Professional Documents
Culture Documents
03 Abdominal Trauma
Uploaded by
bunso padillaOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
03 Abdominal Trauma
Uploaded by
bunso padillaCopyright:
Available Formats
They may hold their left shoulder elevated, so that
ABDOMINAL TRAUMA the diaphragm is raised on the left side, to keep this
from happening
Course Outline Child notices radiated left shoulder pain while lying
in a supine position (Kehr’s sign)
Definition
Assessment Note: Broken rib over the spleen suggesting the extent of the
Diagnostics trauma.
Complications of Abdominal Trauma
- Splenic Rupture Diagnostics
- Live Rupture
□ IV pyelogram
□ MRI
□ FAST
DEFINITION □ CBC
It is a result from object striking the abdomen, such as □ Blood typing
baseball bat or a seatbelt drawn tight in a motor vehicle
crash. Management
Admission
ASSESSMENT IVF
Assess vital signs frequently until stable “E” explore laparotomy
Hypotension (less than 80mmHg systolic Antibiotics
pressure in an older child; less than 60mmHg in
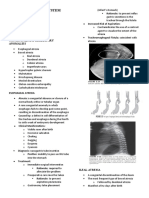
an infant) usually suggests hemorrhage, which LIVER RUPTURE
may be hidden abdominal bleeding
- More prone to rupture in children rather than adults
May have increasing pallor
- Because it is not completely not shattered by the rib
May have rapid respirations
cage.
If internal bleeding is present, blood pressure will
show little improvement when IV fluid is Assessment
administered.
Nasogastric Tube (NGT) is passed and stomach Severe abdominal pain that is most marked on
contents are aspirated to be checked visually for inspiration, when the diaphragm descends and
blood and to test for occult blood touches the liver
Low intermittent suction was done to if Symptoms of blood loss: tachycardia, hypotension,
presence of blood is established. anxiety and pallor
Foley Catheter (IFC) is also inserted to evaluate urine Hematocrit is low or falling
for blood and urine output
Evidence of blood in the urine or decreased Note:
output may indicate accompanying kidney or
bladder trauma. - Communication between an artery and the bile duct occurs
at the time of trauma. (symptoms are not immediate)
DIAGNOSTICS - Gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding such as hematemesis or
melena, may occur in a few days
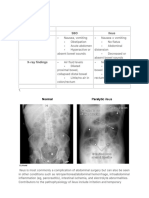
□ Abdominal X-Ray
□ FAST - May have colicky upper abdominal pain that is relieved by
□ Pelvic X-Ray emesis
Note: - Liver arteriogram are necessary to reveal the extent of the
problem
- Air under the diaphragm on the radiograph suggest gastric
or intestinal rupture with escape of air from these organs into After either liver or spleen surgery, children need careful
the peritoneal cavity observation for return of bowel function, assessment for the
possibility that peritonitis may develop, and careful
- Free fluid in the abdomen, shown on the radiograph when reintroduction of oral nutrition.
the child is turned on the side; suggest leakage of bowel fluid
or splenic rupture and pooling of blood.
COMPLICATIONS OF ABDOMINAL TRAUMA
SPLENIC RUPTURE
- Most frequently injured organ, because it is usually
palpable under the lower left ribs
- Frequently injured by inappropriately applied seat
belts and by handlebar injuries in bicycle accidents
Assessment
Have tenderness in the left upper quadrant,
especially on deep inspiration, when the diaphragm
moves down and touches the spleen
@NurseMD_
You might also like
- Abdominal TraumaDocument1 pageAbdominal TraumaYalc LapidNo ratings yet
- Management of Abdominal Trauma: By: Chong Lih YinDocument71 pagesManagement of Abdominal Trauma: By: Chong Lih YinRakaNo ratings yet
- Obscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Chylous AscitesDocument2 pagesObscure Gastrointestinal Bleeding: Chylous AscitesMintdonNo ratings yet
- Health Assessment: AbdomenDocument18 pagesHealth Assessment: AbdomenBatiao Camille ClaireNo ratings yet
- 1 - Abdomen 1Document23 pages1 - Abdomen 1noushad aminNo ratings yet
- Ectopic PregnancyDocument13 pagesEctopic PregnancyJonielyn LagunaNo ratings yet
- Haemorrage During Late PregnencyDocument38 pagesHaemorrage During Late PregnencysuthaNo ratings yet
- Perdarahan Saluran Cerna Bagian BawahDocument33 pagesPerdarahan Saluran Cerna Bagian BawahGiyani LiberthiNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Assessment HA LectureDocument44 pagesAbdominal Assessment HA LectureKatrina BeltranNo ratings yet
- Clinical Radiology For Surgical Conditions of The AbdomenDocument8 pagesClinical Radiology For Surgical Conditions of The AbdomenPreeti Joan Buxani100% (1)
- Postpartum HemorrhageDocument11 pagesPostpartum HemorrhageAisyah ShawtyNo ratings yet
- Sic ReportingDocument6 pagesSic ReportingCHRISTINE JOY. MOLINANo ratings yet
- Surgery Cases: CASE 1: Blunt Abdominal TraumaDocument3 pagesSurgery Cases: CASE 1: Blunt Abdominal TraumaGio Tamaño BalisiNo ratings yet
- Quiz BukasDocument3 pagesQuiz BukasDYRAH GRACE COPAUSNo ratings yet
- Week 2Document5 pagesWeek 2Maica LectanaNo ratings yet
- Toprank Review Pediatric Nursing NotesDocument12 pagesToprank Review Pediatric Nursing NotesCose online shopNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Wall and HerniasDocument17 pagesAbdominal Wall and HerniasananNo ratings yet
- Abdominal TraumaDocument16 pagesAbdominal Traumachehak.kumar2000No ratings yet
- Case Scenario 1 1. Immediate ManagementDocument5 pagesCase Scenario 1 1. Immediate ManagementArtika MalaNo ratings yet
- General Surgery: (Acute Abdomen)Document1 pageGeneral Surgery: (Acute Abdomen)MattNo ratings yet
- Abdominal AssessmentDocument7 pagesAbdominal AssessmentGlen DaleNo ratings yet
- 2.4.5.2.3.a Bowel ObstructionDocument35 pages2.4.5.2.3.a Bowel ObstructionProject ByNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Trauma: (Emergency Department Approaches & Management)Document82 pagesAbdominal Trauma: (Emergency Department Approaches & Management)edward iskandarNo ratings yet
- Trauma Tumpul Abdomen - Dr. Monica, SP.BDocument54 pagesTrauma Tumpul Abdomen - Dr. Monica, SP.Brizky sitanayaNo ratings yet
- ERIA Abdominal Compartment Syndrome - Antonius PudjiadiDocument13 pagesERIA Abdominal Compartment Syndrome - Antonius PudjiadiDennyNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placentae: ALCANTARA, Eduardo L. Ms. Analinda R. Sese, RN, MANDocument45 pagesAbruptio Placentae: ALCANTARA, Eduardo L. Ms. Analinda R. Sese, RN, MANinscenekivir100% (1)
- Gastro HistoryDocument4 pagesGastro HistoryAsma SikanderNo ratings yet
- Assessing AbdomenDocument33 pagesAssessing Abdomenjaypee01No ratings yet
- History Taking For CholelithiasisDocument6 pagesHistory Taking For CholelithiasisToria053No ratings yet
- Bowel ObstructionsDocument24 pagesBowel ObstructionsArchie ZhangNo ratings yet
- ABC AbdomenDocument57 pagesABC AbdomenSyahmi KhalidNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System DiseasesDocument6 pagesGastrointestinal System DiseasesHazel ConjeNo ratings yet
- Surgical AbdomenDocument3 pagesSurgical Abdomendude dNo ratings yet
- CT InfographicDocument1 pageCT Infographiclailatul husnaNo ratings yet
- Bambang Sugeng Bag Bedah FK-UnissulaDocument27 pagesBambang Sugeng Bag Bedah FK-UnissulaRahmat SyahiliNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Truama (Handout)Document6 pagesAbdominal Truama (Handout)Ayuub AbdirizakNo ratings yet
- Abruptio Placentae: (Accidental Hemorrhage, Premature Separation of Placenta)Document25 pagesAbruptio Placentae: (Accidental Hemorrhage, Premature Separation of Placenta)Akashdeep singhNo ratings yet
- GI BLEED - Medicine - Internal MedicineDocument11 pagesGI BLEED - Medicine - Internal Medicinezezma GamingNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Examination DetailedDocument22 pagesAbdominal Examination Detailedsaveetha purushothamanNo ratings yet
- POSTPARTAL HEMORRAGE Editable NotesDocument4 pagesPOSTPARTAL HEMORRAGE Editable NotesJkimNo ratings yet
- .Right Side-Lying With Pillow Under Puncture SiteDocument14 pages.Right Side-Lying With Pillow Under Puncture SiteJay AbasoloNo ratings yet
- Necrotizing EnterocolitisDocument24 pagesNecrotizing Enterocolitisfadhila khairunnisaNo ratings yet
- Esophageal VaricesDocument14 pagesEsophageal VaricesKarla So MejiaNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Trauma: Fatin Amirah KamaruddinDocument29 pagesAbdominal Trauma: Fatin Amirah Kamaruddinvirz23No ratings yet
- 3.1 Acute AppendicitisDocument3 pages3.1 Acute AppendicitisMavi HayalNo ratings yet
- Vi. Nursing Care Plan Cues Analysis Nursing Diagnosis Goal / Plan Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesVi. Nursing Care Plan Cues Analysis Nursing Diagnosis Goal / Plan Intervention Rationale EvaluationRaisa Robelle QuichoNo ratings yet
- The SpleenDocument7 pagesThe Spleeneiuj497No ratings yet
- Abdominal TraumaDocument33 pagesAbdominal TraumaRasYa DINo ratings yet
- Acute Appendicitis: History and ExaminationDocument6 pagesAcute Appendicitis: History and ExaminationPraktek Dokter Umum drjosefdrelsyNo ratings yet
- Radiology GitDocument6 pagesRadiology GitShms GaneemNo ratings yet
- Abdominal Trauma PDFDocument88 pagesAbdominal Trauma PDFNashif RayhanNo ratings yet
- Disease Description Signs and Symptoms Diagnosis Medical/Surgical MGT Description/Rationale Nursing MGTDocument3 pagesDisease Description Signs and Symptoms Diagnosis Medical/Surgical MGT Description/Rationale Nursing MGTNerissa Neri NatataNo ratings yet
- Abdomen AgudoDocument12 pagesAbdomen AgudoMercedes RojasNo ratings yet
- Common Cases in Vascular SurgeryDocument72 pagesCommon Cases in Vascular Surgerynohazz100% (2)
- CH 39Document3 pagesCH 39Nailin RamadsNo ratings yet
- LEC 3 - Abdomen 3 - PERCUSSION 2010Document1 pageLEC 3 - Abdomen 3 - PERCUSSION 2010Elle ReyesNo ratings yet
- Placental Abnormalities Normal Placenta: © Mary Andrea G. Agorilla, Ust-Con 2021 - 1Document3 pagesPlacental Abnormalities Normal Placenta: © Mary Andrea G. Agorilla, Ust-Con 2021 - 1Mary AgorillaNo ratings yet
- Antepartum Haemorrhage: BY: Ms. R. Liangkiuwiliu Assistant Professor, Obg SSNSR, SuDocument44 pagesAntepartum Haemorrhage: BY: Ms. R. Liangkiuwiliu Assistant Professor, Obg SSNSR, SuLiangkiuwiliuNo ratings yet
- Schematic DiagramDocument3 pagesSchematic Diagrambunso padillaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care For Child With Autoimmune Diseases & GI DisordersDocument4 pagesNursing Care For Child With Autoimmune Diseases & GI Disordersbunso padillaNo ratings yet
- RRLDocument2 pagesRRLbunso padillaNo ratings yet
- 04 OxygenationDocument4 pages04 Oxygenationbunso padillaNo ratings yet
- 03 Foreign Body ObstructionDocument2 pages03 Foreign Body Obstructionbunso padillaNo ratings yet
- 04 Pediatric Basic Life SupportDocument2 pages04 Pediatric Basic Life Supportbunso padillaNo ratings yet
- 05 Integrated Management of Childhood IlnessessDocument4 pages05 Integrated Management of Childhood Ilnessessbunso padillaNo ratings yet
- Nucleic AcidsDocument2 pagesNucleic Acidsbunso padillaNo ratings yet
- 1.sphingolipids: Nonglyceride LipidsDocument2 pages1.sphingolipids: Nonglyceride Lipidsbunso padillaNo ratings yet
- 02 IV TherapyDocument3 pages02 IV Therapybunso padillaNo ratings yet
- Preliminary Steps: Dna ReplicationDocument2 pagesPreliminary Steps: Dna Replicationbunso padillaNo ratings yet
- 03 Perioperative NursingDocument2 pages03 Perioperative Nursingbunso padillaNo ratings yet
- Anthropometric ResultDocument2 pagesAnthropometric ResultNaveed AhmedNo ratings yet
- Final ThesisDocument58 pagesFinal Thesisgnanasegaram vithursanNo ratings yet
- Seminar: Sameer Jauhar, Mandy Johnstone, Peter J MckennaDocument14 pagesSeminar: Sameer Jauhar, Mandy Johnstone, Peter J MckennaMagdalena Zepeda MarambioNo ratings yet
- Life Style Wellness Coaching PDFDocument275 pagesLife Style Wellness Coaching PDFSundar Prabhu71% (7)
- Student Copy Conti - Intrapartal Week8Document25 pagesStudent Copy Conti - Intrapartal Week8Toyour EternityNo ratings yet
- OT in The ICU Student PresentationDocument37 pagesOT in The ICU Student PresentationMochammad Syarief HidayatNo ratings yet
- Confined Space PDFDocument4 pagesConfined Space PDFshreyasNo ratings yet
- Rheumatic FeverDocument21 pagesRheumatic FeverUmar Azlan50% (2)
- History of Toxicity TestingDocument4 pagesHistory of Toxicity TestingIja Nur100% (1)
- Chapter 1Document46 pagesChapter 1ZiziNo ratings yet
- Acute Pancriatis Special HDocument9 pagesAcute Pancriatis Special HInga CeagleiNo ratings yet
- MCQ PebcDocument7 pagesMCQ Pebcshamram20050% (1)
- 1 TTP Mozambique - STE EIS Vol - I - Submitted - For - Disclosure - 0Document227 pages1 TTP Mozambique - STE EIS Vol - I - Submitted - For - Disclosure - 0Luciana MirandaNo ratings yet
- HSE Commitment and Policy?Document6 pagesHSE Commitment and Policy?radhesrikrishnaNo ratings yet
- 13 Areas of Assessment Pedia DutyDocument3 pages13 Areas of Assessment Pedia DutyJoshua MendozaNo ratings yet
- Differential Diagnosis of Cervical CancerDocument8 pagesDifferential Diagnosis of Cervical Cancerrey martinoNo ratings yet
- CSHP TEMPLATE (1) - NewDocument14 pagesCSHP TEMPLATE (1) - NewLucky JavellanaNo ratings yet
- Nominal Roll N035 1bnm10jDocument2 pagesNominal Roll N035 1bnm10jsubiNo ratings yet
- Aerobic Exercise Dos and DontsDocument2 pagesAerobic Exercise Dos and DontsSandy NodadoNo ratings yet
- Fecal Occult BloodDocument9 pagesFecal Occult BloodRipu DamanNo ratings yet
- Basic of Ot 1Document2 pagesBasic of Ot 1shubham vermaNo ratings yet
- 2013 Observer - Applicant FormsDocument11 pages2013 Observer - Applicant FormsshengzhoumiNo ratings yet
- Masker 1 2020 - Post Test (Edited)Document12 pagesMasker 1 2020 - Post Test (Edited)Muhammad Ali MaulanaNo ratings yet
- FNCPDocument5 pagesFNCPGwen De CastroNo ratings yet
- Systemic Response To InjuryDocument15 pagesSystemic Response To InjuryJohnVincentPagaddu100% (1)
- Device Related Error in Patient Controlled.17Document6 pagesDevice Related Error in Patient Controlled.17Ali ÖzdemirNo ratings yet
- Pantawid Pamilyang Pilipino Program (4Ps) Act: Implementing Rules and RegulationsDocument44 pagesPantawid Pamilyang Pilipino Program (4Ps) Act: Implementing Rules and RegulationsRyan ZaguirreNo ratings yet
- Epoch Elder Care Provides High Quality Assisted Living HomesDocument17 pagesEpoch Elder Care Provides High Quality Assisted Living HomesMahesh MahtoliaNo ratings yet
- Diabetes Chart.1Document6 pagesDiabetes Chart.1dr_vidyasagar41No ratings yet
- Family DeclarationDocument5 pagesFamily DeclarationVanlal MuanpuiaNo ratings yet