Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Quiz Bukas
Uploaded by
DYRAH GRACE COPAUSOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Quiz Bukas
Uploaded by
DYRAH GRACE COPAUSCopyright:
Available Formats
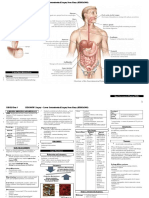
GASTROINTESTINAL FINALS REVIEWER Indicated for surgical revision
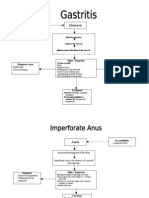
1. HIATAL HERNIA 2. GASTRITIS
- An opening in the diaphragm which esophagus - Inflammation of the gastric mucosa
passes become enlarged and part of stomach
moves up into the lower portion of the thorax - Classifications of Gastritis:
- Etiology: o Erosive Gastritis
Weakened diaphragmatic muscles Due to local irritants
- Types of hiatal hernia: NSAID/aspirin
o Sliding type Alcohol consumption/smoking
Upper stomach and gastroesophageal Gastric radiation therapy
junction are displaced upward and slide o Non-erosive Gastritis
in and out the thorax Due to infection
o Paraesophageal type
Helicobacter Pylori
All or part of the stomach pushes - Types of Gastritis:
through the diaphragm beside o Acute Gastritis
esophagus.
Last for several hours
- Clinical Manifestation
Severe are forms commonly due to
o Pyrosis, regurgitation, dysphagia
strong alkaline ingestion
Common in sliding hernia
Example: shampoo, Bleach
o Epigastric pain or fullness after eating
o Chronic Gastritis
o Nausea and vomiting, intolerance to food
Commonly due to:
Common in large hiatal hernia or
H. Pylori infection
paraesophageal hernia
Duodenal reflux
o Reflux
Complications:
o Hemorrhage
Peptic ulcer
o Obstruction Gastric adenocarcinoma
o Strangulation Gastric mucosal lymphoma
Compression of trachea - Clinical Manifestation
- Diagnostic test o Acute Gastritis
o X-ray studies Epigastric Pain
o Barium Swallow Dyspepsia
o EGD (Esophagealgastroduodenoscopy) Anorexia
o Esophageal Manometry Hiccups or nausea/vomiting
o Chest CT scan Melena/Hematochezia
- Medical and Nursing Management o Chronic Gastritis
o Frequent small feeding Chronic fatigue
o Stay upright position 1 hour after eating Pyrosis after eating
o Elevate head of bed 4 to 8 inches Belching
o Include management of patients with Sour taste in the mouth
GERD Ealy satiety
- Surgical Management
Anorexia
o Surgical hernia repair
Nausea and vomiting
Open/Laparoscopic
Epigastric pain
Open (Transabdominal/Transthoracic)
Spicy or fatty food intolerance
for patients with complications such as
- Diagnostic Findings
bleeding, dense adhesions, or injury to
Upper GI series with biopsy
the spleen
Always obtain informed consent
Post-op dysphagia:
CBC
o Advances the diet slowly from
For anemia
liquid to solids while managing
- Medical Management
nausea and vomiting
o H2 blockers
o Tracking nutritional intake and
o Antibiotics
monitoring weight
Amoxicillin, Clarithromycin
o WOF: Monitor for post-operative
- Surgical Management
bleeding, vomiting, gagging,
o Gastrojejunostomy
abdominal distention and
Anastomosis of jejunum to stomach
epigastric chest pain
to detour around the pylorus
Billroth 2 CBC
- Nursing Management o For anemia
o Reduce Anxiety Tumor makers
o Promoting optimum nutrition o Carcinoembryonic Antigen Test
o Avoid smoking and alcohol drinking (CEA)
o Promoting fluid balance o Carbohydrate Antigen (CA 19-9)
o Monitoring signs of hemorrhagic gastritis o CA 50 is all elevated indicating
o Pain management gastric cancer
o Educate patient and family about home care o Medical Management
and manifestation of possible complications Multimodal management
- Possible Complications: o Surgery, Chemotherapy, targeted
o Vitamin B12 malabsorption therapy, radiation therapy
- Possible Nursing Diagnosis Radiotherapy
o Acute pain The use of radiation in
o Fluid Volume Deficit treating cancer
o Fluid imbalance Teletherapy (External
o Imbalance nutrition: less than body Radiation)
requirements o Most common
o Anxiety method
o Knowledge deficit o Fast 2-5 minutes
3. GASTRIC CANCER o No radiation after
- A disease in which malignant (cancer) cells o Adverse effects:
form in the lining of the stomach o Diarrhea
- Etiology o Cystitis
o Unknown o Erectile dysfunction
- Precipitating factors o Vaginal stenosis (use
o Age: Older adults vaginal dilator 3
o Sex: Men times a week)
o Race: Hispanic and African American, o Sterility
Asia/Pacific Islander Brachytherapy (Internal
o Diet: Smoked, Salted, and Pickled foods, Radiation)
Low fiber intake o Sealed
o Vices: Smoking and alcohol consumption o Unsealed
o H. pylori infection
Most common: 60%
o Chronic inflammation, pernicious anemia,
obesity, gastric ulcer, previous partial
gastrectomy, genetics
- Clinical Manifestation
o Early Stage
Pain relieved by antacids
o Benign ulcer like
o Late Stage
Peptic ulcer like: dyspepsia, early
satiety, weight loss, abdominal pain
above umbilicus, loss or decrease of
appetite, bloating after meals, n/v,
hematemesis, melena, hematochezia
- Assessment and Diagnostic Test - Surgical Management
Physical Exam o Total Gastrectomy
o Palpation on late stage Resection of the midportion or body of
Esophagogastroduodenoscopy (Upper the stomach
Gi Series) with biopsy o Billroth I
Barium swallow Anastomosis to duodenum
Endoscopic ultrasound o Billroth II
Chest, abdominal and pelvis CT scan Anastomosis to duodenum
o To check for malignancy - COMPLICATIONS OF GASTRIC SURGERY
o Hemorrhage
o Dumping Syndrome
o Bile reflux
o Gastric outlet obstruction
- DUMPING SYNDROME
o Rapid gastric emptying
- Clinical manifestation:
o Symptoms occurring 30 minutes after eating
o Nausea and vomiting
o Feelings of abdominal fullness and
abdominal
o Cramping
o Diarrhea
o Palpitations and tachycardia
o Perspiration
o Weakness and dizziness
o Borborygmi sounds
Normal: 6-32 movements
o Steatorrhea
- Dumping syndrome management:
o Lie down after meals
o Avoid sugar, salt, and milk
High gastric motility
o Take anti-spasmodic medications as
prescribed to delay gastric emptying
Example: HNBB, anticholinergics
(atropine, Cogentin, Artane, Benadryl)
- Nursing intervention for gastric cancer
o Reducing Anxiety
o Promote optimal nutrition
o Pain management
o Provide psychosocial support
o Health education on home and
community based and transitional care
- Possible Nursing Diagnosis
o Anxiety
o Acute/Chronic pain
o Imbalance nutrition: less than body
requirements
o Self-care activities
o Knowledge Deficit
You might also like
- MBChB Year 5 Lower GI Surgery Core CurriculumDocument3 pagesMBChB Year 5 Lower GI Surgery Core CurriculumJason HarryNo ratings yet
- GitDocument302 pagesGitjgcriste100% (7)
- Medical Surgical Nursing Study GiudeDocument5 pagesMedical Surgical Nursing Study GiudeRexson Alcantara DalanginNo ratings yet
- Alicia’s CCFP Exam GuideDocument133 pagesAlicia’s CCFP Exam Guidejpdavid95No ratings yet
- Guide to Diverticular Disease, Hemorrhoids, Intestinal Obstruction and Colorectal CancerDocument4 pagesGuide to Diverticular Disease, Hemorrhoids, Intestinal Obstruction and Colorectal CancerJANELLE GIFT SENARLONo ratings yet
- Week 2Document5 pagesWeek 2Maica LectanaNo ratings yet
- Gastric Ulcer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument16 pagesGastric Ulcer Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis and TreatmentTabada NickyNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument1 pagePeptic Ulcer DiseaseEunice CortésNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology diseases and treatmentsDocument4 pagesGastroenterology diseases and treatmentsHafsa AliNo ratings yet
- MS Lec Gi P1Document6 pagesMS Lec Gi P1Julia Rae Delos SantosNo ratings yet
- Surgery EORDocument76 pagesSurgery EORAndrew BowmanNo ratings yet
- 2 Hiatal Hernia ManuscriptDocument4 pages2 Hiatal Hernia Manuscriptkint manlangitNo ratings yet
- Necrotizing Enterocolitis ProtocolDocument3 pagesNecrotizing Enterocolitis Protocoleddy riachyNo ratings yet
- GastroDocument6 pagesGastroKathleen PabalanNo ratings yet
- care of older adult for printDocument5 pagescare of older adult for printGracian Vel AsocsomNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1part 2Document50 pagesLecture 1part 2mashe1No ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Disease FDocument51 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease FSharmila Laxman Dake100% (2)
- Advanced GI Nursing CareDocument13 pagesAdvanced GI Nursing CareBobbi-MarieNo ratings yet
- Other Problems in Inflammatory ResponseDocument62 pagesOther Problems in Inflammatory ResponseJR Rolf NeuqeletNo ratings yet
- Pedia Surg Module, Grp11&2Document91 pagesPedia Surg Module, Grp11&2Jelyn ManipisNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Disease GuideDocument8 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease GuideMisheilPascuaNo ratings yet
- GERD2Document28 pagesGERD2Anonymous 2qUGvwI9No ratings yet
- Dyspepsia FinalDocument52 pagesDyspepsia FinalAfifah SelamatNo ratings yet
- Department of Surgery: Case Presentation Intestinal ObstructionDocument46 pagesDepartment of Surgery: Case Presentation Intestinal Obstructionhadil ayeshNo ratings yet
- Esophageal Achalasia DysphagiaDocument14 pagesEsophageal Achalasia DysphagiaTirtha Taposh100% (1)
- Review Textbook - CompressedDocument72 pagesReview Textbook - CompressedChrista Levina DaniswaraNo ratings yet
- Gastroenterology Division Internal Medicine Department FK-USU/Adam Malik HospitalDocument78 pagesGastroenterology Division Internal Medicine Department FK-USU/Adam Malik HospitalcarinasheliapNo ratings yet
- GI Disorders Problems in Elimiation Absorption DigestionDocument4 pagesGI Disorders Problems in Elimiation Absorption DigestionMikee PaningbatanNo ratings yet
- 1 NCM+116n+Lecture+Care+of+the+Clients+with+Problems+GI+Function+and+NutritionDocument6 pages1 NCM+116n+Lecture+Care+of+the+Clients+with+Problems+GI+Function+and+NutritionKylle AlimosaNo ratings yet
- Lyceum of the Philippines University College of Nursing Drug StudyDocument2 pagesLyceum of the Philippines University College of Nursing Drug Studykaye barrionNo ratings yet
- MS Lec Gi and Icp Reviewer - Limon, Adine Jeminah DDocument8 pagesMS Lec Gi and Icp Reviewer - Limon, Adine Jeminah DShawn TejanoNo ratings yet
- Pediatric Nursing GastroDocument3 pagesPediatric Nursing GastronieacatleyaNo ratings yet
- Gastrointestinal System DiseasesDocument6 pagesGastrointestinal System DiseasesHazel ConjeNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument2 pagesPeptic Ulcer DiseaseAlexander EnnesNo ratings yet
- Disturbances in Ingestion: Prepared By: Jan Paul Valeros Sicat, PHRN, USRNDocument41 pagesDisturbances in Ingestion: Prepared By: Jan Paul Valeros Sicat, PHRN, USRNAriane-Gay Cristobal Duran100% (1)
- Acute AbdomenDocument47 pagesAcute AbdomenDani LeeNo ratings yet
- PancreatitisDocument45 pagesPancreatitisFernando ArancibiaNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument1 pagePeptic Ulcer DiseaseMary GiuntiniNo ratings yet
- Pyloric Stenosis Diagnosis and TreatmentDocument5 pagesPyloric Stenosis Diagnosis and TreatmentIyath SaeedNo ratings yet
- MS-2 GallbladderDocument2 pagesMS-2 Gallbladderelijahdale.guillergan-05No ratings yet
- Acute Abdominal Pain GuideDocument19 pagesAcute Abdominal Pain GuideAudricNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Disease: "Something Is Eating at Me"Document37 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease: "Something Is Eating at Me"bobtaguba100% (1)
- Small Bowel ObstructionDocument38 pagesSmall Bowel ObstructionRUSSELL CILOTNo ratings yet
- Emergency Medicine: Acute AbdomenDocument33 pagesEmergency Medicine: Acute AbdomenPrashant MishraNo ratings yet
- LEC 2 - Abdomen 2 - AUSCULATION 2010Document1 pageLEC 2 - Abdomen 2 - AUSCULATION 2010Elle ReyesNo ratings yet
- GI Stomach PDFDocument65 pagesGI Stomach PDFBatool SherbiniNo ratings yet
- Peptic Ulcer Disease: Manisha 2 Year, M.SC NursingDocument47 pagesPeptic Ulcer Disease: Manisha 2 Year, M.SC NursingManisha ShakyaNo ratings yet
- Gastro PathophysiologyDocument4 pagesGastro PathophysiologyPaul JoloNo ratings yet
- Management of Patients With Gastro-Intestinal DisordersDocument84 pagesManagement of Patients With Gastro-Intestinal DisordersY. Beatrice AbigailNo ratings yet
- Critical Disorders and Complications of The GDocument2 pagesCritical Disorders and Complications of The GVictor MurilloNo ratings yet
- Acute AbdomenDocument25 pagesAcute AbdomenAli TahirNo ratings yet
- Inflammatory Bowel DiseaseDocument3 pagesInflammatory Bowel DiseaseMaria Theresa BuscasNo ratings yet
- NCM 116N - TransDocument9 pagesNCM 116N - TransNEIL NETTE S. REYNALDONo ratings yet
- SummerTerm TopicOutline1Document20 pagesSummerTerm TopicOutline1Rachelle DelantarNo ratings yet
- 2 NCM+116n+Lecture+Care+of+the+Clients+with+Problems+GI+Function+and+NutritionDocument11 pages2 NCM+116n+Lecture+Care+of+the+Clients+with+Problems+GI+Function+and+NutritionKylle AlimosaNo ratings yet
- Gastro Reviewer FinalsDocument5 pagesGastro Reviewer Finalsadd.bdrcNo ratings yet
- Dental Management of Diseases of The Gastrointestinal SystemDocument61 pagesDental Management of Diseases of The Gastrointestinal SystemkomalgorayaNo ratings yet
- 10 StomachDocument10 pages10 StomachApabrita KarmakarNo ratings yet
- Pead 3 - Abdominal Pain and VommitingDocument22 pagesPead 3 - Abdominal Pain and Vommitingbbyes100% (1)
- Symtoms and Signs of The Respiratory SystemDocument33 pagesSymtoms and Signs of The Respiratory SystemmohammedNo ratings yet
- Your Guide To Managing Pyrexia: TAFINLAR in Combination With MEKINIST Is Indicated ForDocument5 pagesYour Guide To Managing Pyrexia: TAFINLAR in Combination With MEKINIST Is Indicated ForAnne Marie ScerriNo ratings yet
- Acute Lung Edema (Pulmo)Document35 pagesAcute Lung Edema (Pulmo)Muhammad DaviqNo ratings yet
- DOH Calendar of ActivitiesDocument4 pagesDOH Calendar of ActivitiesArlene Cerdeña SalcedaNo ratings yet
- Brucellosis in NepalDocument22 pagesBrucellosis in NepalBinayaNo ratings yet
- Diaz - SC23 - Laboratory Activity No. 6Document8 pagesDiaz - SC23 - Laboratory Activity No. 6John Rafael Obera DiazNo ratings yet
- Goat KeratoconjunctivitisDocument12 pagesGoat KeratoconjunctivitisMadhav AjjodiNo ratings yet
- Prostate Cancer Clinical Pathway - July 2020Document4 pagesProstate Cancer Clinical Pathway - July 2020VincentEguzoNo ratings yet
- Healy World Certificate of Conformity en EUDocument38 pagesHealy World Certificate of Conformity en EUJOHANNA BJARNERNo ratings yet
- Full RujiraLeukorrhea, STDS, HIV Infection.02102017 PDFDocument129 pagesFull RujiraLeukorrhea, STDS, HIV Infection.02102017 PDFrujiraNo ratings yet
- Self Completion Medical History Form - PregnancyDocument4 pagesSelf Completion Medical History Form - PregnancymerjenNo ratings yet
- Case PresentationDocument14 pagesCase PresentationFatema RavatNo ratings yet
- Internal MedicineDocument146 pagesInternal MedicineSh. RamNo ratings yet
- COVID PCR TestDocument1 pageCOVID PCR TestStacey ChanNo ratings yet
- DisinfectionDocument528 pagesDisinfectionrajtanniruNo ratings yet
- Fast Review Echinacea For Covid 19Document16 pagesFast Review Echinacea For Covid 19Herlina HasibuanNo ratings yet
- Pass 2022Document4 pagesPass 2022john frits gerard mombayNo ratings yet
- Face-To-Face Classes During COVID-19Document2 pagesFace-To-Face Classes During COVID-19MIZPAH VILLALOBOSNo ratings yet
- LetterDocument3 pagesLetterhudaNo ratings yet
- Flyer SINAS IDAI Lampung 2024 271123Document2 pagesFlyer SINAS IDAI Lampung 2024 271123JayantiNo ratings yet
- DNB Pediatrics Question BankDocument25 pagesDNB Pediatrics Question Bankshalpraba100% (1)
- Relieve pain and swelling with Willgo SP TabletDocument3 pagesRelieve pain and swelling with Willgo SP TabletMazin MohammadNo ratings yet
- Aids 8-12-2013Document6 pagesAids 8-12-2013giancarlo_luzziNo ratings yet
- Laporan Pasien Pulang Per Diagnosa Utama: Tanggal 01/01/2019 31/08/2019 S/DDocument4 pagesLaporan Pasien Pulang Per Diagnosa Utama: Tanggal 01/01/2019 31/08/2019 S/DAhmad IsmadiNo ratings yet
- Cancer Incidence and Mortality Among Fighter.12Document8 pagesCancer Incidence and Mortality Among Fighter.12Adi AndoneNo ratings yet
- NCP Case Study 1Document3 pagesNCP Case Study 1Kristinelou Reyna100% (5)
- Community Health Nursing Answer KeyDocument9 pagesCommunity Health Nursing Answer Keyjeshema87% (45)
- Cancer Lesson Plan - Tutor1Document7 pagesCancer Lesson Plan - Tutor1ta CNo ratings yet
- Poort Et Al. - 2020 - Cognitive Behavioral Therapy or Graded Exercise THDocument8 pagesPoort Et Al. - 2020 - Cognitive Behavioral Therapy or Graded Exercise THIván DelgadoNo ratings yet
- Cardiovascular Diseases: By: Vaheeda Rehman, Dept of Pharmacology, VistasDocument23 pagesCardiovascular Diseases: By: Vaheeda Rehman, Dept of Pharmacology, Vistaspharmazone4uNo ratings yet