Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Thapar University
Uploaded by
DEEPAK KOUNDALOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Thapar University
Uploaded by
DEEPAK KOUNDALCopyright:
Available Formats
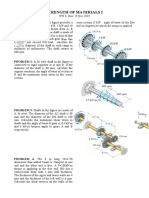
THAPAR UNIVERSITY
UES 010: SOLIDS AND STRUCTURES
B.E. – Second Year Session: 2016-2017
Tutorial Sheet No. 4 (Torsion of circular shafts)
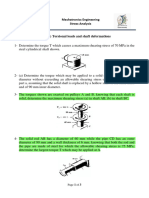
1. A solid steel shaft 5 m long is stressed to 80 MPa when twisted through 40. Using G = 83 GPa, compute the
shaft diameter. What power the shaft at 20 Hz can transmit?
2. What is the minimum diameter of solid steel shaft that will not twist through more than 3 0, in a 6 m
length when subjected to a torque of 12kN-m? What is the maximum shearing stress developed? G = 83
GPa.
3. A steel shaft has to transmit a mean power of 100kW at 250 rpm. The allowable shear stress is 75MPa
and the maximum power transmitted exceeds the mean power by 30%. Determine
a) The suitable diameter for a solid shaft
b) The suitable diameter for a hollow shaft whose inside diameter is 0.8 times the outside diameter
c) Percentage saving in weight when solid shaft is replaced by hollow shaft.
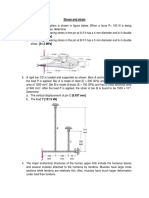
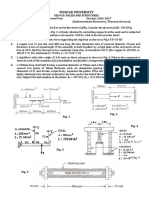
4. A steel shaft ABCD having a total length of 4.8 m consists of three lengths having different sections as
follows
AB Hollow d0 = 12 cm di = 10.2 cm
BC Solid d = 12 cm
CD Solid d = 9.6 cm
If the angle of twist is same for each section, determine the lengths of each section.
Find the value of applied torque and total angle of twist if maximum shear stress in hollow section is
limited to 50MPa, G = 84GPa.
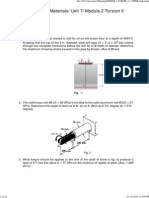
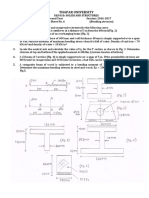
5. A 100kW motor at 40 rpm is driving a line shaft at B (Fig.1). Determine d1 and d2. Also determine the
angle of twist in AB and BC.
Allowable shear stress is 50MPa and G = 80GPa. (Bending is avoided)
32kW off 100kW 68kW off
(Fig.1)
A d1 B d2 C AB = 6m, BC = 3m
You might also like
- Tute Sheet 5 - Tosion in ShaftsDocument1 pageTute Sheet 5 - Tosion in ShaftsSimranjeet SinghNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 3Document3 pagesStrength of Materials - Task 1. Chapter 3NEIVER ALEVIS CASTRO JULIONo ratings yet
- Tutorial Chapter 1Document1 pageTutorial Chapter 1Melvin Shady PereiraNo ratings yet
- Chapter 03Document83 pagesChapter 03Md. Mushfikur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials I: PROBLEM 1. Gear C in The Figure Provides ADocument2 pagesStrength of Materials I: PROBLEM 1. Gear C in The Figure Provides AzıptıNo ratings yet
- Worked Solution To Various QuestionsDocument29 pagesWorked Solution To Various QuestionsJohn MutumaNo ratings yet
- Torsion: Torsion Flanged Bolt Couplings Torsion of Thin-Walled Tube Helical SpringsDocument79 pagesTorsion: Torsion Flanged Bolt Couplings Torsion of Thin-Walled Tube Helical SpringsDaniel ManivoughNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6Document26 pagesChapter 6yuwarajaNo ratings yet
- Elementos Sometidos A TorsiónDocument4 pagesElementos Sometidos A TorsiónAnthony Ash EstradaNo ratings yet
- 3 1-TorsionstressandstrainDocument19 pages3 1-TorsionstressandstrainKim HarlyNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 3Document2 pagesTutorial 3AmrinaAkmal0% (1)
- Exercises of TorsionDocument3 pagesExercises of TorsionPham CongNo ratings yet
- Problem Set No. 3Document2 pagesProblem Set No. 3marcusluismacusiNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 3 - Torsion - Class ExamplesDocument14 pagesChapter - 3 - Torsion - Class ExamplesCandice MdakaNo ratings yet
- Ibong Tiririt (MDSP 3) : MACHINE DESIGN/SHOP PRACTICE (Solved Problems and Answered Elements) Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument33 pagesIbong Tiririt (MDSP 3) : MACHINE DESIGN/SHOP PRACTICE (Solved Problems and Answered Elements) Multiple Choice QuestionsNico Atencio100% (1)
- Tutorial No 4 TorsionDocument7 pagesTutorial No 4 TorsionwaleedkhalillahmedNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Solved ProblemsDocument10 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Solved ProblemsYan NieNo ratings yet
- Torsion 3-1 IntroductionDocument8 pagesTorsion 3-1 IntroductionStephanie Danielle HizoleNo ratings yet
- Paper ID (A08011: B.Tech. (Sem. - 3'd)Document3 pagesPaper ID (A08011: B.Tech. (Sem. - 3'd)bravo16893No ratings yet
- MDSP Diag 1Document3 pagesMDSP Diag 1Tyron RebellonNo ratings yet
- Prelim 2022 SMDocument4 pagesPrelim 2022 SMARJUNANo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials 4th Ed by Ferdinand L Singer Andrew Pytel Www07MettkDocument21 pagesStrength of Materials 4th Ed by Ferdinand L Singer Andrew Pytel Www07Mettkvjereme100% (3)
- Strength of MaterialsDocument6 pagesStrength of MaterialsRafael Santos100% (1)
- Quiz No 2 - Set DDocument2 pagesQuiz No 2 - Set DMayoune Nasinopa GalvezNo ratings yet
- MECHANICS (ME10001) : AluminumDocument2 pagesMECHANICS (ME10001) : AluminumRahulNo ratings yet
- Ce234 Topic 06-07Document31 pagesCe234 Topic 06-07Nicholas Bonn SingNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Solved ProblemsDocument10 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Solved ProblemsIsabelle LunaNo ratings yet
- Mechanics of Deformable Bodies Solved ProblemsDocument10 pagesMechanics of Deformable Bodies Solved ProblemsYan NieNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 4Document6 pagesTutorial 4Ysgn MysgnNo ratings yet
- Mechanics NewDocument56 pagesMechanics NewB LowNo ratings yet
- MECH 2013 DT022 - 023 Ken Keating Sem 2 2010-1Document4 pagesMECH 2013 DT022 - 023 Ken Keating Sem 2 2010-1Shiyas BasheerNo ratings yet
- Exercise No. 2Document2 pagesExercise No. 2mariamaber007No ratings yet
- Sheet 4 Torsional Loads and Shaft Deformations - MechatronicsDocument3 pagesSheet 4 Torsional Loads and Shaft Deformations - MechatronicsAhmed AlaaNo ratings yet
- Som Ese 2021Document7 pagesSom Ese 2021Gaurav ManeNo ratings yet
- Quiz No 2 - Set ADocument2 pagesQuiz No 2 - Set AMayoune Nasinopa Galvez100% (1)
- Civl 2120 Ch3 QsDocument2 pagesCivl 2120 Ch3 QsTina ChenNo ratings yet
- Faculty of Engineering School of Automobile, Mechanical & Mechatronics EngineeringDocument2 pagesFaculty of Engineering School of Automobile, Mechanical & Mechatronics EngineeringpranithNo ratings yet
- Strength of Materials/ Unit 7/ Module 2 Torsion II: Problem SetDocument22 pagesStrength of Materials/ Unit 7/ Module 2 Torsion II: Problem Setneeru143No ratings yet
- MEE 212 Pre - CH 3Document16 pagesMEE 212 Pre - CH 3alhassan Abdul MaleeqNo ratings yet
- SOMDocument14 pagesSOMAditya ojhaNo ratings yet
- SOM Axial Deformation.Document24 pagesSOM Axial Deformation.yas22e5019No ratings yet
- 9A01301 Mechanics of SolidsDocument4 pages9A01301 Mechanics of SolidssivabharathamurthyNo ratings yet
- Solution 304: Hide Click Here To Show or Hide The SolutionDocument21 pagesSolution 304: Hide Click Here To Show or Hide The SolutionRommell Bacos100% (1)
- 3 - Torsional and Bending StressDocument24 pages3 - Torsional and Bending StressAya AyaNo ratings yet
- Draw The SFD BMDDocument12 pagesDraw The SFD BMDAshok PradhanNo ratings yet
- 3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat NoDocument5 pages3 Hours / 70 Marks: Seat Noopwigs444No ratings yet
- Torsion and PowerDocument17 pagesTorsion and PowerMariscotes Jam Jr.No ratings yet
- Mech-nd-2020-Me 8593-Design of Machine Elements-334300796-X10703 (Me8593) Design of Machine ElementsDocument5 pagesMech-nd-2020-Me 8593-Design of Machine Elements-334300796-X10703 (Me8593) Design of Machine ElementsARIGARAN SNo ratings yet
- STL203SDocument6 pagesSTL203SClaudioNo ratings yet
- Torque (Examples and Seatwork)Document4 pagesTorque (Examples and Seatwork)Laurence PaulNo ratings yet
- B - Strength of Materials - SP - SolutionDocument3 pagesB - Strength of Materials - SP - SolutionTanveer Pathan75% (16)
- Torsion ProblemsDocument7 pagesTorsion ProblemsLouie G NavaltaNo ratings yet
- UNC Problem SetDocument67 pagesUNC Problem SetjaysamNo ratings yet
- T 3A TorsionDocument3 pagesT 3A TorsionW. M. HaziqNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - TorsionDocument38 pagesChapter 3 - TorsionJovy NotorioNo ratings yet
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Rating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 3Rating: 3 out of 5 stars3/5 (1)
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1From EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1Rating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (4)
- Thapar UniversityDocument1 pageThapar UniversityDEEPAK KOUNDALNo ratings yet
- Thapar UniversityDocument1 pageThapar UniversityDEEPAK KOUNDALNo ratings yet
- Thapar University: o o - 6 o - 6 oDocument1 pageThapar University: o o - 6 o - 6 oDEEPAK KOUNDALNo ratings yet
- Thapar UniversityDocument1 pageThapar UniversityDEEPAK KOUNDALNo ratings yet
- Food Engineering and Science (UCH716)Document18 pagesFood Engineering and Science (UCH716)DEEPAK KOUNDALNo ratings yet
- Distillation Processes: Sub Code: UCH712Document9 pagesDistillation Processes: Sub Code: UCH712DEEPAK KOUNDALNo ratings yet
- Deepak Koundal: TH THDocument1 pageDeepak Koundal: TH THDEEPAK KOUNDALNo ratings yet
- Group A Chemical EngineeringDocument75 pagesGroup A Chemical EngineeringDEEPAK KOUNDALNo ratings yet
- Innovation &Document11 pagesInnovation &DEEPAK KOUNDALNo ratings yet