Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Project Report Laser Communication System
Project Report Laser Communication System
Uploaded by
pradyumn0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views6 pagesCopyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
11 views6 pagesProject Report Laser Communication System
Project Report Laser Communication System
Uploaded by
pradyumnCopyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 6
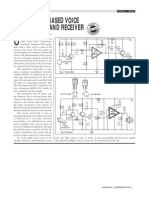
LASER BASED COMMUNICATION SYSTEM
Priyanka Ubale. Rakhi Vishwakarma.
Dept. of EXTC Enginnering , Dept. of EXTC Enginnering ,
Atharva Collage of Enginnering , Atharva Collage of Enginnering ,
Mumbai , Maharashtra , India. Mumbai , Maharashtra,India.
Pradyuman Yadav. Vikas Gupta.
Dept. of EXTC Enginnering , Dept. of EXTC Enginnering ,
Atharva Collage of Enginnering, Atharva Collage of Enginnering,
Mumbai , Maharashtra , India. Mumbai , Maharashtra , India.
volume control for a clear sound. To avoid
Abstract-Using this circuit you can 50Hz hum noise in the speaker, keep the
communicate with your neighbours phototransistor away from AC light sources
wirelessly. Instead of RF signals, light from such as bulbs.
a laser torch is used as the carrier in the Keywords-Laser,communication system,
circuit. The laser torch can transmit light up IC 741,IC 386,phototransistor,one side
to a distance of about 500 meters. The communication
phototransistor of the receiver must be 1.Introduction
accurately oriented towards the laser beam Laser communications systems are wireless
from the torch. If there is any obstruction in connections through the atmosphere. They
the path of the laser beam, no sound will be work similarly to fibre optic links, except the
heard from the receiver. The transmitter beam is transmitted through free space. While
circuit (Fig. 1) comprises condenser the transmitter and receiver must require line-
microphone transistor amplifier BC548 (T1) of-sight conditions, they have the benefit of
followed by an opamp stage built around eliminating the need for broadcast rights and
μA741 (IC1). The gain of the op-amp can be buried cables. Laser communications systems
controlled with the help of 1-mega-ohm pot can be easily deployed since they are
meter VR1. The AF output from IC1 is inexpensive, small, low power and do not
coupled to the base of transistor BD139 (T2), require any radio interference studies. The
which, in turn, modulates the laser beam. carrier used for the transmission signal is
The transmitter uses 9V power supply. typically generated by a laser diode. Two
However, the 3-volt laser torch (after parallel beams are needed, one for transmission
removal of its battery) can be directly and one for reception. Due to budget
connected to the circuit—with the body of restrictions, the system implemented in this
the torch connected to the emitter of BD139 project is only one way.
and the spring-loaded lead protruding from Laser communications have been a hot topic
inside the torch to circuit ground. The lately, as solutions for how to satisfy ever
receiver circuit (Fig. 2) uses an NPN increasing bandwidth needs are in high
phototransistor as the light sensor that is demand. Some have suggested that bandwidth
followed by a two-stage transistor could be distributed in neighbourhoods by
preamplifier and LM386-based audio power putting laser communication systems on top of
amplifier. The receiver does not need any homes and pointing them towards a common
complicated alignment. Just keep the transceiver with a fast link to the Internet. With
phototransistor oriented towards the remote possible transmit speeds of up to a gigabit per
transmitter’s laser point and adjust the second, this is an exciting area. Other
applications for this technology include R5, R6 - 15KΩ
temporary connectivity needs (e.g. sporting R7 - 82Ω
events, disaster scenes, or conventions), or R8 - 6.8KΩ
space based communications. R9 - 4.7KΩ
Using this circuit you can communicate R10 - 470KΩ
with your neighbours wirelessly. Instead of RF R11, R12 - 2.2KΩ
signals, light from a laser torch is used as the R13 - 1KΩ
carrier in the circuit. The laser torch can R14 - 10Ω
transmit light up to a distance of about 500 VR1 - 1MΩ
meters. The phototransistor of the receiver must VR2 - 10KΩ
be accurately oriented towards the laser beam
from the torch. If there is any obstruction in the CAPACITORS
path of the laser beam, no sound will be heard C1, C8 - 1mF, 16V
from the receiver. The transmitter circuit (Fig. C3, C11 - 470mF, 16V
1) comprises condenser microphone transistor C4 - 1000mF, 16V
amplifier BC548 (T1) followed by an opamp C9, C12 - 100mF, 16V
stage built around μA741 (IC1). The gain of the C10 - 10mF, 16V
op-amp can be controlled with the help of 1- C2, C13 - 0.1mF
mega-ohm pot meter VR1. The AF output from C5, C7 - 0.01mF
IC1 is coupled to the base of transistor BD139 C6 - 47Pf
(T2), which, in turn, modulates the laser beam.
The transmitter uses 9V power supply. MISCELLANEOUS
However, the 3-volt laser torch (after removal Condenser Mic
of its battery) can be directly connected to the LASER torch of 3 volt
circuit—with the body of the torch connected to Speaker – 0.5W, 8W
the emitter of BD139 and the spring-loaded
lead protruding from inside the torch to circuit 3.Circuit Diagram and Working
ground. The receiver circuit (Fig. 2) uses an A. Transmitter Circuit :
NPN phototransistor as the light sensor that is
followed by a two-stage transistor preamplifier
and LM386-based audio power amplifier. The
receiver does not need any complicated
alignment. Just keep the phototransistor
oriented towards the remote transmitter’s laser
point and adjust the volume control for a clear
sound. To avoid 50Hz hum noise in the speaker,
keep the phototransistor away from AC light
sources such as bulbs.
2.Components
SEMICONDUCTORS
IC 1 - UA741 OPAMP The circuit is based upon the principle of
IC 2 - LM386 Audio Power Amplifier LIGHT MODULATION where instead of radio
T1 - BC548 NPN Transistor frequency signals; light from a laser torch is
RESISTORS (All ¼ watt, 5% carbon, unless used as the carrier in the circuit. Here, the
stated otherwise) transmitter uses 9V power supply. Audio signal
R1, R3 - 8.2KΩ or voice is taken as input from the condenser
R2 - 2.2MΩ mic, which is, followed transistor amplifier
R4 - 10KΩ BC548 along with op-amp stage built around
UA741. The gain of the op-amp can be Resistors R5 and R6 of its value acts as a
controlled with the help of 1 mega ohms pot voltage-divider network, thus it gives a fixed
meter. The AF output from op-amp UA741 is voltage at the non-inverting pin. Input inverted
coupled to the base of the power transistor audio signal is applied to the inverting pin. Op-
BD139, which in turn, modulates the laser. In amp works on the differences into the applied
the transmitter circuit, audio signal of the non- two input voltage and provide an output at pin
sinusoidal waveform and having a few mV of no. 6. Since, input is applied to the inverting pin
amplitude is taken as input from condenser mic. the output is also an inverting one. Thus, again
Condenser mic is directly followed by the we get in phase high power and high amplitude
transistor amplifier stage consist of BC548. level audio signal. Capacitors C3, C4 and
Transistor BC548 is connected in common resistor R7 are acting as diffusion capacitors
emitter configuration. and feedback resistor respectively. These
diffusion capacitors stored the carriers like
Resistor R1 is the source resistor, which holes and electrons in the base and thus provide
is directly connected to the power-supply R2, self-biasing of the transistor Power dissipation
R3 and capacitor C1 are acting as self-biasing rate of UA741 is very high, which is not
circuits, which is used for the biasing transistor. practical for driving other electronics devices,
These circuit arrangements provide or establish so heat sink power transistor BD139 is used.
a stable operating point. The biasing voltage is Power transistor BD139 absorbs most of the
obtaining by R2 and R3 resistors network. Self- power and supplies the suitable power to drive
bias is used for obtaining entire audio signal as the laser torch. This in turns modulates the laser
input. Capacitor C1 is the coupling capacitor, beam, since laser torch acts like a balanced
since audio input signal is having a non- modulator, where two signals – one is message
sinusoidal waveform of different amplitude and signal (audio signal) and carrier laser signal,
frequency, coupling capacitor is used to reject superimposed. So, laser beam modulates and
some of the dc noise/line as well as level from transmits the signals to large distances.
audio input signal. The self-biased circuit is However, the three volts laser torch can be
connected with the BC548 in CE configuration. directly connected to the emitter of BD139 and
It is transistor amplifier stage, where the low the spring loaded lead protruding from inside
amplitude audio signal is amplified to the the torch to the ground.
desired voltage. The output is taken from the
collector terminal; so inverted audio input B. Receiver Circuit
signal is obtained. Transistor pre-amplifier
stage is coupled with op-amp stage built by
ua741. C2 is the blocking capacitor while R4 is
the op-amp stage resistor.
Op-amp ua741 is easily available general-
purpose operational amplifier. Here pin no. 1
and 5 are not connected in order to nullify input-
offset voltage. Pin no. 7 and 4 are VCC as well
as –VEE supply voltage. Pin no. 3 is non-
inverting input while pin no. 2 is inverting
input. Between pin no. 2 and 6, 1 mega-ohm pot
meter is connected as voltage series negative
feedback, which controls the infinite gain of the
op-amp. The receiver circuit uses an NPN
phototransistor (2N5777) as the light sensor.
Here, the phototransistor receives the audio 5. Reference
signal of low power and low amplitude that is
followed by a two-stage transistor pre- 1.www.google.com
amplifier. In the pre-amplifier stage R8 is a
source resistor, which is directly connected to 2.www.wikipedia.com
the power supply. The pre amplifier stage is RC
coupled amplifier in CE configuration. C5, C6 3.www.nptel.com
are the junction capacitances, which are taken
in to the account when we consider high 4.www.howthestuffsworks.com
frequency response, which is limited by their
presence. Resistors R9 and R12 are used to 5.www.efy.com
establish the biasing of the transistor
BC549.R11 is self-bias resistor, which is used 6.Guide Name-Joslyn Gracias
to avoid degeneration.
C7 is a bypass capacitor, which acts as to
prevent loss of amplification due to negative
feedback arrangement. Transistors BC549 are
the amplifier transistors, which amplifies the
signal because the signal obtained by the
phototransistor is of few mV. C8 is the blocking
capacitor, which is connected to the variable
resistor VR2, which in turn followed by audio
power amplifier IC LM386. Pin configuration
of LM386 is shown in the glossary. Pin no. 1
and 10 is followed by C10, which is an external
capacitor, used to compensate internal error
amplifier and thus avoid instability. Volume
control can be adjusted from variable resistor
VR2 of 10 kilo- ohms. LM386 provides
suitable power output useful for drive the
loudspeaker of 0.5W.From the pin no. 5, the
high power as well as suitable amplitude
received audio signal is taken as output R14 and
C13 are bypass arrangement used to prevent
loss of amplification. C12 capacitor is used for
preventing the noise as well as the hum
produced by the ac sources. From the
loudspeaker, the audio output is heard.
4.Conclusion
We can conclude that using laser based
communication system we can communicate
without any cost except the instrument cost. It
can be used in the places only where one side
communication takes place like instructions
given to workers etc.
You might also like
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 1Rating: 2.5 out of 5 stars2.5/5 (3)
- Audio IC Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesFrom EverandAudio IC Circuits Manual: Newnes Circuits Manual SeriesRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Reference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2From EverandReference Guide To Useful Electronic Circuits And Circuit Design Techniques - Part 2No ratings yet
- Digital Microwave Communication OverviewDocument15 pagesDigital Microwave Communication OverviewHakim KassimiNo ratings yet
- Amplificatore Audio AMDocument5 pagesAmplificatore Audio AMEchizen KinichiNo ratings yet
- Audio IC Projects: A Collection of Useful Circuits Based on Readily Available ChipsFrom EverandAudio IC Projects: A Collection of Useful Circuits Based on Readily Available ChipsNo ratings yet
- 3V FM Transmitter CircuitDocument6 pages3V FM Transmitter CircuitMahmood AhmedNo ratings yet
- How To Make A Long Range FM Transmitter at Low CostDocument24 pagesHow To Make A Long Range FM Transmitter at Low CostRajesh VenkatramanNo ratings yet
- Simple FM Radio Jammer Circuit IntroDocument14 pagesSimple FM Radio Jammer Circuit IntroYoussef lamraniNo ratings yet
- Simple AM Receiver&TransmitterDocument4 pagesSimple AM Receiver&TransmitterGokulk2011100% (2)
- Lambda Technical Manual (MT Lambda)Document236 pagesLambda Technical Manual (MT Lambda)Peter Yli100% (1)
- RF Controlled ApplianceDocument14 pagesRF Controlled ApplianceNEX456No ratings yet
- Ray Prasad, Surface Mount Technology (SMT) 2-Nd Edition (Технология поверхностного монтажа)Document791 pagesRay Prasad, Surface Mount Technology (SMT) 2-Nd Edition (Технология поверхностного монтажа)Михаил100% (1)
- An-791 A Simplified Approach To VHF Power Amplifier DesignDocument10 pagesAn-791 A Simplified Approach To VHF Power Amplifier DesignEdward YanezNo ratings yet
- Laser Torch Based Voice Transmitter and ReceiverDocument30 pagesLaser Torch Based Voice Transmitter and ReceiverUma Mahesh50% (4)
- BS120 Service Traininig - 01.01.ADocument108 pagesBS120 Service Traininig - 01.01.AkirydownloadNo ratings yet
- Voice Transission Using LaserDocument31 pagesVoice Transission Using LaserRaj AryanNo ratings yet
- Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1From EverandNewnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book (Linear IC): Newnes Electronics Circuits Pocket Book, Volume 1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Direct Conversion ReceiversDocument6 pagesDirect Conversion ReceiversAmir ChishtiNo ratings yet
- Laser Torch Based Voice Transmitter and Receiver (Repaired)Document56 pagesLaser Torch Based Voice Transmitter and Receiver (Repaired)1deakz4lu7ge100% (3)
- Contador Hanyoung GE4Document4 pagesContador Hanyoung GE4Juan Felipe Vieira Gaviria0% (1)
- 3172V21 - Synthesised WBFM TransmitterDocument6 pages3172V21 - Synthesised WBFM Transmitterjoniez14No ratings yet
- Atv Transmitter From Microwave OvenDocument5 pagesAtv Transmitter From Microwave Ovensnidely_whiplashNo ratings yet
- Tech Manual MVP Series 2017.1 WIP 3Document73 pagesTech Manual MVP Series 2017.1 WIP 3Chav HoangNo ratings yet
- Laser Communication SystemDocument4 pagesLaser Communication Systemjose273No ratings yet
- Laser Based Communication System PDFDocument3 pagesLaser Based Communication System PDFPawan Kumar100% (1)
- Laser Torch-Based Voice Transmitter and ReceiverDocument3 pagesLaser Torch-Based Voice Transmitter and ReceiverVaibhav PathakNo ratings yet
- Jan02 LasertorchDocument2 pagesJan02 LasertorchPriyanka SinghNo ratings yet
- LasertxandrxDocument1 pageLasertxandrxvibtherockstarNo ratings yet
- Laser Comm - ProjectDocument21 pagesLaser Comm - ProjectJaydeep SinhaNo ratings yet
- Laser Communication System: ABSTRACT: Laser Communication Is One of The Key Area in Wireless CommunicationsDocument8 pagesLaser Communication System: ABSTRACT: Laser Communication Is One of The Key Area in Wireless CommunicationsSaurabh SinhaNo ratings yet
- Laser Communication: Mini Project ReportDocument15 pagesLaser Communication: Mini Project ReportPrasannaKumarReddyKaturuNo ratings yet
- 434MHz SAW-Based Oscillators and TransmittersDocument8 pages434MHz SAW-Based Oscillators and TransmittersAngel MarianoNo ratings yet
- University of Tripoli: Laser Based Wireless Optical Voice Transmission SystemDocument10 pagesUniversity of Tripoli: Laser Based Wireless Optical Voice Transmission SystemOula FraiwanNo ratings yet
- Project 1 (Laser Audio Transmitter)Document4 pagesProject 1 (Laser Audio Transmitter)Komal GargNo ratings yet
- Laser Communication System NaviDocument14 pagesLaser Communication System NaviNaveen Hg G100% (1)
- Laser Torch ProjectDocument41 pagesLaser Torch ProjectAnkush Saini100% (1)
- ProposalDocument5 pagesProposalPatel manav PatelNo ratings yet
- Analogue Electronics: 14. Transistor Circuits For The ConstructorDocument27 pagesAnalogue Electronics: 14. Transistor Circuits For The ConstructorNuraddeen MagajiNo ratings yet
- Report On Electromagnetic Wave DetectorDocument16 pagesReport On Electromagnetic Wave DetectorRahul TripathyNo ratings yet
- Laser Transmitter and ReceiverDocument8 pagesLaser Transmitter and ReceiverMikhael MachaNo ratings yet
- Pulse Oximetry CircuitDocument19 pagesPulse Oximetry Circuitنواف الجهنيNo ratings yet
- Experimentos Con Diodo InfrarrojoDocument5 pagesExperimentos Con Diodo InfrarrojoTammy WashingtonNo ratings yet
- Long Range FM TransmitterDocument2 pagesLong Range FM TransmitterHaspreet SinghNo ratings yet
- Design and Development of Low-Range Frequency ModuDocument7 pagesDesign and Development of Low-Range Frequency ModuMohamed Amine TahiriNo ratings yet
- DcomunDocument11 pagesDcomunzubair tahirNo ratings yet
- Adi Design SolutionDocument7 pagesAdi Design SolutionMark John Servado AgsalogNo ratings yet
- Project ReportDocument35 pagesProject ReportNitish Gupta100% (1)
- Fiber AssignmentDocument4 pagesFiber AssignmentFranch Maverick Arellano LorillaNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Infra Red Remote ControlDocument19 pagesProject Report On Infra Red Remote ControlDIPAK VINAYAK SHIRBHATE88% (8)
- 6 ART Banda de TransmisionDocument3 pages6 ART Banda de TransmisionFELIX PARCA ACEVEDONo ratings yet
- Analog Project ReportDocument3 pagesAnalog Project Reportfahadsaeed93No ratings yet
- Laser Torch Based Voice Transmitter and ReceiverDocument15 pagesLaser Torch Based Voice Transmitter and ReceiverMithun RamNo ratings yet
- Passive RF Receiver Design For Wireless Sensor NetworksDocument4 pagesPassive RF Receiver Design For Wireless Sensor NetworksSarah HeadNo ratings yet
- 1) Wireless Headphone ReceiverDocument28 pages1) Wireless Headphone ReceiverPetarPetrovicNo ratings yet
- 7 - AgcDocument5 pages7 - AgcRadha KrishnaNo ratings yet
- VLF Regen RXDocument6 pagesVLF Regen RXBảo Bình100% (1)
- Linear Wave Shaping: Name of The Component/Equipment Specifications QuantityDocument61 pagesLinear Wave Shaping: Name of The Component/Equipment Specifications QuantitySainadh YerrapragadaNo ratings yet
- Edn Design Ideas IIIDocument5 pagesEdn Design Ideas IIIagmnm1962100% (2)
- Communication ReportDocument47 pagesCommunication Reportitsdriftlover0112No ratings yet
- DSBSC ReportDocument8 pagesDSBSC ReportaravindsnistNo ratings yet
- Ofc Module - 03Document7 pagesOfc Module - 03shameem v.pNo ratings yet
- Universal Paper (19.11.2018)Document4 pagesUniversal Paper (19.11.2018)Prof. M.P. KurveyNo ratings yet
- EC Electronics and Communications: Section 1: Engineering MathematicsDocument3 pagesEC Electronics and Communications: Section 1: Engineering MathematicspradyumnNo ratings yet
- Appendix C: Syllabus Content: GA General AptitudeDocument5 pagesAppendix C: Syllabus Content: GA General AptitudepradyumnNo ratings yet
- SMART GLOVE: Sign To Speech Conversion and Home Automation Control For Mute CommunityDocument5 pagesSMART GLOVE: Sign To Speech Conversion and Home Automation Control For Mute CommunitypradyumnNo ratings yet
- Image Processing Based Speaking System For Mute People Using Hand GesturesDocument5 pagesImage Processing Based Speaking System For Mute People Using Hand GesturespradyumnNo ratings yet
- Hand Gesture Recognition Based On Computer Vision: A Review of TechniquesDocument29 pagesHand Gesture Recognition Based On Computer Vision: A Review of TechniquespradyumnNo ratings yet
- R20 MPMC Unit IiiDocument25 pagesR20 MPMC Unit IiiMaddineni TejaNo ratings yet
- Machines 10 01167 v2Document23 pagesMachines 10 01167 v2Nay Min AungNo ratings yet
- 44 45 25 35 PDFDocument264 pages44 45 25 35 PDFDAVID LOPEZNo ratings yet
- 7-Circuit & Load CalculationDocument5 pages7-Circuit & Load Calculationbuddhika MadusankaNo ratings yet
- Mechanic Power ElectronicsDocument40 pagesMechanic Power ElectronicshaleemNo ratings yet
- Annexure - I SYLLABUS For Test (POST - Assistant Engineer/ Electrical), Now Re-Designated As Assistant Executive Engineer/ ElectricalDocument2 pagesAnnexure - I SYLLABUS For Test (POST - Assistant Engineer/ Electrical), Now Re-Designated As Assistant Executive Engineer/ ElectricalSowmyaNo ratings yet
- B.date of Written Test: C.venue of Written Test: D.reporting Time: 12.45 PM To 01.45 PM E.duration of Written Test: 2 Hours From 02.00 PM To 04.00 PMDocument2 pagesB.date of Written Test: C.venue of Written Test: D.reporting Time: 12.45 PM To 01.45 PM E.duration of Written Test: 2 Hours From 02.00 PM To 04.00 PMSubhash KorumilliNo ratings yet
- 58-14-2130d4 - Torre de Iluminacion MilwakeeDocument8 pages58-14-2130d4 - Torre de Iluminacion MilwakeepridenimrodNo ratings yet
- Bu0040 6070402 en 4923 DeskDocument80 pagesBu0040 6070402 en 4923 Deskolivier.bigouretNo ratings yet
- Scientific Instruments PerformanceDocument3 pagesScientific Instruments PerformancepavanNo ratings yet
- Pitch Deck - Peo-PalDocument19 pagesPitch Deck - Peo-PalGaurav KhannaNo ratings yet
- L3 BB Troubleshooting Guide XT1650-01-XT1650-02-XT1650-03-XT1650-05 V1.0Document100 pagesL3 BB Troubleshooting Guide XT1650-01-XT1650-02-XT1650-03-XT1650-05 V1.0danny1977No ratings yet
- Yaskawa SGDG 01GT ManualDocument83 pagesYaskawa SGDG 01GT ManualAlexander DíazNo ratings yet
- Sessional Test For Electrical. (EDDE-II)Document13 pagesSessional Test For Electrical. (EDDE-II)Deepanshu SinghNo ratings yet
- ACS800 MultiDriveDocument104 pagesACS800 MultiDriveYasir AbdooNo ratings yet
- 16.461E-MagIIHomeworkandAdditionalMaterials 000 PDFDocument138 pages16.461E-MagIIHomeworkandAdditionalMaterials 000 PDFsamwel kadindaNo ratings yet
- Electrolyte-Gated Transistors For Synaptic Electronics, Neuromorphic Computing, and Adaptable BiointerfacingDocument24 pagesElectrolyte-Gated Transistors For Synaptic Electronics, Neuromorphic Computing, and Adaptable Biointerfacingbareya.eztuNo ratings yet
- Installation & User's Instructions: Kit No 5117391Document5 pagesInstallation & User's Instructions: Kit No 5117391PindiNo ratings yet
- Rtl8762cmf Rtl8752cmf Datasheet 0.72Document43 pagesRtl8762cmf Rtl8752cmf Datasheet 0.72Light in The WoodsNo ratings yet
- Communication Systems (ELE 3103) RCS 2017Document2 pagesCommunication Systems (ELE 3103) RCS 2017devangNo ratings yet
- SAEON A Pocket Size Safety Alarm System For Emergency - HATULANDocument34 pagesSAEON A Pocket Size Safety Alarm System For Emergency - HATULANKarl Louie PabustanNo ratings yet
- IET Poster Electrical Safety PDFDocument1 pageIET Poster Electrical Safety PDFZuraimi JohariNo ratings yet
- Jeflea - Victor - Lista Lucrari - 2019 PDFDocument5 pagesJeflea - Victor - Lista Lucrari - 2019 PDFMihaela Liliana ZencencoNo ratings yet
- OEC Elite CFD and II Technical Datasheet Nov 2016 English PDFDocument84 pagesOEC Elite CFD and II Technical Datasheet Nov 2016 English PDFSergio Cabrera ArdayaNo ratings yet
- Penelaahan Rencana Kebutuhan TuDocument2,801 pagesPenelaahan Rencana Kebutuhan TuGalih ListyaniNo ratings yet