Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Week 3 - Lesson 2
Week 3 - Lesson 2
Uploaded by
Afraz Ul Haque Rupak0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views9 pagesThe document defines and provides examples of several set operations:
1) Set union combines elements that are in set A, B, or both. Intersection includes elements only in both sets. Difference includes elements only in the first set.
2) The complement of a set includes all elements not in the original set.
3) The Cartesian product of sets creates ordered pairs of elements, with the first element from the first set and the second from the second set.
Original Description:
Original Title
week 3_lesson 2
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThe document defines and provides examples of several set operations:
1) Set union combines elements that are in set A, B, or both. Intersection includes elements only in both sets. Difference includes elements only in the first set.
2) The complement of a set includes all elements not in the original set.
3) The Cartesian product of sets creates ordered pairs of elements, with the first element from the first set and the second from the second set.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
13 views9 pagesWeek 3 - Lesson 2
Week 3 - Lesson 2
Uploaded by
Afraz Ul Haque RupakThe document defines and provides examples of several set operations:
1) Set union combines elements that are in set A, B, or both. Intersection includes elements only in both sets. Difference includes elements only in the first set.
2) The complement of a set includes all elements not in the original set.
3) The Cartesian product of sets creates ordered pairs of elements, with the first element from the first set and the second from the second set.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 9
Subehenur Latif
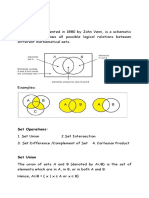
Set Operations include
Set Union,
Set Intersection,
Set Difference,
Complement of Set, and
Cartesian Product.
The union of sets A and B (denoted by A ∪ B) is the set
of elements which are in A, in B, or in both A and B.
Hence, A ∪ B = {x | x ∈ A OR x ∈ B}.
Example − If A = {10, 11, 12, 13} and B = {13, 14, 15},
then A ∪ B = {10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15}. (The common
element occurs only once)
The intersection of sets A and B (denoted by A ∩ B) is the set
of elements which are in both A and B. Hence, A ∩ B = {x |
x ∈ A AND x ∈ B}.
Example − If A = {11, 12, 13} and B = {13, 14, 15}, then A ∩
B = {13}.
The set difference of sets A and B (denoted by A − B)
is the set of elements which are only in A but not in
B. Hence, A − B = {x | x ∈ A AND x ∉ B}.
Example − If A = {10, 11, 12, 13} and B = {13, 14,
15}, then (A− B) = {10, 11, 12} and (B − A) = {14,
15}. Here, we can see (A − B) ≠ (B − A)
Complement of a Set= (U − A) where U is a universal set which
contains all objects.
Example − If A = {x | x belongs to set of odd integers} then A' =
{y | y does not belong to set of odd integers}
The complement of a set A (denoted by A’) is the set of elements
which are not in set A. Hence, A' = {x | x ∉ A}.
More specifically, A
The Cartesian product of n number of sets
A1, A2 .....An, defined as A1 × A2 ×..... × An, are the
ordered pair (x1, x2,....xn) where x1 ∈ A1, x2 ∈ A2, ......
xn ∈ An
Example − If we take two sets A = {a, b} and B = {1,
2},
The Cartesian product of A and B is written as − A × B =
{(a, 1), (a, 2), (b, 1), (b, 2)}
The Cartesian product of B and A is written as − B × A =
{(1, a), (1, b), (2, a), (2, b)}
You might also like
- M1 - Sets and Functions: University of San Agustin Cpe122 - Discrete Math, 2 Sem Ay2020-21Document6 pagesM1 - Sets and Functions: University of San Agustin Cpe122 - Discrete Math, 2 Sem Ay2020-21Stephanie AzucenaNo ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematics Sets Relations FunctionsDocument15 pagesDiscrete Mathematics Sets Relations FunctionsMuhd FarisNo ratings yet
- Set Theory and Real NumbersDocument16 pagesSet Theory and Real NumbersnehaNo ratings yet
- Set TheroyDocument22 pagesSet TheroyManojNo ratings yet
- Sets, Relations and Functions SynopsisDocument8 pagesSets, Relations and Functions Synopsiskhv_19No ratings yet
- Venn DiagramsDocument13 pagesVenn DiagramsAnnjanah AsilomNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Set Theory Operations 1Document13 pagesLecture 2 Set Theory Operations 1TanveerNo ratings yet
- Discrete AssDocument5 pagesDiscrete AssAsk NameNo ratings yet
- Lecture 2 Set Theory Operations 1Document13 pagesLecture 2 Set Theory Operations 1TanveerNo ratings yet
- Monograph PDFDocument49 pagesMonograph PDFĀlok KrNo ratings yet
- P1-Set TheoryDocument41 pagesP1-Set TheoryDipanwita DebnathNo ratings yet
- Sets (Foundation of Math)Document30 pagesSets (Foundation of Math)Azharlina Rizqi ArdinaNo ratings yet
- MFCS Unit - 2Document43 pagesMFCS Unit - 2paavanmokshaNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy LogicDocument40 pagesFuzzy LogicSourabh123456789No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 (Math Preliminaries)Document46 pagesLecture 3 (Math Preliminaries)ملک آصفNo ratings yet
- Venn Diagram: Set OperationsDocument6 pagesVenn Diagram: Set OperationsAkim ApallaNo ratings yet
- Discrete StructureDocument9 pagesDiscrete StructureAhmad AkhtarNo ratings yet
- CMT Fuzzy LogicDocument36 pagesCMT Fuzzy Logiclama209721No ratings yet
- Discrete Structure Unit 1Document15 pagesDiscrete Structure Unit 1Learn UpNo ratings yet
- Struktur Diskrit I-2, Sets (Himpunan) : SubsetsDocument6 pagesStruktur Diskrit I-2, Sets (Himpunan) : Subsetsazi370No ratings yet
- Math Lec 1Document7 pagesMath Lec 1AngelicaJaneA.SuanNo ratings yet
- HO 1 3 Intro Sets RelDocument14 pagesHO 1 3 Intro Sets RelFarjad AliNo ratings yet
- Set Operations: By: Analou Cag-Ong, MscsDocument9 pagesSet Operations: By: Analou Cag-Ong, MscsApril Rose RaymundoNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes Discrete Unit 1Document46 pagesLecture Notes Discrete Unit 1Aryan pathakNo ratings yet
- Lecture 09Document65 pagesLecture 09Raja SaHABNo ratings yet
- And Industral University: Discrete Mathematics and Its ApplicationsDocument28 pagesAnd Industral University: Discrete Mathematics and Its ApplicationsFidan IbadullayevaNo ratings yet
- 07-LEC07 Sets1Document26 pages07-LEC07 Sets1rifat7412548No ratings yet
- Set OperationsDocument4 pagesSet Operationsanh_em5503No ratings yet
- CMT Fuzzy LogicDocument35 pagesCMT Fuzzy LogicN.RAMAKUMARNo ratings yet
- Discrete Mathematics: Adjective SynonymsDocument37 pagesDiscrete Mathematics: Adjective SynonymsHarsh SrivastavaNo ratings yet
- DML Unit 3 (Sets, Functions and Relations) - Lecture SlidesDocument126 pagesDML Unit 3 (Sets, Functions and Relations) - Lecture SlidesAditya JainNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document44 pagesChapter 2معتز منير حسن الحسنيNo ratings yet
- Basic Structures Sets, Functions Sequences, and SumsDocument34 pagesBasic Structures Sets, Functions Sequences, and SumsVũ Thái AnhNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document45 pagesChapter 2مهند شادي عيسى (ابعيسى)No ratings yet
- Chapter 1 Introduction To The Theory of ComputationDocument70 pagesChapter 1 Introduction To The Theory of ComputationdawodNo ratings yet
- Discrete MathematicsDocument75 pagesDiscrete MathematicsJean Rances Amparo RanidoNo ratings yet
- Unit - 1 Set TheoryDocument4 pagesUnit - 1 Set TheoryKRITRIV SARAIWALNo ratings yet
- Sets, Notations and InductionsDocument30 pagesSets, Notations and InductionsChristine Mae CionNo ratings yet
- Algebra and General Mathematics Set TheoryDocument7 pagesAlgebra and General Mathematics Set TheoryJirah GicangaoNo ratings yet
- CS101 - Chapter3 Discrete MathDocument39 pagesCS101 - Chapter3 Discrete MathAlthea PonceNo ratings yet
- Set: in Our Daily Life We Use Phrases Like A Bunch of Keys, A Set of Books, A Tea Set, ADocument20 pagesSet: in Our Daily Life We Use Phrases Like A Bunch of Keys, A Set of Books, A Tea Set, ADeepak SharmaNo ratings yet
- SetsDocument5 pagesSetsSameer NamdeoNo ratings yet
- Sets Lecture NotesDocument5 pagesSets Lecture NotesRhenan WafooNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Discrete Structures - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument29 pagesUnit 1 - Discrete Structures - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inSumit KumarNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 - Part1 - SetDocument59 pagesChapter2 - Part1 - SetliasakinahNo ratings yet
- Discrete Structure 1Document29 pagesDiscrete Structure 1malikabdullah0120No ratings yet
- A Set Is A Collection of Well Defined and Distinct ObjectsDocument3 pagesA Set Is A Collection of Well Defined and Distinct ObjectsTedz Salvador NaragNo ratings yet
- Note That Some Books Include 0 As A Natural NumberDocument5 pagesNote That Some Books Include 0 As A Natural NumberChristian Cedrick OlmonNo ratings yet
- Unit-1 (Cse 245)Document58 pagesUnit-1 (Cse 245)Harsh DubeyNo ratings yet
- Sets TheoryDocument39 pagesSets TheoryArt PlatformNo ratings yet
- MATH 2 1st ReleaseopDocument8 pagesMATH 2 1st Releaseopjohannes bolianNo ratings yet
- BTech 4th Lecture Notes SetsDocument16 pagesBTech 4th Lecture Notes SetsPrabhjot SinghNo ratings yet
- Sets and Relations and Functions - 221129 - 140023Document45 pagesSets and Relations and Functions - 221129 - 140023Kanishk KrishnanNo ratings yet
- Set Theory: Well-Defined Collections and SetsDocument32 pagesSet Theory: Well-Defined Collections and SetsTeacher Arvin OfficialNo ratings yet
- Sets and Cardinality Notes For 620-111: C. F. Miller Semester 1, 2000Document21 pagesSets and Cardinality Notes For 620-111: C. F. Miller Semester 1, 2000DarKevin PerillaNo ratings yet
- Bahan Ajar Materi HimpunanDocument6 pagesBahan Ajar Materi HimpunanMTs Nurul Mukhtariyah SindangkertaNo ratings yet
- All Formulas and Notes For Maths Class 11 Note Download Chapter 1 and 2 Sets and Relations and Func PDFDocument11 pagesAll Formulas and Notes For Maths Class 11 Note Download Chapter 1 and 2 Sets and Relations and Func PDFthirumalaiselvankNo ratings yet
- CH3 SetsDocument79 pagesCH3 SetsirwanNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Lesson 2.2Document10 pagesWeek 2 - Lesson 2.2Afraz Ul Haque RupakNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Lesson 1Document22 pagesWeek 2 - Lesson 1Afraz Ul Haque RupakNo ratings yet
- Week 2 - Lesson 2.1Document16 pagesWeek 2 - Lesson 2.1Afraz Ul Haque RupakNo ratings yet
- Cse212 3Document10 pagesCse212 3Afraz Ul Haque RupakNo ratings yet
- Assignment: Submitted To: Ms. Chowdhury Abida Anjum EraDocument4 pagesAssignment: Submitted To: Ms. Chowdhury Abida Anjum EraAfraz Ul Haque RupakNo ratings yet