Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Trichiasis: Prepared By:pooja Adhikari Roll No.: 27 SMTC
Uploaded by
sushma shrestha0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
192 views27 pagesTrichiasis is a condition where eyelashes grow back towards the eye and touch the cornea and conjunctiva, causing irritation. It is most commonly seen in adults and is usually caused by trachoma, an eye infection. Surgical treatments like electrolysis, cryotherapy, or epilation are used to remove misdirected eyelashes. Nursing care focuses on minimizing pain, reducing anxiety, and preventing injury by ensuring a safe environment and providing eye protection and rest. With proper treatment, prognosis is generally good, though complications like recurrent corneal abrasions can occur if left untreated.
Original Description:
bh
Original Title
Trichiasis(1)
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentTrichiasis is a condition where eyelashes grow back towards the eye and touch the cornea and conjunctiva, causing irritation. It is most commonly seen in adults and is usually caused by trachoma, an eye infection. Surgical treatments like electrolysis, cryotherapy, or epilation are used to remove misdirected eyelashes. Nursing care focuses on minimizing pain, reducing anxiety, and preventing injury by ensuring a safe environment and providing eye protection and rest. With proper treatment, prognosis is generally good, though complications like recurrent corneal abrasions can occur if left untreated.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
192 views27 pagesTrichiasis: Prepared By:pooja Adhikari Roll No.: 27 SMTC
Uploaded by
sushma shresthaTrichiasis is a condition where eyelashes grow back towards the eye and touch the cornea and conjunctiva, causing irritation. It is most commonly seen in adults and is usually caused by trachoma, an eye infection. Surgical treatments like electrolysis, cryotherapy, or epilation are used to remove misdirected eyelashes. Nursing care focuses on minimizing pain, reducing anxiety, and preventing injury by ensuring a safe environment and providing eye protection and rest. With proper treatment, prognosis is generally good, though complications like recurrent corneal abrasions can occur if left untreated.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PPTX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 27
Trichiasis
Prepared by:Pooja Adhikari
Roll no.: 27
SMTC
Introduction
Trichiasis is a common eyelid problem or lid abnormality.
It is a medical term for abnormally positioned eyelashes
that grow back towards the eye, touching the cornea and
conjunctiva. In the trichiasis, there is an anatomic
misalignment of eyelashes. Trichiasis can occur in all
ages however, it is most commonly seen in adult age.
Definition: It is defined as the ingrowths or introversion of
the eyelashes in which the lashes rub against the cornea,
the conjunctiva and the inner surface of the eyelids. This
cause the irritation in the eye.
Incidence
Africa is the worst affected continent, as 18 million
cases of active trachoma and 3.2 million cases of
trichaisis are thought to exist in 29 out of the 47
countries in african region (World Health
Organization [WHO], 2012).
Causes
1. The exact cause of trichiasis is unknown.
2. Trachoma : It is a Commonest cause of the
trichiasis. As, it is a severe eyelid infection that can
impact the eyelashes and even cause blindness. A
repeated cases of trachoma may cause trichiasis.
3. Trauma to the eyelid: Scar tissue that develops
after an injury or trauma can cause eyelashes to
grow in different direction. Eye surgery may also
have this effect.
Cont..
4. Infection and inflammation of the eyelid
5. Developmental changes: The eyelashes and hair
follicles may temporarily change shape as a child
grows. Any resulting trichiasis is usually temporary.
6. Chronic Blepharitis: This is a common and
ongoing condition. Chronic blepharitis involves
inflammation and irritation of the eyelid in which
the eyelids become swollen and oily particles and
bacteria coat in the base of the eyelashes.
Cont..
7. Entropian : This condition causes the eyelid to fold
inward, which can lead to trichasis. Age related
muscle weakness, tissue weakness and infection or
injury can cause entropian.
8. Herpes of the eye: Herpes can infect the eye and
damage the eyelid causing trichiasis.
Sign and symptoms
• The eye becomes red and irritated.
• Foreign body sensation with irritation in the eye.
• Sometimes pain when exposed to the light.
• Watery eyes
• Blurry vision
• Ocular discomfort
• Itching
• Conjunctival congestion
• If the condition persists, scarring of cornea can occur.
Diagnostic Procedures
• No Specific diagnostic procedures are required in the
management of trichiasis. Some diagnostic
procedures are:
1. History Taking
2. Physical Examination
3. Slit lamp examination: It is performed to assess the
distribution of trichiatic eyelashes, to elucidate the
underlying cause and rule out differential diagnosis.
Treatment
Treatment of trichiasis is primarily surgical. Medical
management are aimed at controlling the symptoms
and treating the underlying causes.
Ocular lubricants, such as artificial tears and ointments
provide relief form the irritant effects of lash rubbing.
A single dose of Antibiotics i.e, athizthromycin 20 mg/
kg up to 1g is the treatment of choice in those affected
patients.
Doxycycline may prevent the recurrence of trichiasis
following surgery in the patients.
Surgical Management
The surgical management for trichasis involves:
1. Mechanical Epilation: The mechanical epilation with
forceps is a simple temporary method of removing
misdirected eye lashes, but the lashes grow back in 3
to 6 weeks so, patients should be advised that lashes
will regrow, therefore epilation may need to be
repeated. As, broken cilia are often more irritating to
the cornea than mature long eyelashes. Despite these
drawbacks, epilation is cheap and is generally
acceptable to patients as treatment modality.
Cont..
2. Electrolysis: It is a procedure done by using a high
electrical current for few isolated lashes, but has a
number of drawbacks. It is also the destruction of lash
follicle by passing electric current into the lash root.
It works by passing a small amount of current
through a very fine needle into the hair follicle. This
produces heat, destroying the cells that produce hair
at the base of the follicle. It has a high recurrence rate
causing scarring of the adjacent eyelids margin. It can
be tedious for the patient as well as for the surgeon.
Cont..
3. Cryotherapy: It is a freeze treatment used to treat
number of eye problems especially retina conditions.
The cryoprobe is applied to the affected segment for
approximately 25 seconds, allowed to thaw and then
refrozen for 20 seconds. Then the lashes are
mechanically removed with forceps
Cont..
This removes the eyelashes and follicles by freezing
them. It is effective but has the potential for
complications. It is the extreme use of cold in surgery
to destroy abnormal or diseased tissue. Freon or
nitrous oxide is used to destroy the follicles by
freezing them. The complication include: edema,
necrosis, loss of skin pigmentation and loss of globet
function.
Prognosis
• Prognosis is generally good in the trichiasis. Frequent
follow up care and immediate attention to
complications, recurrence or corneal complications
improve the long term prognosis.
• A single dose of oral azithromycin 1 g after surgery
can help to prevent recurrence rates to 1 year.
Complications
1. Recurrent corneal abrasions.
2. Superficial corneal opacities.
3. Corneal vascularisation.
4. Non healing corneal ulcers.
Nursing Management
• Assessment
1. Assess the patients ability to see and perform the
activities.
2. Assess the subjective findings like blurring of the
vision, watery eyes, lacrimation etc.
3. Assess the patients knowledge of the disease process
and anxiety about the diagnosis.
4. Assess the motivation to participate in the surgical
treatment or procedure.
5. Assess the history and physical examination findings.
Nursing Diagnosis
1. Acute pain related to inflammation of the eyelid.
2. Anxiety related to surgical procedure and its
outcome.
3. Risk for injury related to decreased and blurry
vision.
Nursing Intervention
A. Minimizing pain
1. Provide cold compress in every 2 to 3 times a day to
manage pain and swelling.
2. Antihistamine agents such as benadryl should be used
according to physician prescription.
3. Pain may occur when exposed to bright light so, it
should be minimized.
4. If there is mild cases of eye discomfort then provide
rest to the eyes and take pain relievers medication
such as Advil or acetaminophen.
B. Reducing Anxiety
1 . Provide emotional and psychological support to
reinforce a positive self image.
1. Keep the environment simple, familiar and noise
free, limit changes.
2. Remain calm and unhurried while performing any
procedures or tasks to the patients.
3. Explain the surgical interventions to the patients
and patients visitors adequately.
4. Provide adequate rest and comfortable sleep.
C. To prevent from injury
1. Assess the patient for degree of visual impairment.
2. Ensure the room environment is safe with adequate
lighting. Remove all the objects that could be
potentially hazardous.
3. Keep patients glasses and call bell within easy reach.
4. Instruct patient or family regarding safe lighting.
5. Patient should provide sunglasses to reduce glare.
Evaluation
1. Minimized pain
2. Reduced anxiety levels
3. Free from the injury
References
1. Wiliam L and Tandon R. Lippincott Manual of
Nursing Practice, 9th edition.
2. Williams and Williams. Brunner and siddharths
Textbook of Medical and Surgical Nursing, 12th
edition.
3. Neil J and Kaiser k; Review of Opthalmology, 2nd
edition.
Thank you
You might also like
- Subconjunctival HaemorrhageDocument7 pagesSubconjunctival HaemorrhageTry Ahmad MirzaNo ratings yet
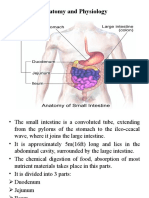
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument42 pagesAnatomy and Physiologysushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Kanski'S: Clinical OphthalmologyDocument504 pagesKanski'S: Clinical OphthalmologyMohin hossain100% (1)
- Understanding Refractive ErrorsDocument55 pagesUnderstanding Refractive ErrorsRaissaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Process: A Critical Thinking ToolDocument15 pagesNursing Process: A Critical Thinking Toolsushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Parts of The Human Eye With DefinitionDocument4 pagesParts of The Human Eye With DefinitionStarsky Allence Puyoc0% (1)
- Malaria: Dr. Shree Narayan Yadav Internal Medicine Resident NamsDocument40 pagesMalaria: Dr. Shree Narayan Yadav Internal Medicine Resident Namsasyanadhikary18No ratings yet
- LASIK Handbook A Case-Based Approach 2nd EdDocument400 pagesLASIK Handbook A Case-Based Approach 2nd EdPhilipe Saraiva CruzNo ratings yet
- Terminology and Guidelines in GlaucomaDocument354 pagesTerminology and Guidelines in GlaucomaAssifa Ridzki100% (1)
- Chicken Pox and Herpes ZosterfinalDocument31 pagesChicken Pox and Herpes ZosterfinalBinayaNo ratings yet
- Sigmoidoscopy: Presented by Kriti Adhikari Roll No: 17Document38 pagesSigmoidoscopy: Presented by Kriti Adhikari Roll No: 17sushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Progressive Lenses History and DevelopmentDocument10 pagesProgressive Lenses History and DevelopmentHasan AnsariNo ratings yet
- Presentation On MeningitisDocument51 pagesPresentation On Meningitissushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Embryo EyeDocument25 pagesEmbryo EyeMarera DomnicNo ratings yet
- Cloudy Eyes and Blurred VisionDocument18 pagesCloudy Eyes and Blurred VisionJustin Faye VibarNo ratings yet
- Corneal Ulcer: Prepared By: Renuka Shrestha Roll No: 29 PBBN 3rd Year SMTCDocument41 pagesCorneal Ulcer: Prepared By: Renuka Shrestha Roll No: 29 PBBN 3rd Year SMTCsushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Corneal Ulcer: Prepared By: Renuka Shrestha Roll No: 29 PBBN 3rd Year SMTCDocument41 pagesCorneal Ulcer: Prepared By: Renuka Shrestha Roll No: 29 PBBN 3rd Year SMTCsushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Case Study CLD 1Document12 pagesCase Study CLD 1MoonNo ratings yet
- India's Growing Cervical Cancer EpidemicDocument54 pagesIndia's Growing Cervical Cancer EpidemicJetty Elizabeth JoseNo ratings yet
- Vaginitis Slides 2013Document97 pagesVaginitis Slides 2013leilacarvalho880% (1)
- Case Study of HypospadiaDocument19 pagesCase Study of Hypospadialicservernoida100% (2)
- Spinal Cord InjuryDocument17 pagesSpinal Cord InjuryMuhammad FaridNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmia NeonatorumDocument19 pagesOphthalmia NeonatorumJisha Annie JohnNo ratings yet
- Osteoarticular TuberculosisDocument28 pagesOsteoarticular TuberculosisKaizar Ennis100% (2)
- Patient Scenario, Chapter 45, Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has A Gastrointestinal DisorderDocument93 pagesPatient Scenario, Chapter 45, Nursing Care of A Family When A Child Has A Gastrointestinal DisorderDay MedsNo ratings yet
- Mrs. D, 37 Yo. Post Modified Radical MastectomyDocument17 pagesMrs. D, 37 Yo. Post Modified Radical MastectomyElisabethLisyeKonnyNo ratings yet
- Opthalmia UmDocument23 pagesOpthalmia Umnanu-jenuNo ratings yet
- Keratomalacia Eye DiseaseDocument9 pagesKeratomalacia Eye DiseaseUsama ElahiNo ratings yet
- Chronic Otitis MediaDocument4 pagesChronic Otitis MediaOvyanda Eka MItraNo ratings yet
- Acute Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Case PresentationDocument28 pagesAcute Pelvic Inflammatory Disease Case Presentationpravallika vanguruNo ratings yet
- Ophthalmia NeonatorumDocument30 pagesOphthalmia NeonatorumManish ShresthaNo ratings yet
- 847 - Protein Energy MalnutritionDocument20 pages847 - Protein Energy MalnutritionPriyanka Vikas TakNo ratings yet
- Lens Related GlaucomaDocument19 pagesLens Related GlaucomaUsama ButtNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument50 pagesCase Presentationapi-19762967No ratings yet
- Case Study On Fibroid UterusDocument68 pagesCase Study On Fibroid UterusSeenha DewanNo ratings yet
- Breast Self ExaminationDocument13 pagesBreast Self ExaminationChanDa DasNo ratings yet
- National Leprosy Eradication Programme DetailsDocument4 pagesNational Leprosy Eradication Programme DetailsSaiyan VegetaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation On MalariaDocument13 pagesCase Presentation On Malarialavate amol bhimraoNo ratings yet
- CSOM TreatmentDocument21 pagesCSOM TreatmentSarwinder SinghNo ratings yet
- Management of patients with meningitis and encephalitisDocument71 pagesManagement of patients with meningitis and encephalitisSachin DwivediNo ratings yet
- Sigmoid Volvulus: Rashid Swed S. (Md4) Mwanyingili John A. (Md3)Document46 pagesSigmoid Volvulus: Rashid Swed S. (Md4) Mwanyingili John A. (Md3)Amani Twaha MsemakweliNo ratings yet
- Lecture Notes On AphDocument41 pagesLecture Notes On AphEyob MizanNo ratings yet
- RicketsDocument5 pagesRicketsNader SmadiNo ratings yet
- Breast Exam Checklist UCC School of MedicineDocument2 pagesBreast Exam Checklist UCC School of Medicinehector100% (1)
- Diagnosis and treatment of gangrene in 40 charactersDocument3 pagesDiagnosis and treatment of gangrene in 40 charactersmksayshiNo ratings yet
- Trachoma Causes Blindness Bacteria ChlamydiaDocument11 pagesTrachoma Causes Blindness Bacteria ChlamydiajisooNo ratings yet
- Identification of Microorganisms: Unknown SpecimensDocument10 pagesIdentification of Microorganisms: Unknown SpecimensAnonymous wVgEAr6No ratings yet
- Corneal UlcerDocument28 pagesCorneal Ulcerdevanand21100% (1)
- CASE STUDY: B-ALL WITH APLASTIC ANEMIADocument15 pagesCASE STUDY: B-ALL WITH APLASTIC ANEMIAShakira HashimNo ratings yet
- Febrile Seizure Case FileDocument4 pagesFebrile Seizure Case Filehttps://medical-phd.blogspot.comNo ratings yet
- AnorectalmalformationDocument126 pagesAnorectalmalformationNinaNo ratings yet
- Extremely Low Birth Weight (ELBW) InfantDocument48 pagesExtremely Low Birth Weight (ELBW) InfanthannanyusofNo ratings yet
- Rupture of Tubal Pregnancy in The Vilnius Population: Pasquale Berlingieri, Grazina Bogdanskiene, Jurgis G. GrudzinskasDocument4 pagesRupture of Tubal Pregnancy in The Vilnius Population: Pasquale Berlingieri, Grazina Bogdanskiene, Jurgis G. Grudzinskaslilis lestariNo ratings yet
- Genetic Screening and Prenatal DiagnosisDocument18 pagesGenetic Screening and Prenatal DiagnosisA B ONo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Hyperemesis Gravidarum Maricar Abonado Midwifery IIDocument27 pagesCase Presentation Hyperemesis Gravidarum Maricar Abonado Midwifery IIMaricar Crescini AbonadoNo ratings yet
- Hydatidiform MoleDocument10 pagesHydatidiform MoleLisa TurnerNo ratings yet
- Epidemiological Traid JayaDocument25 pagesEpidemiological Traid JayajayalakshmiNo ratings yet
- Pelvic Inflammatory DiseaseDocument3 pagesPelvic Inflammatory DiseaseokaciaNo ratings yet
- Case Report On Fibroid UterusDocument4 pagesCase Report On Fibroid UterusInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- A Seminar On The Topic TetanusDocument16 pagesA Seminar On The Topic TetanusRajat PadhanNo ratings yet
- Ectopic Pregnancy: DR .Urmila KarkiDocument27 pagesEctopic Pregnancy: DR .Urmila KarkiBasudev chNo ratings yet
- Tracheostomy Care GuideDocument4 pagesTracheostomy Care GuideSuchismita SethiNo ratings yet
- National Programme For Control of Blindness PDFDocument23 pagesNational Programme For Control of Blindness PDFRabiu Hassan MusaNo ratings yet
- Polyhydraminos and OligohydraminosDocument11 pagesPolyhydraminos and OligohydraminosMelissa Catherine ChinNo ratings yet
- Case Study of Bacterial MeningitisDocument125 pagesCase Study of Bacterial MeningitisNap IchNo ratings yet
- 01 Postpartum EndometritisDocument12 pages01 Postpartum EndometritisDimitri Santillán AlarcónNo ratings yet
- Intrauterine Growth Restriction IUGR: TH THDocument2 pagesIntrauterine Growth Restriction IUGR: TH THZahra AlaradiNo ratings yet
- FundosDocument13 pagesFundosLi FaungNo ratings yet
- Posterior Urethral ValveDocument6 pagesPosterior Urethral ValveMustafa AadanNo ratings yet
- Phimosis and ParaphimosisDocument3 pagesPhimosis and ParaphimosisJoshua PowersNo ratings yet
- Physical Assessment - AnemiaDocument14 pagesPhysical Assessment - AnemiaMerrrks100% (1)
- Complications of The Third Stage of LabourDocument6 pagesComplications of The Third Stage of LabourSong QianNo ratings yet
- The Abnormal PuerperiumDocument25 pagesThe Abnormal PuerperiumMartijn JohanNo ratings yet
- Bharatpur Hospital Nursing College Bharatpur-10, Chitwan Subject: Fundamental of Nursing Unit TestDocument3 pagesBharatpur Hospital Nursing College Bharatpur-10, Chitwan Subject: Fundamental of Nursing Unit Testsushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document2 pagesPresentation 1sushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Z-Test For Single MeanDocument32 pagesZ-Test For Single Meansushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- News Orint NoteDocument2 pagesNews Orint Notesushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Palliative Care in Non Cancer Patients NotesDocument19 pagesPalliative Care in Non Cancer Patients Notessushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Chest Xray 2Document39 pagesChest Xray 2sushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- 18.2 Pain Management - PBNDocument21 pages18.2 Pain Management - PBNsushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Purbanchal University Shree Medical and Technical College Bharatpur 10, ChitwanDocument10 pagesPurbanchal University Shree Medical and Technical College Bharatpur 10, Chitwansushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Psychosocial Communication Palliative CareDocument49 pagesPsychosocial Communication Palliative Caresushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Drugs For Cancer Patients: Mona Shrestha MN (Adult Nursing)Document77 pagesDrugs For Cancer Patients: Mona Shrestha MN (Adult Nursing)sushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Treatment of EntropionDocument34 pagesAnatomy and Treatment of Entropionsushma shrestha100% (1)
- Chest Xray 2Document39 pagesChest Xray 2sushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Retinal Vascular DisordersDocument52 pagesRetinal Vascular Disorderssushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Welcome To Presentation: Presented by Karishma Mahato Roll No. 15Document18 pagesWelcome To Presentation: Presented by Karishma Mahato Roll No. 15sushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Presentation on Cerebral Angiography and EEG ProceduresDocument25 pagesPresentation on Cerebral Angiography and EEG Proceduressushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Intravenous Urography (IVU)Document35 pagesIntravenous Urography (IVU)sushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer's Disease: Name: Pooja Adhikari Rollno: 27 SMTCDocument40 pagesAlzheimer's Disease: Name: Pooja Adhikari Rollno: 27 SMTCsushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Retinal Vascular DisordersDocument52 pagesRetinal Vascular Disorderssushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Catheterization GuideDocument28 pagesCatheterization Guidesushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Alzheimer's Disease: Name: Pooja Adhikari Rollno: 27 SMTCDocument40 pagesAlzheimer's Disease: Name: Pooja Adhikari Rollno: 27 SMTCsushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Chest Tube Insertion GuideDocument39 pagesChest Tube Insertion Guidesushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- EsophagusDocument72 pagesEsophagussushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- Modified Curriculum: Use of Restraints Precautions Danger Associated With RestraintsDocument3 pagesModified Curriculum: Use of Restraints Precautions Danger Associated With Restraintssushma shresthaNo ratings yet
- 2018 List of DoctorsDocument28 pages2018 List of Doctorsvishwa.curingbusyNo ratings yet
- Tonoref Iiie 8P 5Document8 pagesTonoref Iiie 8P 5FelipeMeloNo ratings yet
- Cataract Surgery, 3rd Edition: PART VII - Management of Complications Chapter 49 - Corneal Edema After Cataract SurgeryDocument14 pagesCataract Surgery, 3rd Edition: PART VII - Management of Complications Chapter 49 - Corneal Edema After Cataract Surgerymithaa octoviagnesNo ratings yet
- Fisio - Faal Special SenseDocument107 pagesFisio - Faal Special SensetiffsbronteNo ratings yet
- Issue 95 Ocular Surface DisordersDocument35 pagesIssue 95 Ocular Surface DisordersAnonymous M9HvzpUNo ratings yet
- Eye Exam Skill SheetDocument1 pageEye Exam Skill SheetMuhammed ElgasimNo ratings yet
- Myopia: By: Mu'amar Aldo ArhatuDocument9 pagesMyopia: By: Mu'amar Aldo ArhatuMuamar Aldo ArhatuNo ratings yet
- TC TRK 2p Brochure Eng 210x297mm Rev7 17072021 Lrs Single PagesDocument8 pagesTC TRK 2p Brochure Eng 210x297mm Rev7 17072021 Lrs Single Pagesneophantom00No ratings yet
- SA Corneal UlcersDocument70 pagesSA Corneal UlcersFikri AnandaNo ratings yet
- LU6 Ang, GGT Ophtha251 CataractAssignmentDocument2 pagesLU6 Ang, GGT Ophtha251 CataractAssignmentPJ PJNo ratings yet
- Anatomy and Treatment of EntropionDocument34 pagesAnatomy and Treatment of Entropionsushma shrestha100% (1)
- Spec 1252557782Document6 pagesSpec 1252557782Mukarram AbdulnabeeNo ratings yet
- Evaluation of Proptosis FinalDocument61 pagesEvaluation of Proptosis FinalPrathibha M Chachadi100% (1)
- Penjelasan Dan Jawaban CRVODocument4 pagesPenjelasan Dan Jawaban CRVONuruel SazaNo ratings yet
- Current Management of PresbyopiaDocument8 pagesCurrent Management of PresbyopiaElrach CorpNo ratings yet
- Chapter 6 Corrective LensesDocument24 pagesChapter 6 Corrective LensesSoorav MlicNo ratings yet
- The Sensitivity of The Bielschowsky Head-Tilt Test in Diagnosing Acquired Bilateral Superior Oblique ParesisDocument10 pagesThe Sensitivity of The Bielschowsky Head-Tilt Test in Diagnosing Acquired Bilateral Superior Oblique ParesisAnonymous mvNUtwidNo ratings yet
- Clinical and Histological Presentation After Plexr Application, Needle Shaping (Vibrance) and O.F.FDocument9 pagesClinical and Histological Presentation After Plexr Application, Needle Shaping (Vibrance) and O.F.Falejandro GonzàlezNo ratings yet
- CM8 Vision Ocular Optic 22 - 23Document50 pagesCM8 Vision Ocular Optic 22 - 23Douaa lkNo ratings yet
- AstigmatismDocument5 pagesAstigmatismTaimur RashidNo ratings yet
- Pitfalls in Intraocular Pressure Measurement by Goldmann-Type Applanation TonometersDocument3 pagesPitfalls in Intraocular Pressure Measurement by Goldmann-Type Applanation TonometersLucas HoldereggerNo ratings yet
- 2018 - 22nd Brochure PagesDocument6 pages2018 - 22nd Brochure Pagesyos_peace86No ratings yet