Professional Documents
Culture Documents
3 Determination of Voltage Drop: G - Sizing and Protection of Conductors
Uploaded by
ashraf atefOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
3 Determination of Voltage Drop: G - Sizing and Protection of Conductors
Uploaded by
ashraf atefCopyright:
Available Formats
G - Sizing and protection of conductors
3 Determination of voltage drop
3.2 Calculation of voltage drop in steady load
conditions
Use of formulae
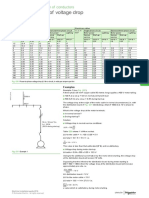
Fig. G29 below gives formulae commonly used to calculate voltage drop in a given
circuit per kilometre of length (copper cable with XLPE insulation).
If:
b IB: The full load current in amps
b L: Length of the cable in kilometres
b R: Resistance of the cable conductor in Ω/km
23.7
[1]
Ω mm2 / km
R= for copper
(
S c.s.a. in mm2 )
37.6
[1]
Ω mm2 / km
R= for aluminium
(
S c.s.a. in mm2 )
Note: R is negligible above a c.s.a. of 500 mm2
b X: inductive reactance of a conductor in Ω/km
Note: X is negligible for conductors of c.s.a. less than 50 mm2. In the absence of
any other information, take X as being equal to 0.08 Ω/km.
b φ: phase angle between voltage and current in the circuit considered, generally:
G20 v Incandescent lighting: cos φ = 1
v Led lighting: cos φ > 0.9
v Fluorescent with electronic ballast: cos φ > 0.9
v Motor power:
- At start-up: cos φ = 0.35
- In normal service: cos φ = 0.8
b Un: phase-to-phase voltage
b Vn: phase-to-neutral voltage
For prefabricated pre-wired ducts and busways (busbar trunking systems),
resistance and inductive reactance values are given by the manufacturer.
Circuit Voltage drop (ΔU)
in volts in %
Phase/phase 100 ∆U
∆U = 2 I B(R cos ϕ + X sin ϕ) L
Un
Phase/neutral
∆U = 2 I B(R cos ϕ + X sin ϕ) L 100 ∆U
Vn
Balanced 3-phase: 3 phases
(with or without neutral) ∆U = 3 I B(R cos ϕ + X sin ϕ) L 100 ∆U
Un
Fig. G29 Voltage-drop formulae
Simplified table
Calculations may be avoided by using Fig. G30 next page, which gives, with an
ampere, in terms of:
b Kinds of circuit use: motor circuits with cos φ close to 0.8, or lighting with a cos φ
close to 1.
b Type of circuit; single-phase or 3-phase
Voltage drop in a cable is then given by:
K x IB x L
K is given by the table,
IB is the full-load current in amps,
L is the length of cable in km.
The column motor power “cos φ = 0.35” of Fig. G30 may be used to compute the
voltage drop occurring during the start-up period of a motor (see example no. 1
[1] Values of r according to IEC60909-0 after the Fig. G30).
and Cenelec TR 50480. See Fig. G38.
Electrical installation guide 2018
© Schneider Electric - all rights reserved
You might also like
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)From EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (122)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryFrom EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceFrom EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (589)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingFrom EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (401)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeFrom EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (537)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItFrom EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (842)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceFrom EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (897)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeFrom EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (5806)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersFrom EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (345)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaFrom EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerFrom EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (271)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnFrom EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyFrom EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2259)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesFrom EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (821)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreFrom EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1091)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureFrom EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealFrom EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)From EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Rating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (98)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaFrom EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- Electronics Devices & Circuit Lab ManualDocument53 pagesElectronics Devices & Circuit Lab Manualbiswajit7sarkar100% (1)
- Facts Worth Knowing About Frequency ConvertersDocument167 pagesFacts Worth Knowing About Frequency ConvertersEduardo SuarezNo ratings yet
- UPS Maintenance GuidelinesDocument5 pagesUPS Maintenance GuidelinessunilNo ratings yet
- 2.3 Main Busbar, HorizontalDocument1 page2.3 Main Busbar, Horizontalashraf atefNo ratings yet
- Shop DWGDocument25 pagesShop DWGashraf atefNo ratings yet
- Pages From IC1000-G320-A220-V3-7600 - Planning - Manual - SIVACON - S8-2Document1 pagePages From IC1000-G320-A220-V3-7600 - Planning - Manual - SIVACON - S8-2ashraf atefNo ratings yet
- 2 SIVACON S8 - System Overview: Technical Data, Standards and Approvals For The SIVACON S8 SwitchboardDocument1 page2 SIVACON S8 - System Overview: Technical Data, Standards and Approvals For The SIVACON S8 Switchboardashraf atefNo ratings yet
- 3 Determination of Voltage Drop: G - Sizing and Protection of ConductorsDocument1 page3 Determination of Voltage Drop: G - Sizing and Protection of Conductorsashraf atefNo ratings yet
- I'm Not Gonna (Going To) Be Able To Example SentencesDocument2 pagesI'm Not Gonna (Going To) Be Able To Example Sentencesashraf atefNo ratings yet
- I'm Afraid (That) Example SentencesDocument2 pagesI'm Afraid (That) Example Sentencesashraf atefNo ratings yet
- Cut Sheet:: (Air Insulated-Vacuum C.B)Document4 pagesCut Sheet:: (Air Insulated-Vacuum C.B)ashraf atefNo ratings yet
- I Can't Wait Example SentencesDocument2 pagesI Can't Wait Example Sentencesashraf atefNo ratings yet
- Technical Tip: Sizing of Protective Devices "Circuit Breakers" and Disconnect Switches For Air Conditioners (A/C)Document4 pagesTechnical Tip: Sizing of Protective Devices "Circuit Breakers" and Disconnect Switches For Air Conditioners (A/C)ashraf atefNo ratings yet
- VD SC CodedDocument32 pagesVD SC Codedashraf atefNo ratings yet
- Pages From Small PowerDocument3 pagesPages From Small Powerashraf atefNo ratings yet
- RMU Construction:: Standard No. of Cells (2,3,4) WaysDocument8 pagesRMU Construction:: Standard No. of Cells (2,3,4) Waysashraf atefNo ratings yet
- Errors in MeasurementDocument1 pageErrors in Measurementashraf atefNo ratings yet
- 3 - Dry TransformerDocument1 page3 - Dry Transformerashraf atefNo ratings yet
- Pages From Siemens Installation Guide-2Document2 pagesPages From Siemens Installation Guide-2ashraf atefNo ratings yet
- Cut Sheet:: (Air Insulated-Vacuum C.B)Document4 pagesCut Sheet:: (Air Insulated-Vacuum C.B)ashraf atefNo ratings yet
- Guide To en 50160Document44 pagesGuide To en 50160ashraf atefNo ratings yet
- Quiz - Solved PDFDocument3 pagesQuiz - Solved PDFashraf atefNo ratings yet
- Junction Leakage and GIDLDocument3 pagesJunction Leakage and GIDLThabasum Aara SNo ratings yet
- Tibc-10 Battery Charger Installation and Maintenance ManualDocument19 pagesTibc-10 Battery Charger Installation and Maintenance Manualagsan.algabh2718No ratings yet
- LM2907 FVCDocument20 pagesLM2907 FVCLookman FajarNo ratings yet
- Types of AlternatorDocument8 pagesTypes of AlternatorOmar SelamiNo ratings yet
- Solid-State Off-Delay Timer Relay: Vehicle Control ModulesDocument2 pagesSolid-State Off-Delay Timer Relay: Vehicle Control ModulesJoseph VincentNo ratings yet
- SC471MLTRT DatasheetDocument27 pagesSC471MLTRT DatasheetFiskoaujNo ratings yet
- What Is The Cause of Generator Overfluxing and Overcxcitation - QuoraDocument2 pagesWhat Is The Cause of Generator Overfluxing and Overcxcitation - QuoraCharles RobiansyahNo ratings yet
- PFC8 PFC14Document3 pagesPFC8 PFC14pinku_thakkar73% (11)
- 174 2075K2Document1 page174 2075K2bojanNo ratings yet
- Field Guide To ResistorsDocument1 pageField Guide To ResistorsMioma KeraNo ratings yet
- Flash Code 12 - VSG High: SectionDocument10 pagesFlash Code 12 - VSG High: SectionlibertyplusNo ratings yet
- lcr-t4 Transistor Tester ManualDocument2 pageslcr-t4 Transistor Tester ManualJoseph YumulNo ratings yet
- D.C Machine DesignDocument23 pagesD.C Machine DesignMAsifNazeerNo ratings yet
- Low Voltage Products: Motor Protection Relay, SPEMDocument12 pagesLow Voltage Products: Motor Protection Relay, SPEMlouiswang1964No ratings yet
- Operator'S Manual: E-Series Ultraviolet Hand LampsDocument9 pagesOperator'S Manual: E-Series Ultraviolet Hand LampsGuiss LemaNo ratings yet
- 2VAA001694 - en S Control NTDO02 Digital Output Termination UnitDocument41 pages2VAA001694 - en S Control NTDO02 Digital Output Termination UnitanbarasanNo ratings yet
- Battery Charger Circuit Using SCRDocument5 pagesBattery Charger Circuit Using SCRlokesh100% (2)
- Chapter 7 Start PDFDocument25 pagesChapter 7 Start PDFMe himpNo ratings yet
- Six Pac ManualDocument9 pagesSix Pac ManualgkoulNo ratings yet
- Three Phase Winding TechnologyDocument24 pagesThree Phase Winding Technologynir205No ratings yet
- Zenit Installation ManualDocument45 pagesZenit Installation ManualchauhanrinkuNo ratings yet
- CuadrosDocument11 pagesCuadrosgustavo andres ortizNo ratings yet
- Blueprint Sheet E7Document1 pageBlueprint Sheet E7Harsh PatelNo ratings yet
- Zelio Plug-In Relays RXM2AB1JDDocument6 pagesZelio Plug-In Relays RXM2AB1JDAhmedNo ratings yet
- APM4500AKDocument13 pagesAPM4500AKFlavianoSilvaNo ratings yet
- ACX 57xx Series Controller Installation InstructionsDocument12 pagesACX 57xx Series Controller Installation Instructionsanas.iajNo ratings yet
- Completo FMF 2023 Vf2 BCDocument180 pagesCompleto FMF 2023 Vf2 BCIván QuirozNo ratings yet