Professional Documents
Culture Documents
The Learning Curve For In-Vivo Characterisation of Small Colonic Polyps: Number Needed To Train (NNT) Is 200 Polyps
Uploaded by
russell1530 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views1 pageThis study aimed to determine the learning curve for an expert endoscopist using a new electronic chromoendoscopy technology (Pentax iScan) to characterize small colonic polyps in vivo. The endoscopist assessed 400 polyps from 168 patients using white light and iScan. Accuracy improved significantly from the first to third set of 100 polyps, reaching over 90% for both modalities. The number of polyps needed to achieve high accuracy (sensitivity >90%, specificity >75%) was determined to be 200, demonstrating the learning curve for proper use of the new technology. Excellent results were obtained once the endoscopist was proficient with iScan after reviewing over 200 polyps.
Original Description:
Original Title
P0650
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis study aimed to determine the learning curve for an expert endoscopist using a new electronic chromoendoscopy technology (Pentax iScan) to characterize small colonic polyps in vivo. The endoscopist assessed 400 polyps from 168 patients using white light and iScan. Accuracy improved significantly from the first to third set of 100 polyps, reaching over 90% for both modalities. The number of polyps needed to achieve high accuracy (sensitivity >90%, specificity >75%) was determined to be 200, demonstrating the learning curve for proper use of the new technology. Excellent results were obtained once the endoscopist was proficient with iScan after reviewing over 200 polyps.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
37 views1 pageThe Learning Curve For In-Vivo Characterisation of Small Colonic Polyps: Number Needed To Train (NNT) Is 200 Polyps
Uploaded by
russell153This study aimed to determine the learning curve for an expert endoscopist using a new electronic chromoendoscopy technology (Pentax iScan) to characterize small colonic polyps in vivo. The endoscopist assessed 400 polyps from 168 patients using white light and iScan. Accuracy improved significantly from the first to third set of 100 polyps, reaching over 90% for both modalities. The number of polyps needed to achieve high accuracy (sensitivity >90%, specificity >75%) was determined to be 200, demonstrating the learning curve for proper use of the new technology. Excellent results were obtained once the endoscopist was proficient with iScan after reviewing over 200 polyps.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
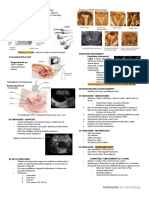
The learning curve for in-vivo characterisation of small colonic
polyps: number needed to train (NNT) is 200 polyps
PJ Basford, GR Longcroft-Wheaton, P Bhandari
Portsmouth Hospitals NHS Trust, Portsmouth, UK
Introduction & Aims Results cont.
• Indigocarmine (IC), narrow-band imaging (NBI) and • 154 polyps were non-neoplastic, 245 were adenomatous
Flexible Spectral Imaging Colour Enhancement (FICE) and 1 contained adenocarcinoma.
have been shown to be effective in the in-vivo diagnosis • Sensitivity and overall accuracy improved significantly for
of small colonic polyps. both imaging modalities in the 3rd set of polyps as
• The learning curve for achieving high level of accuracy compared to sets 1 and 2 (p<0.05). In Set 3&4 combined
with a new technology for real-time diagnosis of small
WL overall accuracies of 93.5% and 95.0% were achieved
colonic polyps has not been determined. with WL and iScan respectively. There were no significant
differences in overall accuracy between the 2 modalities
in Sets 3 and 4.
Methods • Negative predictive values for adenomatous histology of
• We aimed to assess the learning curve of a novel recto-sigmoid polyps ≤5mm for the entire study were
electronic in-vivo diagnosis technology (Pentax iScan) for 97.4% and 95.1% for WL and iScan respectively.
an expert endoscopist. iScan Overall Accuracy - Learning Curve
• Patients presenting for screening colonoscopy through
100
the UK Bowel Cancer Screening Programme were
Accuracy of In-vivo predicted histology %
90
prospectively recruited.
80
• All colonoscopies were performed by a single expert
70
endoscopist, with extensive experience in in-vivo 60
diagnosis, using Pentax EC-3890Li 1.2 Megapixel HD 50
colonoscopes and EPKi processor. 40
• Polyps <10mm in size were assessed sequentially using 3 30
modalities 1) White light HD endoscopy (WL), 2) Pentax 20
iScan surface, contrast and tone enhancement. Optical 10
magnification was not used. 0
1 to 100 101-200 201-300 301-400
• Predicted histology (non-neoplastic, adenoma, cancer)
WL 75 83 92 95
was recorded for each modality and compared to the WL (%) iScan (%)
iScan 82 82 93 97
final histopathological diagnosis. Set 1 Sensitivity 78.8 86.8
• Results were analysed for sensitivity and specificity for (Polyps 1-100) Specificity 70.8 76.6
neoplasia, and overall accuracy. Accuracy 75.0 82.0
• To assess any learning effect results were analysed in 4 Conclusions
sets of 100 consecutive polyps. Set 2 Sensitivity 86.6 85.1 1. Even in expert hands there is a significant learning curve
(Polyps 101-200) Specificity 75.8 75.8 for using a new technology for the in-vivo diagnosis of
Accuracy 83.0 82.0 small colonic polyps, with improvement in performance
over the first 200 polyps assessed.
Results Set 3 Sensitivity 96.2 98.7 2. Excellent results can be achieved once the new
• A total of 400 polyps in 168 patients were eligible for (Polyps 201-309) Specificity 77.3 72.7 technology has been mastered.
inclusion in the study. Accuracy 92.0 93.0 3. This is the first report of results achieved with high-
• Mean polyp diameter was 4.0mm, median 3mm. 169 definition white light endoscopy which are comparable
polyps were in the proximal colon and 231 in the distal Set 4 Sensitivity 92.3 94.2 with electronic chromoendoscopy and IC
(Polyps 301-400) Specificity 97.9 100.0
colon. chromoendoscopy.
Accuracy 95.0 97.0
You might also like
- Cheng, P. M. Et Al 2018Document9 pagesCheng, P. M. Et Al 2018Anonymous N7KGZx9rNo ratings yet
- Anoscopy: Top 10 Forgotten Diagnostic ProceduresDocument1 pageAnoscopy: Top 10 Forgotten Diagnostic ProceduresI G. A. Ratna DewiNo ratings yet
- Introduction To RadiologyDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Radiologysarguss14No ratings yet
- Results of A Technically Difficult Patient Study: Six Sites in North America and EuropeDocument8 pagesResults of A Technically Difficult Patient Study: Six Sites in North America and Europerichardpr8No ratings yet
- Dual-Energy CT Characteristics of Colon and Rectal Cancer Allows Differentiation From Stool by Dual-Source CTDocument6 pagesDual-Energy CT Characteristics of Colon and Rectal Cancer Allows Differentiation From Stool by Dual-Source CTRyana Fitriana IINo ratings yet
- CT Scan in Woman Oncology GynecologyDocument109 pagesCT Scan in Woman Oncology GynecologyAstien SuzmanNo ratings yet
- Torabinejad 2018Document6 pagesTorabinejad 2018viena mutmainnahNo ratings yet
- 433 FullDocument6 pages433 FullBhargav YagnikNo ratings yet
- Gutjnl 2012 303965.fullDocument11 pagesGutjnl 2012 303965.fullOngky AristianNo ratings yet
- 2018 Torabinejad Periapical Radiolucencies Using CBCT JOEDocument6 pages2018 Torabinejad Periapical Radiolucencies Using CBCT JOEJonatan Arroyo BautistaNo ratings yet
- Endoscopic Management of Early Adenocarcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of The Esophagus - Screening, Diagnosis, and Therapy AGA 2018Document16 pagesEndoscopic Management of Early Adenocarcinoma and Squamous Cell Carcinoma of The Esophagus - Screening, Diagnosis, and Therapy AGA 2018Nishiby PhạmNo ratings yet
- Investigations of Oral Cancer Revised 2022Document32 pagesInvestigations of Oral Cancer Revised 2022elle70503No ratings yet
- 2020 - LN Imaging Breast CR - Concurrent Diagnostic Tools - MarinoDocument12 pages2020 - LN Imaging Breast CR - Concurrent Diagnostic Tools - MarinoГаянэ АллахвердянNo ratings yet
- 2161 FullDocument6 pages2161 Fullpiano freakNo ratings yet
- Impact of Endoscopy System, High Definition, and Virtual Chromo-Endoscopy in Daily Routine Colonoscopy: A Randomized TrialDocument7 pagesImpact of Endoscopy System, High Definition, and Virtual Chromo-Endoscopy in Daily Routine Colonoscopy: A Randomized Trialm_manuela2002No ratings yet
- Correlation of Visual Inspection With Cytological and Histopathological Findings in Cervical NeoplasiaDocument4 pagesCorrelation of Visual Inspection With Cytological and Histopathological Findings in Cervical NeoplasiakushalNo ratings yet
- Ca NasofaringDocument7 pagesCa Nasofaringrangga hilmiNo ratings yet
- As OctDocument7 pagesAs OctRasha Mounir Abdel-Kader El-TanamlyNo ratings yet
- Den 12190Document9 pagesDen 12190Siska HarapanNo ratings yet
- RadiographyDocument49 pagesRadiographyluna zeidNo ratings yet
- Effectiveness of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy With Pre-Epiglottic Tc99 InjectionDocument6 pagesEffectiveness of Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy With Pre-Epiglottic Tc99 InjectionGöksel TurhalNo ratings yet
- AI em CPREDocument9 pagesAI em CPRECarlos AmaralNo ratings yet
- Wale 2016Document12 pagesWale 2016Radiologi RSPDNo ratings yet
- Video Capsule EndosDocument3 pagesVideo Capsule EndosRobert GodeanuNo ratings yet
- Real-Life Chromoendoscopy For Neoplasia Detection and Characterisation in Long-Standing IBDDocument9 pagesReal-Life Chromoendoscopy For Neoplasia Detection and Characterisation in Long-Standing IBDdeniadillaNo ratings yet
- Normal Dental Radiography in RabbitsDocument9 pagesNormal Dental Radiography in RabbitsMarcelo Anibal AlvarezNo ratings yet
- Ajr.11.7349 Radiologist WorkshopDocument7 pagesAjr.11.7349 Radiologist WorkshopNashaat H. AlshawabkehNo ratings yet
- Cytology of The Vulva: Feasibility and Preliminary Results of A New BrushDocument5 pagesCytology of The Vulva: Feasibility and Preliminary Results of A New BrushAnonymous vBIhLaNo ratings yet
- C5 PureWave TDP Study WhitepaperDocument8 pagesC5 PureWave TDP Study WhitepaperA. A.G.No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S2214180421000490 MainDocument7 pages1 s2.0 S2214180421000490 MainSorina CiopleaNo ratings yet
- Ournal Watch: Ga S TroenterologyDocument8 pagesOurnal Watch: Ga S TroenterologymayaNo ratings yet
- Can We Perform CT of The Appendix With Less Than 1 MSV? A De-Escalating Dose-Simulation StudyDocument9 pagesCan We Perform CT of The Appendix With Less Than 1 MSV? A De-Escalating Dose-Simulation StudyKostiantyn BiriukovNo ratings yet
- Semiquantitative, Fully Automated Urine Test Strip AnalysisDocument7 pagesSemiquantitative, Fully Automated Urine Test Strip AnalysisDewi PradnyaNo ratings yet
- BF 01887304Document4 pagesBF 01887304zuhdi azzyumar dhiniNo ratings yet
- (Gyne) 1.5 Diagnostic Procedures (Marinas) - AOBDocument5 pages(Gyne) 1.5 Diagnostic Procedures (Marinas) - AOBDexter IanNo ratings yet
- PathopysiologyDocument14 pagesPathopysiologyAbigail Faith PretestoNo ratings yet
- UrinaryDocument19 pagesUrinaryfiel borataNo ratings yet
- Polyp Nature OA2020Document8 pagesPolyp Nature OA2020muhammadasif_5839675No ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis in Young AdultsDocument9 pagesAcute Appendicitis in Young AdultsAtika RahmahNo ratings yet
- Intensivist Use of Hand-Carried Ultrasonography To Measure IVC Collapsibility in Estimating Intravascular Volume Status: Correlations With CVPDocument2 pagesIntensivist Use of Hand-Carried Ultrasonography To Measure IVC Collapsibility in Estimating Intravascular Volume Status: Correlations With CVPArjun RajagopalanNo ratings yet
- Safely Reducing Manual Urine Microscopy Analyses by Combining Urine Flow Cytometer and Strip ResultsDocument7 pagesSafely Reducing Manual Urine Microscopy Analyses by Combining Urine Flow Cytometer and Strip ResultsFearless AngelNo ratings yet
- Ajr 183 6 01831661Document5 pagesAjr 183 6 01831661adssaNo ratings yet
- Intraductal Biliopancreatic Imaging: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Technology ReviewDocument15 pagesIntraductal Biliopancreatic Imaging: European Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy (ESGE) Technology ReviewMadalina StoicescuNo ratings yet
- Accuracy of Intraoral Scans An in Vivo Study of DiDocument7 pagesAccuracy of Intraoral Scans An in Vivo Study of DiRaul Alfonsin SanchezNo ratings yet
- Optics and Laser TechnologyDocument11 pagesOptics and Laser TechnologyMd. Sazzad Mia 191-15-2503No ratings yet
- 1 s2.0 S0016510703025082 MainDocument8 pages1 s2.0 S0016510703025082 MainJosé Moreira Lima NetoNo ratings yet
- 8 Ortho Oncology - 210217 - 194331Document11 pages8 Ortho Oncology - 210217 - 194331Nabil AhmedNo ratings yet
- Comparison of Exophthalmos Measurements: Hertel Exophthalmometer Versus Orbital Parameters in 2-Dimensional Computed TomographyDocument32 pagesComparison of Exophthalmos Measurements: Hertel Exophthalmometer Versus Orbital Parameters in 2-Dimensional Computed TomographyAlfinKamalNo ratings yet
- HIRSCHSPRUNGInternatinalJogya KozDocument20 pagesHIRSCHSPRUNGInternatinalJogya KozRieza NurdinsyahNo ratings yet
- Narrow Band Imaging To Differentiate Neoplastic and NonDocument8 pagesNarrow Band Imaging To Differentiate Neoplastic and NonНиколай АрутюновNo ratings yet
- Endoscopic OCT With Forward-Looking Prob PDFDocument15 pagesEndoscopic OCT With Forward-Looking Prob PDFDrágus EmőkeNo ratings yet
- Diagnostic Procedures in Gynecology (2023)Document3 pagesDiagnostic Procedures in Gynecology (2023)RONALDO CUANo ratings yet
- Automated Diagnosis of Congenital Dislocation of The: Index TeamsDocument6 pagesAutomated Diagnosis of Congenital Dislocation of The: Index Teamsdiablo3 3No ratings yet
- Ajr 10 4198Document5 pagesAjr 10 4198Jasleen KaurNo ratings yet
- Usg 20179Document10 pagesUsg 20179Danvid WilpeNo ratings yet
- Cancer Screening and Prevention:: Eliminating Deaths From Cervical CancerDocument45 pagesCancer Screening and Prevention:: Eliminating Deaths From Cervical CancerYingting ZooNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System Three Phases of Gastric SecretionDocument21 pagesGastrointestinal System Three Phases of Gastric SecretiontychynNo ratings yet
- 2009 PelvimetryDocument5 pages2009 PelvimetryayupurnamasariiNo ratings yet
- Detection of The Mandibular Canal and The Mental Foramen in Panoramic Radiographs: Intraexaminer AgreementDocument5 pagesDetection of The Mandibular Canal and The Mental Foramen in Panoramic Radiographs: Intraexaminer AgreementDragos CiongaruNo ratings yet
- Community Based Health Care-1Document14 pagesCommunity Based Health Care-1Otema JamesNo ratings yet
- Psychological Support For People Living With HIV: Report: July 2010Document28 pagesPsychological Support For People Living With HIV: Report: July 2010Ikponmwosa EseosaNo ratings yet
- Population Intervention Q1, Q4: Neurofeedback Provided by A Health ProfessionalDocument1 pagePopulation Intervention Q1, Q4: Neurofeedback Provided by A Health ProfessionalfrancistsyNo ratings yet
- Ash Sap 2016Document672 pagesAsh Sap 2016honeyworksNo ratings yet
- American Red CrossDocument484 pagesAmerican Red CrossAngelika LowderNo ratings yet
- Memory Processes NotesDocument48 pagesMemory Processes NotesChryseisAliceNo ratings yet
- Cognitive Remediation Therapy For Anorexia Nervosa Kate TchanturaDocument156 pagesCognitive Remediation Therapy For Anorexia Nervosa Kate TchanturaIndriNo ratings yet
- BLOOD Physiology Guyton 14th Edition Chapter 33Document57 pagesBLOOD Physiology Guyton 14th Edition Chapter 33Dr Alamzeb Jadoon100% (1)
- Anatomy & Assessment of The Endocrine System - HandoutDocument12 pagesAnatomy & Assessment of The Endocrine System - HandoutGil Raphael Ganiban0% (2)
- Elderly Care and AbuseDocument35 pagesElderly Care and AbuseChew Keng ShengNo ratings yet
- Answer Guidlines and TipsDocument15 pagesAnswer Guidlines and TipsRoy Van de SimanjuntakNo ratings yet
- Gen Ana Oral Ana Naprostho Dent Mat RevalidaDocument29 pagesGen Ana Oral Ana Naprostho Dent Mat RevalidaWilbert YaoNo ratings yet
- HCC Easl 2018Document55 pagesHCC Easl 2018Agam ChekmatNo ratings yet
- Susan Schultz AdvocateDocument7 pagesSusan Schultz Advocateapi-340394987No ratings yet
- Building Blocks VCS Commissioning GuideDocument35 pagesBuilding Blocks VCS Commissioning Guidekate_greenaNo ratings yet
- 11 - Chemistry & EnvironmentDocument11 pages11 - Chemistry & Environmentsirsa11No ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Ft. RanitidineDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY Ft. RanitidinePao LaurenteNo ratings yet
- Peran Keluarga Pada Kepatuhan Minum Obat Penderita TB Di Kawedanan Pedan KlatenDocument10 pagesPeran Keluarga Pada Kepatuhan Minum Obat Penderita TB Di Kawedanan Pedan KlatenDede Yusuf HatamiNo ratings yet
- Plug and Transplant Production For Organic SystemsDocument16 pagesPlug and Transplant Production For Organic SystemsGreater Charlotte Harbor Sierra ClubNo ratings yet
- Anaemia: What Is Anemia?Document21 pagesAnaemia: What Is Anemia?Rashed ShatnawiNo ratings yet
- Care of Patient With Liver Cirrhosis For Nursing Process Related Nursing CareDocument89 pagesCare of Patient With Liver Cirrhosis For Nursing Process Related Nursing CareMohamed Anwer Naleef100% (3)
- NHS Tayside Flowchart For Systemic HRT Prescribing: AbbreviationsDocument2 pagesNHS Tayside Flowchart For Systemic HRT Prescribing: AbbreviationspiNo ratings yet
- MR - Nagula Prashanth (Corpahcrya1711230377) Male 26 Years: This Document Holds The Written Radiology Report ForDocument3 pagesMR - Nagula Prashanth (Corpahcrya1711230377) Male 26 Years: This Document Holds The Written Radiology Report Forp13607091No ratings yet
- MCQ THDocument200 pagesMCQ THarushrushNo ratings yet
- Aspen Consensus Recommendations For Refeeding Syndrome 2020Document18 pagesAspen Consensus Recommendations For Refeeding Syndrome 2020VisakhaRevanaNo ratings yet
- Laser Acne VulgaryDocument6 pagesLaser Acne VulgaryAngie QuillaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal EpilepsyDocument4 pagesAbdominal EpilepsyErnesto Ochoa MonroyNo ratings yet
- Hernia Repair and Colectomy Course: TR400.HCOL - SiDocument2 pagesHernia Repair and Colectomy Course: TR400.HCOL - SiShayne JacobsonNo ratings yet
- Summary of Normal Laboratory ValuesDocument7 pagesSummary of Normal Laboratory ValuesIvan Matthew SuperioNo ratings yet
- Craniotomy: Craniectomy / CranioplastyDocument30 pagesCraniotomy: Craniectomy / CranioplastyYuji TanakaNo ratings yet