Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Handbook - Weld Defects 1
Uploaded by
Danilova SonjaCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Handbook - Weld Defects 1
Uploaded by
Danilova SonjaCopyright:
Available Formats
8/13/13 Handbook - Weld Defects
Variations-
Metal
Transfer
Equipment
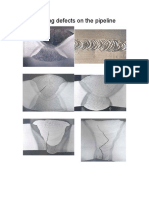
LONGITUDINAL CRACKING
Longitudinal or centerline cracking, of the weld bead is not often encountered in mig welding. However, that
Power which does occur can be one of two types: hot cracks and cold cracks. Typical hot cracks are shown in
Supply Figure 10-5. Hot cracks are those that occur while the weld bead is between the liquidus (melting) and
solidus (solidifying) temperatures. In this temperature range the weld bead is ”mushy”. Hot cracks usually
result from the use of an incorrect wire electrode (particularly in aluminum and stainless steel alloys). The
Shielding chemistry of the base plate can also promote this defect (an example would be any high carbon stainless
Gases
steel casting). Any combination of the joint design, welding conditions and welding techniques that results in
a weld bead with an excessively concave surface can promote cracking.
Wire
One form of this defect which may often be encountered, particularly with any 5000 series aluminum, is
Electrodes
called a crater crack. These are small cracks which appear at the end of the weld where the arc has been
broken. Although small, these cracks are troublesome since they can propagate into the weld bead. A crater
crack is shown in Figure 10-6. The major reason for this defect is the incorrect technique for ending the
Safety
weld. To properly end a weld, the crater should be filled. This is done by reversing the arc travel direction
before breaking the arc. This technique is depicted in Figure 10-7. In addition, if the welding control is
designed to supply gas for a short time after the arc is broken, the crater should be shielded until it is
Welding
completely solidified.
Techniques
Figure 10-6 - Example of Crater Cracking
Welding
Conditions
Introduction
Economics
Incomplete
Penetration
Lack of
Weld Fusion
Defects Undercutting
Figure 10-5 - Example of Longitudinal
Porosity Cracking
Mig Spot
Welding Longitudinal
Cracking
9
Tables
www.esabna.com/EUWeb/MIG_handbook/592mig10_9.htm 1/1
You might also like
- Weld Quality Inspection and DefectsDocument9 pagesWeld Quality Inspection and DefectsNIDHOM IQBAL RAMADHANNo ratings yet
- Weld Defects Handbook - Lack of FusionDocument1 pageWeld Defects Handbook - Lack of FusionDanilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- When A Refractory Failure Isn't - Some Anchor IssuesDocument8 pagesWhen A Refractory Failure Isn't - Some Anchor IssuesBerkan FidanNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld DefectsDocument1 pageHandbook - Weld Defectskaveh-bahiraeeNo ratings yet
- Welding Defect: Major CausesDocument9 pagesWelding Defect: Major CausesCarlos BustamanteNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld Defects 05Document1 pageHandbook - Weld Defects 05Danilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- 10 Welding Defects & RemediesDocument12 pages10 Welding Defects & RemediesvilukNo ratings yet
- Welding Defects and Remedies: Lack of Fusion Incomplete Penetration Undercutting Porosity Longitudinal CrackingDocument9 pagesWelding Defects and Remedies: Lack of Fusion Incomplete Penetration Undercutting Porosity Longitudinal Crackinglakshmigsr6610No ratings yet
- Visual 001Document11 pagesVisual 001kattabommanNo ratings yet
- Welds CracksDocument8 pagesWelds Cracksaltaf94No ratings yet
- 03 Welding Imperfections 29-11-03Document17 pages03 Welding Imperfections 29-11-03bizhanjNo ratings yet
- Welding DefectsDocument38 pagesWelding DefectsvvpvarunNo ratings yet
- Welding Defect: Hydrogen EmbrittlementDocument8 pagesWelding Defect: Hydrogen EmbrittlementShajin Mohammed ShamsudhinNo ratings yet
- Weld Failures A CompendiaryDocument3 pagesWeld Failures A CompendiaryTC Capulcu Mustafa MNo ratings yet
- Weld DefectsDocument45 pagesWeld Defectsanon_256154377No ratings yet
- Defects - Solidification Cracking - TWIDocument8 pagesDefects - Solidification Cracking - TWIJlkKumarNo ratings yet
- Welding Defects - 5Document61 pagesWelding Defects - 5me0906840087No ratings yet
- Weld Defect - WikeepidiaDocument5 pagesWeld Defect - Wikeepidiapuri16No ratings yet
- Pipeline Inspector 1667834732Document57 pagesPipeline Inspector 1667834732Dhani de EngineurNo ratings yet
- Lamellar TearingDocument6 pagesLamellar TearingAndreaNo ratings yet
- Weld Defects or Imperfections in Welds - Lack of Sidewall and Inter-Run FusionDocument4 pagesWeld Defects or Imperfections in Welds - Lack of Sidewall and Inter-Run FusionmanimaranNo ratings yet
- Welding Defects Part 4Document56 pagesWelding Defects Part 4Nanang Cesc UttaNo ratings yet
- Identifying Casting DefectsDocument4 pagesIdentifying Casting Defectsdarwin_huaNo ratings yet
- Welding Failure Causes and PreventionDocument5 pagesWelding Failure Causes and Preventionmangalraj900No ratings yet
- 03 Welding Imperfections 30-03-07 (2Document20 pages03 Welding Imperfections 30-03-07 (2geokovoorNo ratings yet
- Welding Defects Causes & SolutionsDocument30 pagesWelding Defects Causes & SolutionsAkshay Kumar100% (1)
- Types of CrackingDocument26 pagesTypes of CrackingAnonymous c3eiDyWNo ratings yet
- Visual Inspection 3.0Document69 pagesVisual Inspection 3.0Ari GandaraNo ratings yet
- Prevent CrackingDocument2 pagesPrevent CrackingRafeek ShaikhNo ratings yet
- Identifying Casting DefectsDocument5 pagesIdentifying Casting Defectsrajeevkv4No ratings yet
- Geometric shape imperfections types and causes reviewDocument18 pagesGeometric shape imperfections types and causes reviewamit4709No ratings yet
- Hard Surface Overlay Welding Crack E - Weldone-Letter - FEBRUARY-2017 - Ver - 1Document1 pageHard Surface Overlay Welding Crack E - Weldone-Letter - FEBRUARY-2017 - Ver - 1convmech enggNo ratings yet
- Weld Failure Causes and PreventionDocument5 pagesWeld Failure Causes and PreventionMidhun K ChandraboseNo ratings yet
- Defects Reheat CrackingDocument5 pagesDefects Reheat Crackingguru_terexNo ratings yet
- Detecting and preventing lack of sidewall and inter-run fusion in weldsDocument4 pagesDetecting and preventing lack of sidewall and inter-run fusion in weldsguru_terexNo ratings yet
- LamelerDocument5 pagesLamelerPrasetyaOne NugraHantoeNo ratings yet
- Avoidance of Discontinuities in The Joint HardoxDocument10 pagesAvoidance of Discontinuities in The Joint HardoxfsfunbNo ratings yet
- WJM Technologies: Excellence in Material JoiningDocument5 pagesWJM Technologies: Excellence in Material Joiningarjun prajapatiNo ratings yet
- Geometric shape welding imperfections causes and typesDocument12 pagesGeometric shape welding imperfections causes and typesbipete69No ratings yet
- Geometric Shape Imperfections in Welding - Causes and Acceptance StandardsDocument16 pagesGeometric Shape Imperfections in Welding - Causes and Acceptance StandardsGabriel PanaNo ratings yet
- 01 - Welding Lectures 1-6Document113 pages01 - Welding Lectures 1-6Govind GuptaNo ratings yet
- Defects/imperfections in Welds - Reheat Cracking: IdentificationDocument4 pagesDefects/imperfections in Welds - Reheat Cracking: IdentificationtuanNo ratings yet
- Weld DefectsDocument45 pagesWeld DefectsEhigiator Joseph100% (5)
- Handbook - Weld Defects 06Document1 pageHandbook - Weld Defects 06Danilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Weld Defects and How To Avoid Them: ContinuedDocument5 pagesWeld Defects and How To Avoid Them: ContinuedFaizPuadNo ratings yet
- Weld Defects and Imperfections GuideDocument43 pagesWeld Defects and Imperfections Guideraju100% (1)
- A General Review of Geometric Shape Imperfections - Types and Causes - Part 1 - Job Knowledge 67Document5 pagesA General Review of Geometric Shape Imperfections - Types and Causes - Part 1 - Job Knowledge 67tuanNo ratings yet
- Weld Defects TWIDocument96 pagesWeld Defects TWISabir Shabbir100% (7)
- FEM_Modelling_of_Weld_Damage_in_Continuous_Cold_RoDocument11 pagesFEM_Modelling_of_Weld_Damage_in_Continuous_Cold_RoAimen AouniNo ratings yet
- What Are Wormholes and How Can They Be PreventedDocument13 pagesWhat Are Wormholes and How Can They Be PreventedElvin MenlibaiNo ratings yet
- TVL - SM 11 - w6Document4 pagesTVL - SM 11 - w6CrisTopher L CablaidaNo ratings yet
- Lack of Fusion PDFDocument6 pagesLack of Fusion PDFDhinesh GnanadhasNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Structural Welding: Processes, Materials and Methods Used in the Welding of Major Structures, Pipelines and Process PlantFrom EverandHandbook of Structural Welding: Processes, Materials and Methods Used in the Welding of Major Structures, Pipelines and Process PlantRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Brittle Fracture in Steel StructuresFrom EverandBrittle Fracture in Steel StructuresG.M. BoydNo ratings yet
- Spot Welding Interview Success: An Introduction to Spot WeldingFrom EverandSpot Welding Interview Success: An Introduction to Spot WeldingNo ratings yet
- Principles of Welding: Processes, Physics, Chemistry, and MetallurgyFrom EverandPrinciples of Welding: Processes, Physics, Chemistry, and MetallurgyRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- 25 Best Things To Do in StuttgartDocument42 pages25 Best Things To Do in StuttgartDanilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Stuttgard 2019Document8 pagesStuttgard 2019Danilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- 5 whyTableAnalysis Step by StepDocument18 pages5 whyTableAnalysis Step by StepJoaquina_JoaquinaNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld Defects 10Document1 pageHandbook - Weld Defects 10Danilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld Defects 12Document1 pageHandbook - Weld Defects 12Danilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Weld Defects Handbook - Causes and SolutionsDocument1 pageWeld Defects Handbook - Causes and SolutionsDanilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld Defects 1Document1 pageHandbook - Weld Defects 1Danilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld Defects 11Document1 pageHandbook - Weld Defects 11Danilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Figure 10-2 - Example of Lack of FusionDocument1 pageFigure 10-2 - Example of Lack of FusionDanilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld Defects 07Document1 pageHandbook - Weld Defects 07Danilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld Defects 05Document1 pageHandbook - Weld Defects 05Danilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Electron Beam Welding SafetyDocument1 pageElectron Beam Welding SafetyDanilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld Defects 06Document1 pageHandbook - Weld Defects 06Danilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld Defects 02Document1 pageHandbook - Weld Defects 02Danilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Handbook - Weld Defects 01Document1 pageHandbook - Weld Defects 01Danilova SonjaNo ratings yet
- Standard For Protection of Austenitic Stainless Steel and Nickel Alloy MaterialsDocument4 pagesStandard For Protection of Austenitic Stainless Steel and Nickel Alloy Materialsharry100% (1)
- Tubacex: Your global technological partner for powergen pipes and tubesDocument20 pagesTubacex: Your global technological partner for powergen pipes and tubesvalli rajuNo ratings yet
- 01-Pet Eng Design - PTE - 470 - IntroductionDocument30 pages01-Pet Eng Design - PTE - 470 - IntroductionHassan KhalifeNo ratings yet
- Astm B 464-2010Document3 pagesAstm B 464-2010reza acbariNo ratings yet
- Grillete - MCLEAN ASH-55Document1 pageGrillete - MCLEAN ASH-55RogerNo ratings yet
- SEC VIII D1 B PT UF - Part UF Requirements For Pressure Vessels Fabricated by ForgingDocument6 pagesSEC VIII D1 B PT UF - Part UF Requirements For Pressure Vessels Fabricated by ForgingJoel SantaellaNo ratings yet
- Welding 3&4 REV21Document40 pagesWelding 3&4 REV21Muhd Shabeeb ANo ratings yet
- Karakteristik Kawat LasDocument36 pagesKarakteristik Kawat LasKen RanggaNo ratings yet
- STEEL GRADE COMPARISON FACT SHEETDocument1 pageSTEEL GRADE COMPARISON FACT SHEETCandra YuniartoNo ratings yet
- NOR - Steel Sucker Rods and Pony Rods - V2Document8 pagesNOR - Steel Sucker Rods and Pony Rods - V2Cosersum Int C ANo ratings yet
- WOMBAT-2.2TA - K27-ST150 (1) PioneerDocument8 pagesWOMBAT-2.2TA - K27-ST150 (1) Pioneer57jfx7y86xNo ratings yet
- PEMBUATAN SERTA PENGUJIAN KEKERASAN DAN KOMPOSISI KIMIA PRODUK CINDERAMATA BERLOGO SOLIDARITY M FOREVER DENGAN METODE PENGECORAN LOGAM MENGGUNAKAN BAHAN ALUMUNIUM 6063Document46 pagesPEMBUATAN SERTA PENGUJIAN KEKERASAN DAN KOMPOSISI KIMIA PRODUK CINDERAMATA BERLOGO SOLIDARITY M FOREVER DENGAN METODE PENGECORAN LOGAM MENGGUNAKAN BAHAN ALUMUNIUM 6063Ridwan NugrahaNo ratings yet
- DENR Administrative Order No-2017-10Document2 pagesDENR Administrative Order No-2017-10Manila Today100% (1)
- SA-517 Grades for Pressure Vessel SteelDocument2 pagesSA-517 Grades for Pressure Vessel SteelsepackltdaNo ratings yet
- Rail Wheel FactorDocument11 pagesRail Wheel Factorkiran mNo ratings yet
- The Evolution of Chamfer Cutting: Cover StoryDocument2 pagesThe Evolution of Chamfer Cutting: Cover StorythisisjineshNo ratings yet
- GripperSlings WEBDocument8 pagesGripperSlings WEBbman0051401No ratings yet
- Learn Manufacturing Processes by Building a G-ClampDocument6 pagesLearn Manufacturing Processes by Building a G-ClampPei Shan Choong100% (2)
- Handtools Measuring Device PDFDocument26 pagesHandtools Measuring Device PDFGus Dur0% (1)
- ASME BPVC - II.A-2017 SA-182/SA-182M: Table 2Document1 pageASME BPVC - II.A-2017 SA-182/SA-182M: Table 2rajeshNo ratings yet
- F 670 - 02 - Rjy3maDocument3 pagesF 670 - 02 - Rjy3maSting TejadaNo ratings yet
- Is 814 2004 PDFDocument34 pagesIs 814 2004 PDFSantosh Kumar60% (5)
- C&P WITCHLINER Insulated 3-Bolt Pipe ClampDocument1 pageC&P WITCHLINER Insulated 3-Bolt Pipe ClampAchraf BoudayaNo ratings yet
- ASTM A240-A240M-05aDocument12 pagesASTM A240-A240M-05aNadhiraNo ratings yet
- Information Sheet 1.2-2docxDocument5 pagesInformation Sheet 1.2-2docxMarc GelacioNo ratings yet
- BRINELL HARDNESS TEST FinalizedDocument1 pageBRINELL HARDNESS TEST FinalizedMohsin QaziNo ratings yet
- ASTM A449 Tech InfoDocument2 pagesASTM A449 Tech InfoBoz Van DuynNo ratings yet
- Thread Types - James Glen PDFDocument7 pagesThread Types - James Glen PDFVikranth ReddyNo ratings yet
- ASTM A29-16 Standard Specification For General Requirements For Steel Bars, Carbon and Alloy, Hot-WroughtDocument17 pagesASTM A29-16 Standard Specification For General Requirements For Steel Bars, Carbon and Alloy, Hot-WroughtMalaz Abdul JalilNo ratings yet
- FG-Spiral Classifier Operating ManualDocument5 pagesFG-Spiral Classifier Operating ManualRogelio Israel LedesmaNo ratings yet