Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chronic Pharyngitis
Uploaded by
Hannah Angelu CabadingCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Chronic Pharyngitis
Uploaded by
Hannah Angelu CabadingCopyright:
Available Formats
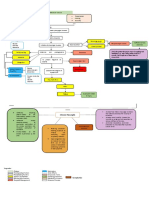
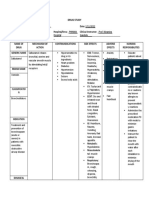
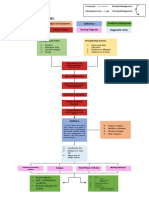
Streptococcus Group A
Environment Throat cancer
Age Smoking
Allergies Tonsillitis
Fever Streptococcus bacteria invades pharyngeal mucosa.
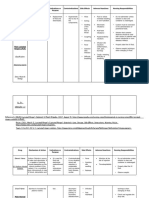
Penicillin
Local inflammatory response.
Disturbing cough
Nasopharyngeal culture Ineffective airway
Nausea
Irritation of pharyngeal mucosa. Nasal Secretion. clearance
Diarrhea Scratchy throat
Headache
Histamine and prostaglandins release Teach the patient the proper ways of coughing and
Facial Swelling Blood test
breathing. (e.g., take a deep breath, hold for 2
seconds, and cough two or three times in
Headache succession).
M protein fragment of
GABHS Rapid Antigen Test
Congestion
Guaifenesin (Mucinex)
Nausea
Acetaminophen/ Tonsillectomy
Abdominal pain Sarcolemma antigens of Drowsiness.
Ibuprofen
Drowsiness myocardium Decreased uric acid
levels.
Oxymetazoline Dryness inside Stomach pain.
the nose. Nausea.
Nausea. Rheumatic fever Headache.
Dizziness.
Fever
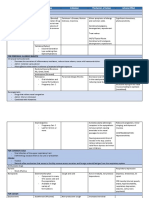
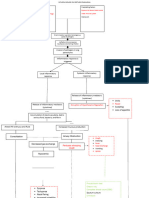
Fatigue Acute pain related
to injury.
Increase fluid intake. Encourage increased
Ineffective breathing fluid intake to decrease the viscosity of
pattern related to the Chronic Pharyngitis
secretions.
inflammatory process in the Increase room humidity. Increase the
respiratory tract. humidity by using cool mist vaporizers to
Ineffective airway relieve stuffiness of the nose.
clearance related to Administer medications. Administer
mechanical obstruction of antibiotics as prescribed after a positive
the airway secretions and Sepsis (bacterial culture result.
increased production of Relieving symptoms- Infection)
secretions. avoiding exposure to
Anxiety related to the irritants and
disease experienced by the correcting upper
child. respiratory infection.
Nasal congestion may
be relieved by short-
term use of nasal
sprays or
medications
containing ephedrine
or phenylephrine.
Complication
You might also like
- Chronic PharyngitisDocument1 pageChronic PharyngitisHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- CHECK-IN ACTIVITY Module 5.2Document4 pagesCHECK-IN ACTIVITY Module 5.2Thea MarieNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument16 pagesDrug StudyBadgal BazingaNo ratings yet
- Alf (Drug Study)Document6 pagesAlf (Drug Study)timmisarmientoNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System DrugsDocument4 pagesRespiratory System DrugsArienne Janine MalabananNo ratings yet
- Decongestant Mucolytic and Expectorant Nasal Corticosteroids Antihistamines Leukotriene Inhibitors MOADocument4 pagesDecongestant Mucolytic and Expectorant Nasal Corticosteroids Antihistamines Leukotriene Inhibitors MOAimperiouxxNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyatchiekNo ratings yet
- Drugs 2Document7 pagesDrugs 2Beverly Beauchamp-SatterwhiteNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classificatio N Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication S Adverse Effects Side EffectsDocument7 pagesName of Drug Classificatio N Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication S Adverse Effects Side EffectsHilario. Hayascent.Reign.M.No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studyeizhel8No ratings yet
- ParacetamolDocument2 pagesParacetamolAbdelmar SusulanNo ratings yet
- Drugs Case StudyDocument2 pagesDrugs Case StudyGwen De CastroNo ratings yet
- DRUG-STUDY-FORMAT-Binangonan Lakeview 3rdDocument2 pagesDRUG-STUDY-FORMAT-Binangonan Lakeview 3rdDianne UlandayNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Emergencies and Critical CareDocument11 pagesPediatric Emergencies and Critical CareShivaniNo ratings yet
- Fluticasone Drug StudyDocument3 pagesFluticasone Drug StudyArabelle GONo ratings yet
- N AcetylcysteineDocument1 pageN AcetylcysteineHanna Se50% (2)
- Bot Med Final CHARTDocument33 pagesBot Med Final CHARTapi-26938624100% (3)
- Acetylcysteine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesAcetylcysteine Drug StudyJulienFrayNo ratings yet
- Drug Study - Penicillin GDocument1 pageDrug Study - Penicillin GAngela CancinoNo ratings yet
- ParacetamolDocument5 pagesParacetamolAlyssa Moutrie Dulay ArabeNo ratings yet
- Budesonide Inhalation Drug StudyDocument2 pagesBudesonide Inhalation Drug StudyAijeelene NalapoNo ratings yet
- Cetirizine 2Document2 pagesCetirizine 2ianNo ratings yet
- DRUG StudyDocument6 pagesDRUG StudyDonna ClaritoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyPsalms Aubrey Domingo AcostaNo ratings yet
- Allergic Rhinnitis-DoneDocument11 pagesAllergic Rhinnitis-Donecory kurdapyaNo ratings yet
- Bab Vii Peta Konsep: Cuci Telinga H O 3% 3-5hrDocument1 pageBab Vii Peta Konsep: Cuci Telinga H O 3% 3-5hrika nurnailaNo ratings yet
- CS4 Asthma Drug StudyDocument10 pagesCS4 Asthma Drug StudyAudrie Allyson GabalesNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic AcidDocument2 pagesMefenamic AcidAbijah Leris SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyManuel PascualNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyHarold Dave IgcalinosNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - CopdDocument4 pagesDRUG STUDY - CopdMaye ArugayNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudyElisha Faith Sevilla EspineliNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyGel Marie LobatonNo ratings yet
- Nose and Throat Lecture-3Document3 pagesNose and Throat Lecture-3Rue Cheng MaNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - SALBUTAMOL (Revised)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY - SALBUTAMOL (Revised)Jelaveil De VeraNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studyjanedone098765No ratings yet
- Swine DiseaseDocument1 pageSwine DiseaseknocknockNo ratings yet
- Drug Study RleDocument3 pagesDrug Study RleJuzteen TandangNo ratings yet
- Albuterol SalbutamolDocument2 pagesAlbuterol SalbutamolPePpER29No ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Consideration Generic Name: HematologicDocument2 pagesName of Drug Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindication Adverse Effect Nursing Consideration Generic Name: HematologicEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- ParacetamolDocument2 pagesParacetamolEsmareldah Henry SirueNo ratings yet
- Respi Drugs 1Document10 pagesRespi Drugs 1TpdNo ratings yet
- Drug Study DisudrinDocument1 pageDrug Study DisudrinGrant Kenneth Dumo AmigableNo ratings yet
- Communicable DiseaseDocument5 pagesCommunicable DiseaseYana VillapacibeNo ratings yet
- Drug Study PneumoniaDocument2 pagesDrug Study Pneumoniamadelaine_espirituNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CetirizineDocument1 pageDrug Study CetirizineBunnie AlphaNo ratings yet
- Concept Map March 11Document1 pageConcept Map March 11Dinah Rose VitorilloNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudyKristine Marie YlayaNo ratings yet
- Full Details of Pathophysiology of Upper Tract Respiratory DiseaseDocument11 pagesFull Details of Pathophysiology of Upper Tract Respiratory DiseaseSittie Aliah SALAHUDINNo ratings yet
- DRUG SpirivaDocument1 pageDRUG SpirivarholiboiNo ratings yet
- Therapeutics in Allergies: Dr. Jorge D. Méndez Profesor of Immunology Universidad Interamericana de PanamaDocument11 pagesTherapeutics in Allergies: Dr. Jorge D. Méndez Profesor of Immunology Universidad Interamericana de PanamaByron Emerson Gonzales GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Generic Name Brand Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Cetirizine Pharmacological BeforeDocument2 pagesGeneric Name Brand Name Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Adverse Effects Nursing Considerations Cetirizine Pharmacological BeforeDenise Louise Po100% (4)
- Asia Pacific College of Advanced StudiesDocument4 pagesAsia Pacific College of Advanced Studiesaella gracieNo ratings yet
- DoxofyllineDocument2 pagesDoxofylline3C LAGRANA, Rea Lyn F.No ratings yet
- Albuterol DsDocument2 pagesAlbuterol DsCalvin Keith YadaoNo ratings yet
- GRANDPAR-PATHOPHYSIOLOGY-4 (1) Pertusis Whooping Cough Secondary To PneumoniaDocument5 pagesGRANDPAR-PATHOPHYSIOLOGY-4 (1) Pertusis Whooping Cough Secondary To PneumoniaJustin AlejoNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument7 pagesDrug StudyizzittyNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument1 pageDrug StudyZek ComidoyNo ratings yet
- C.2 Computing and Justifying Score of Health ProblemsDocument3 pagesC.2 Computing and Justifying Score of Health ProblemsHannah Angelu Cabading100% (1)
- C.3 Ranking of Health Problems According To PriorityDocument1 pageC.3 Ranking of Health Problems According To PriorityHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Tonsillitis and AdenoiditisDocument12 pagesTonsillitis and AdenoiditisHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- B.2 Family Health Assessment Guide 1Document8 pagesB.2 Family Health Assessment Guide 1Hannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Cigarette Smoking: What It Is & What It'S NotDocument12 pagesCigarette Smoking: What It Is & What It'S NotHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- NCP Dengue CabadingDocument3 pagesNCP Dengue CabadingHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Breathing Techniques During Labor (Lamaze Method) : Procedure Rationale Rating RemarksDocument4 pagesBreathing Techniques During Labor (Lamaze Method) : Procedure Rationale Rating RemarksHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- ) : Acute Pain Related To Abdominal Discomfort As Evidenced of Epigastric Pain, Vomiting and FeverDocument6 pages) : Acute Pain Related To Abdominal Discomfort As Evidenced of Epigastric Pain, Vomiting and FeverHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- IVF Drug StudyDocument5 pagesIVF Drug StudyHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Balcos, Andrea A.: Post Partum Exercises DefinitionDocument4 pagesBalcos, Andrea A.: Post Partum Exercises DefinitionHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Family Case Study (Sample)Document25 pagesFamily Case Study (Sample)Hannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Questions: Answer: Being A PHN Is Not As Simple As Some People Believe It Entails A Great Deal ofDocument1 pageQuestions: Answer: Being A PHN Is Not As Simple As Some People Believe It Entails A Great Deal ofHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Immediate Newborn CareDocument5 pagesImmediate Newborn CareHannah Angelu Cabading50% (2)
- Breathing Techniques During Labor (Lamaze Method) : Procedure Rationale Rating RemarksDocument4 pagesBreathing Techniques During Labor (Lamaze Method) : Procedure Rationale Rating RemarksHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Questions: Answer: Being A PHN Is Not As Simple As Some People Believe It Entails A Great Deal ofDocument1 pageQuestions: Answer: Being A PHN Is Not As Simple As Some People Believe It Entails A Great Deal ofHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Immediate Newborn CareDocument5 pagesImmediate Newborn CareHannah Angelu Cabading50% (2)
- IVF Drug StudyDocument5 pagesIVF Drug StudyHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Family Case Study (Sample)Document25 pagesFamily Case Study (Sample)Hannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- ESSENTIAL INTRAPARTUM NEWBORN CARE (Assisting and Handling Delivery)Document4 pagesESSENTIAL INTRAPARTUM NEWBORN CARE (Assisting and Handling Delivery)Hannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Balcos, Andrea A.: Post Partum Exercises DefinitionDocument4 pagesBalcos, Andrea A.: Post Partum Exercises DefinitionHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- PharmaDocument3 pagesPharmaHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Research ArticleDocument5 pagesResearch ArticleHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- NCP Dengue CabadingDocument3 pagesNCP Dengue CabadingHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- MCN RLE Sitz Bath Procedure ChecklistDocument3 pagesMCN RLE Sitz Bath Procedure ChecklistHannah Angelu Cabading100% (1)
- Case Analysis Format Final DraftDocument53 pagesCase Analysis Format Final DraftHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Drug Study MetoprololDocument2 pagesDrug Study MetoprololHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- C.3 Ranking of Health Problems According To PriorityDocument1 pageC.3 Ranking of Health Problems According To PriorityHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Module 4Document6 pagesDrug Study Module 4Hannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7odeDocument29 pagesChapter 7odeRoberto NascimentoNo ratings yet
- Pu3-Mo A1 MoversDocument40 pagesPu3-Mo A1 MoversMiss María José SalasNo ratings yet
- Sharp Product-Catalogue 2019 enDocument48 pagesSharp Product-Catalogue 2019 enMiki di KaprioNo ratings yet
- Fall 20122Document98 pagesFall 20122DobarCovek67% (3)
- 3rd Quarter SUMMATIVE TEST in MAPEHDocument3 pages3rd Quarter SUMMATIVE TEST in MAPEHzaile felineNo ratings yet
- 064 DIR - Launching Whipping Creme & Skimmed Milk Di Channel Horeka (Subdist Masuya)Document3 pages064 DIR - Launching Whipping Creme & Skimmed Milk Di Channel Horeka (Subdist Masuya)indra sapta PrahardikaNo ratings yet
- Technical Assistance Plan School Year 2020-2021 Prioritized Needs of The Clients Objectives Strategies Activities MOV Time-Frame ResourcesDocument3 pagesTechnical Assistance Plan School Year 2020-2021 Prioritized Needs of The Clients Objectives Strategies Activities MOV Time-Frame ResourcesDon Angelo De Guzman95% (19)
- GCG Damri SurabayaDocument11 pagesGCG Damri SurabayaEndang SusilawatiNo ratings yet
- International Rice Research Newsletter Vol12 No.4Document67 pagesInternational Rice Research Newsletter Vol12 No.4ccquintosNo ratings yet
- DD 3600 3500 3000 Parts CatalogDocument46 pagesDD 3600 3500 3000 Parts CatalogAndres Fdo Mora D100% (2)
- Light Dimmer CircuitsDocument14 pagesLight Dimmer CircuitskapilasriNo ratings yet
- Epidemiological Triad of HIV/AIDS: AgentDocument8 pagesEpidemiological Triad of HIV/AIDS: AgentRakib HossainNo ratings yet
- Neuroscience Core ConceptsDocument2 pagesNeuroscience Core Conceptseglantina alishollariNo ratings yet
- 234567890Document37 pages234567890erppibuNo ratings yet
- MT4 EA Installation Guide Digital - EnglishDocument7 pagesMT4 EA Installation Guide Digital - EnglishThe Trading PitNo ratings yet
- Game On Series BibleDocument28 pagesGame On Series Bibleapi-513832615No ratings yet
- Stitch2421 1 Kit PDFDocument8 pagesStitch2421 1 Kit PDFJoshua Robertson100% (1)
- Automatic Coconut Dehusking MachineDocument12 pagesAutomatic Coconut Dehusking MachineKumaresh Salem0% (1)
- Nursing EnglishDocument139 pagesNursing EnglishSara Williams100% (3)
- Grammar Review A2-B1Document5 pagesGrammar Review A2-B1Lena Silva SouzaNo ratings yet
- Family School Project Lesson Plan AstrologyDocument3 pagesFamily School Project Lesson Plan Astrologyapi-529488210No ratings yet
- (Essential Skills For Nurses Series) Philippa Sully - Joan Dallas-Essential Communication Skills For Nursing and Midwifery-Mosby - Elsevier (2010) PDFDocument250 pages(Essential Skills For Nurses Series) Philippa Sully - Joan Dallas-Essential Communication Skills For Nursing and Midwifery-Mosby - Elsevier (2010) PDFRetno SumaraNo ratings yet
- Daewoo SJ-210H DSJ-6000LHMDocument44 pagesDaewoo SJ-210H DSJ-6000LHMMarco Antonio100% (5)
- Geography Paper 1Document7 pagesGeography Paper 1Sudhir TewatiaNo ratings yet
- Luyện nghe Tiếng Anh có đáp án: I/ Listen and complete the textDocument3 pagesLuyện nghe Tiếng Anh có đáp án: I/ Listen and complete the textVN LenaNo ratings yet
- Hybrid Neural-Network - Genetic Algorithm Technique For Aircraft Engine Performance Diagnostics Developed and DemonstratedDocument4 pagesHybrid Neural-Network - Genetic Algorithm Technique For Aircraft Engine Performance Diagnostics Developed and Demonstratedmohamad theibechNo ratings yet
- CalculusDocument101 pagesCalculuskusnoNo ratings yet
- A Control Method For Power-Assist Devices Using A BLDC Motor For Manual WheelchairsDocument7 pagesA Control Method For Power-Assist Devices Using A BLDC Motor For Manual WheelchairsAhmed ShoeebNo ratings yet
- Augmentation of Labour: Nabhan A, Boulvain MDocument8 pagesAugmentation of Labour: Nabhan A, Boulvain MMade SuryaNo ratings yet