Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Conceptual Framework
Uploaded by
LEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOS0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views5 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views5 pagesConceptual Framework
Uploaded by
LEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 5
CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK
Financial Reporting and Assumptions
Conceptual Framework 2. Lenders and Other Creditors
− Summary of the terms and concepts that underlie − To help them determine if the amounts
the preparation and presentation of financial owing to them will be paid when due
statements Other Users
− Promulgated by the International Accounting − They find the general purpose financial reports
Standards Board (IASB) useful but the reports are not directed to them
− Overall theoretical foundation for accounting primarily
− Intended to guide standard-setters, preparers, and 1. Employees
users − Interested in the stability and profitability of
− The underlying theory for the development of the entity
accounting standards and revisions − To know if the entity can provide raises,
− Concerned with general purpose financial remuneration, retirement benefits, and
statements employment opportunities
Purposes of Conceptual Framework 2. Customers
a.To assist in developing accounting standards and − Interested in the continuance of an entity,
reviewing existing standards especially when they have long-term
b.To assist preparers of financial statements in involvement, or dependent to it
applying accounting standards and in dealing with 3. Governments and their Agencies
issue not yet covered by GAAP − Interested in the allocation of resources and
c. To assist the FRSC in the review and adoption of activities of the entity
International Financial Reporting Standards − For regulating activities, determining
d.To assist auditors in forming an opinion whether taxation policies, and basis of statistics
financial statement conform with Phil. GAAP 4. Public
e. To provide information to those interested in the − Providing information about trends and
work of the FRSC in the formulation of PFRS range of entity’s activities
Authoritative Status of Conceptual Framework Scope of Conceptual Framework
In the absence of a standard: a. Objective of financial reporting
- the management shall consider the applicability of b.Qualitative characteristics of useful financial
the Conceptual Framework in developing and information
applying an accounting policy c. Definition, recognition, and measurement of the
Conceptual Framework is not a Philippine elements from which financial statements are
Financial Reporting Standard constructed
- it does not define standard for any particular d.Concepts of capital and capital maintenance
measurement or disclosure issue Financial Reporting
In case of conflict: − Provision of financial information useful for
- Philippine Financial Reporting Standard shall external users in making economic decisions and
prevail over the Conceptual Framework assessing the effectiveness of the entity’s
Users of Financial Information management
Primary Users − Also refer to other means of communicating
− To whom general purpose financial reports are information such as nonfinancial information
primarily directed
− They cannot require entities to provide information
directly to them
1. Existing and Potential Investors
− Concerned with the risk inherent in and OBJECTIVE OF FINANCIAL REPORTING
return provided by their investments − Forms the foundation of the Conceptual Framework
− Helps them to decide whether to buy, hold, − Overall objective: To provide financial
or sell information useful for primary uses in making
− To asses the ability of the entity to pay decisions about providing resources
dividends − The “why”, purpose, or goal of accounting
Target Users Present: asses the ability to generate future cash
− These are the existing and potential investors, inflows from operations
lenders, and other creditors who can provide Accrual Accounting
resources to the entity − Effects of transactions are recognized when
− The have the most critical and Immediate need for occurred and not as cash is received or paid
information − Income is recognized when earned regardless of
Specific Objective of Financial Reporting when received, and expense is recognized when
a. To provide information useful in making decisions incurred regardless of when paid
about providing resources Limitations of Financial Reporting
Investors: whether to buy, sell, or hold equity a. It does not and cannot provide all of the
investments information needed
Lenders and other Creditors: whether to b.It is not designed to show the value of an entity
provide or settle loans and other credit form rather it helps estimate the value of an entity
b.To provide information useful in assessing the cash c. It only provides common information and cannot
flow prospects accommodate every request
Investors: decisions depend on the returns that d.It is based on estimate and judgment
they expect from an investment UNDERLYING ASSUMPTION
Lenders and other Creditors: depend on the Accounting Assumptions
principal and interest payments or other returns − The basic notions or fundamental premises on
they expect which the accounting process is based
c. To provide information about entity resources, − Also known as “postulates”
claims, and changes in resources and claims − Serve as the foundation or bedrock of accounting to
Financial Position enhance the understanding and usefulness of
- Refer to the economic resources and claims financial statements
- Comprise of assets (economic resources), 1.Going Concern
liabilities and equity (claims) - Entity will continue in operations for the
- Helps users identify the entity’s financial foreseeable future
strength and weakness - The very foundation of the cost principle
o Liquidity – availability of cash to cover - Thus, assets are normally recorded at cost
currently maturing obligations 2.Accounting Entity
o Solvency – availability of cash to meet - Entity is separate from the owners, managers, and
financial commitments when fall due employees
- Help users predict how future cash flows - Transactions of the entity shall not be merged with
will be distributed the transaction of the owners
- For a fair presentation of financial statements
Financial Performance
- Each business is an independent entity
- Refer to the changes in economic resources
- However, when parent and subsidiary relationship
and claims
exists, consolidated statements for affiliates is
- The level of income earned by the entity
prepared, but, it does not eliminate legal
through the efficient and effective use of its
boundaries.
resources
3.Time Period
- Comprises of revenue, expenses, and net
- the indefinite life of an entity is subdivided into
income or loss
accounting periods of equal length
- The results of operations and portrayed in
- One-year period: traditional accounting period
the income statement and statement of
comprehensive income Calendar Year – ends on December 31
Usefulness of Financial Performance Fiscal Year/Natural Business Year – end on
− Helps users to understand the return produced by any month when the business is at the lowest or
the entity on the economic resources at its slack season
− Provides an indication of how well management 4.Monetary Unit
has discharged its responsibilities Quantifiability – items should be stated in terms
Past: predict future returns of a unit of measure – Peso in the Phil.
Stability of the Peso – purchasing power of the b.Neutrality
peso is stable or constant - Information is not slanted, weighted,
Stable Peso Postulate – amplification of the emphasized, de-emphasized, or manipulated
going concern assumption, so, adjustments are - Information does not favor one party
unnecessary to reflect any changes in purchasing - “Principle of Fairness”
power c. Free from Error
Accounting Function – to account for nominal - No errors or omissions in the description
pesos only and not for constant pesos or changes - The amount is described clearly and accurately
in purchasing power Substance over Form
QUALITATIVE CHARACTERISTICS - Transactions and events are accounted in
− The qualities or attributes that make financial accordance with their substance and
accounting information useful to other users reality and not in their legal form
Fundamental Qualitative Characteristics Conservatism
− Relate to the content or substance - When alternatives exist, the alternative
− Information must be both relevant and faithfully which has the least effect on equity
represented should be chosen
1.Relevance - In case of doubt, record any loss and do
- The capacity of the information to influence a not record any gain
decision - It is not a license to deliberately
- Information should be related or pertinent to the understate net income and net assets
economic decision Prudence
Predictive Value – forecast outcome of - The desire to exercise care and caution
events (what might happen in the future) when dealing with the uncertainties
Confirmatory Value – confirms or corrects Enhancing Qualitative Characteristics
previous predictions (feedback value) − Relate to the presentation or form
a.Materiality − Intended to increase the usefulness
- “Doctrine of Convenience” 1.Comparability
- Materiality of an item depends on relative size - The ability to bring together for the purpose or
- It is a matter of good judgment, professional noting points of likeness and difference of items
expertise, and common sense Horizontal Comparability/Intracomparability
- Information is material if its omission or Dimensional Comparability/Intercomparability
misstatement of information could influence a.Consistency
the economic decision - Use of the same method for the same item
- Factors of materiality: size and nature of the - If there is a change, there shall be full
item disclosure
2.Faithful Representation
- The descriptions and figures must match what
really existed or happened 2.Understandability
- The actual effects of the transactions shall be - Information should be presented in a form and
properly accounted for and reported expressed in terminology that user understands
a.Completeness 3.Verifiability
- Information should be presented in a way that - Different knowledgeable and independent
facilitates understanding and avoids erroneous observers could reach consensus
implication Direct – through direct observation
- Includes all information necessary for a user to Indirect – checking the inputs to a model,
understand the phenomenon being depicted formula, or other technique and recalculating
Standard of Adequate Disclosure using the same method
- Disclosure of any financial facts 4.Timeliness
significant enough to influence the - Financial information must be available or
judgment of user communicated early enough when a decision is to
- Financial statement shall be accompanied be made
by notes to financial statement
Cost Constraint – the benefit derived from the - Replacement of the obligation with another
information should exceed the cost incurred in obligation
obtaining the information - Conversion of an obligation into equity
ELEMENTS OF FINANCIAL STATEMENT 3.Income Recognition Principle
- The quantitative information presented − Income shall be recognized when earned
- “Building blocks” Income
- Financial Position: Asset, Liability, and Equity - Increase in economic benefit through
- Financial Performance: Income, and Expense inflow/increase in asset or decrease in liability
Recognition of Elements a.Revenue – arise from the ordinary regular
- Reporting of an asset, liability, income, or expense activities of the entity
1.Asset Recognition Principle b.Gain – do not arise in the regular course
− Assets should be recorded initially at original Conditions for Recognition
acquisition cost - Probable flow of future economic benefits
Asset (result of increase in asset or decrease in
- A resource controlled by the entity as a result liability)
of past events with future economic benefits - Economic benefits can be measure reliably
Conditions for Recognition Point of Sale
- Probable flow of future economic benefit - Point of income recognition
- Cost or value be measured reliably - It is where the legal title of the goods passes to
Ways for Asset to Flow the buyer
- Production of goods or services to be sold by Methods in Income Recognition
the entity a.Installment Method – recognized at the point
- Exchange of other assets of collection; collections multiplied by gross
- Used to settle a liability profit rate
- Distribute to the owners of the entity b.Cost Recovery Method (Sunk Cost) –
Initial Cost recognized at the point of collection; all
- Carried w/o change collections are applied to the cost of
- Changed by depreciation, amortization or merchandise sold
write-off c. Percentage of Completion Method (Stage of
- Shifted to other categories (raw Materials to Completion) - revenue from contracts; contract
finished goods) cost shall be recognized as revenue and
Cost of the Asset expense
- Cash Transaction: cash payment d.Production Method - recognized at the point
- Non-Cash Transaction: fair value/carrying of production (agricultural, forest and mineral
amount products)
2.Liability Recognition Principle Other Income Recognition
Liability a.Interest Revenue – recognized based on a time
- A present obligation arising from a past event proportion basis; effective yield of the assets
Conditions for Recognition b.Royalties – recognized in an accrual basis
- Probability of an outflow for the settlement based on the substance or regular agreement
- Amount of obligation can be measured reliably c. Dividends – recognized upon declaration of the
Kinds of Obligation dividend at the Stockholders’ Meeting
a.Legally Enforceable – consequence of a d.Subscription – recognized on a straight-line
binding contract or statutory requirement basis over the subscription period
b.Constructive Obligation - arise from normal e. Admission fees – recognized when the event
business practice, custom or desire to maintain takes place
good business relations or act in an equitable f. Tuition fees – recognized over the period in
manner which tuition is provided
Ways to Settle Liability 4.Expense Recognition Principle
- Payment of cash − Expenses are recognized when incurred
- Transfer of Non-Cash Assets Expense
- Provision of services
- A decrease in economic benefit in the form of MEASUREMENT OF ELEMENTS
an outflow/decrease in asset or increase in − The process of determining the monetary amounts
liability the elements are to be recognized and carried
Conditions for Recognition 1.Historical Cost
- Probable decrease in economic benefit (result - Amount of cash or cash equivalent paid of the fair
of decrease in asset or increase in liability) value at the time of acquisition
- Economic benefit can be measured reliably - “Past Purchase Exchange Rate”
Matching Principle - Most commonly adopted
- Costs and expenses incurred in earning a 2.Current Cost
revenue shall be reported - Amount of cash or cash equivalent to be paid if the
- There is a cost in earning a revenue same or equivalent asset was acquired currently
a.Cause and Effect Association - “Current Purchase Exchange Price”
- Expense is recognized when the revenue 3.Realizable Value
is already recognized - Amount of cash or cash equivalent that could be
- “Strict Matching Concept” or the obtained by selling the asset
matching cost with revenue - “Current Sale Exchange Price”
- The simultaneous or combined 4.Present Value
recognition of revenue and expenses - The discounted value of the future net cash
Examples: inflows
> Merchandise Sold (COGS) - “Future Exchange Price”
> Doubtful Accounts, Warranty
Expense, and Sales Commission
b.Systematic and Rational Allocation
- Some costs are expensed by simply
allocating them over the periods
benefited
- Cost incurred will benefit future periods
and there is an absence of a direct or
clear association of the expense
Examples:
> Depreciation of PPE
> Amortization of Intangibles
> Allocation of Prepaid Rent, Insurance,
and other Prepayments
c. Immediate Recognition
- Cost incurred is expensed outright
because of uncertainty of economic
benefit
Conditions for Immediate
Recognition:
- Expenditure produces no future
economic benefit
- Cost incurred ceases/does not
qualify for recognition as an asset
Examples:
> Salaries, Administrative,
Advertising, Selling, Expenses
> Settlement of Lawsuits or Worthless
Intangibles
> Losses from Disposal of PPE or
Investment
> Casualty Losses (Fire, Flood Etc.)
You might also like
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- Module 7 13 No 11Document6 pagesModule 7 13 No 11LEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- Pas 36: Impairment of Assets: ObjectiveDocument6 pagesPas 36: Impairment of Assets: ObjectiveLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Pas 20 - 23Document6 pagesPas 20 - 23LEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- PAS 24, 28, and 29 QuestionsDocument4 pagesPAS 24, 28, and 29 QuestionsLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- PAS 32: Financial Instruments - Presentation (Questions)Document6 pagesPAS 32: Financial Instruments - Presentation (Questions)LEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Cfas SummarizeDocument26 pagesCfas SummarizeLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- Theories of LearningDocument6 pagesTheories of LearningLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Theories of EmotionDocument4 pagesTheories of EmotionLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Philippines Population and Demography Demography Life Expectancy Birth RateDocument3 pagesPhilippines Population and Demography Demography Life Expectancy Birth RateLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- Psychological Properties of Colors: RED. PhysicalDocument9 pagesPsychological Properties of Colors: RED. PhysicalLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Top Ten Countries With The Highest Population: 2050 Expected PopDocument8 pagesTop Ten Countries With The Highest Population: 2050 Expected PopLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Intelligence: "General Intelligence" or The "G Factor". His Definition Was A Result of A Mental Aptitude Test That HeDocument7 pagesIntelligence: "General Intelligence" or The "G Factor". His Definition Was A Result of A Mental Aptitude Test That HeLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- Traits & Characteristics Nature NurtureDocument2 pagesTraits & Characteristics Nature NurtureLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- A. Responsible ParenthoodDocument4 pagesA. Responsible ParenthoodLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- Competitiveness, Strategy, ProductivityDocument49 pagesCompetitiveness, Strategy, ProductivityLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Prelims - EconomicsDocument4 pagesPrelims - EconomicsLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Purposive CommunicationDocument6 pagesPurposive CommunicationLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- CybercrimeDocument6 pagesCybercrimeLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Prelims - Org. ManDocument11 pagesPrelims - Org. ManLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Operations ManagementDocument41 pagesIntroduction To Operations ManagementLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Work Design and Measurement: Group 7Document87 pagesWork Design and Measurement: Group 7LEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Finals - Org. Man.Document30 pagesFinals - Org. Man.LEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Speaker Speech Audience: Which Channel To, Whom and With WhatDocument2 pagesSpeaker Speech Audience: Which Channel To, Whom and With WhatLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Strategic Capacity Planning For Products & ServicesDocument74 pagesStrategic Capacity Planning For Products & ServicesLEIGHANNE ZYRIL SANTOSNo ratings yet
- Home About Us Executive Body Bar Council Contact UsDocument5 pagesHome About Us Executive Body Bar Council Contact UsT v subbareddyNo ratings yet
- Acronyms: RLWL: Remote Location Waitlist PQWL: Pooled Quota Waitlist RSWL: Road-Side WaitlistDocument1 pageAcronyms: RLWL: Remote Location Waitlist PQWL: Pooled Quota Waitlist RSWL: Road-Side WaitlistAdinarayana RaoNo ratings yet
- AWS Operational Excellence Pillar PDFDocument23 pagesAWS Operational Excellence Pillar PDFCharley RajNo ratings yet
- A2093 18022 2018 ST01 Iss - WDDocument1 pageA2093 18022 2018 ST01 Iss - WDprompt consortiumNo ratings yet
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- PD233 Lecture16Document17 pagesPD233 Lecture16Sameer GautamNo ratings yet
- MKT516Document646 pagesMKT516nischal krishnaNo ratings yet
- Flight Ops Eng PDFDocument6 pagesFlight Ops Eng PDFIrfan Azmi0% (2)
- Marsha Mellow Doesn T Care Whether She Consumes in Period 1Document1 pageMarsha Mellow Doesn T Care Whether She Consumes in Period 1trilocksp SinghNo ratings yet
- Senior Construction Project Manager Resume - EPCDocument18 pagesSenior Construction Project Manager Resume - EPCpapmonNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SynthesisDocument2 pagesChapter 2 SynthesisjonaNo ratings yet
- This Study Resource Was: Ben & Jerry's Unveils Pecan Resist Flavor Ahead of MidtermsDocument3 pagesThis Study Resource Was: Ben & Jerry's Unveils Pecan Resist Flavor Ahead of Midtermsfahad BataviaNo ratings yet
- Bop Systems Function / Field Drawdown TestDocument1 pageBop Systems Function / Field Drawdown Testislam atifNo ratings yet
- MetallicaDocument2 pagesMetallicarubinsonNo ratings yet
- Open Hole Wireline LoggingDocument32 pagesOpen Hole Wireline Loggingsanjeet giriNo ratings yet
- Managing Time and CostDocument2 pagesManaging Time and CostLovelace Love-HardingNo ratings yet
- Examples of Instructional MaterialsDocument4 pagesExamples of Instructional MaterialsFeelin YepNo ratings yet
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
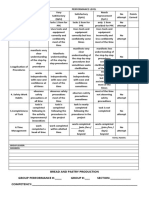
- Performance RubricsDocument2 pagesPerformance RubricsMaria Manoa GantalaNo ratings yet
- Calculating Average Cycle StockDocument6 pagesCalculating Average Cycle StockPuneet PuriNo ratings yet
- Wartsila O E RT Flex68 D MIM Part 1.Document379 pagesWartsila O E RT Flex68 D MIM Part 1.Uhrin Imre100% (1)
- Log Vsszzz1pzcr030942Document6 pagesLog Vsszzz1pzcr030942Abdula TanerNo ratings yet
- BSNL Project MbaDocument92 pagesBSNL Project MbaSathish Ssathish100% (1)
- Austria Oracle LocalizationDocument8 pagesAustria Oracle LocalizationGanesh VenugopalNo ratings yet
- Hysys Installation V 7.3Document1 pageHysys Installation V 7.3Naik LarkaNo ratings yet
- Hunger Affect Children in AfricaDocument7 pagesHunger Affect Children in AfricaNguyen Hoang Tran VanNo ratings yet
- 9G Visa Process MapDocument1 page9G Visa Process MapJohn Lawrence de lunaNo ratings yet
- Local Government Marketing ModelDocument160 pagesLocal Government Marketing ModeladiNo ratings yet
- CostcoDocument96 pagesCostcoChris DavidsonNo ratings yet
- Logic GatesDocument11 pagesLogic GatesXharmei ThereseNo ratings yet
- EDPS - (Guidelines) On Processing PI in Whistleblowing Procedure A 17-12-19Document16 pagesEDPS - (Guidelines) On Processing PI in Whistleblowing Procedure A 17-12-19Mario Gomez100% (1)
- Challenges of International BusinessDocument4 pagesChallenges of International BusinessRikesh SapkotaNo ratings yet
- Getting to Yes: How to Negotiate Agreement Without Giving InFrom EverandGetting to Yes: How to Negotiate Agreement Without Giving InRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (652)
- I Will Teach You to Be Rich: No Guilt. No Excuses. No B.S. Just a 6-Week Program That Works (Second Edition)From EverandI Will Teach You to Be Rich: No Guilt. No Excuses. No B.S. Just a 6-Week Program That Works (Second Edition)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (16)
- The Science of Prosperity: How to Attract Wealth, Health, and Happiness Through the Power of Your MindFrom EverandThe Science of Prosperity: How to Attract Wealth, Health, and Happiness Through the Power of Your MindRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (231)
- Love Your Life Not Theirs: 7 Money Habits for Living the Life You WantFrom EverandLove Your Life Not Theirs: 7 Money Habits for Living the Life You WantRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (146)
- The ZERO Percent: Secrets of the United States, the Power of Trust, Nationality, Banking and ZERO TAXES!From EverandThe ZERO Percent: Secrets of the United States, the Power of Trust, Nationality, Banking and ZERO TAXES!Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (14)