67% found this document useful (3 votes)
3K views6 pagesEntrepreneurship Quarter 2 - Module 10 Bookkeeping Pre - Test
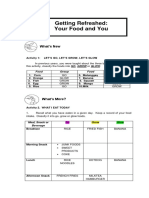
This document contains a pre-test, activities and lessons on bookkeeping concepts for an entrepreneurship course. It discusses topics like journal entries, T-accounts, trial balances, revenue, expenses, and calculating net income. The activities guide students through recording business transactions, posting journal entries to ledgers, preparing a trial balance, and computing adjustments for depreciation, prepaid expenses and accrued income/revenue. The assessments test the students' understanding of key bookkeeping terms and calculations.
Uploaded by
Dinahrae VallenteCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd
67% found this document useful (3 votes)
3K views6 pagesEntrepreneurship Quarter 2 - Module 10 Bookkeeping Pre - Test
This document contains a pre-test, activities and lessons on bookkeeping concepts for an entrepreneurship course. It discusses topics like journal entries, T-accounts, trial balances, revenue, expenses, and calculating net income. The activities guide students through recording business transactions, posting journal entries to ledgers, preparing a trial balance, and computing adjustments for depreciation, prepaid expenses and accrued income/revenue. The assessments test the students' understanding of key bookkeeping terms and calculations.
Uploaded by
Dinahrae VallenteCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
We take content rights seriously. If you suspect this is your content, claim it here.
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online on Scribd