Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Least Learned Most Essential Learning Competencies
Uploaded by
Nathaniel Artajo Galopo0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesThis document lists the least learned competencies in mathematics for different grade levels based on assessments conducted by the Department of Education. It includes competencies such as interpreting data from pictographs, multiplying fractions, writing proofs of triangle congruence, transforming quadratic functions, and determining limits, derivatives and integrals for various math functions. The document aims to identify the concepts students struggle with the most so they can be targeted for remediation.
Original Description:
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document lists the least learned competencies in mathematics for different grade levels based on assessments conducted by the Department of Education. It includes competencies such as interpreting data from pictographs, multiplying fractions, writing proofs of triangle congruence, transforming quadratic functions, and determining limits, derivatives and integrals for various math functions. The document aims to identify the concepts students struggle with the most so they can be targeted for remediation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
22 views2 pagesLeast Learned Most Essential Learning Competencies
Uploaded by
Nathaniel Artajo GalopoThis document lists the least learned competencies in mathematics for different grade levels based on assessments conducted by the Department of Education. It includes competencies such as interpreting data from pictographs, multiplying fractions, writing proofs of triangle congruence, transforming quadratic functions, and determining limits, derivatives and integrals for various math functions. The document aims to identify the concepts students struggle with the most so they can be targeted for remediation.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
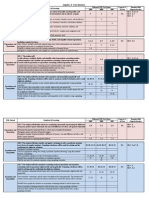
Least Learned Most Essential Learning Competencies (LLMELCs) in MATHEMATICS
Grade Level LEAST LEARNED COMPETENCIES
1 infers and interprets data presented in a pictograph without scales. e.g. finding out from the title
what the pictograph is all about, comparing which has the least or greatest …
solves routine and non-routine problems using data presented in pictograph without scales.
2 illustrates and writes a related equation for each type of multiplication: repeated addition, array,
counting by multiples, and equal jumps on the number line.
illustrates that multiplication and division are inverse operations.
3 Represents, compares and arranges dissimilar fractions in increasing or decreasing order.
visualizes, and represents, and solves routine and non-routine problems Involving conversions of
common units of measure.
4 visualizes addition and subtraction of similar and dissimilar fractions.
solves routine and non-routine problems using data presented in a single or double-bar graph.
5 visualizes multiplication of fractions using models.
formulates the rule in finding the next term in a sequence. e.g. 1, 3, 7,15, (15 x 2+1) Possible
answers: (x 2 + 1) (+2, +4, +8, +16)
6 describes and interprets the basic operations on integers using materials such as algebra tiles,
counters, chips, and cards.
determines the relationship of the volume between a rectangular prism and a pyramid; a
cylinder and a cone; and a cylinder and sphere.
reads and interprets electric and water meter readings.
solves routine and non-routine problems involving electric and water consumption.
7 performs operations on rational numbers
uses models and algebraic methods to find the: (a) product of two binomials; (b) product of the
sum and difference of two terms; (c) square of a binomial; (d) cube of a binomial; (e) product of a
binomial and a trinomial.
uses a compass and straightedge to bisect line segments and angles and construct
perpendiculars and parallels.
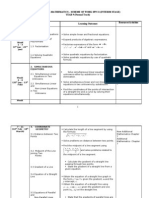
8 writes a proof (both direct and indirect).
proves two triangles are congruent.
proves statements on triangle congruence.
9 transforms the quadratic function defined by y = ax 2+ bx + c into the form y = a(x – h)2 + k.
proves the conditions for similarity of triangles.
1.1 SAS similarity theorem
1.2 SSS similarity theorem
1.3 AA similarity theorem
1.4 right triangle similarity theorem
1.5 special right triangle theorems
solves problems involving oblique triangles.
10 proves theorems related to chords, arcs, central angles, and inscribed angles.
proves theorems on secants, tangents, and segments.
SHS – GEN. determines the intercepts, zeroes, and asymptotes of an exponential function.
MATH.
determines the intercepts, zeroes, and asymptotes of logarithmic functions.
establishes the validity and falsity of real-life
arguments using logical propositions, syllogisms, and fallacies.
SHS – STAT. interprets the mean and the variance of a discrete random variable.
AND PROB.
illustrates the Central Limit Theorem.
solves problems involving test of hypothesis on the population mean.
SHS – BUS. solve problems involving buying and selling products
MATH.
analyze and interprets the data presented in the table using measures of central tendency and
variability and tests of significant differences
analyze and interpret the data presented in a graph/table
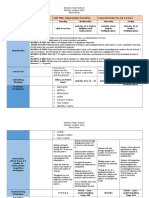
SHS – BASIC compute the limits of exponential, logarithmic, and trigonometric functions using tables of
CALCULUS values and graphs of the functions
determine the relationship between differentiability and continuity of a function
illustrate the Extreme Value Theorem
illustrate the definite integral as the limit of the Riemann sums
illustrate the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus
solve problems involving areas of plane regions
SHS – PRE- solve situational problems involving circular functions
CALCULUS
apply trigonometric identities to find other trigonometric values
solve situational problems involving trigonometric identities
You might also like
- Least Learned Most Essential Learning CompetenciesDocument2 pagesLeast Learned Most Essential Learning CompetenciesNathaniel Artajo GalopoNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 MathxDocument5 pagesGrade 8 Mathxapi-2542992270% (1)
- Algebra 2Document7 pagesAlgebra 2api-262893996No ratings yet
- Grade-8 Curriculum GuideDocument3 pagesGrade-8 Curriculum Guideアレリア あっェルあNo ratings yet
- Overland TrailDocument8 pagesOverland Trailapi-245623862No ratings yet
- Ican Statements For Pre AlgebraDocument3 pagesIcan Statements For Pre Algebraapi-256187467No ratings yet
- Standards-K-12 8th GradeDocument3 pagesStandards-K-12 8th Gradeapi-296039056No ratings yet
- 21-22 Algebra I-StandardsDocument6 pages21-22 Algebra I-Standardsapi-471242393No ratings yet
- Ccss 8Document3 pagesCcss 8api-237676777No ratings yet
- Map Math 3-8 Blueprint Interpretive GuideDocument6 pagesMap Math 3-8 Blueprint Interpretive Guideapi-431340065No ratings yet
- Objectives:: Fall Semester Exam Review - Algebra IDocument9 pagesObjectives:: Fall Semester Exam Review - Algebra IxneoNo ratings yet
- Algebra II Honors Common Core Standards: Greenville CountyDocument4 pagesAlgebra II Honors Common Core Standards: Greenville CountyStephanie ClareyNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade StandardDocument7 pages8th Grade Standardapi-251069371No ratings yet
- Mathematics 8 2022 2023Document8 pagesMathematics 8 2022 2023Princess Mae LumawagNo ratings yet
- 8th Grade CcssDocument1 page8th Grade Ccssapi-237059911No ratings yet
- Add Maths Fast Track Sow Year 9 310807 v2Document9 pagesAdd Maths Fast Track Sow Year 9 310807 v2Ya YaNo ratings yet
- Algebra 2 CriticalDocument10 pagesAlgebra 2 Criticalapi-115680157No ratings yet
- CcssDocument5 pagesCcssapi-237229475No ratings yet
- Midterm Exam Review GuideDocument4 pagesMidterm Exam Review GuidexneoNo ratings yet
- MELC's: Identify What Is Being Asked (Knowledge /skill/ Process/ Understanding)Document18 pagesMELC's: Identify What Is Being Asked (Knowledge /skill/ Process/ Understanding)Marife Faustino GanNo ratings yet
- Iloilo Sacred Heart School, Inc.: First Quarter Patterns and AlgebraDocument6 pagesIloilo Sacred Heart School, Inc.: First Quarter Patterns and AlgebraGianmarie Sumagaysay HiladoNo ratings yet
- 8 MathDocument12 pages8 Mathdestiny_eastepNo ratings yet
- A Visual Inspection of The Real Roots of A Polynomial FunctionDocument10 pagesA Visual Inspection of The Real Roots of A Polynomial FunctionxcrunitccNo ratings yet
- Math 7 Syllabus 2014-2015Document5 pagesMath 7 Syllabus 2014-2015api-266524097No ratings yet
- Title Marine Engineering MathematicsDocument10 pagesTitle Marine Engineering MathematicsgunapalshettyNo ratings yet
- Mathematics IGCSE Syllabus ExtendedDocument10 pagesMathematics IGCSE Syllabus ExtendedTristan DawsonNo ratings yet
- North Carolina Standard Course of Study North Carolina Math 3Document8 pagesNorth Carolina Standard Course of Study North Carolina Math 3Alex WellmanNo ratings yet
- Mccrs-Compacted Math 8Document7 pagesMccrs-Compacted Math 8api-318685719No ratings yet
- 8th Grade Mathematics Curriculum MapDocument6 pages8th Grade Mathematics Curriculum MapMarcos ShepardNo ratings yet
- Alg 2 Math Correlations 2010Document6 pagesAlg 2 Math Correlations 2010Harish MulevaNo ratings yet
- 21-22 8th Grade Pacing (EnVision)Document4 pages21-22 8th Grade Pacing (EnVision)Greg WalkerNo ratings yet
- Eighth Grade Math Curriculum MapDocument14 pagesEighth Grade Math Curriculum MapMicheal CarabbacanNo ratings yet
- Tennessee's State Mathematics Standards - Grade 8Document4 pagesTennessee's State Mathematics Standards - Grade 8api-333440532No ratings yet
- Polynomial Degree and Finite DifferencesDocument32 pagesPolynomial Degree and Finite DifferencesJesús Mancilla RomeroNo ratings yet
- Yr 9 Add Math Normal Track 2010Document9 pagesYr 9 Add Math Normal Track 2010Lim Chee ChangNo ratings yet
- Week of The Quarter/ Grading Period Inventory of Power Point, Videos in Mathematics 4Document3 pagesWeek of The Quarter/ Grading Period Inventory of Power Point, Videos in Mathematics 4Hanna Clarisse Baccay BangayanNo ratings yet
- Exam Topics To Focus On Grade Ten 1793Document2 pagesExam Topics To Focus On Grade Ten 1793lerafi1309No ratings yet
- 8th Math Curriculum MapDocument7 pages8th Math Curriculum Mapapi-261608473No ratings yet
- Ut3 ConceptsDocument2 pagesUt3 Conceptsapi-261139685No ratings yet
- Business Mathematics and StatisticsDocument229 pagesBusiness Mathematics and Statisticsthuosam96No ratings yet
- Algebra II Standards Final ChartDocument6 pagesAlgebra II Standards Final Chartapi-273248611No ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument12 pagesLesson PlanAnnmarie McGonagleNo ratings yet
- Pre-Calculus: Updated 09/15/04Document14 pagesPre-Calculus: Updated 09/15/04Neha SinghNo ratings yet
- 2nd Nine WeeksDocument2 pages2nd Nine Weeksapi-233072472No ratings yet
- Iskl Grade 7 MathsDocument5 pagesIskl Grade 7 MathsMathiarasu MuthumanickamNo ratings yet
- Learning Competency DirectoryDocument3 pagesLearning Competency DirectoryRaymond Gorda88% (8)
- Igcse Accelerated Mathematics 0580 (Extended 2 Years) Scheme of Work For Year 9 (2011)Document74 pagesIgcse Accelerated Mathematics 0580 (Extended 2 Years) Scheme of Work For Year 9 (2011)Steve JonzieNo ratings yet
- FunctionsDocument44 pagesFunctionsSudhakar Chollangi100% (1)
- PreCalculus CCSS Curriculum Map Unit 4 Draft - 6!12!14revDocument8 pagesPreCalculus CCSS Curriculum Map Unit 4 Draft - 6!12!14revraymart zalunNo ratings yet
- NUET 2022 Mathematics SpecificationDocument9 pagesNUET 2022 Mathematics SpecificationАдина Сагнаева100% (1)
- Solving Equations Unit PlanDocument10 pagesSolving Equations Unit Planapi-253299522No ratings yet
- Seventh Math StandardsDocument3 pagesSeventh Math Standardsapi-233655908No ratings yet
- K-12 Math Crosswalks Algebra IDocument17 pagesK-12 Math Crosswalks Algebra Iestabloid1169No ratings yet
- Eighth Grade Math May 2014Document2 pagesEighth Grade Math May 2014destiny_eastepNo ratings yet
- Math Grade 7 Learning Competency K-12Document4 pagesMath Grade 7 Learning Competency K-12Lino Garcia63% (8)
- Foundation Year Program Entrance Tests Mathematics Specification For Nufyp Set 2020Document9 pagesFoundation Year Program Entrance Tests Mathematics Specification For Nufyp Set 2020Даниал ГабдоллаNo ratings yet
- Standards-K-12 6th GradeDocument3 pagesStandards-K-12 6th Gradeapi-296039056No ratings yet
- Algebra 2 Curriculum AlignmentDocument43 pagesAlgebra 2 Curriculum Alignmentapi-254765842No ratings yet
- Tnready Blueprint g6 MathDocument9 pagesTnready Blueprint g6 Mathapi-282869532No ratings yet
- RPMS Portfolio 2020 2021 CoverDocument28 pagesRPMS Portfolio 2020 2021 CoverNathaniel Artajo GalopoNo ratings yet
- List of Division LAS (Q1 and Q2) Writers/Developers and DQUAT MembersDocument3 pagesList of Division LAS (Q1 and Q2) Writers/Developers and DQUAT MembersNathaniel Artajo GalopoNo ratings yet
- Alabel National High SchoolDocument4 pagesAlabel National High SchoolNathaniel Artajo GalopoNo ratings yet
- List of Division LAS (Q1 and Q2) Writers/Developers and DQUAT MembersDocument3 pagesList of Division LAS (Q1 and Q2) Writers/Developers and DQUAT MembersNathaniel Artajo GalopoNo ratings yet
- Cover Page For PromotionDocument1 pageCover Page For PromotionNathaniel Artajo Galopo100% (1)
- Cover Page For PromotionDocument1 pageCover Page For PromotionNathaniel Artajo Galopo100% (1)
- Alabel National High SchoolDocument4 pagesAlabel National High SchoolNathaniel Artajo GalopoNo ratings yet
- Annex 1a - School Forms Checking ReportDocument2 pagesAnnex 1a - School Forms Checking ReportQuinric Bontilao Sevillejo94% (69)
- Nathaniel A. Galopo: Activity 2.1Document8 pagesNathaniel A. Galopo: Activity 2.1Nathaniel Artajo GalopoNo ratings yet
- Nathaniel A. Galopo Activity 2.2Document6 pagesNathaniel A. Galopo Activity 2.2Nathaniel Artajo GalopoNo ratings yet
- 2020-2021 Reports Monitoring ChecklistDocument2 pages2020-2021 Reports Monitoring ChecklistNathaniel Artajo GalopoNo ratings yet
- Composition of Rigid Motions M Notations and Examples:: R T As Follows: R T R (T T Acts First R (-2, - 1)Document2 pagesComposition of Rigid Motions M Notations and Examples:: R T As Follows: R T R (T T Acts First R (-2, - 1)Nathaniel Artajo GalopoNo ratings yet
- 1 InterestsDocument18 pages1 InterestsNathaniel Artajo GalopoNo ratings yet
- BSI Complex Variables Cloplos, Fall 2020Document5 pagesBSI Complex Variables Cloplos, Fall 2020Ahmar KhanNo ratings yet
- Lesson PlanDocument3 pagesLesson Planapi-248632074100% (2)
- Linear Programming Examples Using MatlabDocument8 pagesLinear Programming Examples Using MatlabAnu G KumarNo ratings yet
- Unit2 - Numerical DifferentationDocument24 pagesUnit2 - Numerical Differentationadityapawar1865No ratings yet
- Introduction To Sets: Whole NumbersDocument17 pagesIntroduction To Sets: Whole NumbersGigi G. Bullanday100% (1)
- Lesson 2 Families of CurveDocument16 pagesLesson 2 Families of CurveeulaNo ratings yet
- 17mat41 PDFDocument3 pages17mat41 PDFBroNo ratings yet
- Factoring Quadratics Practice CDocument3 pagesFactoring Quadratics Practice Capi-314809600No ratings yet
- 5th Grade 13-14 Math Common Core Standards by QuarterDocument3 pages5th Grade 13-14 Math Common Core Standards by QuartermrkballNo ratings yet
- Fraction Mixed ImproperDocument32 pagesFraction Mixed ImproperCher PipzNo ratings yet
- MA1511 Chapter 3Document20 pagesMA1511 Chapter 3Kang Le LimNo ratings yet
- Lecture 4Document36 pagesLecture 4Abdul RashidNo ratings yet
- Acoustics Homework 3 SolutionDocument6 pagesAcoustics Homework 3 SolutionAnshul GoyalNo ratings yet
- Math10 Week3Day4 Polynomial-EqnsDocument44 pagesMath10 Week3Day4 Polynomial-EqnsMark Cañete PunongbayanNo ratings yet
- Curvature and Radius of CurvatureDocument1 pageCurvature and Radius of CurvatureMad MaxNo ratings yet
- IMO Shortlist 2022Document6 pagesIMO Shortlist 2022[canal temporalmente inactivo]No ratings yet
- Add Math Project 1/2010Document29 pagesAdd Math Project 1/2010Yokyi 玉仪93% (14)
- Limit of A FunctionDocument33 pagesLimit of A FunctionAlvin ManansalaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1Document88 pagesUnit 1shiva surya83% (6)
- Filipp Zoltán-Basic-Mathematics-Precalculus-2019 PDFDocument99 pagesFilipp Zoltán-Basic-Mathematics-Precalculus-2019 PDFNicolasCisfNo ratings yet
- Foa G Dec 1712 PublicDocument711 pagesFoa G Dec 1712 PublicKadir EmirNo ratings yet
- Properties of LogarithmsDocument5 pagesProperties of Logarithmsapi-320083551No ratings yet
- Zero and Negative Exponents: Quarter 2Document16 pagesZero and Negative Exponents: Quarter 2Carmi Formentera LuchavezNo ratings yet
- Math 8 Lesson 11 System of Linear EquationsDocument44 pagesMath 8 Lesson 11 System of Linear EquationsAllah Rizza MarquesesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6: Complex NumberDocument14 pagesChapter 6: Complex Numbercrye shotNo ratings yet
- Basic Calculus - Q4 - Week3 Edited VersionDocument18 pagesBasic Calculus - Q4 - Week3 Edited VersionAdaill JosephNo ratings yet
- 11 Mathematics Binomial Theorem Test 01Document1 page11 Mathematics Binomial Theorem Test 01DeepakNo ratings yet
- Math 8 Module First QuarterDocument46 pagesMath 8 Module First QuarterVanesaVirtudazo100% (1)
- Properties of The Trinomial DistributionDocument2 pagesProperties of The Trinomial DistributionPerry01No ratings yet
- The Strange Numbers That Birthed Modern Algebra - Quanta MagazineDocument5 pagesThe Strange Numbers That Birthed Modern Algebra - Quanta MagazinezentropiaNo ratings yet