR Push hard (≥⅓ of anteroposterior
• Give oxygen diameter of chest) and fast (100-
• Attach monitor/defibrillator 120/min) and allow complete chest
recoil.
Minimize interruptions in compres-
sions.
Avoid excessive ventilation.
Yes Rhythm No Rotate compressor every 2 minutes,
2 shockable?
or sooner if fatigued.
If no advanced airway,
15:2 compression-ventilation ratio.
VF/pVT 9 Asystole/PEA
SHOCK ENERGY
FOR DEFIBRILLATION
3
First shock 2 J/kg
Shock Second shock 4 J/kg
4 Subsequent shocks ≥4 J/kg,
maximum 10 J/kg or adult dose
CPR 2 min DRUG THERAPY
• IO/IV access
Epinephrine IO/IV dose:
-- 0.01 mg/kg (0.1 mL/kg of 1:10
000 concentration). Repeat every
3-5 minutes.
If no IO/IV access, may give
Rhythm No endotracheal dose: 0.1 mg/kg (0.1
shockable? mL/kg of 1:1000 concentration).
Amiodarone IO/IV dose:
Yes -- 5 mg/kg bolus during cardiac ar-
rest. May repeat up to 2 times for
5 refractory VF/pulseless VT.
Shock Lidocaine IO/IV dose:
-- Initial: 1 mg/kg loading dose.
6 10
-- Maintenance: 20-50 mcg/kg per
minute infusion (repeat bolus
CPR 2 min CPR 2 min dose if infusion initiated >15 min-
utes after initial bolus therapy).
• Epinephrine every 3-5 min • IO/IV access
• Consider advanced airway • Epinephrine every 3-5 min
• Consider advanced airway
ADVANCED AIRWAY
Endotracheal intubation or supra-
glottic advanced airway
Waveform capnography or capnom-
etry to confirm and monitor ET tube
No Yes placement
Rhythm Rhythm
Once advanced airway in place,
shockable? shockable? give 1 breath every 6 seconds (10
breaths/min) with continuous chest
compressions
Yes
7 RETURN OF
Shock No
SPONTANEOUS
8 11 CIRCULATION
(ROSC)
CPR 2 min CPR 2 min Pulse and blood pressure
• Amiodarone or lidocaine • Treat reversible causes Spontaneous arterial pressure
• Treat reversible causes waves with intra-arterial monitoring
REVERSIBLE
CAUSES
Hypovolemia
No Yes
Rhythm Hypoxia
shockable? Hydrogen ion (acidosis)
Hypo-/hyperkalemia
12
Hypothermia
Tension pneumothorax
• Asystole/PEA 10 or 11 Go to 5 or 7 Tamponade, cardiac
• Organized rhythm check pulse Toxins
• Pulse present (ROSC) Thrombosis, pulmonary
© 2015 American post–cardiac arrest care Thrombosis, coronary
Heart Association
©2016 Physio-Control, Inc. 1.800.442.1142 www.physio-control.com Reprinted with permission
CL7178-00 2015 American Heart Association
Pediatric Tachycardia with a Pulse and Poor Perfusion Algorithm
AHA 2015 Update
Pediatric Tachycardia With a Pulse and Poor Perfusion Algorithm
SYNCHRONIZED
Identify and treat underlying cause
• Maintain patent airway; assist breathing as necessary
CARDIOVERSION
• Oxygen Begin with 0.5-1 J/kg;
• Cardiac monitor to identify rhythm; monitor blood pressure and oximetry if not effective, increase to 2 J/kg.
• IO/IV access Sedate if needed, but don’t delay
• 12-Lead ECG if available; don’t delay therapy cardioversion.
Narrow Wide
(≤0.09 sec) (>0.09 sec)
DRUG THERAPY
Evaluate
Adenosine IO/IV dose:
QRS duration
-- First dose:
1.1 mg/kg rapid bolus
Evaluate rhythm (maximum: 6 mg).
with 12-lead ECG -- Second dose:
or monitor 1.2 mg/kg rapid bolus
(maximum second dose: 12 mg).
Amiodarone IO/IV dose:
Probable Probable Possible -- 5 mg/kg over 20-60 minutes
ventricular or
sinus supraventricular
tachycardia tachycardia tachycardia Procainamide IO/IV dose:
• Compatible • Compatible history -- 15 mg/kg over 30-60 minutes
history (vague, nonspecific); -- Do not routinely administer
consistent with history of abrupt amiodarone and procainamide
together.
known cause rate changes
• P waves • P waves absent/
present/normal abnormal
• Variable R-R; • HR not variable
constant PR
• Infants: • Infants: rate usually
rate usually ≥220/min
<220/min
• Children: rate • Children: rate usually
usually <180/min ≥180/min Cardiopulmonary
compromise?
• Hypotension
• Acutely altered
mental status
• Signs of shock
Yes No
Search for Consider Synchronized Consider
and vagal cardioversion adenosine
treat cause maneuvers if rhythm regular
(No delays) and QRS
monomorphic
• If IO/IV access present, give adenosine Expert
or consultation
• If IO/IV access not available, or if adenosine advised
ineffective, synchronized cardioversion • Amiodarone
• Procainamide
© 2015 American Heart Association
©2016 Physio-Control, Inc. 1.800.442.1142 www.physio-control.com Reprinted with permission
CL7178-00 2015 American Heart Association
You might also like
- Acls 2023Document5 pagesAcls 2023Mohamed Helal100% (5)
- ACLS Pocket Card PDFDocument6 pagesACLS Pocket Card PDFdang vu hoang ducNo ratings yet
- Pals Pre TestDocument20 pagesPals Pre TestLawrence Gabriel80% (5)
- Adult Cardiac Arrest Algorithm: VF/PVT Asystole/PEADocument8 pagesAdult Cardiac Arrest Algorithm: VF/PVT Asystole/PEAVitor Hugo100% (2)
- Checklist & Algoritma ACLSDocument16 pagesChecklist & Algoritma ACLSNadhif JovaldyNo ratings yet
- Algo ArrestDocument2 pagesAlgo ArrestLocomotorica FK UkiNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac ArrestDocument1 pageAdvanced Cardiac ArrestDebbie MeyerNo ratings yet
- Contrast Reaction Card PediatricDocument2 pagesContrast Reaction Card PediatricJenniffer FlorenciaNo ratings yet
- 2019 Practice of Anesthesia For Infants and ChildrenDocument2 pages2019 Practice of Anesthesia For Infants and ChildrenJavier GlezqNo ratings yet
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs - AMBOSS TWO PDFDocument6 pagesAntiarrhythmic Drugs - AMBOSS TWO PDFRuva Oscass JimmyNo ratings yet
- VF & Pulseless VTDocument1 pageVF & Pulseless VTmadimadi11No ratings yet
- Algorithm-ACLS CA 200731Document1 pageAlgorithm-ACLS CA 200731Hyunsoo EllisNo ratings yet
- Checklist & Algoritma ACLSDocument16 pagesChecklist & Algoritma ACLSNadhif JovaldyNo ratings yet
- Shock: Shout For Help/Activate Emergency ResponseDocument6 pagesShock: Shout For Help/Activate Emergency ResponseandiyanimalikNo ratings yet
- Wa0000.Document7 pagesWa0000.benitez1228No ratings yet
- Figure 4 AlgorithmACLS CACOVID 220101Document1 pageFigure 4 AlgorithmACLS CACOVID 220101AndhikaNo ratings yet
- Algorithms - Paediatric Advanced Life Support PDFDocument1 pageAlgorithms - Paediatric Advanced Life Support PDFLenox BlackNo ratings yet
- Algo Pals Pediatric Cardiac ArrestDocument1 pageAlgo Pals Pediatric Cardiac Arrestpedjoang fkupr2017No ratings yet
- AclsDocument1 pageAclsJoice DasNo ratings yet
- Perkembangan Baru Resusitasi Jantung ParuDocument27 pagesPerkembangan Baru Resusitasi Jantung ParuMarcelina Aprisia PrimadiNo ratings yet
- ACLS 2015 Algorithm and Anesthesia ACLS PDFDocument14 pagesACLS 2015 Algorithm and Anesthesia ACLS PDFTaufiqurrahman RizkiNo ratings yet
- Algo Pals Pediatric Cardiac ArrestDocument1 pageAlgo Pals Pediatric Cardiac ArrestDevi ChrestellaNo ratings yet
- Paediatric Advanced Life Support: Call For Help 2222 Commence/continue CPR (5 Initial Breaths Then CV Ratio 15:2)Document1 pagePaediatric Advanced Life Support: Call For Help 2222 Commence/continue CPR (5 Initial Breaths Then CV Ratio 15:2)Vijay RNo ratings yet
- Dilution Protocol For AdultsDocument23 pagesDilution Protocol For AdultsSharumathi ChandraNo ratings yet
- Dosis Ketamin Dan Xylazine RabbitDocument1 pageDosis Ketamin Dan Xylazine RabbitRais RyuzakiNo ratings yet
- ICE DrugsDocument2 pagesICE DrugsRichelle FrondaNo ratings yet
- Advance Life Support MaterialDocument2 pagesAdvance Life Support MaterialmayNo ratings yet
- Drug List: Medication Adult Dosing Pediatric DosingDocument14 pagesDrug List: Medication Adult Dosing Pediatric DosingAndrew JamesNo ratings yet
- Drug Main ACLS Use Dose/Route NotesDocument4 pagesDrug Main ACLS Use Dose/Route NotesshadyNo ratings yet
- Acls Patient Algorithms: Greg Cook's Version of A Phoenix Fire DPT ClasicDocument4 pagesAcls Patient Algorithms: Greg Cook's Version of A Phoenix Fire DPT ClasicDouglas Greg CookNo ratings yet
- Adenosine: Rapid IV PushDocument4 pagesAdenosine: Rapid IV PushsabboNo ratings yet
- PalsDocument1 pagePalslordroentgenNo ratings yet
- Start CPR Shout For Help/Activate Emergency Response: Give Oxygen Attach Monitor/DefibrillatorDocument2 pagesStart CPR Shout For Help/Activate Emergency Response: Give Oxygen Attach Monitor/DefibrillatorFelicia ErikaNo ratings yet
- Adult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityDocument1 pageAdult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityChris LeeNo ratings yet
- Adult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityDocument1 pageAdult Cardiac Arrest Circular Algorithm: Monitor CPR QualityAlexis HospitalNo ratings yet
- ACLS Algorithm Pulse No Yes: Stable Patient Unstable Patient Stable PatientDocument1 pageACLS Algorithm Pulse No Yes: Stable Patient Unstable Patient Stable PatientAhmed AlkhaqaniNo ratings yet
- Farmacos Reanimacion PediatricaDocument1 pageFarmacos Reanimacion PediatricaMiriam C. F. TapiaNo ratings yet
- ACLS ChartDocument1 pageACLS ChartJev DespiNo ratings yet
- 3 Combined AHA BLS ACLS Updates CombinedDocument5 pages3 Combined AHA BLS ACLS Updates Combinedamanrup randhawa100% (1)
- Ventricular Fibrillation/ Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia AlgorithmDocument2 pagesVentricular Fibrillation/ Pulseless Ventricular Tachycardia AlgorithmsafasayedNo ratings yet
- Advanced Paediatric Life Support - A0 PDFDocument1 pageAdvanced Paediatric Life Support - A0 PDFiulia-uroNo ratings yet
- Cardiac Arrest Circular AlgorhythmDocument4 pagesCardiac Arrest Circular AlgorhythmAisyah Nur KarimahNo ratings yet
- PalsalgoDocument1 pagePalsalgozacklim_2000No ratings yet
- Obtain 12 Lead ECG and Cardiology ConsultationDocument2 pagesObtain 12 Lead ECG and Cardiology ConsultationPauline ChanNo ratings yet
- Cardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation: American Heart Assocation Guidelines CPR ECC 2010Document79 pagesCardio-Pulmonary Resuscitation: American Heart Assocation Guidelines CPR ECC 2010Deepa BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- ACLS Book (New)Document23 pagesACLS Book (New)Essa AyazNo ratings yet
- Reanimacion CardiopulmonarDocument15 pagesReanimacion CardiopulmonarVictoriano ValienteNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Emergency Pocket GuideDocument2 pagesPediatric Emergency Pocket GuideHongMingNo ratings yet
- Rabbit Formulary: Inhalation AnestheticsDocument3 pagesRabbit Formulary: Inhalation AnestheticsMiriam CervantesNo ratings yet
- #15 The Progrm Elite 2019 Week 15 For LEONARDODocument6 pages#15 The Progrm Elite 2019 Week 15 For LEONARDOleonardolaboissiere68No ratings yet
- 2-Cardiac Arrest AlgrthmDocument1 page2-Cardiac Arrest AlgrthmterminallllNo ratings yet
- ER Clinical NotesDocument23 pagesER Clinical NotesmngaNo ratings yet
- Critical Care Drug Reference SheetDocument12 pagesCritical Care Drug Reference SheetYanina CoxNo ratings yet
- CPR Updated 2022Document32 pagesCPR Updated 2022Tathagata Bakuli100% (1)
- GambarDocument27 pagesGambarAnonymous feLB4alTNo ratings yet
- Adult Immediate Post Cardiac Arrest Care Algorithm 2015 UpdateDocument1 pageAdult Immediate Post Cardiac Arrest Care Algorithm 2015 UpdateRyggie Comelon0% (1)
- RCP TripticoDocument2 pagesRCP Tripticoqg4r5srcnpNo ratings yet
- ÷ Weight (KG) Dilute 1 ML (500mcg) of PGE1 With NS/ D5% To Yield The Total Volume From #1Document14 pages÷ Weight (KG) Dilute 1 ML (500mcg) of PGE1 With NS/ D5% To Yield The Total Volume From #1Nesreen G MohammedNo ratings yet
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesFrom EverandAdvanced Cardiac Life Support Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Pediatric Advanced Life Support Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesFrom EverandPediatric Advanced Life Support Quick Study Guide 2015 Updated GuidelinesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- COVID-19 Vaccine Third Dose RecommendationsDocument20 pagesCOVID-19 Vaccine Third Dose RecommendationsKholida UlfaNo ratings yet
- Procedures Skin Tag RemovalDocument5 pagesProcedures Skin Tag RemovalKholida UlfaNo ratings yet
- Jadwal Jaga Igd-1Document5 pagesJadwal Jaga Igd-1Kholida UlfaNo ratings yet
- Novo Mix 30 Flex PenDocument12 pagesNovo Mix 30 Flex PenKholida UlfaNo ratings yet
- Bab 4Document21 pagesBab 4Kholida UlfaNo ratings yet
- ACLS PharmacologyDocument5 pagesACLS PharmacologyKim Still ChunnNo ratings yet
- NGFD 678 UjtyDocument291 pagesNGFD 678 UjtyAlfredo MunguíaNo ratings yet
- CAFFEINEDocument2 pagesCAFFEINEVALDEZ, Teresita B.No ratings yet
- Medicine: Most Recent QuestionsDocument11 pagesMedicine: Most Recent QuestionsskNo ratings yet
- Abbreviations and SymbolsDocument8 pagesAbbreviations and SymbolsLomi LambarNo ratings yet
- Antiaritmia: Frans D. Suyatna Modified by Sulistia 1010 Departemen Farmakologi & Terapeutik FKUIDocument56 pagesAntiaritmia: Frans D. Suyatna Modified by Sulistia 1010 Departemen Farmakologi & Terapeutik FKUIJoshua ObrienNo ratings yet
- CaffeineDocument24 pagesCaffeineMitko100% (1)
- Adenosine ReceptorDocument53 pagesAdenosine Receptormirza_baig_46100% (1)
- Wellington ICU Drug Manual 2013Document444 pagesWellington ICU Drug Manual 2013khangsiean89No ratings yet
- Canadian-Exam-Answers-2007 من امتحانات الجامعةDocument189 pagesCanadian-Exam-Answers-2007 من امتحانات الجامعةAli Toma HmedatNo ratings yet
- Making Magic by Peter GormanDocument10 pagesMaking Magic by Peter GormanKambo Viva100% (1)
- Neonatal Drugs Section Fifth Edition2012 PDFDocument163 pagesNeonatal Drugs Section Fifth Edition2012 PDFAhmed MohammedNo ratings yet
- Opies Cardiovascular Drugs A Companion To Braunwalds Heart Disease Expert Consult 9Th Edition Bhatt MD MPH Download PDF ChapterDocument52 pagesOpies Cardiovascular Drugs A Companion To Braunwalds Heart Disease Expert Consult 9Th Edition Bhatt MD MPH Download PDF Chaptermary.hanna173100% (3)
- Aha Acls Prep Packet 2020Document69 pagesAha Acls Prep Packet 2020VP The Hacker100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument22 pagesDrug StudyShenna RegaspiNo ratings yet
- 30 - Toronto Notes 2011 - Common Unit Conversions - Commonly Measured Laboratory Values - Abbreviations - IndexDocument28 pages30 - Toronto Notes 2011 - Common Unit Conversions - Commonly Measured Laboratory Values - Abbreviations - IndexRazrin RazakNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Supraventricular Tachycardia Case PresentationDocument23 pagesPediatric Supraventricular Tachycardia Case Presentationapi-602288180No ratings yet
- Drugs in CPR - M.H.farjooDocument37 pagesDrugs in CPR - M.H.farjooAnonymous 34umhBmBENo ratings yet
- Kuwait Pediatric GuideLinesDocument124 pagesKuwait Pediatric GuideLinesemicurudimov100% (1)
- TMP 5 F7 CDocument10 pagesTMP 5 F7 CFrontiersNo ratings yet
- Caffeine in The Treatment of Pain: Cristiane Tavares, TSA, Rioko Kimiko Sakata, TSADocument15 pagesCaffeine in The Treatment of Pain: Cristiane Tavares, TSA, Rioko Kimiko Sakata, TSAYoselin GomezNo ratings yet
- I. Background A. Lexiscan: August 25, 2021Document10 pagesI. Background A. Lexiscan: August 25, 2021я таNo ratings yet
- TPS2 B Ing Pert 4.Document8 pagesTPS2 B Ing Pert 4.Ulya Tala Hanifa20No ratings yet
- Advances in Imaging Techniques in Ischemic Heart Disease PDFDocument167 pagesAdvances in Imaging Techniques in Ischemic Heart Disease PDFGhenadie BostanNo ratings yet
- Drugs Used in CcuDocument169 pagesDrugs Used in CcuAnusha Verghese100% (3)
- Understanding The Mechanisms of Action of MethotrexateDocument6 pagesUnderstanding The Mechanisms of Action of MethotrexateMuhamad Rizqy MaulanaNo ratings yet
- IV. Antiarrhythmic Drugs: PHRM 537 Summer 2020Document19 pagesIV. Antiarrhythmic Drugs: PHRM 537 Summer 2020SaulNo ratings yet
- AntitussivesDocument5 pagesAntitussivesAditya PrajapatiNo ratings yet