Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Enhancement Course For Clerks Biochem Examination Part 1
Uploaded by
Kevin AlonzoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Enhancement Course For Clerks Biochem Examination Part 1
Uploaded by
Kevin AlonzoCopyright:
Available Formats
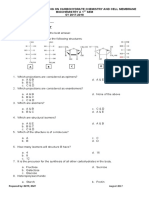
ENHANCEMENT COURSE FOR CLERKS C.
Phosphoglycerate and pyruvate
BIOCHEM EXAMINATION PART 1 kinase
D. Pyruvate kinase
1. Control enzyme(s) of the citric acid
cycle: 6. Vitamin(s) that act as coenzyme(s) in
the citric acid cycle:
A. Succinate thiokinase
B. Isocitrate dehydrogenase and A. Vit B5 and B2
citrate synthase B. Pyridoxine
C. Isocitrate dehydrogenase C. Panthothenic acid
D. Citrate synthase D. Riboflavin
2. If the energy requirement of the cell 7. Entry points of amino acids
is high: undergoing gluconeogenesis:
A. AMP level is high A. Acetyl-coA
B. PEPCK is stimulated B. Dihydroxyacetone phosphate
C. ATP/ADP ratio is high C. Alpha-ketoglutarate
D. PEPCK is activated D. Phosphoenolpyruvate
3. True of the rate limiting enzyme of 8. True regarding glycogenesis and
glycolysis: glycogenolysis:
A. It is activated by fructose-2,6 A. Glucose is added to the glycogen
biphosphate primer in the form of D-glucose
B. It is reversed by glucose-6- B. Insulin promotes glycogenesis by
phosphatase stimulating glycogen synthase
C. It is stimulated by glucagon C. Insulin prevents glycogenesis by
D. All items are correct stimulating glycogen synthase
D. Glucagon inhibits liver
4. Glucose-6-phosphate is an glycogenolysis by stimulating
intermediate in the following phosphorylase
pathways:
9. What are the major end-products of
A. Uronic acid pathway lipolysis of a triacylglycerol in the
B. Glycogenolysis adipose tissue?
C. All items are included
D. Gluconeogenesis A. 2-monoacylglycerol + 2 fatty
acids
5. Enzyme/s catalysing substrate level B. 1-monoacylglycerol +
of phosphorylation in the cytosol: diacylglycerol
C. 1-monoacylglycerol + 2-
A. Phosphoglycerate kinase monoacylglycerol
B. Succinate thiokinase D. 3 fatty acids + glycerol
10. Which of the following hormones 15. The committed step in cholesterol
inhibits lipolysis? synthesis results in the formation of:
A. Thyroxine A. Mevalonate
B. Insulin B. Isopentenyl pyrophosphate
C. Growth hormone C. Squalene
D. Cortisol D. Lanosterol
11. The committed step in 16. The steroid ring is produced when
extramitochondrial lipogenesis this intermediate metabolite is
involves the formation of: formed during cholesterol synthesis:
A. Malonyl CoA A. Squalene
B. Proprionyl CoA B. Zymosterol
C. Acetyl CoA C. 7-dehydrocholesterol
D. Succinyl CoA D. Lanosterol
12. What fatty acid is produced in 17. HMG-CoA reductase is inhibited by
extramitochondrial lipogenesis? this hypocholesterolemic agent:
A. Oleic acid A. Simvastatin
B. Palmitoleic acid B. Cholestyramine
C. Stearic acid C. Orlistat
D. Palmitic acid D. Nicotinamide
13. Which of the following is the 18. Which of these lipoproteins is
product of the action of involved in the reverse transport of
lipoxygenase? cholesterol?
A. Leukotriene A. LDL
B. Thromboxane B. VLDL
C. Prostaglandin C. Chylomicron
D. Prostacyclin D. HDL
14. Which of these is the substance of 19. This lipoprotein mobilizes the
cyclooxygenase that results in the triacylglycerols produced in hepatic
formation of series 2 cells thereby preventing the
prostaglandins? development of fatty liver:
A. Cervonic acid A. LDL
B. Palmitoleic acid B. Chylomicron
C. Arachidonic acid C. HDL
D. Timnodonic acid D. VLDL
A. Phospholipase D
20. What is the cause of familial B. Phospholipase A2
hypercholesterolemia? C. Phospholipase C
D. Phospholipase B
A. Deficiency of LDL receptor
B. Increased activity of 25. This is the most important lipolytic
oxidoxyclase enzyme in the digestive tract
C. Excess lipoprotein(a) deficiency of which will cause
D. Overactivity of HMG-CoA steatorrhea:
reductase
A. Pancreatic lipase
21. Beta-oxidation of fatty acid is B. Lingual lipase
primarilu regulated at the level of C. Hepatic lipase
this enzyme: D. Gastric lipase
A. Hepatic lipase
B. Thiokinase
C. Phospholipase B
D. Fatty acyl-carnitine translocase
22. Which of the following enzymes
catalyzes the conversion of
cholesterol to cholic acid?
A. 19-beta hydroxylase
B. 17-alpha hydroxylase
C. 7-alpha hydroxylase
D. 9-beta hydroxylase
23. Which of these steps in beta
oxidation is rate-limiting?
A. Activation of free fatty acid to
fatty acyl CoA
B. Carnitine transport of the fatty
acid
C. Thiolytic cleavage of ketoacyl
CoA
D. Oxidation of fatty acyl CoA
24. Which of the following
phospholipases is inhibited by
steroid drugs?
You might also like
- Lettice and Lovage PDFDocument1 pageLettice and Lovage PDFapi-2452366370% (2)
- Biochemisrty Question Bank-1Document51 pagesBiochemisrty Question Bank-1Abd El-Rahman Salah0% (1)
- Shattered Pixel Dungeon The Newb Adventurer's Guide: Chapter I: The BasicsDocument15 pagesShattered Pixel Dungeon The Newb Adventurer's Guide: Chapter I: The BasicsFishing ManiaNo ratings yet
- Endicrine MCQ-QuestionsDocument4 pagesEndicrine MCQ-QuestionsThe White Army100% (1)
- Semi Final Examination (Ips 1) : EsculentaDocument8 pagesSemi Final Examination (Ips 1) : EsculentaKenny TuanNo ratings yet
- Biological Chemistry. The Bank of MCQ Test Questions) 2016-2017Document32 pagesBiological Chemistry. The Bank of MCQ Test Questions) 2016-2017AGM EBNo ratings yet
- Proposal 4psDocument6 pagesProposal 4psCaridad Avila67% (3)
- MILLER Testable ConceptsDocument109 pagesMILLER Testable ConceptsMohammedGooda100% (1)
- بايو بيبر 1 د.جميلة السمهريDocument8 pagesبايو بيبر 1 د.جميلة السمهريOzgan SüleymanNo ratings yet
- TRẮC NGHIỆM SHĐCDocument33 pagesTRẮC NGHIỆM SHĐCsylvester.powell100% (1)
- 00018Document92 pages00018Fernandez-De Ala NicaNo ratings yet
- A. Ground Nut Oil B. Palm Oil C. Margarine D. Soya Bean OilDocument8 pagesA. Ground Nut Oil B. Palm Oil C. Margarine D. Soya Bean Oildrpnnreddy100% (1)
- Carbohydrate Metabolism SamplexDocument13 pagesCarbohydrate Metabolism SamplexCherie ThompsonNo ratings yet
- (مكتملة) اسئلة البايو د.ج السمهري (.)Document10 pages(مكتملة) اسئلة البايو د.ج السمهري (.)Ozgan SüleymanNo ratings yet
- 70 Multiple Choice QuestionsDocument10 pages70 Multiple Choice QuestionsChiku MteghaNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter 3Document5 pagesBiochemistry Chapter 3brownhazelNo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument12 pagesBiochemistryKitkat CasacopNo ratings yet
- 15 Lecture 3 Endo 2 Tutorial PDFDocument2 pages15 Lecture 3 Endo 2 Tutorial PDFFafa MusNo ratings yet
- 3 Metabolism of Proteins & Amino AcidsDocument79 pages3 Metabolism of Proteins & Amino AcidsYashfa YasinNo ratings yet
- Lipoprotein MetabolismDocument23 pagesLipoprotein MetabolismDarien LiewNo ratings yet
- En-Metabolism LipidicDocument25 pagesEn-Metabolism LipidicCristina THCSNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry MLT EXAMDocument8 pagesBiochemistry MLT EXAMLeonel NkwetiNo ratings yet
- MCQ Biochemistry LipidsDocument38 pagesMCQ Biochemistry LipidsstuffNo ratings yet
- Endocrine SystemDocument51 pagesEndocrine SystemMahenor Emad100% (1)
- Biochemistry (GREEN)Document18 pagesBiochemistry (GREEN)BRYAN BALDOMERONo ratings yet
- BiochemistryDocument22 pagesBiochemistryChia JoseNo ratings yet
- MCQ On VitaminsDocument5 pagesMCQ On VitaminsNikhil raj Yadav100% (1)
- 1st Sec - Homework - Unit 1 - CH 1 - CarbohydratesDocument14 pages1st Sec - Homework - Unit 1 - CH 1 - Carbohydratesali SaidNo ratings yet
- (Biochem A) 2017 Carbo Chem Mock SamplexDocument4 pages(Biochem A) 2017 Carbo Chem Mock SamplexMcycy MiNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry MCQS - VitaminsDocument3 pagesBiochemistry MCQS - VitaminsRati PotateNo ratings yet
- Biopolymers Structure and PropertiesDocument78 pagesBiopolymers Structure and PropertiesgautamahujaNo ratings yet
- ch20-22 - Probleme SetDocument8 pagesch20-22 - Probleme SetReese VespertineNo ratings yet
- Battery ExamDocument7 pagesBattery ExamKani Mahal KitahNo ratings yet
- Biochem 2Document7 pagesBiochem 2Aleena KarimNo ratings yet
- Quiz On Nucleic Acids - Lecture - BIOCHEMISTRYDocument13 pagesQuiz On Nucleic Acids - Lecture - BIOCHEMISTRYAlliah Turingan100% (1)
- Biochemistry I MCQ PDFDocument2 pagesBiochemistry I MCQ PDFumar khan50% (2)
- Biomolecules & Polymers Exercise 1Document90 pagesBiomolecules & Polymers Exercise 1Aditya ShahNo ratings yet
- Metabolism MCQ ADocument0 pagesMetabolism MCQ ASurajit BhattacharjeeNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Control Questions. Module 1Document2 pagesBiochemistry Control Questions. Module 1Valeriy MelnykNo ratings yet
- Biochem Practical QuestionsDocument13 pagesBiochem Practical QuestionsBurhan HameedNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Page 1 of 12Document12 pagesBiochemistry Page 1 of 12Viviengail GalosNo ratings yet
- Carbohydrate Mbc201Document9 pagesCarbohydrate Mbc201LoisNo ratings yet
- TestDocument23 pagesTestParth sarthi Sen guptaNo ratings yet
- Biochem QbankDocument16 pagesBiochem Qbank786waqar786No ratings yet
- Bichem Module - 1-2014 With 1 and 2Document41 pagesBichem Module - 1-2014 With 1 and 2Mukunda MurariNo ratings yet
- Chapter - 08 - Lipids Membranes-TestDocument10 pagesChapter - 08 - Lipids Membranes-Testendang dian lestariNo ratings yet
- Second Year ExamDocument4 pagesSecond Year ExamSyamil AzharNo ratings yet
- Digestion and Absorption of Dietary LipidsDocument35 pagesDigestion and Absorption of Dietary LipidsCharmaine Luc100% (2)
- Problem Set 2 EndocrinologyDocument12 pagesProblem Set 2 EndocrinologyJessica EtieneNo ratings yet
- Biochem Sample Test-2-2016-AnswersDocument6 pagesBiochem Sample Test-2-2016-Answerssuperfr3shmNo ratings yet
- Enzymes MCQ Topic Quiz Lesson ElementDocument19 pagesEnzymes MCQ Topic Quiz Lesson ElementArvin DiNozzoNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument22 pagesAmino Acidskarli geethanjaliNo ratings yet
- Cycle, or The Szent-Györgyi-Krebs CycleDocument6 pagesCycle, or The Szent-Györgyi-Krebs CyclejayrajsenNo ratings yet
- As Biochemistry QuizDocument7 pagesAs Biochemistry QuizFati QuaynorNo ratings yet
- Lipid and Amino Acid Metabolism: Chapter ObjectivesDocument11 pagesLipid and Amino Acid Metabolism: Chapter ObjectivesLarry411100% (1)
- BCH MCQs1Document304 pagesBCH MCQs1moxdegr8100% (1)
- 11 - Biochemistry MCQs Amino Acid & PROTEINSDocument8 pages11 - Biochemistry MCQs Amino Acid & PROTEINSMohamed YahiaNo ratings yet
- Metabolism Lippincott's Q&ADocument86 pagesMetabolism Lippincott's Q&Alina amjadNo ratings yet
- Chapter 25: Lipid Metabolism: Multiple ChoiceDocument7 pagesChapter 25: Lipid Metabolism: Multiple ChoiceMaxinefgc Baculo100% (1)
- Edited - Chapter 6 Test BankDocument18 pagesEdited - Chapter 6 Test BankRod De Guzman100% (1)
- MCQ Biochemistry CarbohydrateDocument21 pagesMCQ Biochemistry Carbohydratestuff100% (1)
- Biochemistry Blue PrintDocument10 pagesBiochemistry Blue PrintAradhanaRamchandaniNo ratings yet
- Handbook of Endocrine Research TechniquesFrom EverandHandbook of Endocrine Research TechniquesFlora de PabloNo ratings yet
- Selected Topics in the History of Biochemistry. Personal Recollections. Part IIIFrom EverandSelected Topics in the History of Biochemistry. Personal Recollections. Part IIIRating: 1 out of 5 stars1/5 (1)
- VedicReport2 28 202412 53 08PMDocument55 pagesVedicReport2 28 202412 53 08PM처곧ᄉJimmyNo ratings yet
- Joseph Brazier, Ltd. Et Al v. Specialty Bar Products Company - Document No. 7Document3 pagesJoseph Brazier, Ltd. Et Al v. Specialty Bar Products Company - Document No. 7Justia.comNo ratings yet
- Effect of Soil Deformability On RigidityDocument11 pagesEffect of Soil Deformability On RigidityCesar Basantes AvalosNo ratings yet
- Data Mining ToolsDocument9 pagesData Mining Toolspuneet0303No ratings yet
- Best Freight Forwarding ERP Software - CargoNet PDFDocument19 pagesBest Freight Forwarding ERP Software - CargoNet PDFGo cargonetNo ratings yet
- Biosash Order Form Latest - 2019-9281576348996003Document3 pagesBiosash Order Form Latest - 2019-9281576348996003Amer Suhail ShareefNo ratings yet
- Stochastic Epidemic ModellingDocument15 pagesStochastic Epidemic ModellingIRJMETS JOURNALNo ratings yet
- 2011 07 IDIP Unit A Past PaperDocument4 pages2011 07 IDIP Unit A Past Paperfh71No ratings yet
- Ecosystem ScriptDocument7 pagesEcosystem ScriptGeraldine Co TolentinoNo ratings yet
- Linux CommandDocument128 pagesLinux CommandZakNo ratings yet
- E3nn Euclidean Neural NetworksDocument22 pagesE3nn Euclidean Neural Networksmohammed ezzatNo ratings yet
- Bicol State College of Applied Sciences and Technology: JANUARY 2021Document11 pagesBicol State College of Applied Sciences and Technology: JANUARY 2021Jay Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- 360 Peoplesoft Interview QuestionsDocument10 pages360 Peoplesoft Interview QuestionsRaghu Nandepu100% (1)
- Grlweap 2005Document3 pagesGrlweap 2005José RuizNo ratings yet
- Program Istp17Document17 pagesProgram Istp17pverma4622No ratings yet
- Scribd Sap SD Pricing in Depth Configuration GuideDocument136 pagesScribd Sap SD Pricing in Depth Configuration GuideRavi SubramanianNo ratings yet
- Skoda Annual Report 2015Document128 pagesSkoda Annual Report 2015D'Invisible KatNo ratings yet
- Ronald Allan Talisay CV 2017 - 1Document6 pagesRonald Allan Talisay CV 2017 - 1Ronald AllanNo ratings yet
- Capital Budgeting Practices by Corporates in India PPTDocument13 pagesCapital Budgeting Practices by Corporates in India PPTRVijaySai0% (1)
- CLI Basics: Laboratory ExerciseDocument5 pagesCLI Basics: Laboratory ExerciseJhalen Shaq CarrascoNo ratings yet
- Mvo 1965Document113 pagesMvo 1965younisNo ratings yet
- Alxion: For Direct DriveDocument56 pagesAlxion: For Direct DriveAnselmo Aguado cortesNo ratings yet
- ColsonCatalogR27!11!11 15Document124 pagesColsonCatalogR27!11!11 15Roberto SolorzanoNo ratings yet
- Automatic Summarization of Youtube Video Transcription Text Using Term Frequency-Inverse Document FrequencyDocument9 pagesAutomatic Summarization of Youtube Video Transcription Text Using Term Frequency-Inverse Document FrequencyKarunya ChavanNo ratings yet
- Project Report On Working-CapitalDocument74 pagesProject Report On Working-Capitalravikant2105100% (1)
- How Fractions, Decimals and Percentages Work TogetherDocument9 pagesHow Fractions, Decimals and Percentages Work TogetherjohnteecubeNo ratings yet