Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Chapter 9 - Common Probability Distributions
Uploaded by
dar shil0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pages1. Common probability distributions include the discrete uniform, binomial, normal (Gaussian), and lognormal distributions. The normal distribution is a symmetrical bell-shaped curve used to represent variables and the lognormal distribution models values that are always positive.
2. Monte Carlo simulation is a technique used to understand the impact of risk and uncertainty. It involves generating thousands of possible outcomes based on probability distributions and risk factors to estimate outcomes of a project or investment.
3. Historical simulation is another forecasting technique that uses actual historical changes in values or risk factors over a prior period to simulate possible future outcomes without estimating distributions. While it avoids estimation, future outcomes may fall outside the historical range.
Original Description:
Original Title
R9 Common Probability Distributions
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this Document1. Common probability distributions include the discrete uniform, binomial, normal (Gaussian), and lognormal distributions. The normal distribution is a symmetrical bell-shaped curve used to represent variables and the lognormal distribution models values that are always positive.
2. Monte Carlo simulation is a technique used to understand the impact of risk and uncertainty. It involves generating thousands of possible outcomes based on probability distributions and risk factors to estimate outcomes of a project or investment.
3. Historical simulation is another forecasting technique that uses actual historical changes in values or risk factors over a prior period to simulate possible future outcomes without estimating distributions. While it avoids estimation, future outcomes may fall outside the historical range.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
4 views2 pagesChapter 9 - Common Probability Distributions
Uploaded by
dar shil1. Common probability distributions include the discrete uniform, binomial, normal (Gaussian), and lognormal distributions. The normal distribution is a symmetrical bell-shaped curve used to represent variables and the lognormal distribution models values that are always positive.
2. Monte Carlo simulation is a technique used to understand the impact of risk and uncertainty. It involves generating thousands of possible outcomes based on probability distributions and risk factors to estimate outcomes of a project or investment.
3. Historical simulation is another forecasting technique that uses actual historical changes in values or risk factors over a prior period to simulate possible future outcomes without estimating distributions. While it avoids estimation, future outcomes may fall outside the historical range.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 2
R9 Common Probability Distributions 01
Chapter 9 - Common Probability Distributions
Study online at quizlet.com/_82w2yc
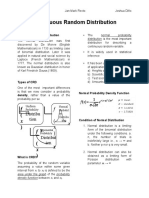
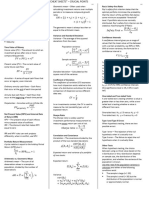
1. Probability - All possible outcomes for a variable 14. Continuous
Distribution - Probabilities of all possible outcomes = 1 Uniform
Distribution
2. Discrete - Number of possible outcomes that can be
Formula
Random counted
Variable - Each outcomes there is a measurable and
15. Normal - Function that represents the distribution of
positive probability
Distribution variables as a symmetrical bell-shaped
3. Probability - Denoted p(x) graph
Function - Random variable is equal to specific value - Skewness = 0
- Kurtosis = 3
4. Key 0 < p(x) < 1
Properties of ∑p(x) = 1 16. Multivariate - Specifies the probabilities for a group of
Probability Distribution related random variables
Function - meaningful only if those variables are
dependent on each other
5. Continuous - the number of possible outcomes is infinite,
Random even if lower and upper bounds exist 17. Confidence the range of values within which a
Variable - time is a variable Interval population parameter is estimated to lie
6. Discrete p(x) = 0 when x cannot occur 18. Three Popular 90% confidence interval = mean of - 1.65 to
Distribution p(x) > 0 when x can occur Confidence +1.65
Intervals 95% confidence interval = mean of - 1.96 to
7. Continuous p(x) = 0 when x can occur
+1.96
Distribution p(x₁ < x < x₂) where x₁/x₂ are actual numbers
99% confidence interval = mean of - 2.58 to
8. Cumulative - Another name is "distribution function" +2.58
Distribution - Defines the probability that a random
19. Standard A normal distribution with a mean of 0 and
Function variable takes on a value equal to or less
Normal a standard deviation of 1
(cdf) than a specific
Distribution
- Typically F(X) = P(X) plus everything before
that 20. Z-Value Number of standard errors that a point is
away from the mean
9. Discrete probabilities for all possible outcomes for a
Uniform discrete random variable are equal. 21. Z-Value Forula
Random
Variable
10. Binomial - The number of "successes" in a given 22. Roy's Safety- The optimal portfolio minimizes the
Random number of trials, whereby the outcome can First Ratio probability that the return of the portfolio
Variable be either "success" or "failure" falls below a minimum acceptable level;
- Only 2 trials = (Historical Return - Return
Threshold)/(Volatility)
11. Binomial
Probability 23. SF Ratio
Formula Formula
12. Expected 24. Lognormal - Function e^x where x is normally
Value of a Distribution distributed;
Binomial - Positively skewed;
Probability - Bound to the left by 0
- if x is normal, e^x is lognormal
25. Discretely Compound returns we are familiar with
Compounded given some discrete compounding period
Returns - Same as EAR (effective annual rate)
13. Continuous defined over a range that spans between
Uniform some lower limit, a, and some upper limit b,
Distribution which serves as the parameters of the
distribution
R9 Common Probability Distributions 02
26. Continuous - Shorter and shorter periods of compounding
Compounding - Formula: e^r - 1
- Formula: ln(S1/S2)
- Formula: ln(1 + HPR)
27. Monte Carlo A process which generates hundreds or thousands of probable performance outcomes based on probability
Simulation distributions for cost and schedule on individual tasks. The outcomes are then used to generate a probability
distribution for the project as a whole
28. Historical - Based on actual changes in value or actual changes in risk factors over some prior period
Simulation - Pros: Don't have to estimate distribution of risk factors
- Cons: Future outcomes for risk factors may be outside the historical range
You might also like
- Continuous Probability DistributionDocument32 pagesContinuous Probability DistributionsampritcNo ratings yet
- Continuous DistnDocument18 pagesContinuous DistnNamrata SinghNo ratings yet
- Session 13 &14 Continuous Probability DistributionDocument50 pagesSession 13 &14 Continuous Probability DistributionRajneesh SarojNo ratings yet
- Statistics For Managers Using Microsoft Excel: EditionDocument56 pagesStatistics For Managers Using Microsoft Excel: EditionTsoi Yun PuiNo ratings yet
- Continuous DistributionsDocument22 pagesContinuous DistributionschelloNo ratings yet
- Quantitative Risk Assessment in Geotechnical Engineering: Presented byDocument27 pagesQuantitative Risk Assessment in Geotechnical Engineering: Presented byCarlos RiveraNo ratings yet
- Lesson 6Document55 pagesLesson 6İbrahim KaraoğlanNo ratings yet
- Continuous Probability Distribution-FinalDocument56 pagesContinuous Probability Distribution-Finalshashank vyas100% (1)
- Continuous Random DistributionDocument5 pagesContinuous Random DistributionJethro MiñanoNo ratings yet
- Statistika Ekonomi Lanjutan: DR. Deden Dinar Iskandar, SE, MADocument28 pagesStatistika Ekonomi Lanjutan: DR. Deden Dinar Iskandar, SE, MAIlham ramadhanNo ratings yet
- STATSDocument4 pagesSTATSdennisalejaga08No ratings yet
- Continuous Probability Distributions N Hypothesis TestingDocument28 pagesContinuous Probability Distributions N Hypothesis Testingayesha.No ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Probability ConceptsDocument2 pagesChapter 8 - Probability Conceptsdar shilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 Part B: Probability DistributionDocument42 pagesChapter 3 Part B: Probability Distributionalexbell2k12No ratings yet
- Quizlet PDFDocument2 pagesQuizlet PDFgulzira3amirovnaNo ratings yet
- Math 102 Midterms Reviewer (With Mock Tests)Document3 pagesMath 102 Midterms Reviewer (With Mock Tests)Jirish RiveraNo ratings yet
- DGFGHFDocument4 pagesDGFGHFmadhurNo ratings yet
- Quiz 2 Covered Materials In: - Chapter 5 - Chapter 6 - Chapter 7Document27 pagesQuiz 2 Covered Materials In: - Chapter 5 - Chapter 6 - Chapter 7Aaron Hayyat0% (1)
- Algebra 7Document3 pagesAlgebra 7Sherwin ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- 11 - Normal Random Variables & DistributionsDocument42 pages11 - Normal Random Variables & Distributionsarpanksidhu044No ratings yet
- Chapter 5Document3 pagesChapter 5Christine AltamarinoNo ratings yet
- Normal DistributionDocument50 pagesNormal Distributionscropian 9997No ratings yet
- BUSN 2429 Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distribution - SDocument70 pagesBUSN 2429 Chapter 6 Continuous Probability Distribution - SAwais SadaqatNo ratings yet
- CS For Stats ExamDocument4 pagesCS For Stats ExamTaza Ilham AssidiqhiNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability ReviewerDocument4 pagesStatistics and Probability ReviewerJezreel BonillaNo ratings yet
- PQRS Manual enDocument20 pagesPQRS Manual enjfmagar-1No ratings yet
- Ch06.continous Probability DistributionsDocument26 pagesCh06.continous Probability DistributionsGladys Oryz BerlianNo ratings yet
- Chap 7Document7 pagesChap 7Mike SerafinoNo ratings yet
- Outline: Continuous Probability DistributionsDocument33 pagesOutline: Continuous Probability DistributionsBasil Irfan Muhammed AslamNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Mathematics and Statistics B: Notes A3Document4 pagesIntroduction To Mathematics and Statistics B: Notes A3Harawa WonaNo ratings yet
- Excel Formulas Functions ListDocument17 pagesExcel Formulas Functions ListCekasCGNo ratings yet
- Uniform Probability Distribution Normal Probability Distribution Exponential Probability DistributionDocument29 pagesUniform Probability Distribution Normal Probability Distribution Exponential Probability DistributionHuseynov AliNo ratings yet
- Continuous Distribution SVDocument31 pagesContinuous Distribution SVMai Ý NhưNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability Finals ReviewerDocument2 pagesStatistics and Probability Finals ReviewerJanelle ArañaNo ratings yet
- 04 B DsitrbutionsDocument43 pages04 B DsitrbutionsUpasana PattnaikNo ratings yet
- EC202 Notes 2 ConsumerDocument49 pagesEC202 Notes 2 ConsumerSwaggyVBros MNo ratings yet
- CHAPTER 6 Continuous ProbabilityDocument3 pagesCHAPTER 6 Continuous ProbabilityPark MinaNo ratings yet
- Continuous Random VariableDocument44 pagesContinuous Random Variableranjitbiswal547No ratings yet
- Lecture 3 - Normal Probability DistributionsDocument21 pagesLecture 3 - Normal Probability DistributionsSanaiya JokhiNo ratings yet
- Statistik 1 - 6 Distribusi Probabilitas NormalDocument49 pagesStatistik 1 - 6 Distribusi Probabilitas Normalnur aida afrilyaNo ratings yet
- Unidad 2 Tarea 3 - Martha MuñozDocument5 pagesUnidad 2 Tarea 3 - Martha MuñozMIGUEL ANGEL PADILLA DIAZNo ratings yet
- How To Derive A Formula Peekaboo - 5Document1 pageHow To Derive A Formula Peekaboo - 5anirban dasNo ratings yet
- Cor 006Document2 pagesCor 006maricrisc.cagaNo ratings yet
- Statistics and Probability ReviewerDocument4 pagesStatistics and Probability Reviewermiel noahNo ratings yet
- Basics Statistics For Data AnalysisDocument75 pagesBasics Statistics For Data AnalysisGonzalo FranklinNo ratings yet
- Cheat Sheet (Bloomberg's Level I CFA (R) Exam Prep)Document7 pagesCheat Sheet (Bloomberg's Level I CFA (R) Exam Prep)codepicaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer 4th QuarterDocument3 pagesReviewer 4th Quarterjohn earl cosioNo ratings yet
- Statistical Intervals Based On A Single Sample: Basic Properties of Confidence IntervalsDocument2 pagesStatistical Intervals Based On A Single Sample: Basic Properties of Confidence IntervalsPoonam NaiduNo ratings yet
- Print Mda 3Document24 pagesPrint Mda 3surekhaNo ratings yet
- Reviewer in Statistics and Probability: Measures of Central Tendencies Constructing Probability DistributionDocument2 pagesReviewer in Statistics and Probability: Measures of Central Tendencies Constructing Probability DistributionHyana Imm MedalladaNo ratings yet
- 2019 Lecture 9 - Continuous Probablility Distribution 1 (1) - 2Document58 pages2019 Lecture 9 - Continuous Probablility Distribution 1 (1) - 2farhan srgNo ratings yet
- Random Variables and Probability Distributions: Topic 5Document7 pagesRandom Variables and Probability Distributions: Topic 5Sana SiniNo ratings yet
- Sta416 - Topic 5 - 2Document29 pagesSta416 - Topic 5 - 2sofia the firstNo ratings yet
- Types of Random VariablesDocument4 pagesTypes of Random VariablesHazell DNo ratings yet
- Session 3Document60 pagesSession 3Aditi BadwayaNo ratings yet
- FBA1202 Statistics W10Document104 pagesFBA1202 Statistics W10ilayda demirNo ratings yet
- M6 2020 Normal Distribution Lecture NotesDocument31 pagesM6 2020 Normal Distribution Lecture Notescoyite8695No ratings yet
- Unit 1 - Digital Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.inDocument11 pagesUnit 1 - Digital Communication - WWW - Rgpvnotes.in0111ec211064.pallaviNo ratings yet
- Classifications of Probability Distributions: Random VariableDocument37 pagesClassifications of Probability Distributions: Random VariableHamzaBaigNo ratings yet
- R12 Topics in Demand and Supply AnalysisDocument3 pagesR12 Topics in Demand and Supply Analysisdar shilNo ratings yet
- R14 Aggregate Output, Prices, and Economic GrowthDocument8 pagesR14 Aggregate Output, Prices, and Economic Growthdar shilNo ratings yet
- Chapter 8 - Probability ConceptsDocument2 pagesChapter 8 - Probability Conceptsdar shilNo ratings yet
- R6 The Time Value of MoneyDocument3 pagesR6 The Time Value of Moneydar shilNo ratings yet
- R7 Statistical Concepts and Market ReturnsDocument2 pagesR7 Statistical Concepts and Market Returnsdar shilNo ratings yet
- R3 Guidance For Standards 1 To 7Document10 pagesR3 Guidance For Standards 1 To 7dar shilNo ratings yet
- R11 Hypothesis TestingDocument3 pagesR11 Hypothesis Testingdar shilNo ratings yet
- R21 Understanding Income StatementsDocument3 pagesR21 Understanding Income Statementsdar shilNo ratings yet
- R23 Understanding Cash Flow StatementsDocument2 pagesR23 Understanding Cash Flow Statementsdar shilNo ratings yet
- R1 Ethics and Trust in The Investment ProfessionDocument2 pagesR1 Ethics and Trust in The Investment Professiondar shilNo ratings yet
- Micron - Tech Note - TemperatureDocument14 pagesMicron - Tech Note - TemperatureRavishankarNo ratings yet
- Acceptable Quality Level (AQL) - Issues and ResolutionDocument4 pagesAcceptable Quality Level (AQL) - Issues and Resolutionb-consultant960No ratings yet
- Methodology and Application of One-Way ANOVA: KeywordsDocument6 pagesMethodology and Application of One-Way ANOVA: KeywordsDan Lhery Susano GregoriousNo ratings yet
- Hallmarks of Scientific InvestigationDocument23 pagesHallmarks of Scientific InvestigationSaad Bin Tariq100% (2)
- Mediating SEMDocument31 pagesMediating SEMZei ZiaNo ratings yet
- Recycled Glass Utilization in Highway Construction Isaac Finkle, GRA, EITDocument25 pagesRecycled Glass Utilization in Highway Construction Isaac Finkle, GRA, EITUsama HeneashNo ratings yet
- Data Types:: Basic StatisticsDocument23 pagesData Types:: Basic StatisticsmaheshsakharpeNo ratings yet
- Uncertainty Presentation Digital MultimeterDocument76 pagesUncertainty Presentation Digital MultimeterAHMAD YAGHI100% (1)
- Normal Dist and CIDocument3 pagesNormal Dist and CINimra AzherNo ratings yet
- ENVIRONMENTAL CHAMBER Measure Uncertainty Iss1Document35 pagesENVIRONMENTAL CHAMBER Measure Uncertainty Iss1Fërnando Rodrîguëz Herrerä100% (1)
- GMM and OLS Estimation and Inference For New Keynesian Phillips CurveDocument26 pagesGMM and OLS Estimation and Inference For New Keynesian Phillips CurveQuang Kien TaNo ratings yet
- Using Levene's Test For Equality of Variance To Perform An Independent Sample T-TestDocument3 pagesUsing Levene's Test For Equality of Variance To Perform An Independent Sample T-TestZoom Zoom ZoomNo ratings yet
- Assignment # 1Document28 pagesAssignment # 1Hashim javedNo ratings yet
- Sustained Attention in Infancy - A Foundation For The Development of Multiple Aspects of Self-Regulation For Children in PovertyDocument18 pagesSustained Attention in Infancy - A Foundation For The Development of Multiple Aspects of Self-Regulation For Children in PovertyMACARENA VASQUEZ TORRESNo ratings yet
- Biostatistics 203. Survival Analysis: YhchanDocument8 pagesBiostatistics 203. Survival Analysis: YhchanselinblueNo ratings yet
- O5 ReliabilityDocument68 pagesO5 ReliabilityArin NimtrakulNo ratings yet
- CASP Critical Appraisal Checklist - RCTDocument4 pagesCASP Critical Appraisal Checklist - RCTHesty YuliandiniNo ratings yet
- Solutions To Problems: X 0 ZX X yDocument19 pagesSolutions To Problems: X 0 ZX X yrohitvanNo ratings yet
- Dabbawalla MUMBAIDocument27 pagesDabbawalla MUMBAIAditi AgarwalNo ratings yet
- Business Analytics Module 6Document47 pagesBusiness Analytics Module 6Adoree RamosNo ratings yet
- CH 10Document16 pagesCH 10xxxxxxxxxNo ratings yet
- Using The Point Load Test To Determine The Uniaxial Compressive Strength of Coal Measure RockDocument10 pagesUsing The Point Load Test To Determine The Uniaxial Compressive Strength of Coal Measure RockgbutulescuNo ratings yet
- Assignment 2Document22 pagesAssignment 2Nurul Absar RashedNo ratings yet
- Usp 81 PDFDocument15 pagesUsp 81 PDFSreedurgalakshmi KNo ratings yet
- Chapter2 Sampling Simple Random Sampling PDFDocument23 pagesChapter2 Sampling Simple Random Sampling PDFsricharitha6702No ratings yet
- Class Test 2 Solution 2019Document3 pagesClass Test 2 Solution 2019Ne PaNo ratings yet
- Confidence Interval EstimationDocument39 pagesConfidence Interval EstimationSamantha WeinertNo ratings yet
- T-Tests For DummiesDocument10 pagesT-Tests For DummiesMeganAislingNo ratings yet
- Driving Pressure and Survival in ARDS-Amato-ESM-NEJM 2015Document57 pagesDriving Pressure and Survival in ARDS-Amato-ESM-NEJM 2015SumroachNo ratings yet
- CPHQ PrepDocument50 pagesCPHQ PrepTOBIN6319_39572798689% (9)