Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Etap Software Introduction
Uploaded by
Akhter IqbalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Etap Software Introduction
Uploaded by
Akhter IqbalCopyright:
Available Formats
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
LAB#07
To become familiar with ETAP (Electrical Transient Analysis Program)
OBJECTIVE
To learn the modeling of an electrical power system on ETAP software
THEORY
ETAP SOFTWARE INTRODUCTION:
ETAP stands for Electrical Transient Analysis Program; this amazing software suite covers a
wide range of electrical engineering domains; from software for network analysis to power
distribution. The wide range of software modules from ETAP are one of the most beneficial and
effective for electrical engineers. The Arc flash analysis software from ETAP allows engineers to
use simulation models to identify and mitigate arc flash hazards in the electrical power system
and other arc flash related issues. Here we are using this software to analyze basic operation of
power system during transients, normal operation and fault conditions without actually
interfacing with practical power system.
ETAP is used for following purposes:
a) Designing electrical Power system
b) Load Flow analysis
c) Fault Analysis/ Short circuit analysis
d) Arc flash analysis
e) Contingency Analysis
f) Protection & Coordination
g) Network Optimization
POWER SYSTEM COMPONENTS IN ETAP:
The main parts of a power system that we generally come across are as follows:
1. Power Grid
2. Bus bar
3. Power Cable
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Sharae Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
4. Transformer
5. Circuit breaker
6. Relays
7. Fuse
8. Load (motor)
The detailed meaning of them is given below:
1. Power Grid: An electrical grid is an interconnected network for delivering electricity to
consumers. It consists of generating stations that produce electrical power, high voltage
transmission lines that carry electrical power from distance sources to demand centres
and distribution lines that connect individual consumers. It looks as shown below in
ETAP.
2. Bus bar: A bus as regard to the power system is an electrical junction (node) .It is a strip
or bar of copper, brass or aluminium that conducts electricity within a switchboard,
distribution board, substation, battery bank, or other electrical apparatus. Its main purpose
is to conduct a substantial current of electricity.
3. Power Cable: A power cable is an assembly of one or more electrical conductors,
usually held together with an overall sheath. The assembly is used for transmission of
electrical power. Power cables may be installed as permanent wiring within buildings,
buried in the ground, run overhead, or exposed. In ETAP it looks as:
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Sharae Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
4. Transformer: Electrical power transformer is a static device which transforms electrical
energy from one circuit to another without any direct electrical connection and with the
help of mutual induction between two windings. It transforms power from one circuit to
another without changing its frequency but may be in different voltage level. It steps up
or steps down the voltage by changing the number of windings in primary and secondary.
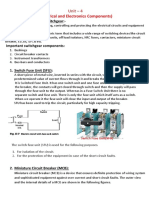
5. Circuit breaker: A circuit breaker is an automatically operated electrical switch
designed to protect an electrical circuit from damage caused by overload or short circuit.
Its basic function is to detect a fault condition and interrupt current flow. Unlike a fuse,
which operates once and then must be replaced, a circuit breaker can be reset (either
manually or automatically) to resume normal operation. Mainly here we come across two
types of CB’s. They are
High Voltage Circuit Breaker (HVCB): High-voltage breakers are nearly always
solenoid-operated, with current sensing protective relays operated through current
transformers of about 72.5KV or higher.
Low Voltage Circuit Breaker (LVCB): Low-voltage (less than 1,000 VAC) types are
common in domestic, commercial and industrial application.
6. Relays: A relay is an electrically operated switch. Many relays use an electromagnet
to mechanically operate a switch. Relays are used where it is necessary to control a
circuit by a low-power signal (with complete electrical isolation between control and
controlled circuits), or where several circuits must be controlled by one signal. There are
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Sharae Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
mainly relays we use in ETAP. They are Over Current Relay, In-line Overload Protection
Relay, Voltage Relay, Differential Relay, Frequency Relay.
i) In-line Overload Relay: A relay that opens a circuit when the load in the circuit
exceeds a preset value, in order to provide overload protection; usually respondsto
excessive current, but ma y respond to excessive values of power, temperature, or
other quantities Also known as overload release. In ETAP it is denoted by 49
which is ANSI code for Inline overload relay.
ii) Over Current Relay: A digital over current relay is a type of protective relay
which operates when the load current exceeds a pickup value. The ANSI device
number is 50 for an instantaneous over current (IOC) and 51 for a time over
current (TOC). In a typical application the over current relay is connected to a
current transformer and calibrated to operate at or above a specific current level.
When the relay operates, one or more contacts will operate and energize to trip
(open) a circuit breaker.
iii) Voltage Relay: A relay which operates when the system voltage when the system
falls below or above a certain preset value. For an under voltage relay the ANSI
code is 27, which is used as a standard in ETAP.
iv) Differential Relay: A relay which responds to a difference in two voltages or
currents. For example, such a relay may have two coils and only respond when
the respective currents of said coils vary beyond a specified amount. It’s denoted
by the ANSI code no.87 in ETAP.
v) Frequency Relay: Relay which functions at a predetermined value of frequency;
may be an overfrequency relay, an under-frequency relay, or a combinationof
both. It is denoted by the ANSI code no. 81 in ETAP to determine it’s specific
function.
7. Fuse: A fuse is a type of low resistance resistor that acts as a sacrificial device to
provide overcurrent protection, of either the load or source circuit. Its essential
component is a metal wire or strip that melts when too much current flows through it,
interrupting the circuit that it connects. Short circuits, overloading, mismatched loads, or
device failure are the prime reasons for excessive current. Fuses are an alternative to
circuit breakers. It can be seen in ETAP as:
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Sharae Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
FACULTY OF ENGINEERING SCIENCES AND TECHNOLOGY
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology
Hamdard University
8. Load (Motor): The electric power delivered by a power source to a power user. If
variations in voltage are small, load can be characterized by magnitude of current. The
term “load” is also often applied to the device consuming the electric power—that is, to a
piece of equipment, such as a motor or a lighting device. In ETAP we come across
mainly Induction Motor, Synchronous Motor and Lumped load.
LAB TASK:
Design any Electrical Power System using ETAP and attach the SLD.
Learning Outcomes:
Upon successful completion of the lab, students will be able to:
LO1: Get familiar with ETAP software
LO2: To learn to design power system on ETAP
Lab Report:
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
______________________________________________________________________________
Hamdard Institute of Engineering & Technology, Hamdard University
Sharae Madinat Al-Hikmah, Muhammad Bin Qasim Avenue, Karachi 74600, Pakistan.
You might also like
- Power+Electronics+for+Technology+By+Ashfaq+Ahmed+ 1 PDFDocument438 pagesPower+Electronics+for+Technology+By+Ashfaq+Ahmed+ 1 PDFAbdullah Mahsud100% (5)
- Switches PresentationDocument20 pagesSwitches PresentationAnushree Gupta100% (3)
- UET Electronics Lab Provides Platform for Student ProjectsDocument7 pagesUET Electronics Lab Provides Platform for Student ProjectsMr_asad_20No ratings yet
- PV PQ Bus Switching Power Flow Pscc2008 - 128Document7 pagesPV PQ Bus Switching Power Flow Pscc2008 - 128kcirrenwodNo ratings yet
- III II Ps Lab ManualDocument87 pagesIII II Ps Lab ManualAadil Rehman100% (1)
- EE454 PowerSystemProtection Course Outline 2016Document4 pagesEE454 PowerSystemProtection Course Outline 2016Hafsa IjazNo ratings yet
- Lab 4: C A C: Lippers ND LampersDocument9 pagesLab 4: C A C: Lippers ND LampersAhmed ChNo ratings yet
- Pdu Lab Manual 104Document94 pagesPdu Lab Manual 104Rana FaizanNo ratings yet
- Performance Analysis of Multilevel Inverter Using Matlab/SimulinkDocument63 pagesPerformance Analysis of Multilevel Inverter Using Matlab/Simulinkvinayak jith100% (1)
- Electrical Engineering by M.handa, A. HANDADocument358 pagesElectrical Engineering by M.handa, A. HANDAraheemNo ratings yet
- Simulation of Power System Transient DisturbancesDocument6 pagesSimulation of Power System Transient DisturbancesAhmed58seribegawanNo ratings yet
- VK MEHTA One liner MCQsDocument203 pagesVK MEHTA One liner MCQsFakherNo ratings yet
- Substation Automation Basics - The Next GenerationDocument8 pagesSubstation Automation Basics - The Next GenerationAlly RaxaNo ratings yet
- Hvdc&Facts SyllabusDocument2 pagesHvdc&Facts SyllabusChristopher Ortega100% (1)
- Design of Unified Power Quality Conditioner Using Fuzzy Logic Controller To Improve Power QualityDocument76 pagesDesign of Unified Power Quality Conditioner Using Fuzzy Logic Controller To Improve Power QualityPhani PhaniNo ratings yet
- Fast Methods For Transient Stability Prediction in Power SystemsDocument20 pagesFast Methods For Transient Stability Prediction in Power SystemslisusedNo ratings yet
- Simple Mips Processor in VerilogDocument18 pagesSimple Mips Processor in VerilogMALIK AWAIS UR REHMANNo ratings yet
- Pscad Manual v4 6 PDFDocument529 pagesPscad Manual v4 6 PDFAsdera CodigoNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document2 pagesAssignment 1Shareef ChampNo ratings yet
- Automatic Power Supply Control From Four Different SourcesDocument21 pagesAutomatic Power Supply Control From Four Different SourcesJishnu Ps100% (1)
- E M 1 Lab ManualDocument63 pagesE M 1 Lab ManualdsparanthamanNo ratings yet
- Distribution System Design For Smart CityDocument167 pagesDistribution System Design For Smart Cityعمل الخيرNo ratings yet
- TQM Principles and Tools for Quality ImprovementDocument23 pagesTQM Principles and Tools for Quality ImprovementKanimozhivendhan Vendhan0% (1)
- High Voltage EngineeringDocument54 pagesHigh Voltage EngineeringJakeNo ratings yet
- HVDC transmission line from Ethiopia to Isinya (KenyaDocument9 pagesHVDC transmission line from Ethiopia to Isinya (KenyakarthikNo ratings yet
- Projects Titles For Protection - W2017Document3 pagesProjects Titles For Protection - W2017Ahmad AbunassarNo ratings yet
- Project Report EngineeringDocument48 pagesProject Report EngineeringSonu DhangarNo ratings yet
- Verilog Code For Digital Clock ProjectDocument10 pagesVerilog Code For Digital Clock ProjectTalat KhAnNo ratings yet
- HVDC SyllabusDocument1 pageHVDC Syllabussk.karimeeeNo ratings yet
- PS7008 Smart GridDocument2 pagesPS7008 Smart GridLakshmi Zahara100% (1)
- The University of Lahore, Islamabad Campus Course: Power System Protection Lab Work Sheet 4Document8 pagesThe University of Lahore, Islamabad Campus Course: Power System Protection Lab Work Sheet 4Hayat AnsariNo ratings yet
- Power Switches and Their Applications in Power ElectronicsDocument58 pagesPower Switches and Their Applications in Power ElectronicsMuhammad NazeerNo ratings yet
- Sivan Aga RajuDocument12 pagesSivan Aga RajuSatish Moupuri100% (1)
- Electrical InstallationsDocument48 pagesElectrical InstallationsSyed Muzammil AliNo ratings yet
- CH 1 Intro 2 InstrumentationDocument22 pagesCH 1 Intro 2 InstrumentationNorkarlina Binti Khairul AriffinNo ratings yet
- Experiment No. 5 Darlington Pair Connection: (CITATION Ele /L 1033)Document4 pagesExperiment No. 5 Darlington Pair Connection: (CITATION Ele /L 1033)Dan BautistaNo ratings yet
- Over Under Voltage and Over Current Protection SystemDocument8 pagesOver Under Voltage and Over Current Protection SystemHassan AliNo ratings yet
- Modeling of Three-Winding Transformers PDFDocument20 pagesModeling of Three-Winding Transformers PDFGhislainNo ratings yet
- The University of Lahore, Islamabad Campus Course: Power System Protection Lab Work Sheet 6Document7 pagesThe University of Lahore, Islamabad Campus Course: Power System Protection Lab Work Sheet 6Hayat AnsariNo ratings yet
- Taswar Abbas 1Document62 pagesTaswar Abbas 1Sumaira SaifNo ratings yet
- Modeling Transformers With Internal Incipient FaultsDocument8 pagesModeling Transformers With Internal Incipient Faultsdbhargavreddy100% (1)
- 3 Voltage Level Improving by Using Static VARDocument7 pages3 Voltage Level Improving by Using Static VAREngr Muhammad Imran KhanNo ratings yet
- BEE Assignment Unit 4Document13 pagesBEE Assignment Unit 4Abhishek RaoNo ratings yet
- CESC Training on Distribution SystemsDocument44 pagesCESC Training on Distribution SystemsqswerNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics Lab Manual Safety GuideDocument68 pagesPower Electronics Lab Manual Safety GuideJonathan727No ratings yet
- M.E.Electrical Power System - 2 PDFDocument32 pagesM.E.Electrical Power System - 2 PDFAnonymous 9VcxlFErfNo ratings yet
- Optimal SVC Placement for Voltage Improvement and Loss ReductionDocument10 pagesOptimal SVC Placement for Voltage Improvement and Loss Reductionkubera uNo ratings yet
- CEP Impulse VoltageDocument10 pagesCEP Impulse VoltageKASHIF zamanNo ratings yet
- DC DC Converter Simulation White PaperDocument12 pagesDC DC Converter Simulation White PaperGiulio Tucobenedictopacifjuamar RamírezbettiNo ratings yet
- Impulse Voltage Generator Modelling Using MATLAB PDFDocument8 pagesImpulse Voltage Generator Modelling Using MATLAB PDFAsmaNo ratings yet
- Expt 3 - EEM - Dielectric Strength of Liquid Insulating MaterialDocument6 pagesExpt 3 - EEM - Dielectric Strength of Liquid Insulating MaterialAvaniPujaraNo ratings yet
- Types of AC power distribution systems overviewDocument20 pagesTypes of AC power distribution systems overviewMario Abd El NourNo ratings yet
- Integration of Green and Renewable Energy in Electric Power SystemsFrom EverandIntegration of Green and Renewable Energy in Electric Power SystemsNo ratings yet
- Top-Down Digital VLSI Design: From Architectures to Gate-Level Circuits and FPGAsFrom EverandTop-Down Digital VLSI Design: From Architectures to Gate-Level Circuits and FPGAsNo ratings yet
- SCADA supervisory control and data acquisition Third EditionFrom EverandSCADA supervisory control and data acquisition Third EditionNo ratings yet
- Time Current Characteristics of Over-Current Relay Suing ETAPDocument8 pagesTime Current Characteristics of Over-Current Relay Suing ETAPAkhter IqbalNo ratings yet
- Time Current Characteristics of Fuse Using ETAPDocument7 pagesTime Current Characteristics of Fuse Using ETAPAkhter IqbalNo ratings yet
- Short Circuit Analysis For A Given Network Using ETAPDocument4 pagesShort Circuit Analysis For A Given Network Using ETAPAkhter Iqbal100% (1)
- Load Flow Analysis For A Given Network Using ETAPDocument4 pagesLoad Flow Analysis For A Given Network Using ETAPAkhter IqbalNo ratings yet
- Open Ended Lab: (Freedom To Develop Own Experiment Without Guidelines)Document2 pagesOpen Ended Lab: (Freedom To Develop Own Experiment Without Guidelines)Akhter IqbalNo ratings yet
- Open Ended Lab: (Freedom To Develop Own Experiment Without Guidelines)Document1 pageOpen Ended Lab: (Freedom To Develop Own Experiment Without Guidelines)Akhter IqbalNo ratings yet
- Open Ended Lab: (Freedom To Develop Own Experiment Without Guidelines)Document2 pagesOpen Ended Lab: (Freedom To Develop Own Experiment Without Guidelines)Akhter IqbalNo ratings yet
- Earth 2Document25 pagesEarth 2Vikas Srivastav75% (4)
- 7SG11 Argus 1 2 4 and 6 Catalogue SheetDocument22 pages7SG11 Argus 1 2 4 and 6 Catalogue SheetGyan SagarNo ratings yet
- Eddy CurrentsDocument5 pagesEddy CurrentsDivyanshu KaushikNo ratings yet
- TC Media Tension Abb - ELECTRICADocument2 pagesTC Media Tension Abb - ELECTRICAagvega69109No ratings yet
- Minutes of SOUTHCO Performance Review for 2009-10Document18 pagesMinutes of SOUTHCO Performance Review for 2009-10havejsnjNo ratings yet
- Type Approval Certificate: ABB AB, Control ProductsDocument3 pagesType Approval Certificate: ABB AB, Control ProductsChief EngineerNo ratings yet
- Otc 25777 MS PDFDocument9 pagesOtc 25777 MS PDFObi MogboNo ratings yet
- Technical Data Sheet Damper Actuator TMC24ADocument4 pagesTechnical Data Sheet Damper Actuator TMC24AdbricchiNo ratings yet
- Lm1205/Lm1207 130 Mhz/85 MHZ RGB Video Amplifier System With BlankingDocument24 pagesLm1205/Lm1207 130 Mhz/85 MHZ RGB Video Amplifier System With BlankingedgarlibanioNo ratings yet
- Standard Operating Procedure MaintenanceDocument6 pagesStandard Operating Procedure MaintenancePADCL100% (1)
- KM3NET RAMS Analysis WRS SCB 20102017Document910 pagesKM3NET RAMS Analysis WRS SCB 20102017Ikhtiander IkhtianderNo ratings yet
- E Advanced Service Functional Blocks C-Arm C-ArmDocument78 pagesE Advanced Service Functional Blocks C-Arm C-ArmNirav Barot100% (3)
- Topics Covered in Introduction To Batteries The Voltaic Cell Common Types of Primary Cells Lead-Acid Wet Cell Additional Types of Secondary CellsDocument32 pagesTopics Covered in Introduction To Batteries The Voltaic Cell Common Types of Primary Cells Lead-Acid Wet Cell Additional Types of Secondary CellsArvind VNo ratings yet
- Software-Defined-Radio: National University of Science and TechnologyDocument19 pagesSoftware-Defined-Radio: National University of Science and TechnologyZain ShabbirNo ratings yet
- 08 SwitchDisconnectors LV10 042023 EN 202306011354213745Document156 pages08 SwitchDisconnectors LV10 042023 EN 202306011354213745hssvaldirNo ratings yet
- Properties of Copper and Copper AlloysDocument1 pageProperties of Copper and Copper Alloysankesh_ghoghariNo ratings yet
- Datasheet 117 KW Diesel Generator 146 Kva 3 Phase Sdmo John Deere J120uDocument5 pagesDatasheet 117 KW Diesel Generator 146 Kva 3 Phase Sdmo John Deere J120uIsbelia ContrerasNo ratings yet
- Elco Power CapacitorDocument2 pagesElco Power CapacitorFrancis SalviejoNo ratings yet
- TV Tuner Functions and Front-End ServicingDocument32 pagesTV Tuner Functions and Front-End ServicingAriel BecerraNo ratings yet
- Fire Alarm Project ReportDocument28 pagesFire Alarm Project ReportPooja MehtaNo ratings yet
- Catalog5 ASFMDocument10 pagesCatalog5 ASFMccdcatNo ratings yet
- Rechargeable Lithium Battery SpecificationDocument9 pagesRechargeable Lithium Battery SpecificationGrzegorz KamińskiNo ratings yet
- DD-5000 enDocument28 pagesDD-5000 enDobrescu VictorNo ratings yet
- Atv11 HU18M2E - Actionare Masina de Masurat Grosimi PDFDocument25 pagesAtv11 HU18M2E - Actionare Masina de Masurat Grosimi PDFRata IonNo ratings yet
- Borri B400 Datasheet Com5Document2 pagesBorri B400 Datasheet Com5Anonymous RlEl9pZFbtNo ratings yet
- QUINT4-PS/1AC/24DC/5: Power Supply UnitDocument50 pagesQUINT4-PS/1AC/24DC/5: Power Supply UnitOmar Alfredo Del Castillo QuispeNo ratings yet
- Re Voltage StabilityDocument27 pagesRe Voltage StabilityTravis WoodNo ratings yet
- LSQ5 Man-0964 V3.1.0 enDocument48 pagesLSQ5 Man-0964 V3.1.0 enDiego Mondragon100% (1)
- Electrostatis Worksheet McqsDocument23 pagesElectrostatis Worksheet Mcqsns857471No ratings yet