Professional Documents
Culture Documents
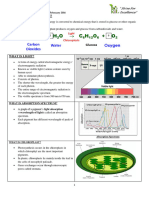
Herbicide - Photosynthesis & Pigment Synthesis Inhibitors
Uploaded by
Catherine TangOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Herbicide - Photosynthesis & Pigment Synthesis Inhibitors
Uploaded by
Catherine TangCopyright:
Available Formats
Photosynthesis & Pigment Synthesis Inhibitors
Josie Hugie, Research and Development Scientist, Syngenta Crop Protection
Email: josie.hugie@syngenta.com
1. Photosynthesis II (PSII) Inhibitors
Uptake & Translocation
Chemistry: Lipophilic – penetrates cuticle
Basic molecules - Xylem mobile only --> Transpiration stream
Mode & Mechanism of action
PSII inhibitors compete with plastoquinone (PQ) at QB binding site of D1 protein
- Blocks electron flow through photosynthesis
- Creation of reactive oxygen species (ROS)
- ROS damage membranes
Resistance http://www.hracglobal.com/
HRAC Group 5
Triazines (atrazine, simazine), Triazinones, Triazolinones, Uracils, Pyridazinones,
Phenyl-carbamates
HRAC Group 6
Nitriles (bromoxynil), benzothiadiazinones, phenyl-pyridazines
HRAC Group 7
Ureas (diuron), Amides
Resistance: Known mechanisms
Target site resistance: Mutation does not favor binding
Metabolism: Less common - Crop tolerance & selectivity
Symptomology
• Soil Applied Symptoms: Initial injury = first photosynthetic leaves
Chlorosis leaf margins & older leaves
Foliar Applied Symptoms: Chlorosis & necrosis at
leaf tips, older leaves first
• Injury and carryover: greater with late application,
dry season, & soil pH >7.2
2. Pigment synthesis Inhibitors
Mode of action
Depletion of antioxidants (plant protective pigments)
Increases damage from reactive oxygen (ROS)
Damages membranes & cellular compartments
Uptake & translocation
• Weak acids: Penetrate cuticle - Phloem-trapped
• Translocated through phloem to new tissues
Mechanism of action
• HPPD inhibitors: Depletes tocopherols, carotenoids, & plastoquinone
• 1-deoxyxylulose-5-phosphate synthase (DOXPS) inhibitors:
Deplete carotenoids & plastoquinone
• Phytoene desaturase (PDS) inhibitor: Depletes carotenoids
• Lycopene cyclase inhibitor: Depletes carotenoids
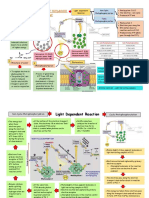
PSII Inhibitors PSII Inhibitors
Photosynthesis review Photosynthesis review
• Photosystem II (PSII) – first • Photosystem II (PSII) – first
site to accept light energy site to accept light energy
• Energy from light drives • Energy from light drives
electron (e-) transfer electron (e-) transfer
• Plastoquinone used to carry • Plastoquinone used to carry
electrons to next protein electrons to next protein
(Cytochrome B6f) (Cytochrome B6f)
Buchanan, 2000 Buchanan, 2000
PSII Inhibitors PSII Inhibitors
Photosynthesis review Mechanism of action
• Photosystem II (PSII) – first
site to accept light energy • PSII inhibitors compete with
PSII inhibitors
plastoquinone (PQ) at QB
• Energy from light drives binding site of D1 protein
electron (e-) transfer
• Blocks electron transfer
• Plastoquinone used to carry through photosynthesis
electrons to next protein
(Cytochrome B6f)
Buchanan, 2000 Buchanan, 2000
PSII Inhibitors
Mechanism of action
ROS
• Compete with plastoquinone
ROS (PQ) as an e- acceptor at QB
ROS
binding site of D1 protein
• Blocks electron transfer
PSII inhibitor
through photosynthesis
• Generates reactive oxygen
species (ROS)
• ROS damage cell walls
• Antioxidants
partial ROS protection
(tocopherols (Vit. E), carotenoids)
Buchanan, 2000
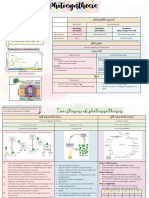
Pigment synthesis Inhibitors
A QUICK BIOCHEMISTRY LESSON
ENZYMES
HPPD – Hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase
PDS – Phytoene desaturase
DOXPS – Deoxyxylulose-5-phosphate synthase
Pigment synthesis Inhibitors Pigment synthesis Inhibitors
HPPD inhibitor
Tyrosine HPPD Tocopherols Tyrosine HPPD Tocopherols
(Vit. E) (Vit. E)
Plastoquinone Plastoquinone
PDS inhibitor
Phytoene PDS Carotenoids (beta-carotene) Phytoene PDS Carotenoids (beta-carotene)
Lycopene cyclase inhibitor
Reactive Oxygen Species Quenchers! Lycopene
DOXPS DOXPS DOXPS inhibitor
ENZYMES ENZYMES
HPPD – Hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase HPPD – Hydroxyphenylpyruvate dioxygenase
PDS – Phytoene desaturase PDS – Phytoene desaturase
DOXPS – Deoxyxylulose-5-phosphate synthase DOXPS – Deoxyxylulose-5-phosphate synthase
Resistance
HRAC Group 11 (lycopene cyclase)
Triazoles (amitrole)
HRAC Group 12 (phytoene desaturase)
Pyridazinones (norflurazon), pyridinecarboxamides, ‘other’ - fluridone
HRAC Group 13 (unknown)
Isoxizolidinones (DOXP synthase inhibitor), Ureas, Diphenyl ethers
HRAC Group 27 (HPPD)
Triketones (mesotrione), isoxazoles, pyrazoles
Symptomology
• New tissue chlorotic or white
• Bleached tissue - necrotic
3. Interaction of PSII & Pigment inhibitors
Photosynthesis inhibitors Photosynthesis inhibitors
AND Pigment inhibitors AND Pigment inhibitors
Tocopherols, • PSII inhibitors Tocopherols, • PSII inhibitors
ROS Carotenoids ROS Carotenoids
- block electron flow - block electron flow
ROS - generate reactive oxygen ROS - generate reactive oxygen
PSII inhibitor PSII inhibitor
• Pigments (tocopherols & • Pigment inhibitors
carotenoids - block synthesis of protective
- Quench ROS & excess energy molecules
- removing protection from ROS
(reactive oxygen species)
Buchanan, 2000 Buchanan, 2000
4. Summary
• Photosystem II (PSII) inhibitors
– Xylem mobile
– Block electron transfer
– Reactive species generation
– Necrosis on leaf margins, older leaves
• Pigment synthesis inhibitors
– Phloem mobile
– Block antioxidant synthesis
– Increased Reactive Oxygen Species damage
– Chlorotic or bleached young tissue
You might also like
- HO 18 PhtosynthesisDocument9 pagesHO 18 PhtosynthesisNo RefundNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis - The Light ReactionsDocument37 pagesPhotosynthesis - The Light ReactionszefotxNo ratings yet
- Goldschmidt Clermont2015Document8 pagesGoldschmidt Clermont2015marcela gomezNo ratings yet
- Bacterial PhotosynthesisDocument21 pagesBacterial PhotosynthesisYuu chanNo ratings yet
- 6.0 PhotosynthesisDocument15 pages6.0 Photosynthesisa200812No ratings yet
- Photosynthesis Part 1Document27 pagesPhotosynthesis Part 1m4h1rstNo ratings yet
- 10 1016@j Cbpa 2003 08 011Document11 pages10 1016@j Cbpa 2003 08 011marcela gomezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 17 PhotosynthesisDocument11 pagesChapter 17 PhotosynthesisSyafiqahNo ratings yet
- 5 FotosintesiDocument29 pages5 FotosintesiSerena DamianNo ratings yet
- Structure of ChlorophyllDocument94 pagesStructure of ChlorophyllSunil Kumar SahuNo ratings yet
- Jacs 3c01682Document18 pagesJacs 3c01682JuanNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument4 pagesPhotosynthesisVanessa AlexanderNo ratings yet
- Chapter 19Document61 pagesChapter 19Michelle Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Oxidative Phosphorylation and Photophosphorylation Mechanisms ExplainedDocument33 pagesOxidative Phosphorylation and Photophosphorylation Mechanisms ExplainedkpsantanaNo ratings yet
- EPR Studies On Photosintetic BacteriaDocument35 pagesEPR Studies On Photosintetic BacteriaBrandon ArceNo ratings yet
- Plant Physiology Lab Fall 2006 and Spring 2009 Photosynthesis Light ReactionsDocument16 pagesPlant Physiology Lab Fall 2006 and Spring 2009 Photosynthesis Light ReactionsdarshanpandaNo ratings yet
- Bio Notes 2.0 Chapter 8Document3 pagesBio Notes 2.0 Chapter 8farrisya zulyazanNo ratings yet
- Molecules 21 00342Document18 pagesMolecules 21 00342Pranati DasNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis - Intro and Light Dependent ReactionsDocument32 pagesPhotosynthesis - Intro and Light Dependent ReactionsMil s100% (1)
- 2021 - J. Phys. Chem. Lett. - BibhisanDocument7 pages2021 - J. Phys. Chem. Lett. - Bibhisanbibhisan royNo ratings yet
- 10 1039@c1ob06020a PDFDocument7 pages10 1039@c1ob06020a PDFPrasanth BitlaNo ratings yet
- Topic 2 Photosynthesis FS2014 STDV Part 2Document29 pagesTopic 2 Photosynthesis FS2014 STDV Part 2宛仪No ratings yet
- Photoelectrochemical Cells Based On Photosynthetic Systems: A ReviewDocument9 pagesPhotoelectrochemical Cells Based On Photosynthetic Systems: A ReviewMaryam SabouriNo ratings yet
- Lemeille-Rochaix2010 Article StateTransitionsAtTheCrossroad PDFDocument14 pagesLemeille-Rochaix2010 Article StateTransitionsAtTheCrossroad PDFGester GutiérrezNo ratings yet
- Fphys 2017 00191Document13 pagesFphys 2017 00191Ashwary Sheel Wali Research Scholar, Dept of Mech Engg., IIT (BHU)No ratings yet
- The Unusual Reaction of Semiquinone Radicals With Molecular OxygenDocument12 pagesThe Unusual Reaction of Semiquinone Radicals With Molecular OxygenZongxin JinNo ratings yet
- CherevatskayaDocument14 pagesCherevatskayaRajesh NorseNo ratings yet
- PHOTOSYNTHESISDocument11 pagesPHOTOSYNTHESISDRISTIE KALITANo ratings yet
- CAPE. Photosystems & Photophosphorylation.Document41 pagesCAPE. Photosystems & Photophosphorylation.Rocheal WhittinghamNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Plant Physiology and DevelopmentDocument46 pagesModule 4 Plant Physiology and DevelopmentMaria Angela Del GallegoNo ratings yet
- Molecular Engineering of Robust Starburst-Based Organic Photosensitizers For Highly E Cient Photocatalytic Hydrogen Generation From WaterDocument13 pagesMolecular Engineering of Robust Starburst-Based Organic Photosensitizers For Highly E Cient Photocatalytic Hydrogen Generation From Waterapi-691399461No ratings yet
- Genbio1 ReviewerDocument3 pagesGenbio1 ReviewerStevenzel EstellaNo ratings yet
- Sr AIIMS Super-60 Key & Solved QuestionsDocument15 pagesSr AIIMS Super-60 Key & Solved QuestionsAdithya BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: The Light and Dark ReactionsDocument3 pagesPhotosynthesis: The Light and Dark ReactionsSuganNo ratings yet
- CSIR Unit 6@lifescience - BiotechDocument164 pagesCSIR Unit 6@lifescience - BiotechJigyasu bNo ratings yet
- Molecules 28 05269Document11 pagesMolecules 28 05269Pilaf PilafNo ratings yet
- Bacterial Photosynthesis by M Jones Free On-Line at WWW - Photobiology.infojones - HTMLDocument17 pagesBacterial Photosynthesis by M Jones Free On-Line at WWW - Photobiology.infojones - HTMLperi peeriNo ratings yet
- PhotosynthesisDocument38 pagesPhotosynthesisAnonno DipNo ratings yet
- Tailoring of Organic Dyes With Oxidoreductive Compounds To Obtain Photocyclic Radical Generator Systems Exhibiting Photocatalytic BehaviorDocument12 pagesTailoring of Organic Dyes With Oxidoreductive Compounds To Obtain Photocyclic Radical Generator Systems Exhibiting Photocatalytic BehaviorMariaNo ratings yet
- General Biology I Activity SheetDocument3 pagesGeneral Biology I Activity SheetAldous Pax ArcangelNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionDocument21 pagesPhotosynthesis: For Campbell Biology, Ninth EditionJovelyn GuerraNo ratings yet
- Stamplecoskie 2015Document8 pagesStamplecoskie 20155osNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: Capturing EnergyDocument26 pagesPhotosynthesis: Capturing EnergyJustineMarieClarisaCruzNo ratings yet
- Lecture of Local Anesthetics PDFDocument12 pagesLecture of Local Anesthetics PDFIbraheem AliNo ratings yet
- BIO C6 @notastpm04Document152 pagesBIO C6 @notastpm04Huey KaNo ratings yet
- 7단원Document9 pages7단원백지연No ratings yet
- FotosíntesisDocument19 pagesFotosíntesisCatalina ignacia kimberlyNo ratings yet
- Biological Photoreceptors: Chromophores and Photoinduced ProcessesDocument37 pagesBiological Photoreceptors: Chromophores and Photoinduced ProcessesAlbaMariaLotoNo ratings yet
- Unit 6 Notes Csir NetDocument163 pagesUnit 6 Notes Csir NetAlma VNo ratings yet
- Patterns of Electron Flow Through Light Reaction EventsDocument25 pagesPatterns of Electron Flow Through Light Reaction EventsMar'J0% (1)
- Photorefractive Protein Bacteriorhodopsin, BR, As A Material For Holographic Data-RecordingDocument7 pagesPhotorefractive Protein Bacteriorhodopsin, BR, As A Material For Holographic Data-Recordingraalbe_autorNo ratings yet
- Cellular and Molecular BiologyDocument29 pagesCellular and Molecular Biologydielleverona2No ratings yet
- Lesson 3 4 Q4Document32 pagesLesson 3 4 Q4Joshua DurogaNo ratings yet
- Rastogi and Pospisil 2010Document7 pagesRastogi and Pospisil 2010anshuslsNo ratings yet
- Principles of Photodynamic Therapy: Also Written AsDocument27 pagesPrinciples of Photodynamic Therapy: Also Written AsWilda PrihastyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 39 Plant Response To SignalsDocument160 pagesChapter 39 Plant Response To SignalsIma kuro-bikeNo ratings yet
- Summary of Notes About Light Dependent ReactionDocument4 pagesSummary of Notes About Light Dependent ReactionGilbert AmanNo ratings yet
- Cellular Transport Process Proteins Involved Energy SourceDocument2 pagesCellular Transport Process Proteins Involved Energy SourceGenalin M. Escobia-BagasNo ratings yet
- Photosynthesis: A2 Biology (9700) 2022-2023Document31 pagesPhotosynthesis: A2 Biology (9700) 2022-2023Youssef AhmedNo ratings yet
- Agropage - 2019 Review 72Document1 pageAgropage - 2019 Review 72Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- High yield but low income for japonica rice farmersDocument1 pageHigh yield but low income for japonica rice farmersCatherine TangNo ratings yet
- Agropage - 2019 Review 69Document1 pageAgropage - 2019 Review 69Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- Agropage - 2019 Review 67Document1 pageAgropage - 2019 Review 67Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- Agropage - 2019 Review 76Document1 pageAgropage - 2019 Review 76Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- Agropage - 2019 Review 71Document1 pageAgropage - 2019 Review 71Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- Agropage - 2019 Review 73Document1 pageAgropage - 2019 Review 73Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- Agropage - 2019 Review 75Document1 pageAgropage - 2019 Review 75Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- Agrochemical Industry in China: From Self-Reliance To Export To Discovery & DevelopmentDocument1 pageAgrochemical Industry in China: From Self-Reliance To Export To Discovery & DevelopmentCatherine TangNo ratings yet
- Agropage - 2019 Review 85Document1 pageAgropage - 2019 Review 85Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- Agropage - 2019 Review 70Document1 pageAgropage - 2019 Review 70Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- Agropage - 2019 Review 81Document1 pageAgropage - 2019 Review 81Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- Agropage - 2019 Review 79Document1 pageAgropage - 2019 Review 79Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- Agropage - 2019 Review 78Document1 pageAgropage - 2019 Review 78Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- Agropage - 2019 Review 83Document1 pageAgropage - 2019 Review 83Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- Agropage - 2019 Review 77Document1 pageAgropage - 2019 Review 77Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- Agropage - 2019 Review 84Document1 pageAgropage - 2019 Review 84Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- 2017 Crop Protection Adjuvants in The US and Canada 4Document1 page2017 Crop Protection Adjuvants in The US and Canada 4Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- Agropage - 2019 Review 86Document1 pageAgropage - 2019 Review 86Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- Chemicals - Revised 2014 Edition: (Photo: Bill Gordon, Bill Gordon Consulting)Document1 pageChemicals - Revised 2014 Edition: (Photo: Bill Gordon, Bill Gordon Consulting)Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- Agropage - 2019 Review 1Document1 pageAgropage - 2019 Review 1Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- Agropage - 2019 Review 87Document1 pageAgropage - 2019 Review 87Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- U.S. Adjuvant Terminology - ASTMDocument1 pageU.S. Adjuvant Terminology - ASTMCatherine TangNo ratings yet
- Oils, Surfactants and Other Additives For Farm Chemicals: Revised 2014 EditionDocument1 pageOils, Surfactants and Other Additives For Farm Chemicals: Revised 2014 EditionCatherine TangNo ratings yet
- 2017 Crop Protection Adjuvants in The US and Canada 5Document1 page2017 Crop Protection Adjuvants in The US and Canada 5Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- 2017 Crop Protection Adjuvants in The US and Canada 3Document1 page2017 Crop Protection Adjuvants in The US and Canada 3Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- Questions? Contact The NAPPC PesticideDocument1 pageQuestions? Contact The NAPPC PesticideCatherine TangNo ratings yet
- 2017 Crop Protection Adjuvants in The US and Canada 1Document1 page2017 Crop Protection Adjuvants in The US and Canada 1Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- 2021 - Seedtreatment Agropages 45Document1 page2021 - Seedtreatment Agropages 45Catherine TangNo ratings yet
- A Full Palette of Vibrant, Customizable, 40 CFR Part 180 Compliant Color SolutionsDocument1 pageA Full Palette of Vibrant, Customizable, 40 CFR Part 180 Compliant Color SolutionsCatherine TangNo ratings yet
- EECP SportDocument8 pagesEECP SportCharles100% (1)
- बायोलोजी 30yearsDocument454 pagesबायोलोजी 30yearsBhanwar PrajpateNo ratings yet
- Chapter-2 Photosynthsis: Made By:zainah Jabr Grade:12-ADocument25 pagesChapter-2 Photosynthsis: Made By:zainah Jabr Grade:12-Azainah jabrNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesMuscular SystemPaul Bronzon DurensNo ratings yet
- Alterations in Body TemperatureDocument108 pagesAlterations in Body TemperatureJosephine George JojoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular DisordersDocument20 pagesCardiovascular DisordersHampson MalekanoNo ratings yet
- Revised Neurophysiology of Pain QuestionnaireDocument2 pagesRevised Neurophysiology of Pain QuestionnaireivanNo ratings yet
- Answer Key 2Document8 pagesAnswer Key 2praveenNo ratings yet
- Sleep Deprivation and Mental HealthDocument4 pagesSleep Deprivation and Mental Healthapi-341198049No ratings yet
- 12 Tips to Stay Awake NaturallyDocument14 pages12 Tips to Stay Awake NaturallyJohayra AbbasNo ratings yet
- General Survey Vital Signs: Donniedex P. Parrocha JD, MSN (C), RNDocument26 pagesGeneral Survey Vital Signs: Donniedex P. Parrocha JD, MSN (C), RNRamzen Raphael DomingoNo ratings yet
- Parasympathomimetic DrugsDocument15 pagesParasympathomimetic DrugsRohit PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- PN Comprehensive Review CD Questions 1001-1100 (COMP: No Equations/formulas No Questions)Document54 pagesPN Comprehensive Review CD Questions 1001-1100 (COMP: No Equations/formulas No Questions)Kaye PatanindagatNo ratings yet
- Acid Base Tutorial - University of ConnecticutDocument47 pagesAcid Base Tutorial - University of ConnecticutClaudioGutierrezFrausto80% (5)
- Ischemic Heart DiseaseDocument47 pagesIschemic Heart DiseaseAbood SamoudiNo ratings yet
- Arritmias en El EmbarazoDocument10 pagesArritmias en El EmbarazoJuan Soto FarfanNo ratings yet
- Bedside Pulmonary Function TestDocument2 pagesBedside Pulmonary Function TestChandan SardarNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular (History Taking)Document6 pagesCardiovascular (History Taking)Deliciousn'tNo ratings yet
- ImmunologyDocument16 pagesImmunologyShyenNo ratings yet
- Body System 2º EnriqueDocument9 pagesBody System 2º EnriqueRUIZ CANO EnriqueNo ratings yet
- Working at Height Rescue PlanDocument1 pageWorking at Height Rescue PlanAbbas AsadNo ratings yet
- Echo Basic Measurement (ENG)Document20 pagesEcho Basic Measurement (ENG)stoicea_katalinNo ratings yet
- Fatty Acid Beta OxidationDocument59 pagesFatty Acid Beta OxidationEve YapNo ratings yet
- Chapter 12 - The Lymphatic System and Body DefensesDocument16 pagesChapter 12 - The Lymphatic System and Body DefensesHannah Lee LumosbogNo ratings yet
- Edexcel IAL A2 Biology: Topic 7 - Run For Your LifeDocument27 pagesEdexcel IAL A2 Biology: Topic 7 - Run For Your LifeErin100% (2)
- Acls Pre Course Self Assessment Study GuideDocument7 pagesAcls Pre Course Self Assessment Study Guidenova939100% (5)
- Post Operative CareDocument25 pagesPost Operative CareS .BNo ratings yet
- Women Hard Body Training Camp NutritionPlanDocument7 pagesWomen Hard Body Training Camp NutritionPlanPușcașu Cătălina100% (1)
- Overview of Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 1Document28 pagesOverview of Anatomy and Physiology Lesson 1Vincent Dajao CimafrancaNo ratings yet
- Circulation WorksheetDocument3 pagesCirculation Worksheetholagato100% (1)