Professional Documents
Culture Documents
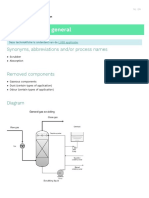
Reverse Osmosis Demineralization
Uploaded by
Mr. MeOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Reverse Osmosis Demineralization
Uploaded by
Mr. MeCopyright:
Available Formats
Home / Processes / Reverse Osmosis Demineralization
Reverse Osmosis Demineralization
Reverse Osmosis, commonly referred as RO, is a process where water is demineralised by flowing under pressure thro
membrane.
To understand the purpose and process of Reverse Osmosis it is necessary to first understand the phenomenon of
Osmosis is a naturally occurring phenomenon in which a weaker saline solution will tend to migrate to a strong saline s
The figure 1 illustrates the phenomenon of the Osmosis. A semi-permeable membrane is placed between 2 compartme
that the membrane is permeable to some species and not permeable to others. In this case, the membrane is permeab
permeable to dissolved ions and other contaminants.
In order to reach the equilibrium (same concentration of salts in both sides of the membrane, fundamental rule of natur
pure water compartment to the salt-containing compartment, to dilute the salt solution.
In Figure 1 you can also see a difference in height of solution on compartment of salt water and pure water. This height
of the column of water (salt solution) is so high that the force of this water column stops the water flow. The equilibrium
height in terms of water pressure against the membrane is called osmotic pressure.
Figure 1 – Phenomenon of Osmosis
Reverse Osmosis
If we consider that we want to produce pure water from the salt water, it is necessary to apply a “force” (pressure) in th
water, to force the water to flow in the reverse direction, making the water molecules to flow through the semi-permeab
compartment. This is the basis of the process called Reverse Osmosis (Figure 2).
The pressure applied has to overcome the osmotic pressure.
You might also like
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5794)
- Linking With The 4th Dimension - Chapter 12 - The Great White BrotherhoodDocument6 pagesLinking With The 4th Dimension - Chapter 12 - The Great White BrotherhoodMr. MeNo ratings yet
- Linking With The 4th Dimension - Chapter 9 - The Great White BrotherhoodDocument4 pagesLinking With The 4th Dimension - Chapter 9 - The Great White BrotherhoodMr. MeNo ratings yet
- Linking With The 4th Dimension - Chapter 13 - The Great White BrotherhoodDocument8 pagesLinking With The 4th Dimension - Chapter 13 - The Great White BrotherhoodMr. Me100% (1)
- Linking With The 4th Dimension - Chapter 2 - The Great White BrotherhoodDocument4 pagesLinking With The 4th Dimension - Chapter 2 - The Great White BrotherhoodMr. MeNo ratings yet
- Linking With The 4th Dimension - Chapter 3 - The Great White BrotherhoodDocument6 pagesLinking With The 4th Dimension - Chapter 3 - The Great White BrotherhoodMr. MeNo ratings yet
- Video Coding Format - WikipediaDocument10 pagesVideo Coding Format - WikipediaMr. MeNo ratings yet
- Gas Scrubbing - General - EMISDocument7 pagesGas Scrubbing - General - EMISMr. MeNo ratings yet
- Polity - WikipediaDocument2 pagesPolity - WikipediaMr. MeNo ratings yet
- Self-Defense (United States) - WikipediaDocument3 pagesSelf-Defense (United States) - WikipediaMr. MeNo ratings yet
- Banggood Floor SweeperDocument14 pagesBanggood Floor SweeperMr. MeNo ratings yet
- Brain RetrainingDocument3 pagesBrain RetrainingMr. Me100% (1)
- Polisens Blanketter 990-2 Skriv UtDocument3 pagesPolisens Blanketter 990-2 Skriv UtMr. MeNo ratings yet
- 9 Home Remedies To Get Rid of Dandruff NaturallyDocument9 pages9 Home Remedies To Get Rid of Dandruff NaturallyMr. MeNo ratings yet
- Iron-On Transfer Paper: DesignDocument1 pageIron-On Transfer Paper: DesignMr. MeNo ratings yet
- How To Use Iron On Transfer Paper The Ultimate Guide - Photo Paper Direct BlogDocument18 pagesHow To Use Iron On Transfer Paper The Ultimate Guide - Photo Paper Direct BlogMr. MeNo ratings yet
- Attorney-In-Fact DefinitionDocument21 pagesAttorney-In-Fact DefinitionMr. Me100% (1)
- 10 Common Mistakes When Using T Shirt Transfer Paper - Photo Paper Direct BlogDocument55 pages10 Common Mistakes When Using T Shirt Transfer Paper - Photo Paper Direct BlogMr. MeNo ratings yet
- List of Emotions: 54 Ways To Say What You're FeelingDocument9 pagesList of Emotions: 54 Ways To Say What You're FeelingMr. Me100% (2)
- Executive (Government) - WikipediaDocument3 pagesExecutive (Government) - WikipediaMr. MeNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)