Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Icdas Report
Uploaded by
Nur KamaliahCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Icdas Report
Uploaded by
Nur KamaliahCopyright:
Available Formats
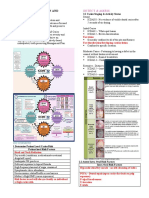
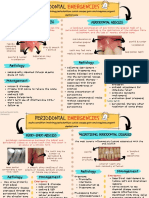
ICDAS REPORT
ICDAS FIRST DIGIT
ICDAS DEFINITION
0 Sound
1 Sealant, partial
2 Sealant, full
3 Tooth coloured restoration
4 Amalgam restoration
5 Stainless steel crown
6 Porcelain or gold or PFM crown or veneer
7 Lost or broken restoration
8 Temporary restoration
97 Tooth extracted because of caries
98 Tooth extracted for reasons other than
caries
99 Unerupted tooth
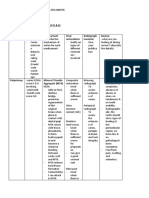
ICDAS SECOND DIGIT
ICDAS DEFINITION HOW TO DETECT MANAGEMENT
Sound tooth surface. No visible caries when viewed wet - Risk-based prevention.
0 or after prolonged air-drying
(5secs).
First visual changes in White or brown lesion can be seen - Oral Health Education
enamel. only after prolonged air-drying (tooth brushing, flossing,
1 (5secs). diet)
- Topical fluoride
application.
A Distinct visual changes in White or brown lesion can be seen - Oral Health Education
enamel. on wet or dry tooth surface. (tooth brushing, flossing,
2 diet)
- Topical fluoride
application.
Localised enamel Air-dry (5secs) and use WHO probe - Preventive resin
breakdown due to caries to gently run across the tooth restoration
3 with no visible dentin or surface to confirm presence of - Tooth preventing
underlying shadow. cavity apparently confined to operative care
enamel.
Underlying dark shadow Best viewed with the tooth surface - Tooth preventing
from dentin with or wet and look for grey/blue/brown operative care
4 without localised enamel shadow.
breakdown.
Distinct cavity with visible Cavitation in opaque or - Tooth preventing
dentin (less than half of discoloured enamel are exposing operative care.
5 tooth surface). the dentin beneath. Air-dry and
WHO probe can be used to gently
run across the tooth surface to
confirm presence of cavity
apparently in dentin. (The deep
pulpal dentin should not be
probed).
Extensive distinct cavity Obvious loss of tooth structure, the - Tooth preventing
with visible dentin (half of cavity is both deep and wide and operative care.
6 tooth surface or more). dentin is clearly visible on the walls
and at the base. An extensive
cavity involves at least half of a
tooth surface or possibly reaching
the pulp.
You might also like
- How to Heal Teeth Naturally & Cure Tooth Decay: The book on holistic dental care, healing cavities, toothaches, dental pains, oil pulling and more...From EverandHow to Heal Teeth Naturally & Cure Tooth Decay: The book on holistic dental care, healing cavities, toothaches, dental pains, oil pulling and more...Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (8)
- Oral Hygiene PharmacotherapyDocument3 pagesOral Hygiene PharmacotherapyMichelle Kristine DonnellyNo ratings yet
- Dental Caries Mini LectureDocument46 pagesDental Caries Mini LectureDestia UtamiNo ratings yet
- 2 - Tooth WearDocument11 pages2 - Tooth Wearحمزة تلاحمةNo ratings yet
- Iccms Caries Prevention and TreatmentDocument3 pagesIccms Caries Prevention and TreatmentJOHN HAROLD CABRADILLANo ratings yet
- Classification of Dental CariesDocument97 pagesClassification of Dental CariesAmna AliNo ratings yet
- VeneersDocument50 pagesVeneersDr FarhatNo ratings yet
- Universitatea de Vest "Vasile Goldiş" Din Arad: Facultatea de Medicina DentaraDocument3 pagesUniversitatea de Vest "Vasile Goldiş" Din Arad: Facultatea de Medicina DentaraP?TR�NJEI BOGDAN- ALEXANDRUNo ratings yet
- Preventive Dental MaterialDocument69 pagesPreventive Dental Materialnadia yasmin100% (1)
- Patho Lec 4THDocument3 pagesPatho Lec 4THJane Krystia TeodoroNo ratings yet
- DENTAL CONDITIONS AND TREATMENTDocument11 pagesDENTAL CONDITIONS AND TREATMENTfatimahNo ratings yet
- Dental CariesDocument43 pagesDental CariesMonojit Dutta100% (1)
- ICDAS (International Caries Detection and Assessment System) Dental CariesDocument4 pagesICDAS (International Caries Detection and Assessment System) Dental CariesJonnica BarrettoNo ratings yet
- All Resto NotesDocument27 pagesAll Resto NotesWinston ZarateNo ratings yet
- Cervical LesionsDocument135 pagesCervical Lesionsrasagna reddyNo ratings yet
- Dis ColorDocument13 pagesDis ColortarekrabiNo ratings yet
- Cariology-The Susceptible Tooth 9Document106 pagesCariology-The Susceptible Tooth 9Vincent De AsisNo ratings yet
- Cracked Tooth Syndrome: Presented by Syed - Khaja Ali Uddin M.SC.D (Endo)Document62 pagesCracked Tooth Syndrome: Presented by Syed - Khaja Ali Uddin M.SC.D (Endo)Ali Syed67% (3)
- Histopathology of Dental Caries (39Document39 pagesHistopathology of Dental Caries (39Diana SuhartiNo ratings yet
- Ortho (Lec)Document2 pagesOrtho (Lec)Leigh BelmonteNo ratings yet
- Assessing The Mouth and Oropharynx Performance:: Lips and Buccal MucosaDocument3 pagesAssessing The Mouth and Oropharynx Performance:: Lips and Buccal MucosaAbigail BrillantesNo ratings yet
- Preventive care for dental patientsDocument14 pagesPreventive care for dental patientsMohamed NabilNo ratings yet
- Dental Cavities Guide: Causes, Types & TreatmentDocument6 pagesDental Cavities Guide: Causes, Types & TreatmentJerryboy69No ratings yet
- Enamel Defects and Clinical ConsiderationsDocument51 pagesEnamel Defects and Clinical ConsiderationsBarnali Misra50% (6)
- Lecture 4 Pit and FissureDocument7 pagesLecture 4 Pit and FissureKhaled Al-haddadNo ratings yet
- Mouth Oropharynx Nose Sinuses AseronDocument51 pagesMouth Oropharynx Nose Sinuses AseronAllyssa Lorraine PrudencioNo ratings yet
- Pathology Notes - GI SystemDocument55 pagesPathology Notes - GI Systems21514.laiNo ratings yet
- Fissure SealantDocument2 pagesFissure SealantAlfonsius JeriNo ratings yet
- Deep Car: By: Group EDocument25 pagesDeep Car: By: Group ENur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Dental Veneers - Types, Procedure & BenefitsDocument14 pagesDental Veneers - Types, Procedure & BenefitsTerry BatoyogNo ratings yet
- Case Report (AESTHETIC REHABILITATION OF A PATIENT WITH DENTAL FLUOROSIS)Document3 pagesCase Report (AESTHETIC REHABILITATION OF A PATIENT WITH DENTAL FLUOROSIS)Maria JabbarNo ratings yet
- CURS 5 Teething Problems and Their ManagementDocument61 pagesCURS 5 Teething Problems and Their Managementtaliya. shvetzNo ratings yet
- Toolbox: Dental Damage, Sequelae, and PreventionDocument3 pagesToolbox: Dental Damage, Sequelae, and PreventionDea Intania DewiNo ratings yet
- Bhañjanaka: Clinical FeaturesDocument5 pagesBhañjanaka: Clinical FeaturesUdaya ShankarNo ratings yet
- اوبرتيف محاضرة الخامسةDocument47 pagesاوبرتيف محاضرة الخامسةdr.klawatNo ratings yet
- White SpotsDocument24 pagesWhite SpotsDonanguyenNo ratings yet
- Tooth Preparation For AmalgamDocument84 pagesTooth Preparation For AmalgamParidhi GargNo ratings yet
- Cariology-The Susceptible Tooth 9Document106 pagesCariology-The Susceptible Tooth 9Free PsPlusNo ratings yet
- Early Childhood Caries GuideDocument28 pagesEarly Childhood Caries GuideDrBhawna AroraNo ratings yet
- Sequelae of Traumatic Injuries To Primary Teeth PedoDocument32 pagesSequelae of Traumatic Injuries To Primary Teeth PedoFourthMolar.com100% (3)
- Epidemiology 6Document6 pagesEpidemiology 6Batool HusseinNo ratings yet
- Clinical ConsiderationsDocument108 pagesClinical ConsiderationsPankaj JainNo ratings yet
- vital pulp therapy الشرقاويDocument3 pagesvital pulp therapy الشرقاويahmed muhammadNo ratings yet
- Ageing Changes in Teeth and PeriodontiumDocument45 pagesAgeing Changes in Teeth and Periodontiumanmol43% (7)
- Dental CariesDocument120 pagesDental CariesSomya Jain100% (5)
- Fissured TongueDocument0 pagesFissured Tonguepink_grcq_sssttt4836No ratings yet
- Seong 2017Document6 pagesSeong 2017VICTOR FERNANDO LAMAS LARANo ratings yet
- Dental Caries First SessionDocument28 pagesDental Caries First SessionKiana TediNo ratings yet
- Icdas Ii PDFDocument30 pagesIcdas Ii PDFFarah ShazwanaNo ratings yet
- Pulp Therapy in ChildrenDocument4 pagesPulp Therapy in ChildrenshahinshamshiriNo ratings yet
- Icdas-Aquino, Madelyn Dolor h.Document6 pagesIcdas-Aquino, Madelyn Dolor h.050765No ratings yet
- Lec 4 Operative (PART 1)Document14 pagesLec 4 Operative (PART 1)Ahmed YousryNo ratings yet
- Oral CareDocument3 pagesOral CareLucy CenizaNo ratings yet
- Dental Caries SitesDocument3 pagesDental Caries SitesFoysal SirazeeNo ratings yet
- Dental Veneer Guide: Everything You Need to KnowDocument48 pagesDental Veneer Guide: Everything You Need to KnowAli IhsanNo ratings yet
- 8&9 Preventive Orthodontics&space MaintainerDocument20 pages8&9 Preventive Orthodontics&space MaintainershawetshaebanNo ratings yet
- Dentin HypersensitivityDocument44 pagesDentin HypersensitivityAME DENTAL COLLEGE RAICHUR, KARNATAKANo ratings yet
- Managing Severely Worn Teeth Through Prosthodontic TreatmentDocument5 pagesManaging Severely Worn Teeth Through Prosthodontic TreatmentMaria Camila Tejada FigueroaNo ratings yet
- SDCEP Prevention and Management of Dental Caries in Children 2nd Edition PDFDocument158 pagesSDCEP Prevention and Management of Dental Caries in Children 2nd Edition PDFanna handayaniNo ratings yet
- Student Account StatementDocument2 pagesStudent Account StatementNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Seminar Y4Document2 pagesSeminar Y4Nur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Behavior Guidance For The Pediatric Dental Patient: Latest RevisionDocument14 pagesBehavior Guidance For The Pediatric Dental Patient: Latest RevisionEnrita DianNo ratings yet
- The Value of Third MolarDocument1 pageThe Value of Third MolarNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- SJ BDJ 2012 1040Document8 pagesSJ BDJ 2012 1040Nur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- G SDF PDFDocument10 pagesG SDF PDFDayana Vargas GarciaNo ratings yet
- Special Care Dentistry ReportDocument1 pageSpecial Care Dentistry ReportNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Seminar 21/10/2019 (Group D & E)Document4 pagesSeminar 21/10/2019 (Group D & E)Nur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Icdas ReportDocument2 pagesIcdas ReportNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Fibrous DysplasiaDocument3 pagesFibrous DysplasiaNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Management of caries risk and lesions for FPM chairsideDocument2 pagesManagement of caries risk and lesions for FPM chairsideNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Fibrous DysplasiaDocument3 pagesFibrous DysplasiaNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Management of Luxation InjuriesDocument2 pagesManagement of Luxation InjuriesNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Deep Car: By: Group EDocument25 pagesDeep Car: By: Group ENur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Icdas ReportDocument2 pagesIcdas ReportNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Management of Adenoid Cystic CarcinomaDocument5 pagesManagement of Adenoid Cystic CarcinomaNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Treatment & Management of T4 HypersensitivityDocument1 pageTreatment & Management of T4 HypersensitivityNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Dental ImplantDocument2 pagesDental ImplantNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Fibrous DysplasiaDocument3 pagesFibrous DysplasiaNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Extension of BaseplateDocument1 pageExtension of BaseplateNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Management of Adenoid Cystic CarcinomaDocument5 pagesManagement of Adenoid Cystic CarcinomaNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Dental Emergencies GuideDocument2 pagesDental Emergencies GuideNur Kamaliah100% (1)
- Treatment & Management of T4 HypersensitivityDocument1 pageTreatment & Management of T4 HypersensitivityNur KamaliahNo ratings yet
- Cover Letter 6Document2 pagesCover Letter 6api-553076081No ratings yet
- Nfluence of Several Fibre-Reinforced Composite Restoration Techniques On Cusp Movement and Fracture Strength of Molar TeethDocument9 pagesNfluence of Several Fibre-Reinforced Composite Restoration Techniques On Cusp Movement and Fracture Strength of Molar TeethEugenioNo ratings yet
- Child Management in Clinical Dentistry - Jaypee Brothers 1 Edition (February 28, 2010)Document142 pagesChild Management in Clinical Dentistry - Jaypee Brothers 1 Edition (February 28, 2010)Rafaela SoareNo ratings yet
- Anatomi Saluran Akar: KG 1.1 Anatomi Internal Dan Histofisiologi Pulpa Dan PeriapeksDocument26 pagesAnatomi Saluran Akar: KG 1.1 Anatomi Internal Dan Histofisiologi Pulpa Dan PeriapeksAnastasia PinkyNo ratings yet
- Minor Connectors and Direct Retainer CompleteDocument57 pagesMinor Connectors and Direct Retainer CompleteHiba ShahNo ratings yet
- MARKETING AssignmentDocument26 pagesMARKETING AssignmentNaveen BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Molar Uprighting - Literature ReviewDocument12 pagesOrthodontic Molar Uprighting - Literature ReviewYaser JasNo ratings yet
- Anterior Teeth Selection and Its ArrangementDocument48 pagesAnterior Teeth Selection and Its ArrangementAnonymous NFiQTb1No ratings yet
- Ortho Biomechanics PrinciplesDocument49 pagesOrtho Biomechanics Principleskailash gorchhiaNo ratings yet
- Public Health Approach to Oral Health DiseaseDocument94 pagesPublic Health Approach to Oral Health DiseaseZerida ZainalNo ratings yet
- Cysts of The Oral RegionDocument14 pagesCysts of The Oral RegionJASTHER LLOYD TOMANENGNo ratings yet
- Gingival Phenotype and Its Relationship With Different Clinical Parameters: A Study in A Dominican Adult SampleDocument7 pagesGingival Phenotype and Its Relationship With Different Clinical Parameters: A Study in A Dominican Adult SampleHarish ShahNo ratings yet
- Registration and renewal criteria for dentists in TelanganaDocument3 pagesRegistration and renewal criteria for dentists in Telanganasatish satzNo ratings yet
- Dental Terminology Lecture Notes Week 3 Prosthodontics and EndodonticsDocument24 pagesDental Terminology Lecture Notes Week 3 Prosthodontics and EndodonticsCatherine AmandaNo ratings yet
- Orthodontic Treatment For Posterior Crossbites (Review) : Harrison JE, Ashby DDocument21 pagesOrthodontic Treatment For Posterior Crossbites (Review) : Harrison JE, Ashby DYuly DurangoNo ratings yet
- Management of Deep Caries 1st PartDocument45 pagesManagement of Deep Caries 1st PartLames Ali Sayed Ahmed AttiaNo ratings yet
- Odontogenic Cysts (Compiled Lecture Videos) - BlankDocument47 pagesOdontogenic Cysts (Compiled Lecture Videos) - BlankDeangelo DavisNo ratings yet
- Bite Force Analysis in Different Types of Angle MalocclusionsDocument12 pagesBite Force Analysis in Different Types of Angle Malocclusionsد.عاصم صويلحNo ratings yet
- Clear Aligners Generations and Orthodontic Tooth Movement: Journal of OrthodonticsDocument10 pagesClear Aligners Generations and Orthodontic Tooth Movement: Journal of OrthodonticsTanushree JainNo ratings yet
- Centric Relation Concepts and ControversiesDocument51 pagesCentric Relation Concepts and ControversiesRohan Grover100% (11)
- Building A Pleasant PersonalityDocument1 pageBuilding A Pleasant PersonalityClarize18 AvendanoNo ratings yet
- Minimal Invasive Techniques in Porcelain Laminate Veneers: Case SeriesDocument4 pagesMinimal Invasive Techniques in Porcelain Laminate Veneers: Case Seriesfanny rizky andriyaniNo ratings yet
- 1 SM PDFDocument3 pages1 SM PDFNurul NoviasariNo ratings yet
- Coronectomy - Assessment and TreatmentDocument4 pagesCoronectomy - Assessment and TreatmentNaventhan ChanthirasekarNo ratings yet
- Frequency of Odontogenic Cysts and Tumors ADocument6 pagesFrequency of Odontogenic Cysts and Tumors AThành Luân NguyễnNo ratings yet
- The Success of Endodontic Therapy Healing and Functionality Friedman PDFDocument11 pagesThe Success of Endodontic Therapy Healing and Functionality Friedman PDFizeldien5870No ratings yet
- 10 Tips and Tricks With Clear AlignersDocument19 pages10 Tips and Tricks With Clear AlignersDaraí Bárbara Sánchez MonteroNo ratings yet
- Effect of Serial Extraction Alone On Crowding...Document6 pagesEffect of Serial Extraction Alone On Crowding...Julio TorresNo ratings yet
- TRANSFER INSTRUMENT FHD PDFDocument12 pagesTRANSFER INSTRUMENT FHD PDFRadikaNo ratings yet
- PD CAT2019 CatalogueProduits E 191119 TempDocument98 pagesPD CAT2019 CatalogueProduits E 191119 TempchimedbatorNo ratings yet