Professional Documents
Culture Documents
2% Cagr: Billions of Mobile Subscribers
Uploaded by
Mohamed Aly SowOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
2% Cagr: Billions of Mobile Subscribers
Uploaded by
Mohamed Aly SowCopyright:
Available Formats
White paper
Cisco public
D. Mobility on the rise
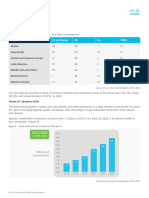
Globally, the total number of mobile subscribers (those subscribing to a cellular service) is going to grow from 5.1
billion in 2018 to 5.7 billion by 2023 at a CAGR of 2 percent. In terms of population this represents 66% of global
population in 2018 and 71% of global population penetration by 2023 (Figure 6). Relative to the growth in Internet
users we see slow down occurring in the mobile subscriber growth – this is primarily as the penetration levels have
already crossed 60 percent range.
Figure 6. Global mobile subscriber growth
2% CAGR
2018–2023 5.8
5.6 5.7
5.6
5.4
Billions of 5.5
Mobile 5.2 5.3
Subscribers 5.2
5.0
5.1
4.8
4.6
2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023
Source: Cisco Annual Internet Report, 2018–2023
While there are regional differences in the mobile subscriber penetration of the regional population (Table 3), the
range of variations is much smaller relative to the overall Internet users that we saw in the previous analysis. While the
region with the highest adoption throughout the forecast period is North America, followed by Western Europe, the
fastest growth is going to occur in Middle East and Africa at 4 percent CAGR from 2018 to 2023. While the adoption
rates for mobile (above 60 percent of the population in 2018) are already quite high across all regions, we do see that
Middle East and Africa has a bit of catch up to do and that is reflected in higher growth rates relative to other regions.
Table 3. Mobile subscribers as a percentage of regional population
Region 2018 2023
Global 66% 71%
Asia Pacific 65% 72%
Central and Eastern Europe 79% 81%
Latin America 75% 78%
Middle East and Africa 53% 57%
North America 86% 88%
Western Europe 84% 85%
Source: Cisco Annual Internet Report, 2018–2023
© 2020 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
White paper
Cisco public
The ever-changing mix and growth of wireless devices that are accessing mobile networks worldwide is one of the
primary contributors to global mobile traffic growth. Each year several new devices in different form factors and increased
capabilities and intelligence are introduced in the market. In the last couple of years, we have seen a rise of phablets
and more recently we have seen many new M2M connections coming into the mix. There were 8.8 billion global mobile
devices and connections in 2018, which will grow to 13.1 billion by 2023 at a CAGR of 8 percent (Figure 7).
By 2023, there will be 8.7 billion handheld or personal mobile-ready devices and 4.4 billion M2M connections (e.g.,
GPS systems in cars, asset tracking systems in shipping and manufacturing sectors, or medical applications making
patient records and health status more readily available, et al.). Regionally, North America and Western Europe are
going to have the fastest growth in mobile devices and connections with 16 percent and 11 percent CAGR from 2018
to 2023, respectively.
Figure 7. Global mobile device and connection growth
8% CAGR 14
2018–2023 Smartphones (46%, 41%)
12
Phablets (9%, 11%)
10
M2M (13%, 34%)
8
Billions of Nonsmartphones (27%, 11%)
Devices 6 Tablets (2%, 2%)
PCs (2%, 2%)
4
Other Portable Devices
2 (0.1%, 0.1%)
* Smartphone category
0 including phablets
2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 * Figures (n) refer to 2018,
2023 device share
Source: Cisco Annual Internet Report, 2018–2023
We see a rapid decline in the share of non-smartphones from 27 percent in 2018 (2.4 billion) to 11 percent by 2023
(1.5 billion). Another significant trend is the growth of smartphones (including phablets) from 4.9 billion in 2018 to
6.7 billion by 2023 at the second highest CAGR of 7 percent. Even though smartphones are growing absolutely, the
relative share is declining from 56 percent in 2018 to 51 percent by 2023. This is because of the most noticeable
growth in M2M connections. M2M mobile connections will cross over a third (34 percent) of total devices and
connections by 2023. The M2M category is going to grow at 30 percent CAGR from 2018 to 2023. Along with the
overall growth in the number of mobile devices and connections, there is clearly a visible shift in the device mix.
Defining Cell Network Advances—2G, 3G, 4G and 5G Projections
Mobile devices are evolving from lower-generation network connectivity (2G) to higher-generation network
connectivity (3G, 3.5G, 4G or LTE and now also 5G). Combining device capabilities with faster, higher bandwidth and
more intelligent networks will facilitate broad experimentation and adoption of advanced multimedia applications that
contribute to increased mobile and Wi-Fi traffic.
The explosion of mobile applications and the expanded reach of mobile connectivity to a growing number of end
users has prompted the need for optimized bandwidth management and new network monetization models to sustain
a maturing mobile industry. In a highly competitive mobile market, we have seen the growth of global 4G deployments
as well as early-stage 5G implementations.
© 2020 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
White paper
Cisco public
Last year we saw that 4G surpassed all other connection types, in this year’s analysis we’ve combined 3G and
below networks into one category – 4G will surpass that category by 2019 and will be the predominant mobile
network connectivity throughout the remaining forecast period. By 2023, 4G connections will be 46% of total mobile
connections, compared to 42% in 2018 (Figure 8). The global mobile 4G connections will grow from 3.7 billion in
2018 to 6.0 billion by 2023 at a CAGR of 10 percent. 5G connections will appear on the scene in 2019 and will
grow over 100-fold from about 13 million in 2019 to 1.4 billion by 2023. 5G connectivity is emerging from nascency
to a strong contender for mobile connectivity driven by mobile IoT growth. By 2023, there will be 11% devices and
connections with 5G capability.
Starting this year, we are combining our analysis of 2G and 3G into 3G and below category as the lack of source data
has made it difficult to split the two categories. There were 55% 3G and below connections in 2018, but by the end of
the forecast period, these will decline to 29%.
Figure 8. Global mobile device and connection growth
7
3G and Below
(55.3%, 29.0%)
6
4G (42.1%, 46.0%)
5
Billions of 5G (0.0%, 10.6%)
4
Devices or
Connections 3 LPWA (2.5%, 14.4%)
2 Note: This view includes
M2M. LPWA includes
cellular LPWA (e.g., NB-IOT)
1 and non-cellular LPWA (e.g.,
LORA)
0
2018 2019 2020 2021 2022 2023 * Figures (n) refer to
2018, 2023 network
connection type share
Source: Cisco Annual Internet Report, 2018–2023
We also include Low-Power Wide-Area (LPWA) connections in our analysis. This type of ultra-narrowband wireless
network connectivity is meant specifically for M2M modules that require low bandwidth and wide geographic
coverage. It provides high coverage with low power consumption, module, and connectivity costs, thereby creating
new M2M use cases for Mobile Network Operators (MNOs) that cellular networks alone could not have addressed.
Examples include utility meters in residential basements, gas or water meters that do not have power connection,
streetlights, and pet or personal asset trackers. The share of LPWA connections (all M2M) will grow from about 2.5
percent in 2018 to 14 percent by 2023, from 223 million in 2018 to 1.9 billion by 2023.
This transition from 3G and below to 4G and now 5G deployment is a global trend (Table 4). In fact, by 2023, nearly
60 percent of the mobile devices and connections globally will have 4G+ capability, surpassing 3G and below-capable
devices and connections by several fold. North America will have the highest share of its devices and connections on
4G+ connectivity – 62 percent, by 2023. Middle East and Africa at 73% will have the highest share of its devices and
connections on 3G and below by 2023. By 2023, North America with 37 percent and Western Europe with 28 percent
share will be the two regions with highest LPWA adoption. By 2023, North America will be the region with highest
share of connections on 5G at 17 percent.
© 2020 Cisco and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved.
You might also like
- 2021 700+ Medical Prefessionals Warns About 5G To FCCDocument30 pages2021 700+ Medical Prefessionals Warns About 5G To FCCJohn Kuhles100% (1)
- Butler Matrix Based Beamforming Networks For Phased Array Antenna Systems A Comprehensive Review and Future Directions For 5G ApplicationsDocument18 pagesButler Matrix Based Beamforming Networks For Phased Array Antenna Systems A Comprehensive Review and Future Directions For 5G Applicationsmid_cycloneNo ratings yet
- B787 CIRCULAR Landing Performance Calculations For An Airport With A 5G C-Band NOTAMDocument4 pagesB787 CIRCULAR Landing Performance Calculations For An Airport With A 5G C-Band NOTAMHarinder SinghNo ratings yet
- GSMA - Global Mobile Trend 2017-2025 PDFDocument105 pagesGSMA - Global Mobile Trend 2017-2025 PDF123 mlmbNo ratings yet
- Statista Digital Economy Compass 2017Document192 pagesStatista Digital Economy Compass 2017urjamehta1991No ratings yet
- Top10GlobalConsumerTrends 2019 Euromonitor PDFDocument49 pagesTop10GlobalConsumerTrends 2019 Euromonitor PDFmarkNo ratings yet
- Emarketer Forecasting Analyst Test - Q3 2022Document11 pagesEmarketer Forecasting Analyst Test - Q3 2022Rishabh BhardwajNo ratings yet
- 5G Radio Access Network Architecture For Terrestrial Broadcast ServicesDocument12 pages5G Radio Access Network Architecture For Terrestrial Broadcast ServicesmbegulekNo ratings yet
- Digital Technologies in Agriculture and Rural Areas: Status ReportFrom EverandDigital Technologies in Agriculture and Rural Areas: Status ReportNo ratings yet
- Matlab BookDocument58 pagesMatlab BookBipin JaiswalNo ratings yet
- 5G NR-2Document74 pages5G NR-2rahul mathurNo ratings yet
- Managing the Development of Digital Marketplaces in AsiaFrom EverandManaging the Development of Digital Marketplaces in AsiaNo ratings yet
- 5g Ran2.1 Power Control Issue1Document33 pages5g Ran2.1 Power Control Issue1Hilal LakhbatNo ratings yet
- Atoll: RF Planning & Optimisation SoftwareDocument50 pagesAtoll: RF Planning & Optimisation SoftwareMohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- Atoll: RF Planning & Optimisation SoftwareDocument50 pagesAtoll: RF Planning & Optimisation SoftwareMohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- ATOLL User - Manual-200Document50 pagesATOLL User - Manual-200Mohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- ATOLL User - Manual-200Document50 pagesATOLL User - Manual-200Mohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- 3GPP 5G End-To-End KPIDocument17 pages3GPP 5G End-To-End KPIA.R.A RiskoNo ratings yet
- ATOLL User - Manual-201-250Document50 pagesATOLL User - Manual-201-250Mohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- 10% CAGR: Billions of DevicesDocument3 pages10% CAGR: Billions of DevicesMohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- Makemytrip Limited: (Nasdaq: Mmyt)Document25 pagesMakemytrip Limited: (Nasdaq: Mmyt)sheebaNo ratings yet
- Driver Electronic Device Use in 2020Document9 pagesDriver Electronic Device Use in 2020Burleson SmithNo ratings yet
- GCA Altium Digital - Media & Internet Monitor Q3 2020Document26 pagesGCA Altium Digital - Media & Internet Monitor Q3 2020John SmithNo ratings yet
- Gridley & Co. Mobile Industry Overview December 2010Document72 pagesGridley & Co. Mobile Industry Overview December 2010Feng HongNo ratings yet
- Future of Devices 2019Document25 pagesFuture of Devices 2019Rudi SusantoNo ratings yet
- Global Mobile Forecasts Q2 2022Document2 pagesGlobal Mobile Forecasts Q2 2022Rudi SusantoNo ratings yet
- Developing Your Mobile Travel Strategy - Hotelicopter's Presentation at EFT Mobile ConferenceDocument24 pagesDeveloping Your Mobile Travel Strategy - Hotelicopter's Presentation at EFT Mobile ConferencesuperhelixNo ratings yet
- Mobile Churn Trends and Customer Retention StrategiesDocument17 pagesMobile Churn Trends and Customer Retention StrategiesAydin KaraerNo ratings yet
- 5G Challanges in BrazilDocument8 pages5G Challanges in BrazilPNG networksNo ratings yet
- ETF Newsletter - February - 23Document20 pagesETF Newsletter - February - 23Chuck CookNo ratings yet
- Cellular-Backhaul H58895 HRDocument4 pagesCellular-Backhaul H58895 HRzakaNo ratings yet
- Vietjet 2018 Business Results - Audited v1Document31 pagesVietjet 2018 Business Results - Audited v1Nhi ChuNo ratings yet
- Gsma Perú 2014Document25 pagesGsma Perú 2014aguilarjmNo ratings yet
- Accenture-Unlocking-Digital-Value-South Africa-Telecoms-Sector PDFDocument26 pagesAccenture-Unlocking-Digital-Value-South Africa-Telecoms-Sector PDFadityaNo ratings yet
- IoT Connections Forecast and Impacts of COVIDDocument22 pagesIoT Connections Forecast and Impacts of COVIDRoberto MachadoNo ratings yet
- Global Cellular M2M Technology Forecasts and AssumptionsDocument17 pagesGlobal Cellular M2M Technology Forecasts and AssumptionsAydin KaraerNo ratings yet
- Puppet State of Devops Market Segmentation Report - 1Document23 pagesPuppet State of Devops Market Segmentation Report - 1bhikshuNo ratings yet
- 1 - SouthEastAsia Ecommerce SpotlightDocument118 pages1 - SouthEastAsia Ecommerce SpotlightChristoper CiaNo ratings yet
- Bangladesh Mobile Market - Executive Summary IDC - 2019Q3Document7 pagesBangladesh Mobile Market - Executive Summary IDC - 2019Q3Ayan MitraNo ratings yet
- Sustainability in TelecommunicationDocument6 pagesSustainability in TelecommunicationSudhir RoutrayNo ratings yet
- Healthcare and Life Science Industry: Quarterly UpdateDocument12 pagesHealthcare and Life Science Industry: Quarterly UpdateMicaela Agostina Del SantoNo ratings yet
- Study Id26515 Fintech-Statista-DossierDocument70 pagesStudy Id26515 Fintech-Statista-DossierAditiNo ratings yet
- There Will Be 5Document8 pagesThere Will Be 5thee89No ratings yet
- EMarketer Forecasting Analyst TestDocument5 pagesEMarketer Forecasting Analyst Testshikhar.guptaNo ratings yet
- Duma Briefs - Mobile Telecom Industry ReviewDocument8 pagesDuma Briefs - Mobile Telecom Industry ReviewanuthabruthaNo ratings yet
- Investor Presentation Digital BankingDocument23 pagesInvestor Presentation Digital BankingPriyanka BanerjeeNo ratings yet
- WFIC - WiMAX and Emerging Economies WS281110Document16 pagesWFIC - WiMAX and Emerging Economies WS281110Kusuma WardanaNo ratings yet
- Internet Landscape in ThailandDocument38 pagesInternet Landscape in ThailandPetch SurasitNo ratings yet
- EPINETFLIXINGLESDocument14 pagesEPINETFLIXINGLESrahul kanchgarNo ratings yet
- MR18 - Dynamics and Perspectives of The Pharmaceutical Market in Latin Ame...Document24 pagesMR18 - Dynamics and Perspectives of The Pharmaceutical Market in Latin Ame...gamallofNo ratings yet
- Latin America Ad Spending Summary 2018 EMarketerDocument10 pagesLatin America Ad Spending Summary 2018 EMarketerPatricio RubioNo ratings yet
- Criteo Insights Travel ReportDocument23 pagesCriteo Insights Travel ReportTatianaNo ratings yet
- Vietnam Country Intelligence Report, 1Q2019Document41 pagesVietnam Country Intelligence Report, 1Q2019Quoc Tuan TranNo ratings yet
- Global Mobile Consumer Trends, 2nd Edition: Mobile Continues Its Global Reach Into All Aspects of Consumers' LivesDocument19 pagesGlobal Mobile Consumer Trends, 2nd Edition: Mobile Continues Its Global Reach Into All Aspects of Consumers' LivesTristan LirioNo ratings yet
- ComScore State of The U.S. Mobile Market 2016-11-02Document37 pagesComScore State of The U.S. Mobile Market 2016-11-02Gökhan YücelNo ratings yet
- Adsota Digital Report 2020 - ENGDocument51 pagesAdsota Digital Report 2020 - ENG188.4No ratings yet
- Choosing The Right Chart For Your It DataDocument17 pagesChoosing The Right Chart For Your It DataFede VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- The Mobile Economy - Latin America and The Caribbean 2017Document56 pagesThe Mobile Economy - Latin America and The Caribbean 2017Patricio J. VásconesNo ratings yet
- Pop Dev Review Material Vol. 1 2023Document71 pagesPop Dev Review Material Vol. 1 2023Arlyn AyagNo ratings yet
- Startup Report 2018 PDFDocument35 pagesStartup Report 2018 PDFbenyhartoNo ratings yet
- Global Mobile Consumer Trends: 1st Edition: Mobile Proves To Be Indispensable in An Always-Connected WorldDocument9 pagesGlobal Mobile Consumer Trends: 1st Edition: Mobile Proves To Be Indispensable in An Always-Connected WorldSamir Fernando Vergara BeltránNo ratings yet
- Facts and Figures: Measuring Digital DevelopmentDocument19 pagesFacts and Figures: Measuring Digital DevelopmentPhương Anh LêNo ratings yet
- GSMA Spotlight On Nigeria ReportDocument4 pagesGSMA Spotlight On Nigeria ReportDipayan GhoshNo ratings yet
- K5-Mr. Francis Zhu-ZTEDocument17 pagesK5-Mr. Francis Zhu-ZTEDao Trung DungNo ratings yet
- Indonesia Digital Transformation Outlook Briefing 2016Document13 pagesIndonesia Digital Transformation Outlook Briefing 2016Ken KurniaNo ratings yet
- 5G NR DeploymentsDocument37 pages5G NR DeploymentsAmmar KhalidNo ratings yet
- A Tidal Wave of Dynamic Web Content Is Coming - How Will You Respond?Document8 pagesA Tidal Wave of Dynamic Web Content Is Coming - How Will You Respond?dinu4u4everNo ratings yet
- Vietnam Social Media and Online Ads 2019Document29 pagesVietnam Social Media and Online Ads 2019Búp CassieNo ratings yet
- IUS 2020 InfographicDocument6 pagesIUS 2020 Infographicahmad azwanNo ratings yet
- 2022年移动互联网报告Document73 pages2022年移动互联网报告Lee MelodyNo ratings yet
- Mobile Value Added Services in India: A Report by Iamai & Etechnology Group@ImrbDocument33 pagesMobile Value Added Services in India: A Report by Iamai & Etechnology Group@ImrbAndrey KovbovichNo ratings yet
- Japan 2020 Forecast HighlightsDocument5 pagesJapan 2020 Forecast HighlightsDavid OrtizNo ratings yet
- ATOLL User - Manual-601-650Document50 pagesATOLL User - Manual-601-650Mohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- ATOLL User - Manual-751-800Document50 pagesATOLL User - Manual-751-800Mohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- ATOLL User - Manual-101-150Document50 pagesATOLL User - Manual-101-150Mohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- ATOLL User - Manual-801-1190Document390 pagesATOLL User - Manual-801-1190Mohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- ATOLL User - Manual-651-700Document50 pagesATOLL User - Manual-651-700Mohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- TasDocument1 pageTasMohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- ATOLL User - Manual-701-750Document50 pagesATOLL User - Manual-701-750Mohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- ATOLL User - Manual-301-350Document50 pagesATOLL User - Manual-301-350Mohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- 1.5.2.2 Adding A Field To An Object Type's Data Table: Chapter 1: The Working EnvironmentDocument50 pages1.5.2.2 Adding A Field To An Object Type's Data Table: Chapter 1: The Working EnvironmentMohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- 1.5.2.2 Adding A Field To An Object Type's Data Table: Chapter 1: The Working EnvironmentDocument50 pages1.5.2.2 Adding A Field To An Object Type's Data Table: Chapter 1: The Working EnvironmentMohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- ATOLL User - Manual-351-400Document50 pagesATOLL User - Manual-351-400Mohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- ATOLL User - Manual-251-300Document50 pagesATOLL User - Manual-251-300Mohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- White Paper c11 741490 12 13Document2 pagesWhite Paper c11 741490 12 13Mohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- Cisco Public: White PaperDocument22 pagesCisco Public: White PaperMohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- White Paper c11 741490 3 5Document3 pagesWhite Paper c11 741490 3 5Mohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- ATOLL User - Manual-101-150Document50 pagesATOLL User - Manual-101-150Mohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- White Paper c11 741490 12 13Document2 pagesWhite Paper c11 741490 12 13Mohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- White Paper c11 741490 16 35Document20 pagesWhite Paper c11 741490 16 35Mohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- White Paper c11 741490 1 2Document2 pagesWhite Paper c11 741490 1 2Mohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- On Three Monotone Approximation: Mayada Ali KareemDocument4 pagesOn Three Monotone Approximation: Mayada Ali KareemMohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- A Review Paper On Scope of Big Data Analysis in Heath INFORMATICSDocument8 pagesA Review Paper On Scope of Big Data Analysis in Heath INFORMATICSMohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- White Paper c11 741490 12 13Document2 pagesWhite Paper c11 741490 12 13Mohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- IJARW - International Journals of Academic Research WorldDocument2 pagesIJARW - International Journals of Academic Research WorldMohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- PHD Position Nokia Bell LabsDocument1 pagePHD Position Nokia Bell LabsJoe MullerNo ratings yet
- Rohde & Schwarz Propels 5G Lbs With Assisted-Gps and 5G NR Fr2 MMW Performance TestingDocument2 pagesRohde & Schwarz Propels 5G Lbs With Assisted-Gps and 5G NR Fr2 MMW Performance TestingmartinscodellerNo ratings yet
- Cellular System E202101Document64 pagesCellular System E202101Độ Ngô QuýNo ratings yet
- Massive MIMO Is A Reality What Is NextDocument19 pagesMassive MIMO Is A Reality What Is NexthibaNo ratings yet
- Yosef Final ThesisDocument97 pagesYosef Final ThesisTsega TeklewoldNo ratings yet
- Wa0003.Document25 pagesWa0003.pang syNo ratings yet
- Ericsson MINI-LINK Family Leads The Microwave Backhaul Market - EricssonDocument4 pagesEricsson MINI-LINK Family Leads The Microwave Backhaul Market - EricssonAhmad Badius Zaman0% (1)
- by Praveen SharmaDocument21 pagesby Praveen Sharmapsharma_950518No ratings yet
- XM Ac2100 DatasheetDocument2 pagesXM Ac2100 DatasheetAbdenago JesusNo ratings yet
- Vehicle-to-Everything V2X Evolution From 4G To 5G in 3GPP Focusing On Resource Allocation AspectsDocument15 pagesVehicle-to-Everything V2X Evolution From 4G To 5G in 3GPP Focusing On Resource Allocation AspectsKallur AkshathaNo ratings yet
- Will Techonlogy and Policy Collide PDFDocument10 pagesWill Techonlogy and Policy Collide PDFWaleed AlmarshediNo ratings yet
- Investigation 6GDocument96 pagesInvestigation 6Gمآب عبد القاهرNo ratings yet
- ReportDocument33 pagesReportAdarsh PriyanshuNo ratings yet
- ETSI Seminar 5-1 3GPPDocument26 pagesETSI Seminar 5-1 3GPPAjay GUNo ratings yet
- White Paper c11 741490 16 35Document20 pagesWhite Paper c11 741490 16 35Mohamed Aly SowNo ratings yet
- Module02 A B C - Introduction To Wireless Communications-NewDocument127 pagesModule02 A B C - Introduction To Wireless Communications-NewmookshoNo ratings yet
- Telecom Hitesh Mini ProjectDocument40 pagesTelecom Hitesh Mini Projectasif ansariNo ratings yet
- WWW - Oeclib.in: Seminar On 5G TechnologyDocument26 pagesWWW - Oeclib.in: Seminar On 5G TechnologyChiranjeet100% (1)
- Huawei Premium Smart Phone Segment: A. External Factors B. 4Ps Framework (YOY)Document8 pagesHuawei Premium Smart Phone Segment: A. External Factors B. 4Ps Framework (YOY)abinash pradhanNo ratings yet
- Dvantages Isadvantages: Technology / Features 4G 5G Start/Deployment Peak Data Rate Standards LatencyDocument2 pagesDvantages Isadvantages: Technology / Features 4G 5G Start/Deployment Peak Data Rate Standards Latencytolossa assefaNo ratings yet
- 22-01-21 Apple IPR Petition Against 10470203Document69 pages22-01-21 Apple IPR Petition Against 10470203Florian MuellerNo ratings yet
- 6G - Rethinking The Foundations of Communications Theory-1Document18 pages6G - Rethinking The Foundations of Communications Theory-1Surabhi KarandikarNo ratings yet