Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DSP Objective Unit 3
DSP Objective Unit 3
Uploaded by
Akshay MalkhedeCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DSP Objective Unit 3
DSP Objective Unit 3
Uploaded by
Akshay MalkhedeCopyright:
Available Formats
NADAR SARSWATHI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, THENI.
Course/Branch : B.E/EEE Year / Semester :III/V Format NAC/TLP-
No. 07a.13
Subject Code :EE8591 Subject Name :Digital Signal Processing Rev. No. 02
Unit No :3 Unit Name :Discrete Fourier Transform Date 30/09/20
and Computation
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTION BANK
S. No. Objective Questions (MCQ /True or False / Fill up with Choices ) BTL
L1
1. Which of the following is true regarding the number of computations requires
to compute an N-point DFT?
a) N2 complex multiplications and N(N-1) complex additions
b) N2 complex additions and N(N-1) complex multiplications
c) N2 complex multiplications and N(N+1) complex additions
d) N2 complex additions and N(N+1) complex multiplications
L4
2. What is the DFT of the four point sequence x(n)={0,1,2,3}?
a) {6,-2+2j-2,-2-2j}
b) {6,-2-2j,2,-2+2j}
c) {6,-2+2j,-2,-2-2j}
d) {6,-2-2j,-2,-2+2j}
L2
100
3. If W4 =Wx200, then what is the value of x?
a) 2
b) 4
c) 8
d) 16
L1
4. If x(n) and X(k) are an N-point DFT pair, then x(n+N)=x(n).
a) True
b) False
5. If x(n) and X(k) are an N-point DFT pair, then X(k+N)=? L1
a) X(-k)
b) -X(k)
c) X(k)
d) None of the mentioned
L2
6. If x(n) is a real sequence and X(k) is its N-point DFT, then which of
thefollowing is true?
a) X(N-k)=X(-k)
Prepared By: B.SHANTHINI Page 1 of 7
NADAR SARSWATHI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, THENI.
Course/Branch : B.E/EEE Year / Semester :III/V Format NAC/TLP-
No. 07a.13
Subject Code :EE8591 Subject Name :Digital Signal Processing Rev. No. 02
Unit No :3 Unit Name :Discrete Fourier Transform Date 30/09/20
and Computation
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTION BANK
b) X(N-k)=X*(k)
c) X(-k)=X*(k)
d) All of the mentioned
L2
If x(n) is real and odd, then what is the IDFT of the given sequence?
7. a) j1N∑N−1k=0x(k)sin2πknN
b) 1N∑N−1k=0x(k)cos2πknN
c) −j1N∑N−1k=0x(k)sin2πknN
d) None of the mentioned
L2
8. If X(k) is the N-point DFT of a sequence x(n), then what is the DFT of x*(n)?
a) X(N-k)
b) X*(k)
c) X*(N-k)
d) None of the mentioned
L1
9. If X(k) is the N-point DFT of a sequence x(n), then circular time shift
property is that N-point DFT of x((n-l))N is X(k)e-j2πkl/N.
a) True
b) False
L3
By means of the DFT and IDFT, determine the response of the FIR filter
10. with impulse response h(n)={1,2,3} to the input sequence x(n)={1,2,2,1}?
a) {1,4,11,9,8,3}
b) {1,4,9,11,8,3}
c) {1,4,9,11,3,8}
d) {1,4,9,3,8,11}
L1
In Overlap save method of long sequence filtering, what is the length of the
11. input sequence block?
a) L+M+1
b) L+M
c) L+M-1
d) None of the mentioned
Prepared By: B.SHANTHINI Page 2 of 7
NADAR SARSWATHI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, THENI.
Course/Branch : B.E/EEE Year / Semester :III/V Format NAC/TLP-
No. 07a.13
Subject Code :EE8591 Subject Name :Digital Signal Processing Rev. No. 02
Unit No :3 Unit Name :Discrete Fourier Transform Date 30/09/20
and Computation
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTION BANK
L4
What is the sequence y(n) that results from the use of four point DFTs if the
12. impulse response is h(n)={1,2,3} and the input sequence x(n)={1,2,2,1}?
a) {9,9,7,11}
b) {1,4,9,11,8,3}
c) {7,9,7,11}
d) {9,7,9,11}
L2
If the signal to be analyzed is an analog signal, we would pass it through an
13. anti-aliasing filter with B as the bandwidth of the filtered signal and then the
signal is sampled at a rate __________
a) Fs ≤ 2B
b) Fs ≤ B
c) Fs ≥ 2B
d) Fs = 2B
L2
What is the highest frequency that is contained in the sampled signal?
14. a) 2Fs
b) Fs/2
c) Fs
d) None of the mentioned
L1
If {x(n)} is the signal to be analyzed, limiting the duration of the sequence to
15. L samples, in the interval 0≤ n≤ L-1, is equivalent to multiplying {x(n)} by?
a) Kaiser window
b) Hamming window
c) Hanning window
d) Rectangular window
L2
What is the Fourier transform of rectangular window of length L?
16. a) sin(ωL2)sin(ω2)ejω(L+1)/2
b) sin(ωL2)sin(ω2)ejω(L−1)/2
c) sin(ωL2)sin(ω2)e−jω(L−1)/2
d) None of the mentioned
Prepared By: B.SHANTHINI Page 3 of 7
NADAR SARSWATHI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, THENI.
Course/Branch : B.E/EEE Year / Semester :III/V Format NAC/TLP-
No. 07a.13
Subject Code :EE8591 Subject Name :Digital Signal Processing Rev. No. 02
Unit No :3 Unit Name :Discrete Fourier Transform Date 30/09/20
and Computation
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTION BANK
L1
Which of the following is the advantage of Hanning window over rectangular
17. window?
a) More side lobes
b) Less side lobes
c) More width of main lobe
d) None of the mentioned
L2
Which of the following is the disadvantage of Hanning window over rectangular
18. window?
a) More side lobes
b) Less side lobes
c) More width of main lobe
d) None of the mentioned
The condition with less number of samples L should be avoided.
19. a) True
b) False L1
L2
Which of the following is true regarding the number of computations required to
20. compute an N-point DFT?
a) N2 complex multiplications and N(N-1) complex additions
b) N2 complex additions and N(N-1) complex multiplications
c) N2 complex multiplications and N(N+1) complex additions
d) N2 complex additions and N(N+1) complex multiplications
WNk+N/2=?
21. a) WNk L2
b) -WNk
c) WN-k
d) None of the mentioned
L1
22. If we split the N point data sequence into two N/2 point data sequences f1(n) and
Prepared By: B.SHANTHINI Page 4 of 7
NADAR SARSWATHI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, THENI.
Course/Branch : B.E/EEE Year / Semester :III/V Format NAC/TLP-
No. 07a.13
Subject Code :EE8591 Subject Name :Digital Signal Processing Rev. No. 02
Unit No :3 Unit Name :Discrete Fourier Transform Date 30/09/20
and Computation
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTION BANK
f2(n) corresponding to the even numbered and odd numbered samples of x(n) and
F1(k) and F2(k) are the N/2 point DFTs of f1(k) and f2(k) respectively, then what
is the N/2 point DFT X(k) of x(n)?
a) F1(k)+F2(k)
b) F1(k)-WNk F2(k)
c) F1(k)+WNk F2(k)
d) None of the mentioned
L2
The total number of complex multiplications required to compute N point DFT
23. by radix-2 FFT is?
a) (N/2)log2N
b) Nlog2N
c) (N/2)logN
d) None of the mentioned
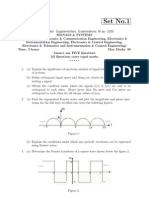
The following butterfly diagram is used in the computation of __________
24.
L4
a)Decimation-in-time FFT
b) Decimation-in-frequency FFT
c) All of the mentioned
d) None of the mentioned
Prepared By: B.SHANTHINI Page 5 of 7
NADAR SARSWATHI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, THENI.
Course/Branch : B.E/EEE Year / Semester :III/V Format NAC/TLP-
No. 07a.13
Subject Code :EE8591 Subject Name :Digital Signal Processing Rev. No. 02
Unit No :3 Unit Name :Discrete Fourier Transform Date 30/09/20
and Computation
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTION BANK
L1
25. How many complex multiplications are required to compute X(k)?
a) N(N+1)
b) N(N-1)/2
c) N2/2
d) N(N+1)/2
26. If x1(n) and x2(n) are two real valued sequences of length N, and let x(n) be a
complex valued sequence defined as x(n)=x1(n)+jx2(n), 0≤n≤N-1, then what is the L2
value of x1(n)?
a) x(n)−x∗(n)2
b) x(n)+x∗(n)2
c) x(n)−x∗(n)2j
d) x(n)+x∗(n)2j
27. The following butterfly diagram is used in the computation of __________
L4
a) Decimation-in-time FFT
b) Decimation-in-frequency FFT
Prepared By: B.SHANTHINI Page 6 of 7
NADAR SARSWATHI COLLEGE OF ENGINEERING AND TECHNOLOGY, THENI.
Course/Branch : B.E/EEE Year / Semester :III/V Format NAC/TLP-
No. 07a.13
Subject Code :EE8591 Subject Name :Digital Signal Processing Rev. No. 02
Unit No :3 Unit Name :Discrete Fourier Transform Date 30/09/20
and Computation
OBJECTIVE TYPE QUESTION BANK
c) All of the mentioned
d) None of the mentioned
L1
28. If X(k) is the DFT of x(n) which is defined as x(n)=x1(n)+jx2(n), 0≤ n≤ N-1, then
what is the DFT of x1(n)?
a) 12[X∗(k)+X∗(N−k)]
b) 12[X∗(k)−X∗(N−k)]
c) 12j[X∗(k)−X∗(N−k)]
d) 12j[X∗(k)+X∗(N−k)]
29. How many complex additions are required to be performed in linear filtering of a
sequence using FFT algorithm?
a) (N/2)logN
b) 2Nlog2N L2
c) (N/2)log2N
d) Nlog2N
L1
30. What is the total number of quantization errors in the computation of single point
DFT of a sequence of length N?
a) 2N
b) 4N
c) 8N
d) 12N
Prepared By: B.SHANTHINI Page 7 of 7
You might also like
- Leet NotesDocument75 pagesLeet Noteslance100% (1)
- Area 51Document23 pagesArea 51Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- A First Course in Aerial Robots and DronesDocument216 pagesA First Course in Aerial Robots and DronesMartijn Hinfelaar100% (1)
- MCQ For DSPDocument38 pagesMCQ For DSPAnonymous JnvCyu85100% (3)
- Dahua Platform SDK (DLL Version) Programming Manual PDFDocument136 pagesDahua Platform SDK (DLL Version) Programming Manual PDFArun SomanNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal ProcessingDocument101 pagesDigital Signal ProcessingDheekshith ShettigaraNo ratings yet
- Basic Digital Signal Processing: Butterworths Basic SeriesFrom EverandBasic Digital Signal Processing: Butterworths Basic SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- DSP Question Bank IV CSE - Cs - 2403docDocument36 pagesDSP Question Bank IV CSE - Cs - 2403docSiva NandanNo ratings yet
- Iso TS 28038-2018Document60 pagesIso TS 28038-2018TSUFANo ratings yet
- S.No. Partner Name Communication Address State CityDocument9 pagesS.No. Partner Name Communication Address State CityKumar Abhishek100% (1)
- ISO-CASCO - ISO-IEC 17043-2023., Conformity Assessment - General Requirements For Proficiency TestingDocument28 pagesISO-CASCO - ISO-IEC 17043-2023., Conformity Assessment - General Requirements For Proficiency Testingabdelhafid0% (1)
- DSP Objective Unit 2 EeeDocument7 pagesDSP Objective Unit 2 EeeSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Question - 1702ec503 Digital Signal ProcessingDocument18 pagesMultiple Choice Question - 1702ec503 Digital Signal ProcessingE20ECR068- SAMEERUDEEN.SNo ratings yet
- 9A04603 Digital Signal Processing16Document4 pages9A04603 Digital Signal Processing16Mahaboob SubahanNo ratings yet
- DSP Objective Unit 1 EeeDocument6 pagesDSP Objective Unit 1 EeeSathish KumarNo ratings yet
- 3Document2 pages3049 Narendran KNo ratings yet
- Ece V Digital Signal Processing (10ec52) SolutionDocument101 pagesEce V Digital Signal Processing (10ec52) SolutionVijay Sai100% (1)
- Ec 2302 - DSPDocument49 pagesEc 2302 - DSPShyam SundarNo ratings yet
- Btech Electrical 5 Sem Digital Signal Processing Pee5i103 2020Document2 pagesBtech Electrical 5 Sem Digital Signal Processing Pee5i103 2020mrout0333No ratings yet
- MCQ For DSP: December 2013Document39 pagesMCQ For DSP: December 2013Zainab FaydhNo ratings yet
- Objective questions-IAT-1Document6 pagesObjective questions-IAT-1SETNHILNo ratings yet
- DSP Objective Unit 4Document6 pagesDSP Objective Unit 4Akshay MalkhedeNo ratings yet
- DSP Objective Unit 4Document6 pagesDSP Objective Unit 4Akshay GiramNo ratings yet
- Ece Odd9Document17 pagesEce Odd9Venkat MuruganNo ratings yet
- DSP (5th) May2019 PDFDocument2 pagesDSP (5th) May2019 PDFs tharunNo ratings yet
- Dream Institute of Technology MCQ Test Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Digital Signal Processing (Ec-602)Document1 pageDream Institute of Technology MCQ Test Department of Electronics and Communication Engineering Digital Signal Processing (Ec-602)sangeeta senNo ratings yet
- R7311902 Digital Signal ProcessingDocument1 pageR7311902 Digital Signal ProcessingsivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- DSP Objective Type QuestionsDocument15 pagesDSP Objective Type QuestionsAdnan Zahid67% (3)
- r05320201 Digital Signal ProcessingDocument8 pagesr05320201 Digital Signal ProcessingSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- 9A04603 Digital Signal Processing23Document1 page9A04603 Digital Signal Processing23Mahaboob SubahanNo ratings yet
- DSP Question BankDocument18 pagesDSP Question BankName isNo ratings yet
- r05320201 Digital Signal ProcessingDocument8 pagesr05320201 Digital Signal ProcessingBharath LudiNo ratings yet
- DSP BitsDocument29 pagesDSP Bitskids montessoriNo ratings yet
- X (N) (1,2,1) H (N) (1, - 2,2)Document2 pagesX (N) (1,2,1) H (N) (1, - 2,2)mugaao8No ratings yet
- Questions On DSP - Basic SignalingDocument10 pagesQuestions On DSP - Basic Signalingkibrom atsbhaNo ratings yet
- X (N) (1,2,1) H (N) (1, - 2,2)Document2 pagesX (N) (1,2,1) H (N) (1, - 2,2)mugaao8No ratings yet
- Ec2314 DSP Nov 2010 QPDocument3 pagesEc2314 DSP Nov 2010 QPRama SubramanianNo ratings yet
- DSP Two MarksDocument33 pagesDSP Two MarksVijayendiran RhNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal ProcessingDocument4 pagesDigital Signal Processingsreenivasroyal8No ratings yet
- DSP-SP Viva ReferenceDocument41 pagesDSP-SP Viva Referenceneelansh88No ratings yet
- EC8553-Discrete Time Signal ProcessingDocument15 pagesEC8553-Discrete Time Signal ProcessingEXAMCELL - EBETiNo ratings yet
- DSP CT SolutionDocument15 pagesDSP CT SolutionSougata GhoshNo ratings yet
- DSP - Manual PartDocument8 pagesDSP - Manual PartShivani AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Course Material (Question Bamk)Document4 pagesCourse Material (Question Bamk)Guna PriyaNo ratings yet
- National Institute of Technology Silchar: Answer All QuestionsDocument1 pageNational Institute of Technology Silchar: Answer All QuestionsRituraj NathNo ratings yet
- FFT ModuleDocument22 pagesFFT ModuleRamya C.N.No ratings yet
- EC2314 DSP Nov 2010 PDFDocument3 pagesEC2314 DSP Nov 2010 PDFSyed MusthafaNo ratings yet
- Signals and Systems Model 1&2 FINAL22Document10 pagesSignals and Systems Model 1&2 FINAL22GiriNo ratings yet
- ECE 461/561-001: Communication Systems Design: R TT E T T E T E TDocument5 pagesECE 461/561-001: Communication Systems Design: R TT E T T E T E TZhenyu HuoNo ratings yet
- Ect303 Digital Signal Processing, December 2022Document3 pagesEct303 Digital Signal Processing, December 2022Dinil DhananjayanNo ratings yet
- Questions On DFT Efficient Computation - Fast Fourier Transform AlgorithmsDocument22 pagesQuestions On DFT Efficient Computation - Fast Fourier Transform Algorithmskibrom atsbha100% (1)
- Digital Signal Processing MCQDocument43 pagesDigital Signal Processing MCQmuhanad alkhalisyNo ratings yet
- Digital Signal Processing (DSP) - Jeppiar CollegeDocument22 pagesDigital Signal Processing (DSP) - Jeppiar CollegeKarthi KeyanNo ratings yet
- Department of Electrical Engineering Gcu Lahore: ExperimentDocument12 pagesDepartment of Electrical Engineering Gcu Lahore: ExperimentAhad AliNo ratings yet
- Lab Manaual 07: University of Engineering and Technology, TaxilaDocument13 pagesLab Manaual 07: University of Engineering and Technology, TaxilaMuhammad HassaanNo ratings yet
- Component - UART V2.50Document11 pagesComponent - UART V2.50ANNAPUREDDY RAVINDER REDDYNo ratings yet
- Lab4 DSPDocument18 pagesLab4 DSPHải ĐăngNo ratings yet
- T FFT: A A W F C U: HE N Lgorithm THE Hole Amily AN SEDocument33 pagesT FFT: A A W F C U: HE N Lgorithm THE Hole Amily AN SEYas HerabNo ratings yet
- Full4 PDFDocument20 pagesFull4 PDFthumatimadhusudhanNo ratings yet
- EC8553 2marksDocument20 pagesEC8553 2marksSNo ratings yet
- Question Paper Code:: Reg. No.Document2 pagesQuestion Paper Code:: Reg. No.Naveen KumarNo ratings yet
- EC2302 QB PDFDocument22 pagesEC2302 QB PDFokhtayaNo ratings yet
- Nr320402-Digital Signal ProcessingDocument8 pagesNr320402-Digital Signal ProcessingSRINIVASA RAO GANTANo ratings yet
- RR210402 Signals - SystemsDocument8 pagesRR210402 Signals - SystemsThanikonda Reddy SreedharNo ratings yet
- Green's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)From EverandGreen's Function Estimates for Lattice Schrödinger Operators and Applications. (AM-158)No ratings yet
- On the Tangent Space to the Space of Algebraic Cycles on a Smooth Algebraic Variety. (AM-157)From EverandOn the Tangent Space to the Space of Algebraic Cycles on a Smooth Algebraic Variety. (AM-157)No ratings yet
- Positive Material Identification by IRIS NDTDocument6 pagesPositive Material Identification by IRIS NDTPaulNo ratings yet
- Sta104 Try 2 - 230615 - 235749Document5 pagesSta104 Try 2 - 230615 - 235749Siti Hajar KhalidahNo ratings yet
- How Geographers Look at The World - HandoutDocument54 pagesHow Geographers Look at The World - Handoutdenny_sitorusNo ratings yet
- Forcepoint Web Security Admin CourseDocument200 pagesForcepoint Web Security Admin CourseAlok KumarNo ratings yet
- HardwareScanLog 20221201 120730Document1 pageHardwareScanLog 20221201 120730Rohan Kumar 2020No ratings yet
- Carbon Capture Project ANNUAL REPORT 2017Document21 pagesCarbon Capture Project ANNUAL REPORT 2017Liang Yann YUANNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Research Design and MethodDocument54 pagesQuantitative Research Design and MethodRonald LucasiaNo ratings yet
- How Does Cloud Computing Work?Document5 pagesHow Does Cloud Computing Work?Tanmay SardesaiNo ratings yet
- (IJCST-V9I2P9) :MD Faizan Zargar, Sakshi D Barshi, Dr. T. K. SivakumarDocument6 pages(IJCST-V9I2P9) :MD Faizan Zargar, Sakshi D Barshi, Dr. T. K. SivakumarEighthSenseGroupNo ratings yet
- Designandimplementationofan AVCgrindingcircuitat BHPBilliton CanningtonDocument7 pagesDesignandimplementationofan AVCgrindingcircuitat BHPBilliton CanningtonJosé Helí Vallejos CoronadoNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plans: Dr. Muhammad NafeesDocument11 pagesLesson Plans: Dr. Muhammad NafeesMah Rukh QadriNo ratings yet
- UNIT I-Part-2Document38 pagesUNIT I-Part-2Suyog JadhavNo ratings yet
- AirtelBroadbandBill Feb2022Document2 pagesAirtelBroadbandBill Feb2022Shivanshu GuptaNo ratings yet
- Curriculum Vitae: Mumbua Judith MutuaDocument3 pagesCurriculum Vitae: Mumbua Judith MutuaMumbua mutuaNo ratings yet
- Stock Market Briefing: S&P 500 Bull & Bear Market Tables: Yardeni Research, IncDocument6 pagesStock Market Briefing: S&P 500 Bull & Bear Market Tables: Yardeni Research, IncRenadNo ratings yet
- PLANOS STANDARD FRAME 7 - v1Document9 pagesPLANOS STANDARD FRAME 7 - v1Daniel NovarioNo ratings yet
- RMM 29 FINAL Compressed 51 120Document70 pagesRMM 29 FINAL Compressed 51 120syedshahabudeen100% (1)
- Dynamics of Microeconomics in The 21st CenturyDocument46 pagesDynamics of Microeconomics in The 21st CenturyNeel Gandhi89% (9)
- Organizational Behavior Assignment: Case Study-Managing A Global TeamDocument1 pageOrganizational Behavior Assignment: Case Study-Managing A Global TeamSimNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Laboratory ActivityDocument5 pagesChemistry Laboratory ActivityRowel AlfonsoNo ratings yet
- JWagner ResumeDocument2 pagesJWagner ResumeAnkur MidhaNo ratings yet
- Eduardo de Campos Valadares - Physics, Fun, and Beyond_ Electrifying Projects and InventionsDocument369 pagesEduardo de Campos Valadares - Physics, Fun, and Beyond_ Electrifying Projects and InventionsDorneles GerusoNo ratings yet