Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CFA Level II Formula Sheet CFA Level II Formula Sheet: Finance (Harvard University) Finance (Harvard University)
Uploaded by
smithOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CFA Level II Formula Sheet CFA Level II Formula Sheet: Finance (Harvard University) Finance (Harvard University)
Uploaded by
smithCopyright:
Available Formats
lOMoARcPSD|9327251
CFA level II formula sheet
Finance (Harvard University)
StuDocu is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university
Downloaded by Smit Gandhi (smith22595@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|9327251
Formula Sheet Level II 2020
FinQuiz Formula Sheet CFA Program Level II
(for single independent variable R2 = r2) 𝑆𝑆𝑇
d
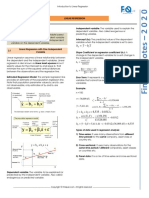
Reading 4: Introduction to Regression
= `(𝑦c
Total
7. SST = SSE + SSR(or RSS) df = n-1
ce5
∑1 / /
-23(,- .,)(0- .0)
− 𝑦U)B
1. Sample Cov (X, Y) =
4.5 8. Hypothesis Testing:
• Null and Alternative hypotheses
789:;
2. Correlation Coefficient = r,0 = (< or Source of Sum of Mean Sum
: )(<; )
• H0: b1 = 0 (no linear relationship) Variability
DoF
Squares of Squares
789(,,0)
r= • H1: b1 ≠ 0 (linear relationship does
=9>?(,)=9>?(0)
exist) Regression MSR =
! (Explained)
1 RSS
RSS/1
3. t-test (for normally distributed variables) = b1 - b1
• Test statistic = t =
?√4.B
t= t distribution with (n −
s b1 Error
n-2 SSE
MSE =
=5.? C (Unexplained) SSE/n-2
2) deg. of freedom • Confidence Interval = b1 ± t c s b1
SST=
Total n-1 RSS +
4. Linear Regression = Yi = b0 + b1Xi + εi, 9. ANOVA (Analysis of variance) = SSE
ANOVA SS MSS F
• Intercept (b0) = b0 = y - b1 x =
pqq
𝑆𝑆𝑅 lmn ( )
• Slope or regression coefficient = b5 = d 𝑆𝑆𝑅g 10. F-Statistic or F-Test = = r
qqs
𝑆𝑆𝑅 lmo ( )
789(S,T) ∑(S.SU)(T.T
/) 𝑘 turu3
= `(𝑦bc
Regression
or = 𝑘 𝑆𝑆𝐸g
9>?(S) ∑(S.SU)C (𝑛 − 𝑘 − 1)
df = k (df numerator = k = 1)
ce5
− 𝑦U)B (df denominator = n – k – 1 = n – 2)
5. Standard Error of Estimate SEE = SW = 𝑆𝑆𝐸
∑1 [ )C
d
𝑆𝑆𝐸
v ± t 7 sx
11. Prediction Intervals = Y
YYW -23(T- .T
X =X = `(𝑦c
Error
𝑛−𝑘−1 5 / )C
(,.,
4.Z.5 4.Z.5
𝑤ℎ𝑒𝑟𝑒 sxB = sB }1 + 4 + (4.5)<C • and
df = n-k-1
ce5
− 𝑦b)
B :
6. Coefficient of Determination (R2) = 2
YY\.YYW ]YY
sf = s
= =
f
where, 0 ≤ R2≤ 1
YY\ YY\
www.finquiz.com All rights reserved
Downloaded by Smit Gandhi (smith22595@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|9327251
Formula Sheet Level II 2020
Reading 5: Multiple Regression & Issues in 2. Log-Linear Trend Models = yt = e
b0 +b1t 8. Smoothing Past Values with n-Period
Regression Analysis Moving Average =
3. Autoregressive Time-Series Models: xt + xt -1 + xt -2 + ..... + xt -( n -1)
1. Yi = b0 + b1X1i + b2X2i + … + bkXki + εi,i = • First order autoregressive AR (1) = xt n
1, 2, … n = b0 + b1 x t-1 + εt 9. Correcting Seasonality in Time Series
Prediction equation = 𝑌•c = 𝑏•ƒ + 𝑏•5 𝑋5c +
• pth-order autoregressive AR (p) = xt Models:
2.
𝑏•B 𝑋Bc +. . . +𝑏•… 𝑋…c + ε‡ , 𝑖
= b0 + b1 x t-1 + b2 x t-2 + …..+ bp x t-p
+εt •For quarterly data = xt = b0 + b1x t-1 +
b0 b2x t-4 + εt
Adjusted R2 = 𝑅UB = 1 − ‰d.….5Š (1 − 𝑅B )
d.5
3. 4. Mean reverting level of xt = • For monthly data = xt = b0 + b1x t-1 +
1 - b1 b2x t-12 + εt
4. Breusch–Pagan test 10. ARCH model =
5. Chain Rule of Forecasting:
• H0 = No conditional eˆ 2 t = a 0 + a1eˆ 2 t -1 + µ t where µt is
Heteroskedasticity exists • One-period ahead forecast =
an error term
• HA = Conditional Heteroskedasticity x̂t+1 = bˆ0 + bˆ1 xt • Predicting variance of errors in period
exists • Two-period ahead forecast= 2 2
• Test statistic = n × R2residuals t+1 = σˆ t+1 = α̂ 0 + α1εˆt
x̂t+2 = bˆ0 + bˆ1 xt+1
5. Durbin-Waston Test = 𝐷𝑊 = 6. Random Walks and Unit Roots: Reading 7: Machine Learning
∑• b Ž .•bŽu3)C
Ž2C(• • Random Walk without drift = xt = x t-
∑Ž23 •bŽ C
•
1 + εt where, b0 = 0 and b1 = 1. LASSO:
1. Penalty term (when l > 0) = 𝜆 ∑’…e5‘𝑏U… ‘
• For Large Sample size DW Statistic • Correcting Random Walk = yt = xt - x
(d) = d ≈ 2 (1 – r) t-1
• Random walk with a drift = xt = b0 + x
2. ∑dce5(𝑌c − 𝑌c )B + 𝜆 ∑’…e5‘𝑏•’ ‘
t-1 +
εt where, b0 ≠ 0 and b1 = 1
• By taking first difference yt = xt - x t-1
3. When l = 0, LASSO penalized regression
= b0 + εt
= OLS regression
Reading 6: Time Series Analysis
7. Using Dickey-Fuller Test = xt - x t-1 = b0 +
Reading 8: Big Data Projects
1. Linear Trend Models = yt = b0 + b1t+ εt (b1 -1) x t-1 + εt
• Predicted/fitted value of yt in period ›œ .›•œt
1. 𝑋c(d“”•–—c˜™š) = ›
•žŸ .›•œt
(T + 1) = yˆ t +1 = bˆ0 + bˆ1 (T + 1)
where Xi = value of observation
www.finquiz.com All rights reserved
Downloaded by Smit Gandhi (smith22595@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|9327251
Formula Sheet Level II 2020
5
Performance Metrics: • (1 + i° ) = S∫ ¹1 + i∫ º » ½ 7. Forward discount or premium as % of spot
g ®∫ /¼
2. Accuracy = (TP + TN)/(TP + FP + TN + ° rate:
5¾‡∫
FN) • F∫ /° = S∫ ‰
(5¾‡¼ )
Š Ff / d - S f / d
g
F1 score = (2*P*R)/(P + R) ° @ (i f - id )
• Using day count convention: S f /d
3. Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC): ' ! Actual $* If uncovered interest rate parity holds
)1+ id # ,=
False positive rate (FPR) = FP/(TN + FP)
( " 360 &%+ • Ff /d − S f /d
and = = %ΔS ef /d ≅ (i f − id )
S f /d
True positive rate (TPR) = TP/(TP + FN), ' ! Actual $*' 1 *
S f /d )1+ i f # ,) ,
which is same as recall
( " 360 &%+)( Ff /d ,+
8. Purchasing Power parity (PPP)
4. Root Mean Square Error (RMSE): • Pf = S f/d × Pd
d
(𝑃𝑟𝑒𝑑𝑖𝑐𝑡𝑒𝑑c − 𝐴𝑐𝑡𝑢𝑎𝑙c )B æ é Actual ù ö • S f/d = Pf / Pd
` ç1+ i f ê
360 úû ÷
÷
𝑛 • ç ë
ce5 Ff / d = S f /d
ç é Actual ù ÷ 9. Relative version of PPP = %∆S f/d = πf – πd
ç 1 + id ê ÷
Reading 9: Excerpt from ‘Probabilistic è ë 360 úû ø
10. Ex ante version of PPP = %∆Sef/d = πef –
Approaches, Scenario Analysis, Decision Tree πed
& Simulations’ 6. Uncovered Interest Rate Parity :
i f - %DS e f / d = id 11. Real Exchange Rate
•
%DS e
= i f - id æ S f / d Pd ö æ ö
Reading 10: Currency Exchange Rates •
f /d
ç ÷ = S f / d ç Pd ÷
ç P ÷ çP ÷
qf/d = è ø è f ø
• Forward premium or discount: f
1. Bid-offer Spread = Offer price – Bid price • For one year horizon =
æ CPI d ö
2. Fwd rate = Spot Exchange rate + Ff /d − S f /d = qf /d = S f /d ç ÷
®8?¯>?° ±8‡4²< ç CPI ÷
5ƒ,ƒƒƒ "i −i % or è f ø
3. Forward premium/discount (in %) =
S f /d $ f d ' ≅ S f /d (i f − id ) 12. Fisher effect:
<±8² µS7¶>4·µ ?>²µ.(x8?¯>?° ±8‡4²</5ƒ,ƒƒƒ)
# 1+ id &
−1 • id = rd + πεd
<±8² µS7¶>4·µ ?>²µ • Using day count convention: • if = rf + πεf
( " Actual % +
* $ - • if – id = (rf – rd) + (πεf- πεd)
4. To convert spot rate into forward quote: # 360 '& - • (rf – rd) = (if – id) - (πεf- πεd)
• Spot exchange rate × (1 + % premium) Ff /d − S f /d = S f /d * (i f − id )
* 1+ i " Actual % -
* d$ -
• Spot exchange rate × (1 - % discount) ) # 360 '& ,
5. Covered interest rate parity:
www.finquiz.com All rights reserved
Downloaded by Smit Gandhi (smith22595@gmail.com)
lOMoARcPSD|9327251
Formula Sheet Level II 2020
Reading 11: Economic Growth & The • Slope of straight line = [δ + n + θ / (1
Investment Decision 9. Contribution of Improvement in – α)]
technology = Labor productivity growth 14. During the transition to the steady state
1. Economic growth = Annual % ∆ in real rate – Capital Deepening growth path:
GDP or in real per capita GDP • Growth rates of output per capita = ∆y
Æ Ç
10. Growth Accounting based on Solow / y = ɉ Š + 𝛼𝑠 ‰’ − 𝛹ŠË =
5. Å
W Á
P = GDP ‰ Š ‰WŠ
Approach = ∆Y /Y = ∆A / A + α ∆K/K +
Æ
2.
¿ÀÁ (1 – α) ∆L/ L ‰5.ÅŠ + 𝛼𝑠 (y/k – Ψ)
3. Expressing in terms of logarithmic rates:
• Capital-to-labor ratio = ∆k / k =
Æ Ç Æ
ɉ Š + 𝑠 ‰’ − 𝛹ŠË = ‰5.ÅŠ + s
11. Labor productivity growth accounting
• (1/T) % ∆P = (1/T) % ∆GDP + (1/T) equation 5. Å
%∆ (E / GDP) + (1/T) % ∆(P / E) • Growth rate in potential GDP = LT g (y/k – Ψ)
• % ∆ in stock MV = % ∆ in GDP + % rate of labor force + LT g rate in labor
∆ in share of earnings (profit) in GDP productivity 15. Proportional impact of the saving rate
+ % ∆ in the P/E multiple change on the capital-to-labor ratio and per
12. Balanced or Steady State Rate of Growth capita income over time:
1
4. A two-factor aggregate production in Neoclassical Growth Theory:
' ! Y $ *α −1
function: Y = AF (K, L) • Growth in physical capital stock = ∆K
)# & ,
= sY – δK knew " K %new ,
=)
5. Cobb-Douglas Production Function = F • kold )!Y $ ,
(K, L) = Kα L1 - α 13. In the steady state: )( #" K &%old ,+
• Growth rate of capital per worker = ∆k
a
6. Under Cobb-Douglas production function: / k = ∆y / y = ∆A / A + α ∆k / k =
ÂÃÄ
y new é k new ù
• Marginal product of capital = MPK =
5. Å
è Steady state growth rate of =ê ú
α AK α-1 L 1-α = α Y/K •
yold ë k old û
labor productivity
• α Y/K = r èα = r (K) / Y = Capital
• Growth rate of Total output = ∆Y / Y
income / Output or GDP 16. Production function in the endogenous
= Growth rate of TFP scaled by labor
force share + Growth rate in the labor growth model = ye = f (ke) = cke
7. Output per worker or Average labor Æ • Growth rate of output per capita =
force = +n
productivity (Y/L or y): 5. Å ∆ye/ye = ∆ke/ke = sc – δ – n
• GDP/Labor input = TFP × capital-to- • Steady state Output-to-capital ratio =
Ç 5 Æ
labor ratio × share of capital in GDP = ‰È Š ɉ5. ÅŠ + 𝛿 + 𝑛Ë = 𝛹
’ Reading 12: Economics of Regulation
• Or y = Y/L = Akα • Gross investment per worker =
8. Contribution of Capital Deepening = Labor Æ
ɉ Š + 𝛿 + 𝑛Ë 𝑘
productivity growth rate – TFP 5. Å
www.finquiz.com All rights reserved
Downloaded by Smit Gandhi (smith22595@gmail.com)
You might also like
- Mock Exam 2023 #2 First Session Ethical and Professional StandardsDocument93 pagesMock Exam 2023 #2 First Session Ethical and Professional StandardsKunal PoddarNo ratings yet
- FinQuiz - CFA Level 2, 2020 - 2021 - Formula SheetDocument33 pagesFinQuiz - CFA Level 2, 2020 - 2021 - Formula SheetDaniel LópezNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2 - 2020Document3 pagesAssignment 2 - 2020Mpho NkuNo ratings yet
- Project On "Study of Venture Capital in India"Document158 pagesProject On "Study of Venture Capital in India"Prashant Jadhav80% (84)
- VSTEP Writing Preparation PDFDocument39 pagesVSTEP Writing Preparation PDFNgân Hà Tô100% (1)
- R27 CFA Level 3Document10 pagesR27 CFA Level 3Ashna0188No ratings yet
- Equity Level II 2019 PracticeDocument119 pagesEquity Level II 2019 Practicehamza omar100% (2)
- CFA Level 2 FSADocument3 pagesCFA Level 2 FSA素直和夫No ratings yet
- FinQuiz Level2Mock2016Version1JunePMSolutionsDocument56 pagesFinQuiz Level2Mock2016Version1JunePMSolutionsDavid LêNo ratings yet
- 2 Cfa l1 2023 Fsa Corporate Issuers Fintree Juice NotesDocument92 pages2 Cfa l1 2023 Fsa Corporate Issuers Fintree Juice NotesАika AuganNo ratings yet
- Cotton Web AssignmentDocument2 pagesCotton Web AssignmentTalha ZubairNo ratings yet
- Level II of CFA Program Mock Exam 1 - Solutions (AM)Document56 pagesLevel II of CFA Program Mock Exam 1 - Solutions (AM)Faizan UllahNo ratings yet
- Excel Shortcuts For ValuationDocument13 pagesExcel Shortcuts For ValuationsmithNo ratings yet
- BP B1 Tests Unit1Document6 pagesBP B1 Tests Unit1JovanaNo ratings yet
- FinQuiz - Curriculum Note, Study Session 2, Reading 5Document1 pageFinQuiz - Curriculum Note, Study Session 2, Reading 5Sankalp Jain0% (1)
- CFA Level 2 Cheat SheetDocument24 pagesCFA Level 2 Cheat SheetdbohnentvNo ratings yet
- 2019 20 CFA Level I Curriculum ChangesDocument20 pages2019 20 CFA Level I Curriculum ChangesNadia JNo ratings yet
- Usgaap, Igaap & IfrsDocument7 pagesUsgaap, Igaap & IfrsdhangarsachinNo ratings yet
- Mock Exam 2023 #1 Second Session Corporate Finance, Equity, FixedDocument88 pagesMock Exam 2023 #1 Second Session Corporate Finance, Equity, Fixedvedant.diwan26100% (1)
- Dokumen - Tips Finquiz Cfa Level I Mock Exam 1 Solutions Am Questions Topic MinutesDocument76 pagesDokumen - Tips Finquiz Cfa Level I Mock Exam 1 Solutions Am Questions Topic MinutesНаталия МорзаNo ratings yet
- Solutions Paper - TVMDocument4 pagesSolutions Paper - TVMsanchita mukherjeeNo ratings yet
- Registered Prep Provider of CFA InstituteDocument18 pagesRegistered Prep Provider of CFA InstituteSergiu CrisanNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Methods: Reading Number Reading Title Study SessionDocument40 pagesQuantitative Methods: Reading Number Reading Title Study SessionNGOC NHINo ratings yet
- 道德、经济、数量、组合、固收、衍生Document170 pages道德、经济、数量、组合、固收、衍生Ariel MengNo ratings yet
- DA4399 CFA Level III Quick SheetDocument9 pagesDA4399 CFA Level III Quick SheetJackNo ratings yet
- CFA III-Performance Evaluation关键词清单Document9 pagesCFA III-Performance Evaluation关键词清单Thanh NguyenNo ratings yet
- CFA - L2 - Quicksheet Sample PDFDocument1 pageCFA - L2 - Quicksheet Sample PDFMohit PrasadNo ratings yet
- Earl CaseDocument5 pagesEarl CaseKamen KamenNo ratings yet
- 2024 l1 Topics CombinedDocument27 pages2024 l1 Topics CombinedShaitan LadkaNo ratings yet
- Management Trainee Application Bangladesh DairyDocument1 pageManagement Trainee Application Bangladesh DairynyeemalahadNo ratings yet
- 2014 CFA Level 3 Mock Exam Afternoon - AnsDocument48 pages2014 CFA Level 3 Mock Exam Afternoon - AnsElsiiieNo ratings yet
- CFA Level 2 Fixed Income 2017Document52 pagesCFA Level 2 Fixed Income 2017EdmundSiauNo ratings yet
- CFA Results - FinalDocument35 pagesCFA Results - FinalJon doeNo ratings yet
- CFA Level II Item-Set - Questions Study Session 3 June 2019: Reading 7 Correlation and RegressionDocument30 pagesCFA Level II Item-Set - Questions Study Session 3 June 2019: Reading 7 Correlation and Regressionkren24No ratings yet
- FinQuiz Level1Mock2016Version1JuneAMQuestions PDFDocument39 pagesFinQuiz Level1Mock2016Version1JuneAMQuestions PDFAnimesh ChoubeyNo ratings yet
- FinQuiz - Curriculum Note, Study Session 2, Reading 4Document5 pagesFinQuiz - Curriculum Note, Study Session 2, Reading 4Daniel LópezNo ratings yet
- Mock Exam - AM Questions AnalysisDocument30 pagesMock Exam - AM Questions Analysis12jdNo ratings yet
- Cfa Level 1 LOS Command WordsDocument0 pagesCfa Level 1 LOS Command WordsHummingbird11688No ratings yet
- CFAI L2 Practice Exam 2017 PM SessionDocument23 pagesCFAI L2 Practice Exam 2017 PM SessionsergiopelaezboverNo ratings yet
- Calculate Financial Equations & ModelsDocument18 pagesCalculate Financial Equations & Modelszev zNo ratings yet
- 2021 CFA Level II Mock Exam - AM Session Alan Watson Case StudyDocument34 pages2021 CFA Level II Mock Exam - AM Session Alan Watson Case StudyMUHAMMAD SAFWAN AHMAD MUSLIMNo ratings yet
- Level III of CFA Program Mock Exam 1 - Questions (AM)Document26 pagesLevel III of CFA Program Mock Exam 1 - Questions (AM)Lê Chấn PhongNo ratings yet
- CFA Level I - 8feb (Optimized)Document55 pagesCFA Level I - 8feb (Optimized)RAHUL AggarwalNo ratings yet
- 2008 L2 Mock01 - QDocument46 pages2008 L2 Mock01 - QRavi RanjanNo ratings yet
- CFA Level III Mock Exam 4 June, 2018 Revision 1Document47 pagesCFA Level III Mock Exam 4 June, 2018 Revision 1Munkhbaatar SanjaasurenNo ratings yet
- Fintree CFA LI 2018 Curriculum ChangesDocument2 pagesFintree CFA LI 2018 Curriculum ChangesMohamed GamalNo ratings yet
- 2018年6月CFA2级Mock Exam PM(试题版)Document27 pages2018年6月CFA2级Mock Exam PM(试题版)merton14No ratings yet
- Cfa Notes IftDocument15 pagesCfa Notes IftShubham SharmaNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Methods: House of KnowledgeDocument11 pagesQuantitative Methods: House of KnowledgeTanvir Ahmed Syed100% (1)
- Benefits FinQuiz Question BankDocument3 pagesBenefits FinQuiz Question BankCratos_PoseidonNo ratings yet
- CFA Level 1 Sample Answers - CFA EssentialsDocument12 pagesCFA Level 1 Sample Answers - CFA EssentialsPhisit SucharitsopitNo ratings yet
- 2024 L1 FsaDocument108 pages2024 L1 Fsahamna wahabNo ratings yet
- Depreciation and Amortization SchedulesDocument36 pagesDepreciation and Amortization SchedulestejaasNo ratings yet
- L1 - Roadmap To Passing The CFA ExamDocument18 pagesL1 - Roadmap To Passing The CFA ExamSaman BajwaNo ratings yet
- FinQuiz Level2Mock2016Version6JuneAMSolutionsDocument61 pagesFinQuiz Level2Mock2016Version6JuneAMSolutionsAjoy RamananNo ratings yet
- CFA Level 2, June, 2017 - Formula SheetDocument34 pagesCFA Level 2, June, 2017 - Formula Sheetpuneetgupta316230891% (11)
- The Standard Model (And Flavour (Anomalies) ) : Andrea Romanino, SISSA, Romanino@sissa - ItDocument36 pagesThe Standard Model (And Flavour (Anomalies) ) : Andrea Romanino, SISSA, Romanino@sissa - ItDennis Diaz TrujilloNo ratings yet
- GRSDocument9 pagesGRSNeemaNo ratings yet
- PDF For Color Printout1Document6 pagesPDF For Color Printout1ankit kumarNo ratings yet
- T5 Moleculardescriptors Models PDFDocument9 pagesT5 Moleculardescriptors Models PDFSuchismita SahuNo ratings yet
- T5 Moleculardescriptors Models PDFDocument9 pagesT5 Moleculardescriptors Models PDFSuchismita SahuNo ratings yet
- A-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsFrom EverandA-level Maths Revision: Cheeky Revision ShortcutsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (8)
- Let's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 8From EverandLet's Practise: Maths Workbook Coursebook 8No ratings yet
- TCS BOB CapsDocument8 pagesTCS BOB CapssmithNo ratings yet
- Infosys BOB CapsDocument8 pagesInfosys BOB CapssmithNo ratings yet
- Sharekhan Mutual Fund Finder Top PicksDocument4 pagesSharekhan Mutual Fund Finder Top PickssmithNo ratings yet
- RBI lifts restriction on HDFC Bank's new credit card sourcingDocument6 pagesRBI lifts restriction on HDFC Bank's new credit card sourcingsmithNo ratings yet
- The Life and Teachings of MahaviraDocument117 pagesThe Life and Teachings of MahavirasmithNo ratings yet
- What Is A Payment Bank PDFDocument76 pagesWhat Is A Payment Bank PDFsmithNo ratings yet
- Payment BanksDocument7 pagesPayment BanksAnkaj MohindrooNo ratings yet
- Ctryprem July 21Document176 pagesCtryprem July 21smith100% (1)
- Challenges Faced by MFIsDocument4 pagesChallenges Faced by MFIsArpit Gupta50% (4)
- Bfil Ar 2018 PDFDocument182 pagesBfil Ar 2018 PDFsmith100% (1)
- Microfinance (D)Document75 pagesMicrofinance (D)smithNo ratings yet
- GST Chapter Wise RateDocument213 pagesGST Chapter Wise RateMoneycontrol News92% (280)
- What Is A Payment Bank PDFDocument76 pagesWhat Is A Payment Bank PDFsmithNo ratings yet
- IndexDocument2 pagesIndexsmithNo ratings yet
- ChangesDocument1 pageChangessmithNo ratings yet
- YES BankDocument36 pagesYES BanksmithNo ratings yet
- Powered by FT Engines: Best Buy Best Sell Exchange Description Qty Price Qty Price Scrip Code Day 4om Expiry Strike PriceDocument6 pagesPowered by FT Engines: Best Buy Best Sell Exchange Description Qty Price Qty Price Scrip Code Day 4om Expiry Strike PricesmithNo ratings yet
- What is Microfinance and How Did it StartDocument22 pagesWhat is Microfinance and How Did it StartsmithNo ratings yet
- Loan Disbursed by SKS Micro Finance From Year 2009 To 2014 ChartDocument12 pagesLoan Disbursed by SKS Micro Finance From Year 2009 To 2014 ChartsmithNo ratings yet
- TO THE ProjectDocument8 pagesTO THE ProjectsmithNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document11 pagesPresentation 1smithNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document11 pagesPresentation 1smithNo ratings yet
- Name:Smit Deepak Gandhi Roll No:15 Course:T.Y (Financial Markets) Topic:Micro Finance Institution in India Guide Name:Sir Prathamesh TawdeDocument2 pagesName:Smit Deepak Gandhi Roll No:15 Course:T.Y (Financial Markets) Topic:Micro Finance Institution in India Guide Name:Sir Prathamesh TawdesmithNo ratings yet
- ArbitrageDocument3 pagesArbitragesmithNo ratings yet
- Dhairya FormDocument2 pagesDhairya FormsmithNo ratings yet
- MicrofinanceDocument71 pagesMicrofinancesmith100% (1)
- Microfinance New FinalisedDocument75 pagesMicrofinance New FinalisedsmithNo ratings yet
- How To Deal With Multiple SAP Logons - Simple Excel VBADocument14 pagesHow To Deal With Multiple SAP Logons - Simple Excel VBAangel saezNo ratings yet
- Communication Education For AdultsDocument7 pagesCommunication Education For AdultsHaechan MarkNo ratings yet
- SYNOPSIS On Retail MarketingDocument23 pagesSYNOPSIS On Retail MarketingHariharasudan HariNo ratings yet
- Termpaper Proposal EDCLDocument5 pagesTermpaper Proposal EDCLAbir MohammadNo ratings yet
- Silo Design1Document20 pagesSilo Design1Sasikumar JothiNo ratings yet
- Bulk Storage Optimization for Large QuantitiesDocument3 pagesBulk Storage Optimization for Large Quantitiesbirojivenkat100% (1)
- The Validity of Beck Depression Inventory - Short Version in Depressed Patients Diagnosed According To ICD10Document11 pagesThe Validity of Beck Depression Inventory - Short Version in Depressed Patients Diagnosed According To ICD10sarhang talebaniNo ratings yet
- Modeling For Simulation and Control of Acid-Base Neutralization SystemsDocument12 pagesModeling For Simulation and Control of Acid-Base Neutralization SystemscacacocoNo ratings yet
- Perbandingan Harga LaptopDocument5 pagesPerbandingan Harga Laptopgihe purnamaNo ratings yet
- OOP With C++ (Assignment - 3) CSE, 3 Semester: Prepared By: Deepak Uniyal (Assistant Professor CSE, GEU)Document2 pagesOOP With C++ (Assignment - 3) CSE, 3 Semester: Prepared By: Deepak Uniyal (Assistant Professor CSE, GEU)Govind TripathiNo ratings yet
- 5239 PLC SplitterDocument3 pages5239 PLC SplittermksayshiNo ratings yet
- Start Here Middle School Public Forum PREVIEWDocument5 pagesStart Here Middle School Public Forum PREVIEWi am henryNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1: Introduction To Change Management: Fundamental Questions For OrganisationsDocument43 pagesLecture 1: Introduction To Change Management: Fundamental Questions For OrganisationsattilashelleyNo ratings yet
- Untitled PresentationDocument14 pagesUntitled PresentationThe BeatableNo ratings yet
- State of Maine DMR Motion To InterveneDocument147 pagesState of Maine DMR Motion To InterveneNEWS CENTER MaineNo ratings yet
- CSS Interview Questions 2022Document21 pagesCSS Interview Questions 2022christianlamb999No ratings yet
- Module 4 - Contemp World - BSA2Document7 pagesModule 4 - Contemp World - BSA2Marian AntipoloNo ratings yet
- Women EmpowermentDocument14 pagesWomen EmpowermentProfessor HappyNo ratings yet
- Accident Investigation, Reporting and Analysis: Safety Engineering and Management For MEDocument38 pagesAccident Investigation, Reporting and Analysis: Safety Engineering and Management For MEAndre De VillaNo ratings yet
- Test Your Knowledge On Pumps - Online Quiz - Chemical Engineering SiteDocument10 pagesTest Your Knowledge On Pumps - Online Quiz - Chemical Engineering Sitemyself_riteshNo ratings yet
- Module 4 Self-Concept, Perceptions and AttributionsDocument25 pagesModule 4 Self-Concept, Perceptions and AttributionsJoebet Debuyan100% (3)
- PCI Medical Catalog DOCS 500Document1 pagePCI Medical Catalog DOCS 500anghello buendiaNo ratings yet
- SAIL Catalogue: DownloadDocument16 pagesSAIL Catalogue: Downloadmishra usNo ratings yet
- How To Write A VHDL Test BenchDocument4 pagesHow To Write A VHDL Test BenchEvliya ÜlkerNo ratings yet
- فايبر L.3Document13 pagesفايبر L.3Alaa AdeebNo ratings yet
- GLA University - Student's No Dues DetailsDocument2 pagesGLA University - Student's No Dues DetailsRishi JakarNo ratings yet
- Eh TW5825Document2 pagesEh TW5825Lim Hendra Kurniawan Halim (Hendra)No ratings yet
- Effects of Financial Problem On Academic Performance: Submitted To: Althea B. OrtizDocument8 pagesEffects of Financial Problem On Academic Performance: Submitted To: Althea B. OrtizSherwin Jay Salanio Solomon25% (4)