Professional Documents
Culture Documents
23-00-00 - COMMUNICATIONS: 23-00-00 PB 001 Conf 00 - Communications - Description and Operation
Uploaded by
YousefOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
23-00-00 - COMMUNICATIONS: 23-00-00 PB 001 Conf 00 - Communications - Description and Operation
Uploaded by
YousefCopyright:
Available Formats
Customer : SVA Manual : AMM
Type : A318/A319/A320/A321 Selected applicability : ALL
Rev. Date : Nov 01, 2019
23-00-00 - COMMUNICATIONS
** ON A/C ALL
23-00-00 - COMMUNICATIONS
23-00-00 PB 001 CONF 00 - COMMUNICATIONS - DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
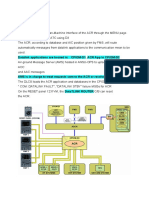
1. General
The communication system is used for speech communications and optionally for data communications.
The communication system is used for communication between the crew members and between the crew
members and the ground personnel.
It is also used to communicate with the passengers, other aircraft and the ground stations (speech and data).
2. Description
A. Speech Communication
(1) High Frequency (HF) system (Ref. 23-11) (optional system)
This system has two transceivers and their related equipment for long-range voice communications.
(2) Very High Frequency (VHF) system (Ref. 23-12)
This system has two or three transceivers and their related equipment for short-range voice
communications.
The VHF3 system (if installed) is also used to transmit data (Aircraft Communication Addressing and
Reporting System (ACARS) or Air Traffic Service Unit (ATSU)).
(3) Radio Management Panels (RMP) (Ref. 23-13)
The RMPs enable a centralized frequency control of the VHF and HF radio communication equipment.
The RMPs also enable the frequency control of the radio navigation equipment (VHF Omnidirectional
Range (VOR), Distance Measuring Equipment (DME), Instrument Landing System (ILS), Automatic
Direction Finder (ADF)) in case of failure of the Flight Management and Guidance System (FMGC).
(4) Voice privacy system (Ref. 23-14)
The voice privacy system provides a means for coding HF communications between the aircraft and
DT.HU.Department in order to protect confidential communications.
B. Data Transmission (optional system)
(1) ACARS (Ref. 23-24) (optional system)
The ACARS management unit allows the management of the data entered by the crews and transmitted
to the ground (SDAC, AIDS, CFDS, FMGEC). It also allows the reception, printing and display of ground
messages on the Multipurpose Control and Display Unit (MCDU).
These data are transmitted through the VHF3 system (or through the Satellite Communication
(SATCOM) system if installed).
(2) SATCOM (Ref. 23-28) (optional system)
The function of the SATCOM system is the reception in the L-Band and processing of signals through
aeronautical services satellites. This system is used for all aeronautical satellite communications
(cockpit voice, passenger telephone and data services) with the ground.
C. Passenger Address and Entertainment
This system comprises: (Ref. 23-30)
· Prerecorded Announcements and Music (PRAM) system (Ref. 23-32)
· Passenger Entertainment System (Music)/Passenger Services System (PES (Music)/PSS) (Ref. 23-33)
· Passenger Visual Information System (PVIS) (Ref. 23-34)
· Passenger Air-to-ground Telephone System (PATS) (Ref. 23-35)
· Passenger Entertainment System (Video) (PES (Video)) (Ref. 23-36)
· Passenger facility (AM/FM radio) (Ref. 23-37)
The Passenger Address System (Ref. 23-31) is part of the Cabin Intercommunication Data System (CIDS)
(Ref. 23-73).
D. Interphone
The Interphone system comprises:
(1) Cockpit-to-ground crew call system (Ref. ATA 23-42)
Print Date: November 18, 2019 Page 1 of 2
© AIRBUS S.A.S. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. CONFIDENTIAL AND PROPRIETARY DOCUMENT.
Customer : SVA Manual : AMM
Type : A318/A319/A320/A321 Selected applicability : ALL
Rev. Date : Nov 01, 2019
23-00-00 - COMMUNICATIONS
Moreover, when the aircraft is battery supplied, the system comprises an aural warning function for the
following status:
· Auxiliaire Power Unit (APU) fire
· ADIRS supplied by batteries
· Equipment ventilation faulty
· Emergency Locator Transmitter (ELT) operation (if installed).
(2) Flight crew interphone (Ref. 23-43)
The cockpit-to-ground crew call system is used to:
· Call a ground mechanic from the cockpit
· Call a crew member from the ground.
The flight crew interphone system is part of the CIDS.
(3) Cabin and service interphone (Ref. 23-44)
The cabin and service interphone system is used for the telephone communications on the ground
between the flight crew and the ground service personnel.
E. Audio Integrating
The Audio Integrating System (AIS):
The AIS integrates and manages all audio signals (audio outputs, microphone inputs, sidetone and push-to-
talk) supplied by and sent to the radio communication and radio navigation systems.
This system also provides the SELCAL function and call and flight interphone functions.
F. Static Discharging (Ref. 23-60)
Static dischargers are installed on the aircraft to protect the communication systems from interference
caused by static electricity.
G. Audio-Video Monitoring and Intercommunication
This system comprises:
(1) Cockpit Voice Recorder (CVR) (Ref. 23-71)
The CVR automatically records the crew conversations and audio communications to help investigation
after an aircraft accident or incident.
(2) CIDS (Ref. 23-73)
The CIDS is a microprocessor-based system.
It is used to do the functional control, operation, testing and monitoring of the cabin systems.
These system functions are provided by the CIDS:
· Passenger address
· Passenger call
· Passenger lighted signs
· General cabin illumination control
· Cabin and flight crew interphone
· Emergency evacuation signalling
· Lavatory smoke warning
· Escape slide reservoir pressure monitoring
· Service interphone (partially integrated into the CIDS)
· Extended emergency lighting test.
(3) Cabin Management System (CMS) (Ref. 23-74) (optional system)
The CMS provides a direct contact for the cabin crew with the ground.
The cabin crew uses the CMS to transmit and receive real-time data (e.g. passenger information and
reservations, maintenance reports, security catering and beverages), through the ACARS.
End of document
Print Date: November 18, 2019 Page 2 of 2
© AIRBUS S.A.S. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED. CONFIDENTIAL AND PROPRIETARY DOCUMENT.
You might also like
- Supply Chain Vulnerabilities Impacting Commercial AviationFrom EverandSupply Chain Vulnerabilities Impacting Commercial AviationNo ratings yet
- Module 5: Digital Techniques and Electronic Instrument SystemsDocument81 pagesModule 5: Digital Techniques and Electronic Instrument SystemsNaseer AbdaljabarNo ratings yet
- 737 Performance Reference Handbook - EASA EditionFrom Everand737 Performance Reference Handbook - EASA EditionRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (3)
- Aircraft Communication Systems ExplainedDocument4 pagesAircraft Communication Systems ExplainedTrung SơnNo ratings yet
- Woii Sedegah DivineDocument69 pagesWoii Sedegah DivineAma Serwaa YeboahNo ratings yet
- Acars Aircraft Communication Addressing and Reporting SystemDocument14 pagesAcars Aircraft Communication Addressing and Reporting SystemAlex SuarezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 14: Navigation and Communication: GeneralDocument32 pagesChapter 14: Navigation and Communication: GeneralMax powersNo ratings yet
- Avionics - Afzal SirDocument29 pagesAvionics - Afzal SirgultusundoriNo ratings yet
- A CarsDocument24 pagesA CarsNaveenn NarraaNo ratings yet
- This AC Paragraph Is Final and Will Be Included in The Upcoming Change 2 UpdateDocument27 pagesThis AC Paragraph Is Final and Will Be Included in The Upcoming Change 2 Updatelacsmm982No ratings yet
- Monitor cabin communications and safety systemsDocument9 pagesMonitor cabin communications and safety systemsNoorul QuamarNo ratings yet
- A320 Flight Controls PaperDocument8 pagesA320 Flight Controls PaperVatsal VakhariaNo ratings yet
- ACARSDocument9 pagesACARSMeet PatelNo ratings yet
- Traffic Collision Avoidance SystemDocument16 pagesTraffic Collision Avoidance SystemWin MinNo ratings yet
- AE6701 - Avionics NotesDocument83 pagesAE6701 - Avionics Notesparantn100% (1)
- Aircraft Communication, Adressing and Reporting System (Acars)Document43 pagesAircraft Communication, Adressing and Reporting System (Acars)adexNo ratings yet
- TCAS AircraftDocument20 pagesTCAS AircraftPrabuddha ChakrabortyNo ratings yet
- Aircraft Rescue and Fire Fighting CommunicationsDocument22 pagesAircraft Rescue and Fire Fighting CommunicationsMelissa Gonzalez TorresNo ratings yet
- Asmgcs KolkataDocument29 pagesAsmgcs KolkataAnandKumarNo ratings yet
- B717 23 COMMUNICATIONS - InitialDocument39 pagesB717 23 COMMUNICATIONS - InitialA WongNo ratings yet
- AAE 3156 Avionics Subsystem Databus and Avionics ArchitectureDocument132 pagesAAE 3156 Avionics Subsystem Databus and Avionics ArchitectureDpt HtegnNo ratings yet
- A320 Communications Systems OverviewDocument450 pagesA320 Communications Systems Overview林至伟No ratings yet
- Airport Authority of IndiaDocument51 pagesAirport Authority of IndiaNeha Bhatia100% (1)
- Avionics Is ADocument13 pagesAvionics Is ARiaz ShahNo ratings yet
- Automatic Dependent Surveillance - BroadcastDocument7 pagesAutomatic Dependent Surveillance - Broadcastgrae16No ratings yet
- AAI Training ReportDocument43 pagesAAI Training ReportRAJIV SINGHNo ratings yet
- A380 Chapter 23 CommunicationDocument5 pagesA380 Chapter 23 CommunicationE DinNo ratings yet
- 1 Introduction AvionicsDocument48 pages1 Introduction AvionicsAkmal Aiman100% (1)
- AAE 3282 Avionics Subsystem Databus and Avionics ArchitectureDocument128 pagesAAE 3282 Avionics Subsystem Databus and Avionics ArchitectureLnsfv100% (1)
- Flight Information Service: Ref. Annex 11Document68 pagesFlight Information Service: Ref. Annex 11Adrian MaximoNo ratings yet
- Revolutionizing Air Traffic ManagementDocument6 pagesRevolutionizing Air Traffic ManagementSaim IrfanNo ratings yet
- A320 Communications Systems OverviewDocument450 pagesA320 Communications Systems OverviewNizar HarbNo ratings yet
- Avionics Unit 1 NotesDocument26 pagesAvionics Unit 1 NotesGowri ShankarNo ratings yet
- Communication, Navigation & Surveillance EquipmentsDocument38 pagesCommunication, Navigation & Surveillance EquipmentsGagneet KaurNo ratings yet
- AIRBUS A320/A330/A340 Electrical Flight Controls A Family of Fault-Tolerant SystemsDocument8 pagesAIRBUS A320/A330/A340 Electrical Flight Controls A Family of Fault-Tolerant SystemsNour El-Din SafwatNo ratings yet
- Avoinics Basic 19-SepDocument8 pagesAvoinics Basic 19-SepJai DeepNo ratings yet
- R Rec M.2059 0 201312 P!!MSW eDocument21 pagesR Rec M.2059 0 201312 P!!MSW esanthoshinigoNo ratings yet
- TCASDocument70 pagesTCASManish Mishra100% (1)
- Communication: Ops Asst (Ats)Document29 pagesCommunication: Ops Asst (Ats)Dileep KumarNo ratings yet
- Backup ATC Centre Maintains Continuous ServicesDocument5 pagesBackup ATC Centre Maintains Continuous ServicesprodigynaveenNo ratings yet
- 23 CommunicationsDocument66 pages23 CommunicationsWilson BenincoreNo ratings yet
- Traffic Collision Avoidance System1Document16 pagesTraffic Collision Avoidance System1ajrio1785No ratings yet
- ATA 23 Notes 2Document5 pagesATA 23 Notes 2Noorul QuamarNo ratings yet
- Single Aisle Aircraft Communications ManualDocument102 pagesSingle Aisle Aircraft Communications ManualCassiano CapellassiNo ratings yet
- Monitoring: Glass CockpitDocument4 pagesMonitoring: Glass CockpitSealtiel1020100% (1)
- 00instrumentation AllDocument161 pages00instrumentation Allkarl bohnNo ratings yet
- Camera Ready Paper PDFDocument7 pagesCamera Ready Paper PDFRamakrishnan RamasubramanianNo ratings yet
- Air Traffic Control SystemsDocument14 pagesAir Traffic Control SystemsMajestyNo ratings yet
- FAA H 8083 16B GlossaryDocument12 pagesFAA H 8083 16B GlossaryVilmaNo ratings yet
- I. AircraftDocument120 pagesI. AircraftMaria KristianiNo ratings yet
- Airports Authority of India Regional Training Center (CNS), ER N.S.C.B.I Airport, Kolkata-700052Document33 pagesAirports Authority of India Regional Training Center (CNS), ER N.S.C.B.I Airport, Kolkata-700052rose whiteNo ratings yet
- Learn About Aircraft Communication SystemsDocument94 pagesLearn About Aircraft Communication SystemsTSuman Jones GiriNo ratings yet
- Module SyllabusDocument3 pagesModule SyllabusKuldeep SinghNo ratings yet
- 44 Cabin Systems PDFDocument40 pages44 Cabin Systems PDFAaron Harvey100% (3)
- Communication A320 PDFDocument41 pagesCommunication A320 PDFAsraf100% (1)
- Avionics Chapter 1Document8 pagesAvionics Chapter 1Anuska DeyNo ratings yet
- History: Avionics Is A Term Used To Describe All of TheDocument5 pagesHistory: Avionics Is A Term Used To Describe All of TheBhukya VenkateshNo ratings yet
- Airports Authority of India (Print)Document31 pagesAirports Authority of India (Print)rahul5843No ratings yet
- Text 62A6AF85894F 1Document1 pageText 62A6AF85894F 1YousefNo ratings yet
- Welcome On Board!Document1 pageWelcome On Board!YousefNo ratings yet
- نعود بحذر - أهمية ارتداء الكمامةDocument1 pageنعود بحذر - أهمية ارتداء الكمامةYousefNo ratings yet
- Welcome On Board!Document1 pageWelcome On Board!YousefNo ratings yet
- Text 62A6AF85894F 1Document1 pageText 62A6AF85894F 1YousefNo ratings yet
- November 2010 (v1) QP - Paper 3 CIE Biology A-Level PDFDocument12 pagesNovember 2010 (v1) QP - Paper 3 CIE Biology A-Level PDFWiji NingNo ratings yet
- Chapter 1 and 2Document67 pagesChapter 1 and 2Tle SupawidNo ratings yet
- Discover Over 70 Player Classes and RacesDocument1 pageDiscover Over 70 Player Classes and RacesFred FrançaNo ratings yet
- GypsumDocument79 pagesGypsumMansi GirotraNo ratings yet
- What Is The Kingdom of GodDocument10 pagesWhat Is The Kingdom of GodSunil ChelladuraiNo ratings yet
- MUSCULAR SYSTEM WORKSHEET Slides 1 To 4Document4 pagesMUSCULAR SYSTEM WORKSHEET Slides 1 To 4kwaiyuen ohnNo ratings yet
- Worthy - Elevation WorshipDocument1 pageWorthy - Elevation WorshipSabine J.100% (1)
- Concept of StateDocument10 pagesConcept of StateAryansh ShuklaNo ratings yet
- Water Quality Notes: Alkalinity and Hardness: P. Chris WilsonDocument6 pagesWater Quality Notes: Alkalinity and Hardness: P. Chris WilsonrishabhNo ratings yet
- LP PG Conversion To Thar CoalDocument3 pagesLP PG Conversion To Thar CoalRaja Zeeshan100% (1)
- Edema Paru Kardiogenik Akut Kak TiaraDocument8 pagesEdema Paru Kardiogenik Akut Kak TiaraTyara LarisaNo ratings yet
- Steel Grid StructureDocument2 pagesSteel Grid StructureKusum RawatNo ratings yet
- Surat Kecil Untuk TuhanDocument9 pagesSurat Kecil Untuk TuhanAsgarPurnamaNo ratings yet
- Imsa Catalog Imsa CatDocument16 pagesImsa Catalog Imsa CatDaniel TelloNo ratings yet
- Aula 4 - Wooten - Organizational FieldsDocument28 pagesAula 4 - Wooten - Organizational FieldsferreiraccarolinaNo ratings yet
- Science: Pure Substances Vs MixturesDocument33 pagesScience: Pure Substances Vs MixturesElle Ma Rie100% (1)
- (New) Adjustable Voltage Power Supply 55 V - 20A High Power and Current - Automatic Fan On - OffDocument1 page(New) Adjustable Voltage Power Supply 55 V - 20A High Power and Current - Automatic Fan On - OffSek PyroNo ratings yet
- Digital control engineering lecture on z-transform and samplingDocument13 pagesDigital control engineering lecture on z-transform and samplingjin kazamaNo ratings yet
- Fundamental aim training routines and benchmarksDocument8 pagesFundamental aim training routines and benchmarksAchilles SeventySevenNo ratings yet
- The Cactus and the SnowsDocument22 pagesThe Cactus and the SnowsCrisNo ratings yet
- Belazo Elastomeric Roof PaintDocument2 pagesBelazo Elastomeric Roof PaintrumahsketchNo ratings yet
- Rate Analysis-Norms 1Document10 pagesRate Analysis-Norms 1yamanta_rajNo ratings yet
- Determine PH by PH Indicator and Universal IndicatorDocument3 pagesDetermine PH by PH Indicator and Universal IndicatorhaleelNo ratings yet
- EKO75 KW VST Air Cooled Electrical DiagramDocument13 pagesEKO75 KW VST Air Cooled Electrical DiagramBerat DeğirmenciNo ratings yet
- XMSDS Sunflower Seed Oil 9925156Document6 pagesXMSDS Sunflower Seed Oil 9925156Lisa RobertsonNo ratings yet
- Biologic License ApplicationDocument16 pagesBiologic License ApplicationJean Sandra PintoNo ratings yet
- Urban Ecology: Concept of Ecology and Its Importance in ArchitectureDocument12 pagesUrban Ecology: Concept of Ecology and Its Importance in ArchitectureNamrata JitendraNo ratings yet
- BMK PDFDocument8 pagesBMK PDFHuỳnh Minh SángNo ratings yet
- Image Processing Based Leaf Rot Disease, Detection of Betel Vine (Piper Betlel.)Document7 pagesImage Processing Based Leaf Rot Disease, Detection of Betel Vine (Piper Betlel.)ManiNo ratings yet
- Understanding and Quantifying Mountain TourismDocument84 pagesUnderstanding and Quantifying Mountain TourismfloridNo ratings yet