Professional Documents
Culture Documents
CHECK-IN ACTIVITY Module 5.2
Uploaded by
Thea MarieCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
CHECK-IN ACTIVITY Module 5.2
Uploaded by
Thea MarieCopyright:
Available Formats
MODULE 5 LESSON 2 (DRUGS FOR COMMON COLD AND COUGH)
CHECK-IN ACTIVITY
After reading the articles provided, make a summary of drugs used for common colds and cough.
YOU CAN ADD MORE ROWS IF NEEDED.
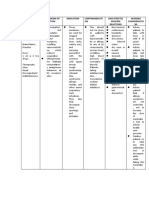
Drugs for common What they do? How does it work? Side effect/s or
colds (pharmacologic action) (MOA) disadvantage
(Specify the DRUG CLASS/specific
agent under each category)
DECONGESTANTS
Pseudoephedrine It relieves congestion It acts on alpha and Feel sick
caused by dilating beta-adrenergic Headache
blood vessels in the receptors, causing Xerostomia
nasal passages. It is vasoconstriction and Fast or irregular
also used to treat a smooth muscle heartbeat
stuffy nose and sinus relaxation in the Increased BP
pressure caused by an bronchi. Alpha-
infection. adrenergic receptors are
located on the muscle
lining walls of blood
vessels.
Phenylephrine It promotes An alpha1 adrenoceptor Mild upset stomach
vasoconstriction, which agonist wherein its Insomnia
reduces edema and nasal decongestant Dizziness
enhances sinus cavity activity activates Trembling
drainage. alpha1 adrenoceptors Tachycardia
in nasal mucosal Nervousness
arterioles.
Headache
Lightheadedness
Oxymetazoline It helps to relieve nasal It stimulates the alpha2 Nausea
and conjunctival adrenergic receptor. Dizziness
congestion. Burning
Stinging
Sneezing
Increased nasal
discharge
Dry inside the nose
Nervousness
ANTIHISTAMINES
Diphenhydramine It is an antihistamine An inverse agonist at Nausea
that is used to treat the H1 receptor, Dizziness
allergies, hay fever, and reversing histamine's Loss of appetite
the common cold. effects on capillaries Drowsiness
and lowering allergic Xerostomia, dry nose
reaction symptoms. H1 and throat
receptors are related
Vomiting
to muscarinic
Increased chest
receptors.
congestion
Constipation
Chlorpheniramine It helps reduce the It inhibits the effects of Nausea
symptoms of a cold or histamine that causes
allergies, but it does allergic symptoms. Headache
not address the Drowsiness
underlying cause of the Xerostomia
symptoms or hasten Dry nose and throat
recovery. Vomiting
Increased chest
congestion
Loss of appetite
Constipation
Brompheniramine It helps to reduce As with other popular Nausea
symptoms but does not antihistamines, it is an Dizziness
treat the underlying antagonist of the H1 Drowsiness
cause of the symptoms histamine receptors Blurred vision
or enhance recovery. with mild Loss of appetite
antimuscarinic Stomach pain
properties. It alleviates
Constipation
the symptoms of
Dry nose
allergies, hay fever, and
the common cold, such Xerostomia
as red, irritated, itchy, Memory problems or
watery eyes, sneezing, concentration
and runny nose. problems
Restless or excited
(especially in
children)
Cetirizine It is categorized as a An antihistamine that Sneezing or blocked
non-drowsy is non-sedating and and runny nose
antihistamine since it acts by inhibiting the Headaches
affects the body's H-1 receptor on cells. Dizziness
natural chemical Nausea
histamine. Xerostomia
Sore throat
Stomach pain
Diarrhea
Clemastine An antihistamine that A selective H1 Drowsiness
lowers the effects of antagonist that binds Dizziness
the body's natural to the H1 receptor. Headache
chemical histamine. Excitement
(especially in
children)
Decreased
coordination
Chest congestion
Nausea
Xerostomia
Dry nose and throat
Fexofenadine It is an antihistamine It inhibits the Headache
that is used to treat production of certain Fever
allergy symptoms. histamines by the body Cough
during an allergic Upper respiratory
reaction. tract infection
Vomiting
Muscle pain
Back pain
Diarrhea
Loratadine It is an antihistamine It inhibits the activity of Headache
that is used to treat histamine, which Nervousness
allergy symptoms. causes allergic Difficulty falling
reactions. asleep or staying
asleep
Weakness
Nosebleed
Xerostomia
Sore throat
Mouth sores
OTHER REMEDIES
Acetaminophen or Antipyretic Inhibits prostaglandin Drowsiness
Ibuprofen production in the CNS Headache
and peripherally to Nausea
prevent pain impulse Loss of appetite
generation. Its Itching
antipyretic activity Rash
stems from its impact on Stomach pain
prostaglandin E2 in the Dark urine
CNS, which causes fever.
Ibuprofen is a COX
enzyme inhibitor
required for
prostaglandin
production, and
inhibiting COX causes an
antipyretic effect in the
CNS due to reduced
prostaglandin E
synthesis.
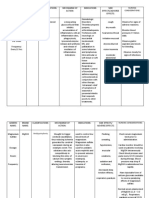
Drugs for COUGH What they do? How does it work? Side effect/s or
(Specify the DRUG CLASS/specific (pharmacologic action)
agent under each category)
(MOA) disadvantage
ANTITUSSIVE
Dextromethorphan It suppresses the cough It has antitussive Nausea
frequently linked with properties. It Dizziness
the common cold and penetrates the blood- Drowsiness
other respiratory brain barrier and works GI upset
diseases. It centrally in the cough Excessive
momentarily soothes center of the medulla consumption
coughing but does not to suppress cough.
produces
cure the underlying
hallucinogenic effects
cause or hasten to
heal. Respiratory and
cardiac arrest
Codeine It is a centrally acting In the liver, CYP2D6 Itchiness
narcotic opioid that has converts it to Lightheadedness
been approved as an morphine. Codeine Vomiting
antitussive. Codeine binds to mu-opioid
has a complex function receptors, which play a Drowsiness
as an analgesic, role in pain Constipation
sedative, and cough transmission all
suppressant. throughout the body
and CNS.
EXPECTORANTS
Guaifenesin It thins and loosens It decreases the surface Drowsiness
mucus in the airways, tension and viscosity of Dizziness
promoting the mucus, making Headache
bronchodilation and expectoration easier. Nausea
relieving congestion. Vomiting
Rash
Stomach pain
Decreased uric acid
levels
MUCOLYTICS
Guaifenesin It thins and loosens It decreases the surface Drowsiness
mucus in the airways, tension and viscosity of Dizziness
promoting the mucus, making Headache
bronchodilation and expectoration easier. Nausea
relieving congestion. Vomiting
Rash
Stomach pain
Decreased uric acid
levels
OTHER REMEDIES
Amoxicillin For persistent coughs During the active Headache
caused by mild chest spread stage, it exerts a Nausea
infections such as bactericidal effect on Vomiting
bronchitis, an antibiotic sensitive bacteria. It Swollen, black, or
is frequently hinders cell wall “hairy” tongue
prescribed. production, causing Rash
bacteria to die. Diarrhea
Vaginal itching or
discharge
You might also like
- Drugs Affecting Respiratory SystemDocument19 pagesDrugs Affecting Respiratory SystemRuby Ann DimayugaNo ratings yet
- Respiratory System DrugsDocument4 pagesRespiratory System DrugsArienne Janine MalabananNo ratings yet
- Emergency TrolleyDocument22 pagesEmergency TrolleyAaron Wallace100% (1)
- Chronic PharyngitisDocument1 pageChronic PharyngitisHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Decongestant Mucolytic and Expectorant Nasal Corticosteroids Antihistamines Leukotriene Inhibitors MOADocument4 pagesDecongestant Mucolytic and Expectorant Nasal Corticosteroids Antihistamines Leukotriene Inhibitors MOAimperiouxxNo ratings yet
- Drugs 2Document7 pagesDrugs 2Beverly Beauchamp-SatterwhiteNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY - SALBUTAMOL (Revised)Document2 pagesDRUG STUDY - SALBUTAMOL (Revised)Jelaveil De VeraNo ratings yet
- Chronic PharyngitisDocument1 pageChronic PharyngitisHannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Lrti Case Drug StudyDocument6 pagesLrti Case Drug Studyn_I_K_K_I02No ratings yet
- Drug Study: D IphenhydramineDocument5 pagesDrug Study: D IphenhydramineAnthonette DaquioagNo ratings yet
- Respi Drugs 1Document10 pagesRespi Drugs 1TpdNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Pulmonary System 2: Dr. Dita Hasni, M.BiomedDocument24 pagesDrugs Acting On The Pulmonary System 2: Dr. Dita Hasni, M.BiomedYeny ElfiyantiNo ratings yet
- Week 10 Medication SummaryDocument16 pagesWeek 10 Medication SummaryuserherwwweNo ratings yet
- Effector OrganDocument2 pagesEffector OrganCamille De JesusNo ratings yet
- Drugs Case StudyDocument2 pagesDrugs Case StudyGwen De CastroNo ratings yet
- Pharma Reviewer (Midterm)Document7 pagesPharma Reviewer (Midterm)SaidinaNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug Studyeizhel8No ratings yet
- Allergic Rhinnitis-DoneDocument11 pagesAllergic Rhinnitis-Donecory kurdapyaNo ratings yet
- Drug Suffixes Cheat Sheet Sorted AlphabeticallyDocument3 pagesDrug Suffixes Cheat Sheet Sorted Alphabeticallystudynote155No ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument11 pagesDrug StudyManuel PascualNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument6 pagesDrug StudyZyra HernandoNo ratings yet
- Crisostomo Micaela Ketamine DSDocument3 pagesCrisostomo Micaela Ketamine DSMicaela CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- Villareal - NCMA216 Drug StudyDocument10 pagesVillareal - NCMA216 Drug StudyRozen VillarealNo ratings yet
- Name of Drug Classificatio N Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication S Adverse Effects Side EffectsDocument7 pagesName of Drug Classificatio N Mechanism of Action Indications Contraindication S Adverse Effects Side EffectsHilario. Hayascent.Reign.M.No ratings yet
- Mefenamic AcidDocument2 pagesMefenamic AcidAbijah Leris SarmientoNo ratings yet
- SNS Summary - ANS Lecture Notes IIDocument9 pagesSNS Summary - ANS Lecture Notes IIZuhar MahomedNo ratings yet
- Patient Care 1 Drugs ChartDocument13 pagesPatient Care 1 Drugs ChartKaitlyn CabreraNo ratings yet
- Cetirizine 2Document2 pagesCetirizine 2ianNo ratings yet
- Drugs Acting On The Upper Respiratory TractDocument12 pagesDrugs Acting On The Upper Respiratory TractPrincess C. SultanNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument16 pagesDrug StudyBadgal BazingaNo ratings yet
- Therapeutics in Allergies: Dr. Jorge D. Méndez Profesor of Immunology Universidad Interamericana de PanamaDocument11 pagesTherapeutics in Allergies: Dr. Jorge D. Méndez Profesor of Immunology Universidad Interamericana de PanamaByron Emerson Gonzales GonzalesNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyGel Marie LobatonNo ratings yet
- Salbutamol Drug SummDocument1 pageSalbutamol Drug SummWarren100% (2)
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyPregielyn RancheNo ratings yet
- DigitalPharmacologyBundle170Pages CompressedDocument170 pagesDigitalPharmacologyBundle170Pages Compressed98b5jc5hgtNo ratings yet
- Ineffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionDocument2 pagesIneffective Breathing Pattern Related To Bronchospasm, Decreased Lung ExpansionReylan Garcia43% (7)
- DoxofyllineDocument2 pagesDoxofylline3C LAGRANA, Rea Lyn F.No ratings yet
- Adrenergic DrugsDocument6 pagesAdrenergic DrugsbezaleeljonelNo ratings yet
- Alf (Drug Study)Document6 pagesAlf (Drug Study)timmisarmientoNo ratings yet
- Pheny ChlorpheDocument1 pagePheny ChlorpheJason AgujaNo ratings yet
- NCP - ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK..2pdfDocument6 pagesNCP - ANAPHYLACTIC SHOCK..2pdfLycah RotoneNo ratings yet
- ParacetamolDocument5 pagesParacetamolAlyssa Moutrie Dulay ArabeNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyatchiekNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyChristine Mae BandiolaNo ratings yet
- Kodex LDocument48 pagesKodex Lamitdwivedi11No ratings yet
- Drug Study and Case Analysis (Salbutamol and Montelukast)Document4 pagesDrug Study and Case Analysis (Salbutamol and Montelukast)Ma. Kaile Shyla LlacarNo ratings yet
- DrugDocument8 pagesDrugAlyzza DagoyNo ratings yet
- Pharyngitis. NCPDocument2 pagesPharyngitis. NCPbiancaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Ify Okwuosa)Document4 pagesDrug Study (Ify Okwuosa)ifyNo ratings yet
- Respiratory Drugs - PSKed 2024Document93 pagesRespiratory Drugs - PSKed 2024JASON WILIAMNo ratings yet
- Respratory Drugs I-IIDocument10 pagesRespratory Drugs I-IITyler Lawrence CoyeNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY Week 9 Charlene Fidellaga BSN Y2-11Document8 pagesDRUG STUDY Week 9 Charlene Fidellaga BSN Y2-11Charlene FidellagaNo ratings yet
- Diphenhydramine Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDiphenhydramine Drug StudyMorrin MylesNo ratings yet
- Pharmacology Week-9-Drug-StudyDocument16 pagesPharmacology Week-9-Drug-StudyyutucnhicajaneNo ratings yet
- Drug Study and Case Analysis (Salbutamol and Montelukast)Document4 pagesDrug Study and Case Analysis (Salbutamol and Montelukast)Ma. Kaile Shyla LlacarNo ratings yet
- If These Are Stimulated It Produces An Array of Effects in The BodyDocument4 pagesIf These Are Stimulated It Produces An Array of Effects in The BodyAnne Giselle PatocNo ratings yet
- Buscopan-Drug StudyDocument2 pagesBuscopan-Drug StudyJoan QuebalayanNo ratings yet
- The Natural Allergy Relief Solution - Best Essential Oils to Use & Why!: Essential Oil WellnessFrom EverandThe Natural Allergy Relief Solution - Best Essential Oils to Use & Why!: Essential Oil WellnessNo ratings yet
- Wonders of Homeopathy : 80 Homeo Remedies for your Health Problems : Healing with Homeopathy: Healing with HomeopathyFrom EverandWonders of Homeopathy : 80 Homeo Remedies for your Health Problems : Healing with Homeopathy: Healing with HomeopathyNo ratings yet
- Martindale The Complete Drug Reference 38th Edition Free Download PDFDocument3 pagesMartindale The Complete Drug Reference 38th Edition Free Download PDFChristian Sosa10% (10)
- Telemetry Recognition WorkbookDocument29 pagesTelemetry Recognition WorkbookQueenNo ratings yet
- Doloplus 2 ToolDocument3 pagesDoloplus 2 ToolHaMy NguyenNo ratings yet
- Hospital 1Document45 pagesHospital 1shaista siddiqueNo ratings yet
- Ojs FianaDocument13 pagesOjs FianadespalitaNo ratings yet
- The Features and Benefits of Broiler Starter Feeds That Include Alphasoy™Document31 pagesThe Features and Benefits of Broiler Starter Feeds That Include Alphasoy™Matute SalmonNo ratings yet
- ConcorDocument40 pagesConcorviczNo ratings yet
- Trichiasis: Prepared By:pooja Adhikari Roll No.: 27 SMTCDocument27 pagesTrichiasis: Prepared By:pooja Adhikari Roll No.: 27 SMTCsushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Disorders of ThinkingDocument11 pagesDisorders of Thinkingjahanavi12No ratings yet
- Gastroenteritis Case ReportDocument12 pagesGastroenteritis Case ReportjisooNo ratings yet
- ThesisDocument35 pagesThesisMuhdFaris67% (3)
- Cummings Otolaryngology Chapter 201Document14 pagesCummings Otolaryngology Chapter 201Zllison Mae Teodoro MangabatNo ratings yet
- Analgesic Efficacy of Ketoprofen in Postpartum, General Surgery, and Chronic Cancer PainDocument8 pagesAnalgesic Efficacy of Ketoprofen in Postpartum, General Surgery, and Chronic Cancer PainYohanna Lawanda da CostaNo ratings yet
- BSC English Notes NewDocument54 pagesBSC English Notes NewFahad HabibNo ratings yet
- MHPSSDocument11 pagesMHPSSVan TotNo ratings yet
- Operator Edge 6 Wkphase 1 V2Document23 pagesOperator Edge 6 Wkphase 1 V2Luis Santamaría Álvarez-Gómez0% (1)
- Republic Act 6972 (Day Care)Document3 pagesRepublic Act 6972 (Day Care)Erly Mae100% (1)
- POST ACTIVITY REPORT-MH Caravan-PalananDocument5 pagesPOST ACTIVITY REPORT-MH Caravan-PalananKeith Clarence BunaganNo ratings yet
- Megan Haky: M.M.Haky@eagle - Clarion.eduDocument2 pagesMegan Haky: M.M.Haky@eagle - Clarion.eduapi-285540869No ratings yet
- Kasus Psi TraumaDocument17 pagesKasus Psi TraumaWulanNo ratings yet
- PE UNIT 1 Active Recreation (Lifestyle and Weight Management)Document26 pagesPE UNIT 1 Active Recreation (Lifestyle and Weight Management)Charmaine RamosNo ratings yet
- The Impact of Nutrition Education On Knowledge, Attitude, and Practiceregarding Iron Deficiency Anemia Among Female Adolescent Studentsin JordanDocument7 pagesThe Impact of Nutrition Education On Knowledge, Attitude, and Practiceregarding Iron Deficiency Anemia Among Female Adolescent Studentsin JordanAppierien 4No ratings yet
- 2020-Indian Journal of Public Health Research and Development (Scopus Q-4)Document5 pages2020-Indian Journal of Public Health Research and Development (Scopus Q-4)NoniAndayaniNo ratings yet
- Attachment Styles View of Self and Negative AffectDocument16 pagesAttachment Styles View of Self and Negative AffectStephanie MokashiNo ratings yet
- Mission HR Handbook Ocb Template Revision May 2018Document12 pagesMission HR Handbook Ocb Template Revision May 2018Mohammed HammadiNo ratings yet
- Septico Tank TreatmentDocument3 pagesSeptico Tank TreatmentfernandaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - Acute Pain Related To Surgical IncisionDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan - Acute Pain Related To Surgical IncisionCamilogs80% (10)
- k.4 B. Inggris Pak ArmanawiDocument8 pagesk.4 B. Inggris Pak ArmanawiUswatun HasanahNo ratings yet
- Medical Lab Technology ScienceDocument2 pagesMedical Lab Technology Sciencecnc_program_pagesNo ratings yet
- Nathan Purdy CV 1Document2 pagesNathan Purdy CV 1api-254786944No ratings yet