Professional Documents
Culture Documents
What Is Reflection of Light?
Uploaded by
MD: Rabiul Awal ShuvoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
What Is Reflection of Light?
Uploaded by
MD: Rabiul Awal ShuvoCopyright:
Available Formats
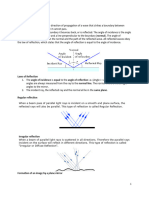
1. What is Reflection of Light?
When a ray of light approaches a smooth polished surface and the light ray bounces back, it is
called the reflection of light. The incident light ray which lands upon the surface is said to be
reflected off the surface. The ray that bounces back is called the reflected ray. If a perpendicular
were to be drawn on reflecting surface, it would be called normal. The figure below shows the
reflection of an incident beam on a plane mirror.
2. Laws of Reflection
The laws of reflection determine the reflection of incident light rays on reflecting surfaces, like
mirrors, smooth metal surfaces, and clear water. Let’s consider a plane mirror as shown in the
figure above. The law of reflection states that
• The incident ray, the reflected ray and the normal all lie in the same plane
• The angle of incidence = Angle of reflection
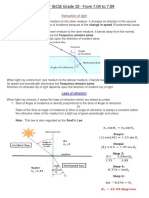
3. What is refraction of light? Write the postulates of refraction of light?
Refraction is the bending of light as it is passes from one substance to another. The bending is
caused by differences in density between the two substances.
Postulates of refraction of light: The Laws of Refraction
(i) Incident ray, reflected ray, refracted ray and the normal of the system lie in the
same plane.
(ii) Incident ray, coming from one medium to the boundary of another medium, is
refracted with a rule derived from a physicist Snells. He found that there is a
constant relation between the angle of incident ray and angle of refracted ray.
This constant is the refractive index of second medium relative to the first
medium.
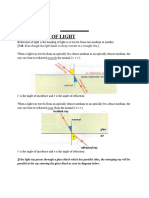
4. What is critical angle? What is total internal reflection?
Critical angle: For a particular value of the angle of incidence, the angle of refraction becomes
90°.The angle of incidence, that cause the refracted ray in the rarer medium to bend through 90°
is called critical angle.
Total internal reflection: When the angle of incidence becomes larger than the critical angle, no
refraction occurs. The entire light is reflected back into the denser medium. This is known as a
total internal reflection of light. Prisms, binoculars, optical fibers are few applications and uses of
Total internal reflection.
When the ray of light traveling in the denser medium enters into a rarer medium, it bends away
from the normal. If the angle of incidence ‘φ1’ increases’ the angle of refraction ‘φ2’ also increases.
Total internal reflection takes place only when:
• The light should pass from a denser medium to a rare medium.
• The angle of incidence must be greater than the critical angle.
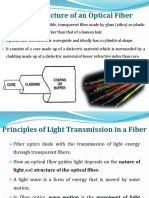
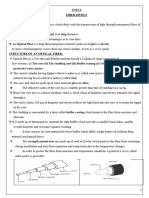
5. What is an optical fiber? Write how optical fibers works?
Optical fiber: Optical fiber is a type of cabling technology that uses light to carry voice and data
communications (telecommunications) over distances both great and small. It is a very thin
strand of plastic or glass that is used to transmit messages via light.
How optical fibers works: The optical fiber works on the principle of total internal reflection by
which light signals can be transmitted from one place to another with a negligible loss of energy.
Light rays can be used to transmit a huge amount of data. The optical cables are designed such that
they bend all the light rays’ inwards. Light rays travel continuously, bouncing off the optical fiber
walls and transmitting end to end data.
The inner part of the fiber optics is called core that carries the light and an outer concentric
shell is called cladding. The core is made of glass or plastic or a relatively high index of refraction.
The cladding is made of glass or plastic, but of relatively low refractive index. Light entering from
one end of the core strikes the core-cladding boundary at an angle of incidence greater than the
critical angle and is refracted back into the core. In this way, light travels many kilometers with a
small loss of energy.
6. What is refractive index?
In optics, the refractive index or index of refraction of a material is a dimensionless number that
describes how fast light travels through the material. it can also be defined as the ratio of the
velocity of a light ray in an empty space to the velocity of light in a substance, n = c/v.
You might also like
- Chapter 2 OFCDocument14 pagesChapter 2 OFCShining StarNo ratings yet
- Difference Between Reflection and RefractionDocument6 pagesDifference Between Reflection and RefractionFarooq TariqNo ratings yet
- Optical Fiber Communication (EEE 4175) : Ray TheoryDocument20 pagesOptical Fiber Communication (EEE 4175) : Ray TheorySaikat MahmudNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Light WaveDocument25 pagesThe Nature of Light WavepankajharitashNo ratings yet
- Fiber OpticsDocument14 pagesFiber OpticsShreeramMohanNo ratings yet
- Physic Project 3Document13 pagesPhysic Project 3Jesmin ChakmaNo ratings yet
- CBSE TERM2 - Ray OpticsDocument132 pagesCBSE TERM2 - Ray Opticsvenom eNo ratings yet
- Refraction and TIRDocument3 pagesRefraction and TIRsurvival vlogsNo ratings yet
- Light PUREDocument9 pagesLight PUREtalithaonkabetse723No ratings yet
- Isc Physics ProjectDocument15 pagesIsc Physics ProjectBhoomi DhokaNo ratings yet
- Class 2 PPT 1 Unit 1Document83 pagesClass 2 PPT 1 Unit 1ece Ms.G.Bhargavi100% (1)
- Physics IP ProjectDocument17 pagesPhysics IP ProjectHimanshu yadavNo ratings yet
- Notes For IGCSE Grade 10 - From 7.04 To 7.09: Refraction of LightDocument9 pagesNotes For IGCSE Grade 10 - From 7.04 To 7.09: Refraction of LightRAMAN KUMARNo ratings yet
- PHYSICS - PROJECT - FINAL by K BharadwajDocument13 pagesPHYSICS - PROJECT - FINAL by K BharadwajKannuri BharadwajNo ratings yet
- Reflection & RefractionDocument50 pagesReflection & Refractionannette.geesiawan1No ratings yet
- Total Internal Reflection - PhyDocument16 pagesTotal Internal Reflection - PhyRishabh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Jashmeet Physics Project File PDF Made by Lallu DadaDocument12 pagesJashmeet Physics Project File PDF Made by Lallu Dadalalit palNo ratings yet
- Snellius's LawDocument20 pagesSnellius's LawAgung MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Relationship Between Critical Angle and Refractive IndexDocument23 pagesRelationship Between Critical Angle and Refractive IndexNurul Syafiqah RoslanNo ratings yet
- SradhaDocument8 pagesSradhameherruzul9No ratings yet
- Chapter 12: LightDocument9 pagesChapter 12: LightLi HongNo ratings yet
- Waves Revision Notes (IGCSE PHYSICS)Document12 pagesWaves Revision Notes (IGCSE PHYSICS)Khushi MehtaNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Light WorksheetDocument45 pagesIGCSE Light WorksheetAsif Ayaz79% (19)
- Physics Project On Total Internal ReflectionDocument8 pagesPhysics Project On Total Internal Reflectionharnaek singhNo ratings yet
- How Does The Phenomenon of Total Internal Reflection Help in Optical FibresDocument29 pagesHow Does The Phenomenon of Total Internal Reflection Help in Optical FibresBleh bleh100% (1)
- Ray Optics: Refraction of LightDocument51 pagesRay Optics: Refraction of LightAbishek ThiyagarajanNo ratings yet
- Fiber OpticsDocument26 pagesFiber OpticsAmol DeshmukhNo ratings yet
- WP2 Light Waves (SDA) 2Document11 pagesWP2 Light Waves (SDA) 2matsweamogelang89No ratings yet
- Optical Fibre CommunicationDocument17 pagesOptical Fibre CommunicationSoumya ShyamasundarNo ratings yet
- Topics: 1) Basic Optical Laws and Definitions 2) Optical Modes and Congigurations Presented by Mrs. N.Beaula, Asst. Prof. / ECE, AcewDocument27 pagesTopics: 1) Basic Optical Laws and Definitions 2) Optical Modes and Congigurations Presented by Mrs. N.Beaula, Asst. Prof. / ECE, AcewbeaulajenishNo ratings yet
- OFC Intro Structure Principle Adv - Disadvantages - LDocument20 pagesOFC Intro Structure Principle Adv - Disadvantages - LAnkit kajla rj10No ratings yet
- RƏ Fraksh (Ə) N/ : Refractive Index, Also Called Index of Refraction, Measure of The Bending ofDocument18 pagesRƏ Fraksh (Ə) N/ : Refractive Index, Also Called Index of Refraction, Measure of The Bending ofChaelaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2: Ray Theory - Part 1: Optical Fiber Communication (EEE 4175)Document20 pagesLecture 2: Ray Theory - Part 1: Optical Fiber Communication (EEE 4175)creed60No ratings yet
- LightDocument17 pagesLightAhmad ZebNo ratings yet
- Wilmer Nossa Pino Paso - 3Document7 pagesWilmer Nossa Pino Paso - 3Eder SolisNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4 - Optical Fiber Waveguides Ray Theory Part - 1Document9 pagesLecture 4 - Optical Fiber Waveguides Ray Theory Part - 1samarthNo ratings yet
- AP Physics 2 - Lights and Optics NotesDocument20 pagesAP Physics 2 - Lights and Optics Notes孙铭阳No ratings yet
- 3.1 Light (1) (1) - 2Document10 pages3.1 Light (1) (1) - 2Dark VariantNo ratings yet
- Ray Thory Transmission or Basic Optical Laws and Definitions PDFDocument17 pagesRay Thory Transmission or Basic Optical Laws and Definitions PDFbeaulajenishNo ratings yet
- 4229 Topper 21 101 4 4 143 294 Total Internal Reflection Up201609191215 1474267517 9593Document6 pages4229 Topper 21 101 4 4 143 294 Total Internal Reflection Up201609191215 1474267517 9593Karan Singh RajawatNo ratings yet
- Specular Diffuse:, or in Other Words, The Angle of Incidence Equals The Angle of ReflectionDocument4 pagesSpecular Diffuse:, or in Other Words, The Angle of Incidence Equals The Angle of ReflectionMaui ShihtzuNo ratings yet
- Optics: The Science of Light Imaging: Phys 3616E, Winter 2017 Dr. Bassam AharmimDocument16 pagesOptics: The Science of Light Imaging: Phys 3616E, Winter 2017 Dr. Bassam AharmimjohnNo ratings yet
- Optical Communication: Presented by Mrs. Naveena A Priyadharsini Asst. Prof. / ECE, AcewDocument20 pagesOptical Communication: Presented by Mrs. Naveena A Priyadharsini Asst. Prof. / ECE, AcewbeaulajenishNo ratings yet
- Laws of ReflectionDocument21 pagesLaws of ReflectionKashaf AbbasiNo ratings yet
- Handout LightDocument7 pagesHandout LightM. Amaan AamirNo ratings yet
- Foc NotesDocument10 pagesFoc NotesSourabh BiswasNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 Refraction of LightDocument5 pagesChapter 4 Refraction of LightAryan YadavNo ratings yet
- Unit-1-Fiber OpticsDocument14 pagesUnit-1-Fiber OpticsZainab 2006No ratings yet
- Experiment 2: Snell's Law of Refraction: CheckpointDocument9 pagesExperiment 2: Snell's Law of Refraction: CheckpointAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- 1.optical FibersDocument23 pages1.optical FibersYashNo ratings yet
- Unit - Vii Fiber Optics Engineering PhysicsDocument12 pagesUnit - Vii Fiber Optics Engineering PhysicsKallur SandilyaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 Summary Sheet WavesDocument15 pagesUnit 1 Summary Sheet WavessalmaNo ratings yet
- Chapter One: Introduction To Optical Communication Systems 1.1Document7 pagesChapter One: Introduction To Optical Communication Systems 1.1Odoch HerbertNo ratings yet
- Total Internal Reflection Meblu Sanand Tom AU1920155Document3 pagesTotal Internal Reflection Meblu Sanand Tom AU1920155YakovNo ratings yet
- Optic ىلولا ا ةرضاحمل ا: Dr.Hasanain Al ShibanyDocument19 pagesOptic ىلولا ا ةرضاحمل ا: Dr.Hasanain Al ShibanySaif HassanNo ratings yet
- General Physics 2 Q4 ADM Module 1 4Document32 pagesGeneral Physics 2 Q4 ADM Module 1 4ROQUE XanderNo ratings yet
- L27 Total Internal ReflectionDocument6 pagesL27 Total Internal ReflectionKristiyan GeorgievNo ratings yet
- IGCSE Light WorksheetDocument45 pagesIGCSE Light WorksheetAref DahabrahNo ratings yet
- Physics Important Definitions and Formulae Light and WavesDocument4 pagesPhysics Important Definitions and Formulae Light and WavesVernon67% (3)
- Physics - 1: PHY-101 Software Engineering DepartmentDocument7 pagesPhysics - 1: PHY-101 Software Engineering DepartmentMD: Rabiul Awal ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Simple Harmonic Oscillator 1Document10 pagesSimple Harmonic Oscillator 1MD: Rabiul Awal Shuvo100% (1)
- Optics Is The Branch of Physics Which Involves The Behavior and Properties of Light, Including Its InteractionsDocument20 pagesOptics Is The Branch of Physics Which Involves The Behavior and Properties of Light, Including Its InteractionsMD: Rabiul Awal ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Work and EnergyDocument10 pagesWork and EnergyMD: Rabiul Awal ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Application of Discrete Math in Real LifeDocument3 pagesApplication of Discrete Math in Real LifeMD: Rabiul Awal ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Physics - 1: PHY-101 Software Engineering DepartmentDocument7 pagesPhysics - 1: PHY-101 Software Engineering DepartmentMD: Rabiul Awal ShuvoNo ratings yet
- Impact of Thermal Aging On The Intermetallic Compound Particle Size andDocument9 pagesImpact of Thermal Aging On The Intermetallic Compound Particle Size andAamir JanNo ratings yet
- Family Safety HandbookDocument12 pagesFamily Safety HandbookAdib_dokterNo ratings yet
- 1 Solid Waste Management in Developing CountriesDocument36 pages1 Solid Waste Management in Developing CountriesM K Kaushik100% (1)
- User Mannual For Student Training Services For RTTC - CTTC - DTTCDocument8 pagesUser Mannual For Student Training Services For RTTC - CTTC - DTTCVijay KumarNo ratings yet
- VLD 6000 AIS Airborne Transponder PDFDocument2 pagesVLD 6000 AIS Airborne Transponder PDFShin Ami IgamiNo ratings yet
- Series QCT and QCB Cylinders With Integrated Guide: Double-Acting, Magnetic Piston, Guided Ø 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, 63 MMDocument5 pagesSeries QCT and QCB Cylinders With Integrated Guide: Double-Acting, Magnetic Piston, Guided Ø 20, 25, 32, 40, 50, 63 MMVanesaNo ratings yet
- UI Design Featuring WPF Part 1 CP114 5Document40 pagesUI Design Featuring WPF Part 1 CP114 5aleiAlhepSNo ratings yet
- What Is The Function of The CMOS Battery?: RAM BiosDocument1 pageWhat Is The Function of The CMOS Battery?: RAM Biosrobert turkoNo ratings yet
- maxDPUTools A1Document117 pagesmaxDPUTools A1Deepak GuptaNo ratings yet
- HeroForge V6.1.0.1Document316 pagesHeroForge V6.1.0.1Tess TecklesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 16 - Nur-WPS OfficeDocument11 pagesChapter 16 - Nur-WPS Officemichelle marquezNo ratings yet
- Bending Machine Centurion ModelDocument4 pagesBending Machine Centurion ModelbharathaninNo ratings yet
- HBSC1203 V2Document6 pagesHBSC1203 V2TAY JIUN HOANG MoeNo ratings yet
- Product Drawing: MillenniumDocument13 pagesProduct Drawing: Millenniumjuan991No ratings yet
- Penjelasan Tentang Direct and Indirect Speech TerlengkapDocument11 pagesPenjelasan Tentang Direct and Indirect Speech TerlengkapHasby HasbyNo ratings yet
- Steel Column - Beams CalcDocument21 pagesSteel Column - Beams CalctmssorinNo ratings yet
- Gozuk Frequency Converter Selection TableDocument1 pageGozuk Frequency Converter Selection TablePham HoaNo ratings yet
- Exam Management System NotesDocument24 pagesExam Management System NotesRanganathan NagendranNo ratings yet
- West Bengal TourismDocument6 pagesWest Bengal TourismJoseph Subham MondalNo ratings yet
- Punk Science - Inside The Mind of GodDocument3 pagesPunk Science - Inside The Mind of GodRobert Garcia0% (2)
- Examination of Nutrition Knowledge, Attitude, and Dietary Behaviors of College Student Vegetarians, Semi-Vegetarians, and Non-VegestariansDocument11 pagesExamination of Nutrition Knowledge, Attitude, and Dietary Behaviors of College Student Vegetarians, Semi-Vegetarians, and Non-VegestariansMeilindaNo ratings yet
- The Way of Tthe Cross - CPdODocument23 pagesThe Way of Tthe Cross - CPdOACCobraGNo ratings yet
- Msu Final Examination Timetable (Finalised) May 2013 Session - VenueDocument63 pagesMsu Final Examination Timetable (Finalised) May 2013 Session - VenueBgx Ezmal Rhiza MokhtarNo ratings yet
- 3a. CONOPS Vigilancia ADS-B Base Terrestre COCESNADocument37 pages3a. CONOPS Vigilancia ADS-B Base Terrestre COCESNADairo FerrerNo ratings yet
- IBIG 04 04 Equity Value Enterprise Value Metrics MultiplesDocument95 pagesIBIG 04 04 Equity Value Enterprise Value Metrics MultiplesGabriel La MottaNo ratings yet
- A Garden of Eden in The Squares of Jerusalem, Zachariah 8,4-6Document12 pagesA Garden of Eden in The Squares of Jerusalem, Zachariah 8,4-6elverefur3587No ratings yet
- Shifting SandsDocument7 pagesShifting Sandsapi-306943014No ratings yet
- Xerox Wc423 SMDocument600 pagesXerox Wc423 SMkerintNo ratings yet
- SS ZG653 (RL1.2) : Software Architecture: BITS PilaniDocument12 pagesSS ZG653 (RL1.2) : Software Architecture: BITS PilaniAditya AggarwalNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document4 pagesAssignment 1hbtalvi100% (1)