Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Multipurpose Mechanical Processed Recycled Waste Plastic As Traffic Barrier and Planter Box
Uploaded by
Arlene Baja ConsumoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Multipurpose Mechanical Processed Recycled Waste Plastic As Traffic Barrier and Planter Box
Uploaded by
Arlene Baja ConsumoCopyright:
Available Formats
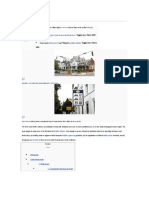
MULTIPURPOSE MECHANICAL PROCESSED RECYCLED WASTE PLASTIC AS TRAFFIC
BARRIER AND PLANTER BOX
STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM
Plastic pollution is one of the major problems in our country.
Plastic pollution can have harmful effects on the land and rivers by affecting wildlife and
habitat, but also on human health.
The Philippines, a paradise for marine diversity, is the third largest contributor to dumped
plastic.
Plastic pollution causes natural disaster such as floods.
Plastic wastes are causing the death of animals by ingestion of plastic objects.
OBJECTIVES
To have an economical traffic barrier to reduce the amount of plastic in the waste stream. By
recycling plastics into a barrier, it can also help the community to avoid natural calamities such
as floods.
To avoid dumping plastic into bodies of water.
SIGNIFICANCE
Advantages
Lightweight compared to concrete
Low cost of materials
Helps our nature
Aesthetic purposes
Disadvantages
It will increase the processing cost
More energy will consume
Air pollution will occur
Benefits
Motor vehicle driver
Community
Government
Environment
ELEVATED BIKE LANE FROM FTI TO ALABANG
STATEMENT OF THE PROBLEM
Workers from Alabang going to FTI and vice versa always experiencing heavy traffic.
Cyclist are in danger due to the congested road and the number of trucks and buses
passing by.
Cyclist is prone to air pollution coming from the vehicles they ride with.
OBJECTIVES
To encourage workers to ride a bicycle instead of commuting public vehicles
SIGNIFICANCE
Advantage:
They lessen their travel time when they go to work.
Cyclist are safer to have their own way than ride with other vehicles or reduce accident.
Less commuters will ride the public vehicles.
Cycling will be their daily exercise
Disadvantage:
Bike lanes can be costly
Obstructions while constructing bike lane
Air current can be dangerous to the cyclists
Benefits:
Cyclists
Community
Environment
Traffic
Lanes dedicated to bike traffic have a high cost-benefit ratio, research has found. In addition, the
lanes provide multiple benefits, including:
Significantly fewer injuries to cyclists.
More people riding bikes because they feel safer, which helps control obesity and promotes
physical fitness in the local population.
Improved safety for vehicles making right turns. Bike lanes add to the turning radius at
driveways and intersections, reducing the risk of rear-end crashes.
Higher probability that drivers can avoid utility poles and other fixed obstacles due to the
greater area cleared of trees and other barriers to visibility.
More space to place bus stops, improving safety for bus riders.
More-confident drivers due to the additional open space created by paved shoulders and
dedicated bike lanes. The additional space improves drivers’ ability to navigate and make
quick stops.
Improved safety for motorists who no longer need to cross into the oncoming traffic lane to
avoid bicyclists. The added space for bikes means that drivers can stay in their own lanes
without swerving to get around.
Available space for vehicles that need to stop temporarily due to an emergency or
breakdown.
Easier passage for emergency vehicles that need to get around congested traffic. Drivers
can pull onto the shoulder or into the bike lane to allow emergency vehicles to pass.
Motorists travel at a more uniform speed without the need to slow down for cyclists,
increasing the traffic carrying capacity of local roads and highways.
Better chances that motorists can avoid accidents or maneuver to make unavoidable
accidents less severe.
Improved working conditions for utility and maintenance crews.
Increased probability that drivers who accidentally swerve out of their travel lane can safely
returning to their own lane.
Better visibility for motorists and cyclists entering a roadway from a driveway or side street,
along with better turning space and sight distance for all drivers.
Improved runoff of storm water from travel lanes, which increases road capacity and traffic
safety.
Better air quality because vehicles no longer need to travel on an unpaved shoulder to get
around cyclists.
Increased functional life of pavement due to structural support, which decreases wear on
the outer pavement edge.
The ability of drivers to safely pass on the right when other vehicles are turning left.
You might also like
- New Chainless Bicycle Project ReportDocument30 pagesNew Chainless Bicycle Project Reportshubham gupta58% (12)
- Planning and Design For Cycle TrackDocument59 pagesPlanning and Design For Cycle TrackAbhishek100% (1)
- NJDOT Bicycle Compatible Roadways and Bikeways - Chapter 2Document24 pagesNJDOT Bicycle Compatible Roadways and Bikeways - Chapter 2John BoyleNo ratings yet
- More 3 2nd Edition Student 39 S BookDocument130 pagesMore 3 2nd Edition Student 39 S BookСветланаNo ratings yet
- LikesDocument12 pagesLikesCamilo Ortiz100% (1)
- Safety ReportDocument15 pagesSafety ReportAbdullah LuqmanNo ratings yet
- Yousif Wameedh ReportDocument7 pagesYousif Wameedh ReportyousifNo ratings yet
- Assignment - IiiDocument11 pagesAssignment - IiiJaskiratNo ratings yet
- Essay On SpeedbreakerDocument10 pagesEssay On SpeedbreakerNaman Mishra100% (1)
- 01 Presto Infrastructure Fact Sheet On Cycle Lanes 1Document6 pages01 Presto Infrastructure Fact Sheet On Cycle Lanes 1nahmaskincareNo ratings yet
- Traffic Calming MeasuresDocument19 pagesTraffic Calming MeasuresKapiya DismasNo ratings yet
- Emergence of A BicycleDocument16 pagesEmergence of A BicycleCaleb KhisaNo ratings yet
- Bicycling and Transportation Demand: ManagementDocument7 pagesBicycling and Transportation Demand: ManagementAuna SandoNo ratings yet
- BfyhfhDocument1 pageBfyhfhgregregegghjtrNo ratings yet
- All About Roundabouts BrochureDocument2 pagesAll About Roundabouts BrochureNikola MiticNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3aDocument49 pagesChapter 3aFarhan AmiraNo ratings yet
- Transportation: / Væl.ə.rəsDocument11 pagesTransportation: / Væl.ə.rəsThảo Duyên Nguyễn ThịNo ratings yet
- Douglas Wentzel Salvi, Schostok & Pritchard, P.C.'s Law School Scholarship Essay Contest Essay Topic 2: Car AccidentsDocument2 pagesDouglas Wentzel Salvi, Schostok & Pritchard, P.C.'s Law School Scholarship Essay Contest Essay Topic 2: Car AccidentsDouglas WentzelNo ratings yet
- Highway Engineering Group 1 BSCE-4CDocument30 pagesHighway Engineering Group 1 BSCE-4CMark RipaniNo ratings yet
- Chapter OneDocument19 pagesChapter OneMahider getachewNo ratings yet
- Road Traffic SafetyDocument11 pagesRoad Traffic SafetySakthivel ShanmugamNo ratings yet
- Five Features ReportDocument2 pagesFive Features Reportdark.mangle10No ratings yet
- Vulnerable Road UsersDocument6 pagesVulnerable Road Usersabdikarim_omarNo ratings yet
- BFC 32302 Revision FinalDocument148 pagesBFC 32302 Revision Finalأفيق .яINo ratings yet
- Cycle Tracks: DescriptionDocument5 pagesCycle Tracks: Descriptionpranshu speedyNo ratings yet
- Geometric DesignDocument10 pagesGeometric DesignGrachelle Andrea CapiralNo ratings yet
- Chm271 Case Study 1Document10 pagesChm271 Case Study 1Athirah ArshadNo ratings yet
- chp3 - Modal Characteristics-1-1Document48 pageschp3 - Modal Characteristics-1-1Wiwie NurNo ratings yet
- IELTS Writing BicyclesDocument1 pageIELTS Writing BicyclesFeroze IshtiaqueNo ratings yet
- Road 2Document8 pagesRoad 2thanshayarNo ratings yet
- Broas Godwin Iñaquib Proj1m1Document33 pagesBroas Godwin Iñaquib Proj1m1Godwin BroasNo ratings yet
- Strength WeaknessDocument9 pagesStrength WeaknessNadarajan PerumalNo ratings yet
- Study of Road Accidents in IndiaDocument51 pagesStudy of Road Accidents in IndiaManish AhujaNo ratings yet
- Slide TAnhDocument7 pagesSlide TAnhChi NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Problem SolutionDocument1 pageProblem Solution하린No ratings yet
- CE 242-2 Properties of Traffic Engg Elements (Spring 2012)Document18 pagesCE 242-2 Properties of Traffic Engg Elements (Spring 2012)faizankhan23No ratings yet
- Should Car Be BannDocument2 pagesShould Car Be BannSukanya ChatterjeeNo ratings yet
- DocumentDocument2 pagesDocumentjohnklientantiguaNo ratings yet
- Road SafetyDocument5 pagesRoad SafetyMark Jerbert GelacioNo ratings yet
- RS - 2019 - IOP - Conf. - Ser. - Earth - Environ. - Sci. - 235 - 012091Document9 pagesRS - 2019 - IOP - Conf. - Ser. - Earth - Environ. - Sci. - 235 - 01209115. Eka Ayu Rossa firaNo ratings yet
- Saron EcoDocument10 pagesSaron EcoMahider getachewNo ratings yet
- In Pursuit of Green MobilityDocument2 pagesIn Pursuit of Green MobilitySandeep SuryavanshiNo ratings yet
- Collingswood Bike Lane StudyDocument40 pagesCollingswood Bike Lane StudyJohn BoyleNo ratings yet
- Essay - City CenterDocument1 pageEssay - City Centerausteja.bartanoviciuteNo ratings yet
- Citizen Guideto Traffic Calming: Ityof Oral AblesDocument6 pagesCitizen Guideto Traffic Calming: Ityof Oral Ablesapi-26568546No ratings yet
- Advantages of Road Transport in GeneralDocument4 pagesAdvantages of Road Transport in GeneralKayigirwa Evemy Calista100% (1)
- Transportation Slide PDFDocument147 pagesTransportation Slide PDFMd ZimNo ratings yet
- Complete Streets: EnvironmentDocument2 pagesComplete Streets: EnvironmentLeague of Michigan BicyclistsNo ratings yet
- Benefits of Flexible Pavements BrochureDocument2 pagesBenefits of Flexible Pavements BrochurefipochNo ratings yet
- English 2010 Project 4 Persuasive EffectDocument4 pagesEnglish 2010 Project 4 Persuasive Effectapi-333446426No ratings yet
- Moving Towards Sustainability: A Green Journey in TransportationFrom EverandMoving Towards Sustainability: A Green Journey in TransportationNo ratings yet
- Tourist Transportation and Its Effect: December 2021 ReportingDocument5 pagesTourist Transportation and Its Effect: December 2021 ReportingELLE GONZALESNo ratings yet
- Chapter 5 - Traffic Safety MeasuresDocument50 pagesChapter 5 - Traffic Safety MeasuresDaniel TesfayeNo ratings yet
- Chola CBNMDocument4 pagesChola CBNMGowli CholaNo ratings yet
- Pertemuan4 PL Konsep Green City of IndonesiaDocument30 pagesPertemuan4 PL Konsep Green City of IndonesiaFerry SidaurukNo ratings yet
- Mrs Han Writing Task 2 Group AssignmentsDocument22 pagesMrs Han Writing Task 2 Group AssignmentsLan NguyenNo ratings yet
- Highway Geometric DesignDocument8 pagesHighway Geometric DesignBin IqbalNo ratings yet
- Samuel Johnson - I Gusti Ngurah Nithyananda Rama - 2201541190Document7 pagesSamuel Johnson - I Gusti Ngurah Nithyananda Rama - 2201541190Gus NityaNo ratings yet
- University of Jordan Civil Engineering Department Advanced Traffic EngineeringDocument44 pagesUniversity of Jordan Civil Engineering Department Advanced Traffic EngineeringEng-Mohammed TwiqatNo ratings yet
- Esej CarsDocument2 pagesEsej CarsPatryk DobkiewiczNo ratings yet
- The Proponents Proposed A Covered Walkway Separated From The Roadway For The Pedestrians in The Cityhall CompoundDocument3 pagesThe Proponents Proposed A Covered Walkway Separated From The Roadway For The Pedestrians in The Cityhall CompoundJewel Emerald Higuit100% (1)
- Design Project 2Document13 pagesDesign Project 2Manoj AlosiousNo ratings yet
- Sustainable Mass Transit: Challenges and Opportunities in Urban Public TransportationFrom EverandSustainable Mass Transit: Challenges and Opportunities in Urban Public TransportationNo ratings yet
- Research Paper-1Document6 pagesResearch Paper-1Yash MalpaniNo ratings yet
- Reading Practice 1+keyDocument9 pagesReading Practice 1+keyTrần Huy100% (1)
- Bike Lane LawsuitDocument47 pagesBike Lane LawsuitmaustermuhleNo ratings yet
- UCICompetitions ROA 2023Document10 pagesUCICompetitions ROA 2023pierril.desplatsNo ratings yet
- Suspension SettingsDocument1 pageSuspension SettingsRicardin BaltazarNo ratings yet
- Cheat Pokemon Fire RedDocument17 pagesCheat Pokemon Fire RedBani AsrorNo ratings yet
- Cuadernillo Starters 11-14Document6 pagesCuadernillo Starters 11-14yylrgmuhdxgnfyyjccNo ratings yet
- Monselice in Rosa MTB 2023Document5 pagesMonselice in Rosa MTB 2023MTB-VCONo ratings yet
- Bici LicuadoraDocument4 pagesBici Licuadoramaxter200No ratings yet
- Ch11 Test File-The Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDocument43 pagesCh11 Test File-The Cell Cycle and Cell DivisionDollar'sCornerNo ratings yet
- Electric Cargo BicycleDocument43 pagesElectric Cargo BicycleNAg RAjNo ratings yet
- Take Test Reading B Midterm Exam - ESLB01-MGW1 EDocument2 pagesTake Test Reading B Midterm Exam - ESLB01-MGW1 ERobert JuniorNo ratings yet
- Unit 8 Introduction To Cell DivisionDocument27 pagesUnit 8 Introduction To Cell DivisionTeo PhiriNo ratings yet
- Amangiri Adventure Guide 13.09.18 Original 14243Document42 pagesAmangiri Adventure Guide 13.09.18 Original 14243Milojka MaksimovicNo ratings yet
- Grammar Practice Pronouns WorksheetDocument2 pagesGrammar Practice Pronouns WorksheetМухиддин НосировNo ratings yet
- How To Choose A SnowboardDocument8 pagesHow To Choose A SnowboardIoana FNo ratings yet
- Nyc Interagency Road Safety PlanDocument9 pagesNyc Interagency Road Safety PlanJesus VillamilNo ratings yet
- Bikers Subculture: Vilnius University Faculty of Communication Emilija Marcinkevičiūtė, Archyvistika, I Group, I CourseDocument7 pagesBikers Subculture: Vilnius University Faculty of Communication Emilija Marcinkevičiūtė, Archyvistika, I Group, I Coursedileema100% (1)
- Roller Ball MurderDocument7 pagesRoller Ball MurderRat829No ratings yet
- Sports Physics 2016 Conference Juan Garcia LopezDocument10 pagesSports Physics 2016 Conference Juan Garcia LopezMarcelo CarvalhoNo ratings yet
- 110 Past Continuous - Questions and Short AnswersDocument1 page110 Past Continuous - Questions and Short AnswersCarlosNo ratings yet
- 2020 UCI MTB World Championships Program - LeogangDocument3 pages2020 UCI MTB World Championships Program - LeogangDaniele ConcordiaNo ratings yet
- Alaska To Argentina: Travel AdventureDocument1 pageAlaska To Argentina: Travel AdventureTrang PhanNo ratings yet
- Bike Comparison: Suzuki Access 125 TVS Jupiter Honda DioDocument4 pagesBike Comparison: Suzuki Access 125 TVS Jupiter Honda Diobookworm76No ratings yet
- Mitosis WorksheetDocument1 pageMitosis WorksheetFrician Bernadette Muyco100% (1)
- Test Builder - Headway Student's Site - Oxford University PressDocument2 pagesTest Builder - Headway Student's Site - Oxford University PressJust FortniteNo ratings yet
- Apache RR 310 BSVI BrochureDocument8 pagesApache RR 310 BSVI BrochureBibtya AgarwalNo ratings yet