Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Labs:: Pulmonary Renal Syndromes (PRS) Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage
Uploaded by
Ronald MoralesOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Labs:: Pulmonary Renal Syndromes (PRS) Diffuse Alveolar Hemorrhage
Uploaded by
Ronald MoralesCopyright:
Available Formats
onepagericu.
com
PULMONARY-RENALSYNDROMES by Nick Mark MD & Mithu Maheswaranathan MD ONE @nickmmark
Link to the
most current
PRESENTATION: WORKUP & DIAGNOSIS @MithuRheum version →
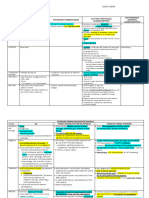
· Pulmonary Renal Syndromes (PRS) are life-threatening Labs:
PULMONARY FINDINGS:
diseases with pulmonary hemorrhage (DAH) & renal failure • BMP (quantify renal injury), Coags (r/o coagulopathy) · AAV or Goodpasture’s cause pulmonary capillaritis leading
(glomerulonephritis). Although pulmonary and renal • CBC w differential (check eosinophil count for EGPA) to diffuse alveolar hemorrhage (DAH)
involvement is the defining feature, PRS can affect many organs: • Auto-antibodies: ANCA antibody, Anti-GBM antibody · Diffuse ground glass or consolidative opacities with sparing
acute respiratory failure glomerulonephritis: • Urine: UA, Urine protein to creatinine (UPC) ratio or the lung periphery is typically seen on chest CT.
or diffuse alveolar acute kidney injury (AKI), • Cardiac: consider BNP, troponin if concern for EGPA · BAL reveals increasing blood return in serial lavages and
hemorrhage (DAH) proteinuria, hematuria • ESR and CRP (non-specific, ESR usually low in anti-GBM) >20% hemosiderin laden macrophages (diagnostic of DAH)
Other tests: Lavage #1 Lavage #2 Lavage #3
inflammatory ENT: sinus, nasal, hearing loss, • CT chest to evaluate pulmonary involvement BAL of airways
eye disease saddle nose deformity • Bronchoscopy: confirm DAH, r/o infection and alveoli
scleritis, uveitis, • Echocardiogram for EGPA (↓ LVEF, pericardial effusion)
episcleritis pulmonary hemorrhage (DAH),
• PFTs (outpatient; increased DLCO after recent DAH)
asthma in EGPA, tracheal Initial
(subglottic stenosis) in GPA, • EMG/NCS for mononeuritis multiplex/neuropathy lavages
cardiac pulmonary nodules, asthma (EGPA) Diagnosis of PRS: biopsy (gold standard) or serologies + clear
(in EGPA) symptoms (not-optimal but may be necessary)
glomerulonephritis (AKI,
digital ischemia proteinuria, hematuria)
AUTO-ANTIBODIES:
• MPA ⇢ usually p-ANCA • Goodpasture’s ⇢ anti-GBM
cutaneous • GPA ⇢ usually c-ANCA •
neuropathy, mononeuritis Subsequent lavages reach more distal airways & alveoli
palpable purpura • EGPA ⇢ ANCA in 40-50%
multiplex ANCA Associated Vasculitis (AAV) · Surgical lung biopsy (not always required) may reveal:
2/2 vasculitis, Anti
ulcers, nodules BM · linear IgG staining along BM (anti-GBM)
MPA GPA EGPA
Pulmonary & · granular immune complex deposition (SLE & rheum dx)
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS: Renal failure P-ANCA · pauci immune (no Ig, immune complex) with neutrophil
65% 15% 45% 20%
C-ANCA (MPO) infiltration of vessels (GPA) or eosinophils (EGPA).
· Cytoplasmic
·“Chocolate Chip C-ANCA OTHER FINDINGS:
Cookie” like 15% 85% 5% 10% Skin lesions: palpable purpura, petechiae, ulcerations, &
Antibody Other Drug induced (PR3)
Other
mediated autoimmune vasculitis occasionally nodules. Nasal or sinus mucosa often involved
X-ANCA Perinuclear pattern (but not MPO)
· Infx organisms that Seen with medications:
in EGPA. Biopsy of skin or nasal mucosa can reveal
· SLE · PTU (elastase,
· APS · methimazole cause lung/renal failure: cathepsin, Levamisole/cocaine, hydralazine vasculitis, such as leukocytoclastic vasculitis of skin
lysozyme, ANCA also seen in many diseases: APPROACH: Initial tx focused on remission-induction
· cryoglobulinemia · hydralazine Leptospirosis, Hantavirus, P-ANCA
TB, CMV, Legionella
· Perinuclear others) SLE, RA, PSC, PBC, AIH, IBD (UC > CD)
· systemic sclerosis · minocycline ·“Popcorn” like Later tx focused on maintenance.
PATHOLOGY
· HSP & IgA vasculitis · others - Post infections (e.g RENAL FINDINGS:
post-strep GN) Linear BM Pauci-immune
U/A: microscopic or gross hematuria, RBC deposition crescentic GN
· Sepsis (e.g. PNA & AKI)
casts, low grade proteinuria
Path: rapidly progressive (crescentic)
SEROLOGY
Autoimmune ANCA vasculitis Anti-basement membrane glomerulonephritis (fibrinoid necrosis, ANCA (-) ANCA (+) ANCA (+)
(AAV) (Goodpasture) hypercellular glomeruli, & cellular crescents) GBM (+) GBM (+) GBM (-)
· GPA (granulomatous with polyangiitis) IF staining patterns in crescentic GN:
v1.0 (2021-06-04) CC BY-SA 3.0
ANTI-GBM DISEASE OVERLAP SYNDROME ANCA VASCULITIS
· EGPA (eosinophilic granulomatosis w polyangiitis) LINEAR PATTERN GRANULAR PATTERN PAUCI IMMUNE
· MPA (microscopic polyangiitis) IG G C3
Pulse dose steroids
Plasmapheresis (PLEX)
INITIAL TX
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY: Rituximab and/or
· AAV: ANCA activates primed neutrophils ⇢ vessel endothelial Cyclophosphamide
cyclophosphamide
damage & inflammation; Granulomatous inflammation (cell- Pulse dose steroids
+/- PLEX
mediated immunity) in some forms of AAV (GPA, EGPA)
· GBM: Auto-antibodies against ⍺3 chain of type IV collagen,
MAINT TX
Linear IgG staining on Complement deposits Absence of IF staining;
Renal transplant Maintenance
distrupting the basement membrane integrity in lungs and kidney. basement membranes in clusters; seen in seen in AAV (MPA, GPA,
· Environmental risk factors: silica exposure (AAV), smoking (GBM) seen in anti-GBM dx SLE, post-strep GN, and EGPA) evaluation therapy
You might also like
- Plabable-Gems-31. Respiratory Plabable GemsDocument68 pagesPlabable-Gems-31. Respiratory Plabable GemsHabo Habo100% (1)
- ICU One Pager Pulmonar Renal Syndrome-JbxqojDocument1 pageICU One Pager Pulmonar Renal Syndrome-JbxqojmujawayezuNo ratings yet
- ANCA Tests Guide: Understanding Interpretation and IndicationsDocument3 pagesANCA Tests Guide: Understanding Interpretation and IndicationsGREENCROSS PALDINo ratings yet
- ANCA Related Vasculitis PDFDocument51 pagesANCA Related Vasculitis PDF陳思任No ratings yet
- Lap Abdominal Surg-1Document4 pagesLap Abdominal Surg-1Rizwan AhmedNo ratings yet
- ICU One Pager Massive Hemoptysis v11Document1 pageICU One Pager Massive Hemoptysis v11Nicholas HelmstetterNo ratings yet
- Cardio Vascular PDFDocument148 pagesCardio Vascular PDFStefana RoxanaNo ratings yet
- Vasculitis: Allison Eunice B. ServandoDocument116 pagesVasculitis: Allison Eunice B. ServandoAllison Eunice ServandoNo ratings yet
- Clinical Approach To: Rapid Progressive GlomerulonephritisDocument38 pagesClinical Approach To: Rapid Progressive GlomerulonephritisMiri PravdaNo ratings yet
- Firman - CKD ST V + CKDMBDDocument28 pagesFirman - CKD ST V + CKDMBDAdinda DianNo ratings yet
- Pedia NephrologyDocument4 pagesPedia NephrologyJulie Anne AciertoNo ratings yet
- 8-Ecg in CovidsDocument35 pages8-Ecg in CovidsyandraNo ratings yet
- Congenital Heart Defects: Part Ii-Duct Dependent ChdsDocument28 pagesCongenital Heart Defects: Part Ii-Duct Dependent ChdslindaNo ratings yet
- 9 - Role of Non InvasiveDocument46 pages9 - Role of Non InvasiveHavara Kausar AkbarNo ratings yet
- Community-Acquired PneumoniaDocument22 pagesCommunity-Acquired PneumoniaIMAFDNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary-Renal SyndromesDocument9 pagesPulmonary-Renal SyndromesJanio Alberto OvalleNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument2 pagesNCPJulianne MagtunaoNo ratings yet
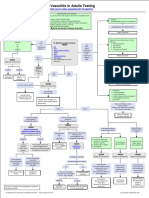
- I Am Sharing 'Vasculitis - in - Adults - Testing - Algorithm' With YouDocument1 pageI Am Sharing 'Vasculitis - in - Adults - Testing - Algorithm' With YouMahmoud AbouemiraNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Hypertension and EchocardiographyDocument57 pagesPulmonary Hypertension and EchocardiographySiska Istanah Wong SintingNo ratings yet
- ICU One Pager - Pulmonary Embolism RX PDFDocument1 pageICU One Pager - Pulmonary Embolism RX PDFAbdul RaufNo ratings yet
- The Role of Blood Gas and D-Dimer Evaluation in The DiagnostDocument18 pagesThe Role of Blood Gas and D-Dimer Evaluation in The Diagnostifan zulfantriNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary ArtesiaDocument6 pagesPulmonary ArtesiaMaulani NurlatifahNo ratings yet
- Shaggy Aorta 6Document2 pagesShaggy Aorta 6Eghet SilviuNo ratings yet
- C19 SPACE ToolKit ChecklistsDocument8 pagesC19 SPACE ToolKit ChecklistsAdrian BălanNo ratings yet
- Diagnosis and Treatment of Radiation ProctitisDocument2 pagesDiagnosis and Treatment of Radiation ProctitispatNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary EmbolismDocument63 pagesPulmonary EmbolismeuniicehahaNo ratings yet
- Approach To Subarachnoid Hemorrhage - DR DikaDocument27 pagesApproach To Subarachnoid Hemorrhage - DR DikaOnyedika EgbujoNo ratings yet
- Imaging of Thoracic Aspergillosis: Prof. G Ferretti Chu GrenobleDocument50 pagesImaging of Thoracic Aspergillosis: Prof. G Ferretti Chu GrenobleIqbal AbdillahNo ratings yet
- Recruitment Checklist: Security Forces Hospital ProgramDocument4 pagesRecruitment Checklist: Security Forces Hospital ProgramDerick RanaNo ratings yet
- IM Part 1Document48 pagesIM Part 1sasghfdgNo ratings yet
- IM Part 1 and 2 CombinedDocument100 pagesIM Part 1 and 2 CombinedsasghfdgNo ratings yet
- Dignostic Investigation in Respiratory SystemDocument99 pagesDignostic Investigation in Respiratory SystemGopi JaladiNo ratings yet
- Uac VS UvcDocument1 pageUac VS UvcJunaidahMubarakAliNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument30 pagesDrug StudyClaire MachicaNo ratings yet
- Thrombosis ManagementDocument14 pagesThrombosis ManagementJessa MaeNo ratings yet
- Acute Chest SyndromeDocument28 pagesAcute Chest SyndromeJohn OkidiNo ratings yet
- Algoritmo-COVID19 PDF pdf81552961419587596081570311557Document1 pageAlgoritmo-COVID19 PDF pdf81552961419587596081570311557Keti JanevskaNo ratings yet
- BRONCHO ALVEOLAR CARCINOMA DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSISDocument3 pagesBRONCHO ALVEOLAR CARCINOMA DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSISmarielleaudreeyNo ratings yet
- Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument27 pagesAcute GlomerulonephritisKumara GuruNo ratings yet
- Acute Glomerulonephritis PDFDocument27 pagesAcute Glomerulonephritis PDFRaj RNo ratings yet
- Incorporates NICE Bacterial Meningitis and Meningococcal Septicaemia Guideline CG102. Distributed in Partnership With NICEDocument1 pageIncorporates NICE Bacterial Meningitis and Meningococcal Septicaemia Guideline CG102. Distributed in Partnership With NICELilisNo ratings yet
- Major Causes of ARF and Clinical FeaturesDocument3 pagesMajor Causes of ARF and Clinical FeaturespurwandinyNo ratings yet
- Monitoring Intra Operatif: Mindi Widayani NRP 122.022.1115 FK UPN "Veteran" JakartaDocument21 pagesMonitoring Intra Operatif: Mindi Widayani NRP 122.022.1115 FK UPN "Veteran" Jakartaputri wulandariNo ratings yet
- ElectrodiagnosticsDocument4 pagesElectrodiagnosticsAndy Delos ReyesNo ratings yet
- PLABABLE Gems Respiratory MedicineDocument68 pagesPLABABLE Gems Respiratory Mediciney æskNo ratings yet
- TID Part 2 Dr. Lu 2014 SalveDocument3 pagesTID Part 2 Dr. Lu 2014 SalveMACATANGAY, GAELLE LISETTENo ratings yet
- Glomerulonephritis MindmapDocument1 pageGlomerulonephritis MindmapAlia AnasNo ratings yet
- Top Ten Family Practice DiagosesDocument6 pagesTop Ten Family Practice DiagosesKatrina HumphreyNo ratings yet
- Road To MEmMedDocument12 pagesRoad To MEmMedWinnie WongNo ratings yet
- Shock in Covid PatientDocument21 pagesShock in Covid PatientGHALEB A. AlmekhlafiNo ratings yet
- Blunt Abdominal Trauma Case ReviewDocument3 pagesBlunt Abdominal Trauma Case ReviewGio Tamaño BalisiNo ratings yet
- Table of Content: Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis 3Document5 pagesTable of Content: Post-Streptococcal Glomerulonephritis 3rup100% (1)
- Ampullary Carcinoma - Dr. Limchiaco, J.Document11 pagesAmpullary Carcinoma - Dr. Limchiaco, J.Neil Victor Ongco PajugotNo ratings yet
- Downloadfile 5Document51 pagesDownloadfile 5Faheem Ul HasanNo ratings yet
- Pulmonary Embolism Diagnosis and InterpretationDocument60 pagesPulmonary Embolism Diagnosis and InterpretationGordana PuzovicNo ratings yet
- Arteriovenous Malformation 1001Document19 pagesArteriovenous Malformation 1001housic1No ratings yet
- Physiomonitoring TransDocument4 pagesPhysiomonitoring TransAimie DagaleaNo ratings yet
- SPIDER WEB ACUTE RENAL FAILURE (ARF/AKIDocument3 pagesSPIDER WEB ACUTE RENAL FAILURE (ARF/AKITien KartiniNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities Adverse Effect Indication / Contraindication Mechanism of Action Drug Name IndicationDocument2 pagesNursing Responsibilities Adverse Effect Indication / Contraindication Mechanism of Action Drug Name IndicationOmar IzzoNo ratings yet
- ICU One Pager Flow Volume LoopsDocument1 pageICU One Pager Flow Volume LoopsRonald MoralesNo ratings yet
- Cremer 2016Document9 pagesCremer 2016Ronald MoralesNo ratings yet
- Hernia Diafragmatica 2019Document7 pagesHernia Diafragmatica 2019Ronald MoralesNo ratings yet
- VENT TROUBLESHOOTING: HIGH PEAK PRESSURESDocument1 pageVENT TROUBLESHOOTING: HIGH PEAK PRESSURESRonald MoralesNo ratings yet
- Nmda - RDocument8 pagesNmda - RRonald MoralesNo ratings yet
- Pain Anxiety Delirium: Rass CAM ICUDocument1 pagePain Anxiety Delirium: Rass CAM ICUNicholas HelmstetterNo ratings yet
- Estandarización Entrevista Apego en Chile para AdultosDocument9 pagesEstandarización Entrevista Apego en Chile para AdultosDaniel GSNo ratings yet
- Neonatal Hypoglycemia: A Review: Mahdi Alsaleem, MD, Lina Saadeh, MD, and Deepak Kamat, MD, PHD, FaapDocument6 pagesNeonatal Hypoglycemia: A Review: Mahdi Alsaleem, MD, Lina Saadeh, MD, and Deepak Kamat, MD, PHD, FaapRonald MoralesNo ratings yet
- Prediciendo SDR Usando Espectroscopía Del Residuo Gástrico - ClínicaDocument6 pagesPrediciendo SDR Usando Espectroscopía Del Residuo Gástrico - ClínicaRonald MoralesNo ratings yet
- Nejm - Eritropoyetina para Neuroprotección en PrematurosDocument11 pagesNejm - Eritropoyetina para Neuroprotección en PrematurosRonald MoralesNo ratings yet
- Efecto Del Surfatante Menos Invasivo Sobre La Oxigenación CerebralDocument9 pagesEfecto Del Surfatante Menos Invasivo Sobre La Oxigenación CerebralRonald MoralesNo ratings yet
- Acog PromDocument14 pagesAcog PromjjlazarteNo ratings yet
- Calidad de Los Probiítcos para PrematurosDocument4 pagesCalidad de Los Probiítcos para PrematurosRonald MoralesNo ratings yet
- QuantifiersDocument19 pagesQuantifiersThelma EstudilloNo ratings yet
- QuantifiersDocument19 pagesQuantifiersThelma EstudilloNo ratings yet
- Gui Ewb Unit01 Print and WorkDocument3 pagesGui Ewb Unit01 Print and WorkRonald MoralesNo ratings yet
- DC 40 S1 FinalDocument4 pagesDC 40 S1 FinalRonald MoralesNo ratings yet
- BW Mc2 XWHM y Na ManualDocument23 pagesBW Mc2 XWHM y Na ManualSatyasrinivas PulavarthiNo ratings yet
- SITE. Defining Project Goals & ObjectivesDocument1 pageSITE. Defining Project Goals & Objectivescoach balaNo ratings yet
- Physics Investigatory Project Class 12Document12 pagesPhysics Investigatory Project Class 12shivanginirai7No ratings yet
- Celecoxib Identification MethodsDocument5 pagesCelecoxib Identification Methodsabc1679No ratings yet
- PCOS Diet Cookbook For Newly Diagnosed IndividualsDocument67 pagesPCOS Diet Cookbook For Newly Diagnosed Individualsmavendave4lifeNo ratings yet
- Rational Choice TheoryDocument6 pagesRational Choice TheoryMaria Theresa HerbolingoNo ratings yet
- Starbucks BSC Project Analyzes Store PerformanceDocument8 pagesStarbucks BSC Project Analyzes Store Performanceandrea100% (1)
- Old Fashioned Southern Tea CakesDocument2 pagesOld Fashioned Southern Tea CakesDB ScottNo ratings yet
- STC Bec Wir Plu D 0209 01 PDFDocument10 pagesSTC Bec Wir Plu D 0209 01 PDFAdel MorsyNo ratings yet
- REMOTE Calculator Tool May 21 2013Document77 pagesREMOTE Calculator Tool May 21 2013Leyner Garcia MezquitaNo ratings yet
- Mill Housings Mangal SinghDocument5 pagesMill Housings Mangal SinghGun SmithNo ratings yet
- Fuente As-IDocument4 pagesFuente As-IadalaviNo ratings yet
- Fosfomycin: Review and Use Criteria BackgroundDocument12 pagesFosfomycin: Review and Use Criteria BackgroundAbu Azzam Al-Hadi100% (1)
- Gaggia Cadorna Milk Full Instruction ManualDocument76 pagesGaggia Cadorna Milk Full Instruction ManualKanen Coffee, LLC.No ratings yet
- Plane Bearings: Material Indicator Shape or SeriesDocument4 pagesPlane Bearings: Material Indicator Shape or SeriesJuan LoaizaNo ratings yet
- RV Failure: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument16 pagesRV Failure: Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and TreatmentRizky Regia TriseynesyaNo ratings yet
- SEN Code of Practice 2001Document148 pagesSEN Code of Practice 2001Matt GrantNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 3: Toxic Effects of Drugs: Pharmacology Page 1Document1 pageCHAPTER 3: Toxic Effects of Drugs: Pharmacology Page 1Gabriel GonzagaNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet Dump ValveDocument2 pagesData Sheet Dump ValveVlade NaumovskiNo ratings yet
- A 1116Document15 pagesA 1116Rama S. SinghNo ratings yet
- Torsion of Circular Shaft: Torque or Turning Moment or Twisting MomentDocument13 pagesTorsion of Circular Shaft: Torque or Turning Moment or Twisting Momentmahmudul adilNo ratings yet
- Trisyl Silica Gel: For Oils/Fats and Biofuel RefiningDocument4 pagesTrisyl Silica Gel: For Oils/Fats and Biofuel RefiningJosé Mauricio Bonilla TobónNo ratings yet
- BiostastisticDocument2 pagesBiostastisticاحمد ماجد زبنNo ratings yet
- Hydrostatic Testing ProcedureDocument21 pagesHydrostatic Testing ProcedureFerdie OSNo ratings yet
- Indian Medical Tourism Industry: A Pathway For The Healthy Future of IndiaDocument13 pagesIndian Medical Tourism Industry: A Pathway For The Healthy Future of IndiaPranjal MaluNo ratings yet
- Qualifications of Public Health NurseDocument2 pagesQualifications of Public Health Nursekaitlein_mdNo ratings yet
- Test A: Reading - Passage 1Document29 pagesTest A: Reading - Passage 1barishyayNo ratings yet
- Revised Provisional Selection List 30122022 1Document150 pagesRevised Provisional Selection List 30122022 1onlinetrash45No ratings yet
- Child Rearing Practices Articles India & ChinaDocument14 pagesChild Rearing Practices Articles India & ChinaGeorgiana GattinaNo ratings yet
- Smoke Stratification - Understanding the DynamicsDocument3 pagesSmoke Stratification - Understanding the DynamicsGagan UpadhyayNo ratings yet