Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Control and Coordination
Uploaded by
varshavishuOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Control and Coordination
Uploaded by
varshavishuCopyright:
Available Formats
Control and Coordination
Introduction
Some basic terms:
Stimulus: An agent or a sudden change of the external and internal environment that results
in a change in the activities of organism.
Impulse: A wave of electric disturbances that travels across the nerve cell and its fibre.
Response: A change in the activity of the organism caused due to stimulus.
Receptors: The nerve cells which on receiving the stimulus, set up wave of impulses
towards the central nervous system (brain and spinal cord)
Effectors: Muscles or glands, which on receiving the impulse from the brain or spinal cord
contract or secrete substances.
Nerve: A bundle of axons (nerve fibres) of seperate neurons connecting the Central nervous
system with other parts of the body.
Sensory (afferent) nerve or the cell; Bringing the impulse from the receptor (sensory organ)
to the main nervous system.
Motor (efferent) nerve or the cell; Carrying the impulse from the main nervous system
towards a muscle or a gland.
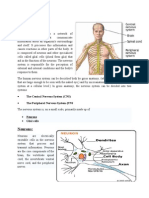
Coordination in animals
Neuron:
The basic structural and functional unit of nervous system. Neuron (nerve cell) is the longest
of human body (up to 100 cm)
Neuron is made up of
Cell body
Cell process (axon and dendron)
FEAT Educational Ventures Pvt. Ltd.
H.O. 83, Heera Panna Mall, Near Jal-Vayu Vihar, Hiranandani Garden, Powai, Mumbai - 76 1
Call: +91-22-3226-8201 | SMS: +91-842-482-1664 | www.edventure.in | info@edventure.in
Foundation – VIII Biology Control and Coordination
A nerve Cell or Neuron
Cell body: or Cyton or Soma or Perikaryon
It is broad, rounded, pyriform or stellate part of the neuron that contains a central nucleus,
abundant cytoplasm and various cell organelles except centrioles.
Because of the absence of centriole, neurons cannot divide. Injured neurons are either
replaced or repaired.
Cytoplasm of cell body is also called neuroplasm. Nucleus is large with a prominent
nucleolus. Special structures present in cell body of a neuron are small ribosome containing
Nissl granules and fine fibrils called neurofibrils.
Cell body maintains the neuron through its metabolic activity and growth.
Cell process:
Axon:
It is a long fibre-like cytoplasmic process that carries impulses away from the cell body.
Axon is branched terminally. The terminal branches are called telodendria or terminal
arborisations.
Axon terminals may end in muscle fibres, glands, other structures or form synapses with
dendrites of other neurons.
Axon terminals are often knob-like (synaptic knobs).
Axon is covered by one or two sheaths. The sheathed axon is called nerve fibre.
A number of nerve fibres are joined to form a nerve.
The cell membrane covering the axon is called axolemma.
Cytoplasm of axon is termed as axoplasm. It lacks Nissl granules. Neurofibrils are
present.
FEAT Educational Ventures Pvt. Ltd.
H.O. 83, Heera Panna Mall, Near Jal-Vayu Vihar, Hiranandani Garden, Powai, Mumbai - 76 2
Call: +91-22-3226-8201 | SMS: +91-842-482-1664 | www.edventure.in | info@edventure.in
Foundation – VIII Biology Control and Coordination
Dendron:
They are fine short and branched protoplasmic processes of the cell body that pick up
sensations (physical, mechanical, electrical, chemical) and transmit the same to the cell
body.
Dendrites contain Nissl granules and neurofibrils.
Types of Neurons:
The neurons are of three types:
Sensory (receptor) neurons:- Sensory organ to CNS
Motor (effector) neurons :- CNS to effector organ
Relaying (connector) neurons:- Joins sensory to motor neuron
Synapse:
The junction between two adjacent neurons i.e. betwen the axon ending of one neuron and
dendrites of the next.
Nerve impulse:
It is an electro-chemical information (signal) passing through neuron.
Neurotransmitters or Neurohormones:
Chemical substances which either transmit or inhibit the message from one neuron to
another.
For Example: Acetyl choline (Ach), GABA
Division of Human Nervous system
FEAT Educational Ventures Pvt. Ltd.
H.O. 83, Heera Panna Mall, Near Jal-Vayu Vihar, Hiranandani Garden, Powai, Mumbai - 76 3
Call: +91-22-3226-8201 | SMS: +91-842-482-1664 | www.edventure.in | info@edventure.in
Foundation – VIII Biology Control and Coordination
Brain
Brain is the most important part of human body.
Brain is situated in a cranial box (cranium) which is made up of bones.
Forebrain (Pros encephalon):
Cerebrum (Telencephalon):
It is highly developed in man and constitutes about 2/3rd of the brain.
It is divided into right and left halves. The two halves are separated by a deep median
groove.
Large bundles of nerves called corpus callosum connect both halves of the cerebrum.
The surface of the cerebrum shows many folds and grooves called gyri and sulci, which
increase the surface area to accommodate large number of nerve cells.
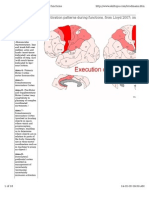
Each cerebral hemisphere is divided into 4 lobes-
Anterior: Frontal lobe for intelligence, knowledge, abstract, reasoning, creative ideas
and memory.
Middle: Parietal lobe for taste, writing, pain, touch and pressure.
Lateral: Temporal lobe for language, hearing and smell.
Posterior: Occipital lobe meant for vision.
Parts of the human brain
FEAT Educational Ventures Pvt. Ltd.
H.O. 83, Heera Panna Mall, Near Jal-Vayu Vihar, Hiranandani Garden, Powai, Mumbai - 76 4
Call: +91-22-3226-8201 | SMS: +91-842-482-1664 | www.edventure.in | info@edventure.in
Foundation – VIII Biology Control and Coordination
Diencephalon:
Thalamus: They receive all sensory impulse from all parts of the body and these impulses
are sending to the cerebral hemispheres.
Hypothalamus; There are centres of temperature control, pain, hunger and thirst.
Mid brain (Mesencephalon):
Cerebral peduncles (Crura cerebri): It controls the limb muscle movement.
Optic lobes (Corpora Quadrigemina): These mainly control vision.
Hind Brain (Rhombencephalon):
Pons or Pons Varolii: It regulates the breathing reaction.
Cerebellum: Function:
It is related with body balance & posture.
Medulla oblongata: Function:
It controls all the involuntary activities of the body. For Example: heartbeat, respiration.
It also concerned with some reflexes-sneezing reflex, coughing reflex, vomiting reflex,
and yawning reflex.
Cavities of brain (Ventricles):
Human brain is hollow. Hollow part of brain is called ventricle. In brain, 4 ventricles are
present. Ventricles are filled with a fluid called cerebrospinal fluid.
Spinal Cord:
It is a downward continuation of the medulla oblongata, which lies in the vertebral
column.
Function of spinal cord-
Spinal cord regulates and conducts the reflex action.
It acts as bridge between brain & organs of the body.
It also provides relay path for the impulses coming from brain.
Reflex Actions
“Marshal Hall” first observed the reflex actions. Reflex actions are spontaneous, automatic,
involuntary, mechanical responses produced by specific stimulating receptors. The path of
completion of reflex action is called “reflex arc”.
FEAT Educational Ventures Pvt. Ltd.
H.O. 83, Heera Panna Mall, Near Jal-Vayu Vihar, Hiranandani Garden, Powai, Mumbai - 76 5
Call: +91-22-3226-8201 | SMS: +91-842-482-1664 | www.edventure.in | info@edventure.in
Foundation – VIII Biology Control and Coordination
A typical reflex action has the following pathway
Reflex Arc
For Example:
Watering in mouth on sight of food
Closing of eyes when flashed with strong light.
Withdrawal of hand when pinched with a needle.
Blinking of eyelids, gut peristalsis, yawning, sneezing, and coughing.
Peripheral Nervous System:
All the nerves arising from brain and spinal cord are included in peripheral nervous system.
PNS consists of two sets of nerve:
Cranial Nerves:
Nerves arising from brain are called cranial nerves.
Nerves may be sensory, motor or mixed.
12 pairs of cranial nerves are found in reptiles, birds and mammals but amphibians
and fishes have only 10 pairs.
Spinal Nerves:
Nerves arising from spinal cord.
Each spinal nerve is mixed type and arises from the roots of the horns of grey matter
of the spinal cord.
In human only 31 pairs of spinal nerves are found.
FEAT Educational Ventures Pvt. Ltd.
H.O. 83, Heera Panna Mall, Near Jal-Vayu Vihar, Hiranandani Garden, Powai, Mumbai - 76 6
Call: +91-22-3226-8201 | SMS: +91-842-482-1664 | www.edventure.in | info@edventure.in
Foundation – VIII Biology Control and Coordination
Autonomic Nervous System (ANS)
The autonomic nervous system is that part of the peripheral nervous system which controls
activities inside the body that are normally involuntary.
ANS plays an important role in maintaining the constant environment. (Homeostasis)
There are the two divisions of the ANS:
Sympathetic Nervous System:
SNS is related with those visceral reactions, which increase the protection of body in
adverse atmospheric conditions.
Para sympathetic Nervous System:
PNS is related with those reactions in which energy is conversed.
In this way, ANS controls the activities of visceral organs double side i.e. antagonistic
to each other.
Cerebrospinal Fluid (C.S.F.):
This fluid is clear and alkaline in nature just like lymph.
C.S.F is present in ventricle of brain, subarachnoid space between arachnoid and piameter
and spinal cord.
It acts as shock absorbing medium.
Broca’s area: It is motor speech area, present in frontal lobe of cerebrum. If it gets destroyed
the animal becomes unable to speak.
In human brain more than 100 billion neurons are present.
In mammals the speed of nerve impulse is 100-130 m /sec.
The Sense of Hearing:
The Ears:
The ears have two types of receptors. They are phonoreceptor and statoresreceptor.
Phonoreceptor receive the auditory stimuli and have power to convert them into auditory
impulses. Statoresreceptor control postural changes and changes the orientation of the body
or balance. There are external ear, the middle ear and the internal ear.
The external ear:
The external ear consists of two parts: pinna and external auditory canal.
FEAT Educational Ventures Pvt. Ltd.
H.O. 83, Heera Panna Mall, Near Jal-Vayu Vihar, Hiranandani Garden, Powai, Mumbai - 76 7
Call: +91-22-3226-8201 | SMS: +91-842-482-1664 | www.edventure.in | info@edventure.in
Foundation – VIII Biology Control and Coordination
Pinna:
Pinna is funnel shaped and has ridges and grooves. Pinna is immovable and it is supported
by an elastic cartilage which has a funnel-shape aperture called concha
External auditory canal:
External auditory canal is an oblique and tubular canal which runs inward from the canal to
the ear drum. The inner wall is provided with ceruminous glands. Its produces ear wax which
protects the eardrum.
The middle ear:
The middle ear consists of an air filled cavity called tympanic cavity. Tympanic cavity
consists of 3 tiny bone called ear ossicles. They are incus, malleus and stapes. Malleus is a
hammer-shaped outer bone. The incus is an anvil-shaped middle bone. Stapes is an inner
bone and attached to the internal ear.
The internal ear:
The internal ear consists of the vestibule, semi-circular canal and cochlea. Vestibule is small
rounded chamber that forms the central part of internal ear. Semi-circular canals are three in
numbers and they are mutually perpendicular to each other. Cochlea is spirally coiled like
snail’s shell which receives the vibration of the sound.
Working mechanism of ears:
The external ear collects the sound waves and the sound waves passes into the auditory
tube. The sound waves then enter the middle ear and strike the eardrum, ear oscicles and
finally reach to cochlea. Sound waves set the fluid of cochlea in motion. The auditory cells
are activated. The stimulus or impulse is carried to the brain by the auditory nerves.
Care and protection of the ears:
We should not take out the earwax from ear normally. If it interferes the hearing, it should be
taken out safely.
We should not use sharp things like tooth pick, key etc. to prick the ears.
We should consult the doctor in case of pain, pus formation, bleeding etc. in ears.
FEAT Educational Ventures Pvt. Ltd.
H.O. 83, Heera Panna Mall, Near Jal-Vayu Vihar, Hiranandani Garden, Powai, Mumbai - 76 8
Call: +91-22-3226-8201 | SMS: +91-842-482-1664 | www.edventure.in | info@edventure.in
Foundation – VIII Biology Control and Coordination
Sense of Sight:
The Eye
The organs which make us aware about the surroundings are called sense organs. The
sense organs are eyes, skin, nose, ear and tongue. Sensation is received by sense organs
and is change into electrical signals called impulse. The impulse is carried to the brain by
nerves.
The sense of sight the eyes:
The eyes are the most important sense organs which give us the sensation of sight.
Eyebrows are hairy which protect the eyes from sweat, dust etc. Eyelids are movable, which
have eyelashes and blink at regular intervals. The eyes are provided with photoreceptor cell
which receive the visible light. The eyeball consists of 3 coats: outer, middle and inner coats.
Outer coat:
Outer coat provides mechanical protection and shape to the eyes. It is formed of 2 unequal
parts: sclera and cornea. The cornea is externally covered by a thin and transparent layer
called conjunctiva.
Middle coat:
The middle coat of the eye is formed of three parts. They are choroid, cilliary body and iris.
Choroid is thin, pigmented and dark brown in colour. Cilliary body is thick and circular
muscles helps in accommodation of the eye. Iris is the thin and muscular disc. The centre
part of iris is called pupil.
Inner coat:
The inner coat of the eyeball is retina where image is formed. The optical part is thick,
pigmented and provide with many layers of nerve fibres called photoreceptor cells. There are
two photoreceptor cells: rods and cones.
The sense organ of smell: the nose
The nasal cavity is divided into two nostrils by a vertical septum. The uppermost is covered
with epithelium which is connected to the nerve fibres of the cranial called olfactory nerve.
When a person suffers from cold, the epithelium is swollen and the particles of odorous
substances cannot reach the olfactory nerves and therefore, he/she does not get the sense
of smell.
Care and protection of nose
We should not have the habit of picking of nose.
We should cover the nose in polluted zones.
In case of infection in the nose, we should consult a doctor.
FEAT Educational Ventures Pvt. Ltd.
H.O. 83, Heera Panna Mall, Near Jal-Vayu Vihar, Hiranandani Garden, Powai, Mumbai - 76 9
Call: +91-22-3226-8201 | SMS: +91-842-482-1664 | www.edventure.in | info@edventure.in
Foundation – VIII Biology Control and Coordination
EXERCISE
Q.1 Objective question:
1. Nerves that carry impulses from the brain to the muscles is called _____ nerves.
(A) Efferent (B) Afferent (C) Mixed (D) Neurons
2. In nervous system communication takes place electrochemical messages called
(A) Neuroglia (B) Hormones (C) Neurons (D) Nerve Impulse
3. One pathway of nerve impulse transmission is called as:
(A) All the above (B) Synapse (C) Reflex action (D) Reflex are
4. Fluid that supports the brain and acts as shock absorber
(A) Cerebrospinal fluid (B) Lymphatic fluid
(C) Vitreous humour (D) None of these
5. The two types of sensitive cells in the retina are:
(A) Rods and cones (B) Neuroglia and neurons
(C) Both (A) and (B) (D) None of these
6. What is an axon?
(A) Long-fibre like cytoplasmic process that carries impulses away from the cell body
(B) Protoplasmic processes of cell body that pick-up sensations
(C) Junction between two adjacent neurons
(D) None of these
7. Cerebral hemisphere is divided into how many lobes
(A) 2 lobes (B) 4 lobes (C) 8 lobes (D) 5 lobes
8. Verticals in brain:
(A) Controls reflex action (B) Controls involuntary action
(C) Regulates breathing reaction (D) Are cavities of brain
9. Which is an example of reflex action?
(A) Watering in mouth on sight of food
(B) Closing of eyes when flashed with strong light
(C) Withdrawal of hand when pinched with a needle
(D) All of the above
10. Nervous system related with protection of body in adverse atmospheric conditions
(A) Sympathetic Nervous system (B) Par-sympathetic
(C) Both (A) & (B) (D) None of these
FEAT Educational Ventures Pvt. Ltd.
H.O. 83, Heera Panna Mall, Near Jal-Vayu Vihar, Hiranandani Garden, Powai, Mumbai - 76 10
Call: +91-22-3226-8201 | SMS: +91-842-482-1664 | www.edventure.in | info@edventure.in
Foundation – VIII Biology Control and Coordination
11. Broca’s area is the
(A) Nerves arising from spinal cord
(B) Nerves arising from brain
(C) Motor-speech area, present in frontal lobe of cerebrum
(D) None of these
12. Part of the eye responsible for image formation
(A) Outer coat (B) Middle coat (C) Inner coat (D) Central coat
13. Middle coat of eyes consist of
(A) Choroid (B) Ciliary body (C) Iris (D) All of the above
14. Which statement is correct?
(A) One should not read or write in dim light
(B) One should not eat vitamin-A-rich tools
(C) One should remove the eyelashes and eyebrows
(D) All of the above
15. Outermost covering of the body i.e. skin, is consist of
(A) Epidermis (B) Dermis (C) Subcutaneous (D) All of the above
Q.2 Subjective question: (1 marks)
1. The point from where optic nerve leaves the eye.
2. The ____ sits within the skill.
3. The transparent part in front of the eyeball is
4. The act of withdrawing the land on touching a hot object is termed as
5. Response done automatically without thinking
Q.3 Match the following: (1 marks)
1. Hunger - Dendron
2. Cyton - Internal stimulus
3. Body balance - 12 pairs
4. Cranial nerves - cerebellum
Q.4 Fill in the blanks: (1 marks)
1. The ________ controls the involuntarily function of the body.
2. The axon is covered by a fatty sheath called ________ which insulates and speeds
up impulses.
3. An ________ stimulus arises within the organism.
4. The part of neuron that carries messages to the muscle is ________.
FEAT Educational Ventures Pvt. Ltd.
H.O. 83, Heera Panna Mall, Near Jal-Vayu Vihar, Hiranandani Garden, Powai, Mumbai - 76 11
Call: +91-22-3226-8201 | SMS: +91-842-482-1664 | www.edventure.in | info@edventure.in
Foundation – VIII Biology Control and Coordination
5. The chamber which maintains the correct pressure and nourishes the
cornea is ________.
Q.5 Long answers: (5 marks)
1. Write a short note on neurons.
2. Explain in detail the different parts of forebrain.
3. What do you mean by Reflex action. Explain it with an example.
4. In brief explain spinal nerves
5. Explain the working mechanism of ear.
FEAT Educational Ventures Pvt. Ltd.
H.O. 83, Heera Panna Mall, Near Jal-Vayu Vihar, Hiranandani Garden, Powai, Mumbai - 76 12
Call: +91-22-3226-8201 | SMS: +91-842-482-1664 | www.edventure.in | info@edventure.in
Foundation – VIII Biology Control and Coordination
ANSWER KEY
Q.1 Objective question:
1. (A) 2. (D) 3. (C) 4. (A) 5. (A) 6. (A)
7. (B) 8. (D) 9. (D) 10. (A) 11. (C) 12. (C)
13. (D) 14. (A) 15. (D)
Q.2 Subjective question:
1. Blind spot
2. Brain
3. Cornea
4. Stimuli
5. Reflex action
Q.3 Match the following:
1. Hunger - Internal stimulus
2. Cyton - Dendrons
3. Body balance - Cerebellum
4. Cranial nerves - 12 pairs
Q.4 Fill in the blanks:
1. Medulla oblongata
2. Myelin sheath
3. Internal
4. Axon
5. Aqueous humour
FEAT Educational Ventures Pvt. Ltd.
H.O. 83, Heera Panna Mall, Near Jal-Vayu Vihar, Hiranandani Garden, Powai, Mumbai - 76 13
Call: +91-22-3226-8201 | SMS: +91-842-482-1664 | www.edventure.in | info@edventure.in
You might also like
- Nervou S System:: NeuronsDocument16 pagesNervou S System:: NeuronsFizzah100% (4)
- The Toxic BrainDocument30 pagesThe Toxic Brainmaxim ivanov67% (3)
- The Central Nervous SystemDocument7 pagesThe Central Nervous Systemjoeywap29No ratings yet
- The Nervous System: by Janelle Liane V. TabaldoDocument68 pagesThe Nervous System: by Janelle Liane V. Tabaldojanelle liane tabaldoNo ratings yet
- Medical Surgical Nursing PinoyDocument85 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing PinoyrosebaseNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Neurological SystemDocument38 pagesAnatomy and Physiology Chapter 19 Neurological SystemBrantNo ratings yet
- 3-17 Nervous HandoutDocument12 pages3-17 Nervous Handoutopthalmology 18No ratings yet
- Cerebellum and Brain Stem: DR Asim Shrestha SRCC Ped Neuro Fellow MumbaiDocument71 pagesCerebellum and Brain Stem: DR Asim Shrestha SRCC Ped Neuro Fellow MumbaiAsim ShresthaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Biological Foundations of BehaviorDocument50 pagesChapter 3 - Biological Foundations of BehaviorShermel Joy SolisNo ratings yet
- Human Physiology: The Nervous System ExplainedDocument29 pagesHuman Physiology: The Nervous System Explainedzandrex delunaNo ratings yet
- Neurochemistry of Music PDFDocument16 pagesNeurochemistry of Music PDFPedro BragançaNo ratings yet
- The Powers of The MindDocument20 pagesThe Powers of The MindGissele AbolucionNo ratings yet
- Reaching The Age of AdolescenceDocument17 pagesReaching The Age of AdolescencevarshavishuNo ratings yet
- Deeper Insights - Appendix 3. Clones, Synthetics, Organic Robotoids and DoublesDocument10 pagesDeeper Insights - Appendix 3. Clones, Synthetics, Organic Robotoids and DoublessabiontNo ratings yet
- Time and Mind: The Journal of Archaeology Consciousness and CultureDocument10 pagesTime and Mind: The Journal of Archaeology Consciousness and CultureBugFxNo ratings yet
- The Nervous SystemDocument110 pagesThe Nervous SystemZeren Joy C. AngelesNo ratings yet
- Evaluating Exam Review and Guide 2018 PDFDocument762 pagesEvaluating Exam Review and Guide 2018 PDFAthullia George83% (24)
- The Nervous System 1Document57 pagesThe Nervous System 1seno.kirzvhan.bmlsNo ratings yet
- Brodman MapDocument18 pagesBrodman MapBecky Edwards0% (1)
- Frontal Lobe SyndromeDocument67 pagesFrontal Lobe SyndromeVIJAYKUMAR HIREMATH100% (1)
- Nervous System Structure and FunctionDocument29 pagesNervous System Structure and Functionsiska yantiNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination ExplainedDocument11 pagesControl and Coordination ExplainedJit AggNo ratings yet
- Nervous System - Summary NotesDocument9 pagesNervous System - Summary NotesHarshNo ratings yet
- Weekly AssignmentDocument7 pagesWeekly AssignmentBajwa AyeshaNo ratings yet
- Science Sofie 10 3 RevDocument11 pagesScience Sofie 10 3 Revjinxtapperhat07No ratings yet
- General Biology II Crib Sheet (Mtes)Document3 pagesGeneral Biology II Crib Sheet (Mtes)JerseyNo ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument22 pagesNervous SystemAppyNo ratings yet
- Human Nervous SystemDocument4 pagesHuman Nervous SystemUmair BasheerNo ratings yet
- Lesson 4 Regulation of Life ProcessesDocument32 pagesLesson 4 Regulation of Life ProcessesJeestin Kent GabineraNo ratings yet
- Bio Module 1Document44 pagesBio Module 1bhongskirnNo ratings yet
- Hlgjdkrthe Nervous SystemDocument8 pagesHlgjdkrthe Nervous SystemBernardo Villavicencio VanNo ratings yet
- Chapter Seven-1Document22 pagesChapter Seven-1SULDAANUL CAASHIQIINNo ratings yet
- BIO 11: Coordination in the Human Nervous SystemDocument44 pagesBIO 11: Coordination in the Human Nervous SystemDyah AnggraeniNo ratings yet
- The BRAIN, NERVOUS SYSTEM AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEM (39Document13 pagesThe BRAIN, NERVOUS SYSTEM AND ENDOCRINE SYSTEM (39Mark Lorenzo A RuizNo ratings yet
- Nerve System and Sensing DeviceDocument16 pagesNerve System and Sensing DeviceFikrah Hafiz SuniNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination...Document8 pagesControl and Coordination...Shreyas PrashanthNo ratings yet
- Chapter 21 Neural Control and CoordinationDocument3 pagesChapter 21 Neural Control and CoordinationcritsdhruvNo ratings yet
- Midterm Reviewer Anaphy LectureDocument15 pagesMidterm Reviewer Anaphy LectureCarlito FantilaganNo ratings yet
- General Biology 2 Finals ExamDocument32 pagesGeneral Biology 2 Finals ExamJohn Lloyd BallaNo ratings yet
- Psicología The NeuronDocument10 pagesPsicología The NeuronDamianLauANo ratings yet
- Lecturer: Aam Amarullah, M.PD Biology and Health Program Center For Foundation Studies (CFS)Document67 pagesLecturer: Aam Amarullah, M.PD Biology and Health Program Center For Foundation Studies (CFS)Universal DiscoveringNo ratings yet
- Lesson 7 Part I Control and CoordinationDocument6 pagesLesson 7 Part I Control and CoordinationDragonAffire 1No ratings yet
- Rullida - EdullantesDocument36 pagesRullida - EdullantesJaleah Gwyneth Fernandez EdullantesNo ratings yet
- Neural Control and CoordinationDocument6 pagesNeural Control and CoordinationRonaldNo ratings yet
- Control and Coordination, PPT, Module-1.3Document22 pagesControl and Coordination, PPT, Module-1.3Khushi GuptaNo ratings yet
- SPM Science Notes - Body CoordinationDocument12 pagesSPM Science Notes - Body CoordinationSPM98% (50)
- Prepared by Dr. Saiful Quasar H#37, RD# 122, GULSHAN-1Document32 pagesPrepared by Dr. Saiful Quasar H#37, RD# 122, GULSHAN-1Coc DonoNo ratings yet
- Form 3 History BookDocument21 pagesForm 3 History BookDISHONNo ratings yet
- Biological Bases, AssignmentDocument6 pagesBiological Bases, AssignmentBenjii CarlosNo ratings yet
- Brain Anatomy and Physiology GuideDocument36 pagesBrain Anatomy and Physiology GuideJaleah Gwyneth Fernandez EdullantesNo ratings yet
- Unit 3 Biology For EngineersDocument16 pagesUnit 3 Biology For Engineers20me006No ratings yet
- Control Coordination (Prashant Kirad)Document16 pagesControl Coordination (Prashant Kirad)shrikantmisal17No ratings yet
- Control and Coordination CL XDocument7 pagesControl and Coordination CL XMukul BanoulaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy & Physiology NSDocument8 pagesAnatomy & Physiology NSIsha BhusalNo ratings yet
- BIOAA1BSP221E - Neutral Conduction - MendozaDocument6 pagesBIOAA1BSP221E - Neutral Conduction - MendozaCassandraNo ratings yet
- Conrtol and Coordination NotesDocument14 pagesConrtol and Coordination NotesShabad SinghNo ratings yet
- Nervous System (Student Version) PDFDocument65 pagesNervous System (Student Version) PDFAlex HigginsNo ratings yet
- 3.1 Nervous System NotesDocument8 pages3.1 Nervous System NotesabaybezawitNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4. The Nervous System - SADocument6 pagesChapter 4. The Nervous System - SAPalakNo ratings yet
- NERVOUS - SYSTEM (Auto-Saved)Document52 pagesNERVOUS - SYSTEM (Auto-Saved)nadeemyakubu47No ratings yet
- Nervous SystemDocument9 pagesNervous SystemMuhamad Hafiz Bin Mohd BakriNo ratings yet
- Zoology Notes: 017 Chapter 13Document3 pagesZoology Notes: 017 Chapter 13humanupgrade100% (1)
- Psychology AssignmentDocument5 pagesPsychology AssignmentAmrutha ChandranNo ratings yet
- (16-17) Brain SummaryDocument57 pages(16-17) Brain SummarybartNo ratings yet
- What Is The Nervous System?Document6 pagesWhat Is The Nervous System?Dee Olivar CamaongayNo ratings yet
- LP 1.2 in PhysioBio PsychologyDocument11 pagesLP 1.2 in PhysioBio PsychologyWayne GodioNo ratings yet
- Assigment About NeurologyDocument5 pagesAssigment About NeurologyYola NoviyanaNo ratings yet
- Neuron, Types of Neuron, Physiology of Nerve, Synapse, NeurogliaDocument24 pagesNeuron, Types of Neuron, Physiology of Nerve, Synapse, NeurogliavarshavishuNo ratings yet
- Sensory Organs: Pre-MedicalDocument19 pagesSensory Organs: Pre-MedicalvarshavishuNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands: Exercise-1Document25 pagesEndocrine Glands: Exercise-1varshavishuNo ratings yet
- 03 Nerv eDocument29 pages03 Nerv evarshavishuNo ratings yet
- Endocrine Glands: BiologyDocument29 pagesEndocrine Glands: BiologyvarshavishuNo ratings yet
- Exercise-1: Histor Y, Va R Iat Ion, Men D Eli SMDocument41 pagesExercise-1: Histor Y, Va R Iat Ion, Men D Eli SMvarshavishuNo ratings yet
- 2629-Article Text-4128-1-10-20130125Document7 pages2629-Article Text-4128-1-10-20130125varshavishuNo ratings yet
- 01 Gene 1Document12 pages01 Gene 1varshavishuNo ratings yet
- Pre-Medical Sex DeterminationDocument34 pagesPre-Medical Sex DeterminationvarshavishuNo ratings yet
- Curriculum VitaeDocument2 pagesCurriculum VitaevarshavishuNo ratings yet
- Human Reproduction Exercise: Pre-MedicalDocument31 pagesHuman Reproduction Exercise: Pre-MedicalvarshavishuNo ratings yet
- Eye & Ear Exercise: BiologyDocument11 pagesEye & Ear Exercise: BiologyvarshavishuNo ratings yet
- Cell and Cell Division Objective &subjective QuestionDocument2 pagesCell and Cell Division Objective &subjective QuestionvarshavishuNo ratings yet
- Session Summary: Bene Ciaries List Bene Ciaries ListDocument1 pageSession Summary: Bene Ciaries List Bene Ciaries ListvarshavishuNo ratings yet
- W N E S: Kitchen Toilet Kitchen Toilet Kitchen ToiletDocument1 pageW N E S: Kitchen Toilet Kitchen Toilet Kitchen ToiletvarshavishuNo ratings yet
- PDFDocument50 pagesPDFM Ali RazaNo ratings yet
- Take A PauseDocument1 pageTake A PausevarshavishuNo ratings yet
- Industrial Discharge Pollutes WaterDocument3 pagesIndustrial Discharge Pollutes WatervarshavishuNo ratings yet
- Transportation in PlantDocument11 pagesTransportation in PlantvarshavishuNo ratings yet
- 02-Plant Morphology (Exercise)Document5 pages02-Plant Morphology (Exercise)varshavishuNo ratings yet
- Edventure - Excretion in AnimalsDocument17 pagesEdventure - Excretion in AnimalsvarshavishuNo ratings yet
- 07-Pollution of Air & WaterDocument3 pages07-Pollution of Air & WatervarshavishuNo ratings yet
- Exercise # 2Document11 pagesExercise # 2varshavishuNo ratings yet
- Exercise # 1: Single Choice Type QuestionsDocument3 pagesExercise # 1: Single Choice Type QuestionsvarshavishuNo ratings yet
- Data Sheet FormatDocument1 pageData Sheet FormatvarshavishuNo ratings yet
- The Cell History Structure of Cell Cell Organelles: Unicellular OrganismsDocument7 pagesThe Cell History Structure of Cell Cell Organelles: Unicellular OrganismsvarshavishuNo ratings yet
- 5 Breathing and Exchange of Gases: SolutionsDocument24 pages5 Breathing and Exchange of Gases: SolutionsvarshavishuNo ratings yet
- 6.conservation of Plants and AnimalsDocument14 pages6.conservation of Plants and AnimalsvarshavishuNo ratings yet
- 5.1 Homeostasis QP - CompressedDocument53 pages5.1 Homeostasis QP - CompressedradhaNo ratings yet
- Physical Development of Infants and ToddlersDocument40 pagesPhysical Development of Infants and ToddlersIcah Mae D. Salo100% (1)
- Synaptic Electronics: Materials, Devices and Applications: NanotechnologyDocument23 pagesSynaptic Electronics: Materials, Devices and Applications: NanotechnologyManishaNo ratings yet
- Pages From (Ab) Normal Psychology 5th Ed. (Intro TXT) - S. Nolen-Hoeksema (McGraw-Hill, 2011) BBS CHAP 2Document73 pagesPages From (Ab) Normal Psychology 5th Ed. (Intro TXT) - S. Nolen-Hoeksema (McGraw-Hill, 2011) BBS CHAP 2Angel LacandulaNo ratings yet
- Meyer 2020Document12 pagesMeyer 2020Administrador OccimetricNo ratings yet
- AlzheimerDocument3 pagesAlzheimerandrewNo ratings yet
- CH - 7 Control and CoordinationDocument8 pagesCH - 7 Control and CoordinationHARSHIT JAINNo ratings yet
- Zimbardo Video: The Behaving Brain AssignmentDocument10 pagesZimbardo Video: The Behaving Brain AssignmentJayNo ratings yet
- Cerebrovascular Accident: TypesDocument10 pagesCerebrovascular Accident: TypesJulia SalvioNo ratings yet
- Depression and Suicide Are Natural Kinds - Implications FoDocument10 pagesDepression and Suicide Are Natural Kinds - Implications Fohector nuñezNo ratings yet
- What, How, When, Why?: "Shadowing"Document4 pagesWhat, How, When, Why?: "Shadowing"David PalomoNo ratings yet
- Galvan, Hare, Voss, Glover y Casey 2007 Risk Taking and The Adolescent Brain PDFDocument7 pagesGalvan, Hare, Voss, Glover y Casey 2007 Risk Taking and The Adolescent Brain PDFSamuel Salinas ÁlvarezNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Human IntelligenceDocument31 pagesThe Nature of Human IntelligenceGoran BogdanovićNo ratings yet
- Thesis Report On Brain Tumor DetectionDocument8 pagesThesis Report On Brain Tumor DetectionWhatShouldIWriteMyPaperAboutLittleRock100% (2)
- "I'm Listening!": Testing Attention and Learning in StudentsDocument10 pages"I'm Listening!": Testing Attention and Learning in Studentsapi-307225300No ratings yet
- The World as Clock: Experimental Ecologies in the Network SocietyDocument23 pagesThe World as Clock: Experimental Ecologies in the Network SocietyTheodoros ChiotisNo ratings yet
- 10th Lesson PlanDocument36 pages10th Lesson Plansowmyaraj7722No ratings yet
- S07-08-Lab Manual Sheep BrainDocument40 pagesS07-08-Lab Manual Sheep BrainRobert MartinNo ratings yet
- Breedlove 2020 - Chap 1 - Behavioral NeuroscienceDocument22 pagesBreedlove 2020 - Chap 1 - Behavioral NeuroscienceGilbertNo ratings yet
- Constructional Apraxia in PatientsDocument9 pagesConstructional Apraxia in Patientsharty86No ratings yet
- Assumptions Underlying Motor Control-HorakDocument17 pagesAssumptions Underlying Motor Control-HorakAngela campoNo ratings yet