Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Management of FPM On Chairside Based On Their Caries Risk and Caries Lesions and Activity
Uploaded by
Nur KamaliahOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Management of FPM On Chairside Based On Their Caries Risk and Caries Lesions and Activity
Uploaded by
Nur KamaliahCopyright:
Available Formats
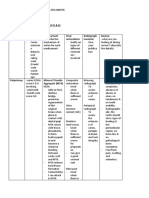
Management of FPM on chairside based on their caries risk and caries lesions and
activity
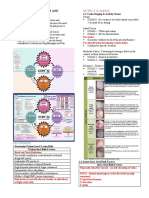
Caries Risk Management
Clinical approach:
- Place sealant in all pits & fissure of first permanent
molars as soon as tooth eruption (use GIC on
uncooperative patient & ensure fluoride varnish
application is optimal)
- Check integrity of sealant every visit
High - Top up worn out or damaged sealant
- If unable to put sealant, ensure fluoride varnish
application is optimal & attempt again as cooperation
improved
- Use GIC for partially erupted tooth
- Fissure seal pits of upper lateral permanent incisor,
occlusal & palatal surface of Ds, first & second
permanent molars.
Homecare approach:
- Brush twice daily
- Use toothpaste containing 1350-1500 ppm of fluoride
Review every 3-6 months
- Place sealant in all pits & fissure of first permanent
molars as soon as tooth eruption, ensure buccal &
palatal fissures are sealed. (use GIC on uncooperative
Low patient & ensure fluoride varnish application is
optimal)
- Check integrity of sealant every visit
- Top up worn out or damaged sealant
Homecare approach:
- Brush twice daily
- Use toothpaste containing 1000-1500 ppm of fluoride
Review every 6-12 months
Caries lesion & activity by tooth Management
surface
Extensive active caries lesion - Stepwise caries removal
- Temporise
- Restore with permanent restoration & seal
remaining fissures
Moderate active caries lesion - Total/selective caries removal
- Restore with permanent restoration & seal
remaining fissures
Initial active caries lesion - Fissure sealant
- Topical fluoride application
Extensive inactive caries lesion - Tooth preserving operative care if lesion is in
plaque stagnation area
Moderate inactive caries lesion - Tooth preserving operative care if lesion is in
plaque stagnation area
Initial inactive caries lesion - Fissure sealant
You might also like
- Lec 1 Operative (PART 3)Document14 pagesLec 1 Operative (PART 3)Mohamed NabilNo ratings yet
- Performance Test 1Document1 pagePerformance Test 1VNo ratings yet
- Iccms Caries Prevention and TreatmentDocument3 pagesIccms Caries Prevention and TreatmentJOHN HAROLD CABRADILLANo ratings yet
- 4 Pit and FissureDocument74 pages4 Pit and FissureAME DENTAL COLLEGE RAICHUR, KARNATAKANo ratings yet
- Adhesives Used in Complete DenturesDocument1 pageAdhesives Used in Complete Denturesezgi gülerNo ratings yet
- Laminates AND Veneers: Dr. Sakshi Rawal Department of Prosthodontics MDS II YearDocument76 pagesLaminates AND Veneers: Dr. Sakshi Rawal Department of Prosthodontics MDS II Yearsapna100% (2)
- Pit and Fissure SealantsDocument44 pagesPit and Fissure Sealantsmksweda10No ratings yet
- What Are The Main Ingredients in - . .: 2. Tooth PasteDocument3 pagesWhat Are The Main Ingredients in - . .: 2. Tooth Pastejhansikirani23No ratings yet
- Support, Replenish Protect The Stroke of A Brush: and WithDocument4 pagesSupport, Replenish Protect The Stroke of A Brush: and Withsmiledesigner_13No ratings yet
- All About AppliancesDocument15 pagesAll About AppliancesAlmekhlafiNo ratings yet
- Inelastic Impression MaterialsDocument58 pagesInelastic Impression Materialskashyap sawantNo ratings yet
- Streptococcus Mutans-In Enamel - Lactobacillus Acidophilus - in Dentin - Actinomyces Viscosus - in RootsDocument25 pagesStreptococcus Mutans-In Enamel - Lactobacillus Acidophilus - in Dentin - Actinomyces Viscosus - in Rootsalvarez.sofiadennieceNo ratings yet
- Sheet 11Document8 pagesSheet 11Hanin AbukhiaraNo ratings yet
- HapticsDocument11 pagesHapticsmehtakruti1021No ratings yet
- TIEDocument4 pagesTIEIrwandi MuslimNo ratings yet
- Preventive Orthodontics / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental AcademyDocument15 pagesPreventive Orthodontics / Orthodontic Courses by Indian Dental Academyindian dental academyNo ratings yet
- Labial Veneers - SummaryDocument51 pagesLabial Veneers - Summaryفاطمة الجش.No ratings yet
- Pulp Therapy - Tables BeatriceDocument7 pagesPulp Therapy - Tables BeatriceMikeNo ratings yet
- Ortho (Lec)Document2 pagesOrtho (Lec)Leigh BelmonteNo ratings yet
- Clinpro White VarnishDocument4 pagesClinpro White VarnishjaneNo ratings yet
- MKT 17 0612 Drcoleman Harmonize Ou EbookDocument7 pagesMKT 17 0612 Drcoleman Harmonize Ou EbookWirya PratamaNo ratings yet
- Pulpdent Embrace Varnish IfuDocument1 pagePulpdent Embrace Varnish IfuCercul CerculNo ratings yet
- Icdas ReportDocument2 pagesIcdas ReportNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Preventive Dental MaterialDocument69 pagesPreventive Dental Materialnadia yasmin100% (1)
- MIH SyndromDocument8 pagesMIH SyndromConttest TestcontNo ratings yet
- Pit Fissure Sealants PedoDocument11 pagesPit Fissure Sealants PedoFourthMolar.comNo ratings yet
- Fissure SealantsfinalDocument1 pageFissure SealantsfinalTracie YWNo ratings yet
- Nterior Estorations: Choose A Job You Love and You Will Never Have To Work A Day in Your LifeDocument20 pagesNterior Estorations: Choose A Job You Love and You Will Never Have To Work A Day in Your LifeABNo ratings yet
- Interim Fixed Restorations (Provisional Restoration) : IndicationsDocument5 pagesInterim Fixed Restorations (Provisional Restoration) : IndicationsGaleri Kreasi SepatukuNo ratings yet
- Molar Incisor Hypomineralisation (MIH) : Treatment SolutionsDocument8 pagesMolar Incisor Hypomineralisation (MIH) : Treatment Solutionscriksuu_795296388No ratings yet
- RETENTION Stability Support ProsthoDocument13 pagesRETENTION Stability Support ProsthoFourthMolar.com100% (1)
- Total Etch Vs Self Etch Adhesives PDFDocument3 pagesTotal Etch Vs Self Etch Adhesives PDFAfia IzzaNo ratings yet
- Chlorhexidine Mouthwash PDFDocument160 pagesChlorhexidine Mouthwash PDFDeepeka PrabhakarNo ratings yet
- University of The East College of Dentistry Orthodontics PDFDocument40 pagesUniversity of The East College of Dentistry Orthodontics PDFPatchNo ratings yet
- Final SplintDocument70 pagesFinal Splintbanupriyabds100% (2)
- مداواة الأسنان الترميمية 5Document50 pagesمداواة الأسنان الترميمية 5د. منالNo ratings yet
- Tooth Preparation For Bonded ExpanderDocument5 pagesTooth Preparation For Bonded ExpanderReliance Orthodontic ProductsNo ratings yet
- Conservative Esthetic Procedures: Part 2Document9 pagesConservative Esthetic Procedures: Part 2Dt omarNo ratings yet
- Advanced Treatments - Designed For Every Day.: 3M Clinpro 5000 3M Clinpro Tooth CrèmeDocument6 pagesAdvanced Treatments - Designed For Every Day.: 3M Clinpro 5000 3M Clinpro Tooth CrèmeFjNo ratings yet
- Pit and Fissure Sealing Is Defined As The Application and Mechanical Bonding of A Resin Material To An AcidDocument2 pagesPit and Fissure Sealing Is Defined As The Application and Mechanical Bonding of A Resin Material To An AcidSanchit RaoNo ratings yet
- Management-Of-Mutilated-Teeth - (1) (1) - 1Document57 pagesManagement-Of-Mutilated-Teeth - (1) (1) - 1Khushboo Gupta75% (4)
- Management-Of-Mutilated-Teeth - (1) (1) - 1Document57 pagesManagement-Of-Mutilated-Teeth - (1) (1) - 1Khushboo GuptaNo ratings yet
- Mouth Preparation - PDF 161301Document127 pagesMouth Preparation - PDF 161301S ل DentistNo ratings yet
- Occlusion in Fixed Prosthodontics PDFDocument37 pagesOcclusion in Fixed Prosthodontics PDFfloraNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Dental CariesDocument37 pagesPrevention of Dental CariesReda IsmaeelNo ratings yet
- Topical Fluorides...Document49 pagesTopical Fluorides...dr parveen bathlaNo ratings yet
- Management of AvulsedDocument7 pagesManagement of AvulsedDr.O.R.GANESAMURTHI100% (1)
- Pediatric Dentistry: Nathalya Bmay A. Subido, DMDDocument173 pagesPediatric Dentistry: Nathalya Bmay A. Subido, DMDMaryjoy Paladan100% (1)
- Clinical ConsiderationsDocument108 pagesClinical ConsiderationsPankaj JainNo ratings yet
- Periodontal Abscess and Periodontal DressingsDocument51 pagesPeriodontal Abscess and Periodontal DressingsHassan QadeerNo ratings yet
- Gange - Paul JR SR - Buckle Up! A Crash Course On Orthodontic BondingDocument15 pagesGange - Paul JR SR - Buckle Up! A Crash Course On Orthodontic BondingAya Ahmed Amin ShabanaNo ratings yet
- A School-Based Fissure Sealant ProgrammeDocument23 pagesA School-Based Fissure Sealant ProgrammeYeoh Wen LiNo ratings yet
- 8&9 Preventive Orthodontics&space MaintainerDocument20 pages8&9 Preventive Orthodontics&space MaintainershawetshaebanNo ratings yet
- Devitalizing Agents, Non-Vital Methods of Root Canal Therapy, Non-Vital Pulpotomy and Pulpectomy, Indications, Description of TechniquesDocument45 pagesDevitalizing Agents, Non-Vital Methods of Root Canal Therapy, Non-Vital Pulpotomy and Pulpectomy, Indications, Description of TechniquesGeorgeNo ratings yet
- Plaque Control: Under The Guidance ofDocument67 pagesPlaque Control: Under The Guidance ofAbdullah MohammadNo ratings yet
- Premature Loss of Deciduous DeentitionDocument45 pagesPremature Loss of Deciduous DeentitionayeshaNo ratings yet
- Department of Conservative & Operative DentistryDocument45 pagesDepartment of Conservative & Operative Dentistrynishtha_singhal_dr0% (1)
- Cement Bases and Cavity LinersDocument8 pagesCement Bases and Cavity Linersمحمد احمد محمدNo ratings yet
- Adhesive Dentistry: Materials & Techniques Simplified Dr. Jeff BruciaDocument14 pagesAdhesive Dentistry: Materials & Techniques Simplified Dr. Jeff Bruciasagarvidya1234567890100% (1)
- SDCEP Prevention and Management of Dental Caries in Children 2nd Edition PDFDocument158 pagesSDCEP Prevention and Management of Dental Caries in Children 2nd Edition PDFanna handayaniNo ratings yet
- Statement of Account: Student Transaction Transaction Reference Debit (RM) Credit (RM) Total (RM)Document2 pagesStatement of Account: Student Transaction Transaction Reference Debit (RM) Credit (RM) Total (RM)Nur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Seminar Y4Document2 pagesSeminar Y4Nur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Behavior Guidance For The Pediatric Dental Patient: Latest RevisionDocument14 pagesBehavior Guidance For The Pediatric Dental Patient: Latest RevisionEnrita DianNo ratings yet
- The Value of Third MolarDocument1 pageThe Value of Third MolarNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- SJ BDJ 2012 1040Document8 pagesSJ BDJ 2012 1040Nur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- G SDF PDFDocument10 pagesG SDF PDFDayana Vargas GarciaNo ratings yet
- Special Care Dentistry ReportDocument1 pageSpecial Care Dentistry ReportNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Seminar 21/10/2019 (Group D & E)Document4 pagesSeminar 21/10/2019 (Group D & E)Nur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Fibrous DysplasiaDocument3 pagesFibrous DysplasiaNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Icdas ReportDocument2 pagesIcdas ReportNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Icdas ReportDocument2 pagesIcdas ReportNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Fibrous DysplasiaDocument3 pagesFibrous DysplasiaNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Icdas ReportDocument2 pagesIcdas ReportNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Management of Luxation InjuriesDocument2 pagesManagement of Luxation InjuriesNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Deep Car: By: Group EDocument25 pagesDeep Car: By: Group ENur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Management of Adenoid Cystic CarcinomaDocument5 pagesManagement of Adenoid Cystic CarcinomaNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Treatment & Management of T4 HypersensitivityDocument1 pageTreatment & Management of T4 HypersensitivityNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Dental ImplantDocument2 pagesDental ImplantNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Fibrous DysplasiaDocument3 pagesFibrous DysplasiaNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Extension of BaseplateDocument1 pageExtension of BaseplateNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Management of Adenoid Cystic CarcinomaDocument5 pagesManagement of Adenoid Cystic CarcinomaNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Periodontal Abscess Gingival AbscessDocument2 pagesPeriodontal Abscess Gingival AbscessNur Kamaliah100% (1)
- Treatment & Management of T4 HypersensitivityDocument1 pageTreatment & Management of T4 HypersensitivityNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Inter 10 - Third ClassDocument96 pagesInter 10 - Third ClassRicardo Jackichan Barzola LopezNo ratings yet
- Leadership's Ramdom MCQsDocument48 pagesLeadership's Ramdom MCQsAhmed NoumanNo ratings yet
- CRC Ace Far 1ST PBDocument9 pagesCRC Ace Far 1ST PBJohn Philip Castro100% (1)
- Aviation EbookDocument36 pagesAviation Ebookmeroka2000No ratings yet
- Multiple Choice Questions: This Activity Contains 15 QuestionsDocument4 pagesMultiple Choice Questions: This Activity Contains 15 QuestionsRaman Kulkarni100% (1)
- W01-Introduction To Materials Modeling and SimulationDocument30 pagesW01-Introduction To Materials Modeling and SimulationMuco İboNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document7 pagesChapter 2Edita O PanuncioNo ratings yet
- Training SCLDocument60 pagesTraining SCLAlu menzikenNo ratings yet
- Survey-Questionnaire For The Study "Factors Affecting The Level of Comprehension in English of Grade 3 Students School Year 2021-2023"Document13 pagesSurvey-Questionnaire For The Study "Factors Affecting The Level of Comprehension in English of Grade 3 Students School Year 2021-2023"Rosalinda SamongNo ratings yet
- Seven Keys To Church GrowthDocument4 pagesSeven Keys To Church GrowthJob0% (1)
- NF en 12953-14Document14 pagesNF en 12953-14Prasanna UmapathyNo ratings yet
- Aims and Principles of Foreign Language TeachingDocument3 pagesAims and Principles of Foreign Language TeachingresearchparksNo ratings yet
- Wilkerson Case Study FinalDocument5 pagesWilkerson Case Study Finalmayer_oferNo ratings yet
- PNAPDocument79 pagesPNAPYu chung yinNo ratings yet
- II If en April2015 EquitycompoundersDocument8 pagesII If en April2015 EquitycompoundersbgyggghjkkNo ratings yet
- Kraft Foods Inc. in FranceDocument25 pagesKraft Foods Inc. in Francevishal211086No ratings yet
- Maintenance of Building ComponentsDocument4 pagesMaintenance of Building ComponentsIZIMBANo ratings yet
- OfficeServ 7200 Service Manual - Ed.0Document351 pagesOfficeServ 7200 Service Manual - Ed.0Richard WybornNo ratings yet
- Stats 2B03 Test #1 (Version 4) October 26th, 2009Document7 pagesStats 2B03 Test #1 (Version 4) October 26th, 2009examkillerNo ratings yet
- Caps Fet Physical Science WebbbbDocument170 pagesCaps Fet Physical Science WebbbbWonder Bee NzamaNo ratings yet
- Past:: Simple Indefinite Continuous Perfect Perfect ContinuousDocument12 pagesPast:: Simple Indefinite Continuous Perfect Perfect ContinuousAhmed Abd El HafeezNo ratings yet
- Type Italian Characters - Online Italian KeyboardDocument3 pagesType Italian Characters - Online Italian KeyboardGabriel PereiraNo ratings yet
- Pressure Transducer Davs 311-1-0 Volt - XCMG PartsDocument1 pagePressure Transducer Davs 311-1-0 Volt - XCMG Partsej ejazNo ratings yet
- h110m Pro VD Plus User GuideDocument19 pagesh110m Pro VD Plus User GuideIgobi LohnNo ratings yet
- PHY130 Lab Report 2Document7 pagesPHY130 Lab Report 2Declan Gale Anak DellyNo ratings yet
- Okuma CL302L Parts List & ManualDocument3 pagesOkuma CL302L Parts List & Manualcoolestkiwi100% (1)
- RCD PDFDocument6 pagesRCD PDFsanjay975No ratings yet
- Well Control - Pore PressureDocument31 pagesWell Control - Pore PressureMiguel Pinto PonceNo ratings yet
- Passive Voice PDFDocument5 pagesPassive Voice PDFJohan FloresNo ratings yet