Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Annex 0 - Delivery Format - Pre Task
Uploaded by
Andrea VargasOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Annex 0 - Delivery Format - Pre Task
Uploaded by
Andrea VargasCopyright:
Available Formats
Pre-task Recognition
Individual work
Yudy Andrea Vargas
203058_39
1049628455
Universidad Nacional Abierta y a Distancia - UNAD
Escuela de Ciencias Básicas, Tecnología e Ingeniería
Teoría Electromagnética y Ondas
2021 16-04
Solution of the questions
Activity
Solve the following questions:
1. What is an electromagnetic wave? Describe with your words.
Wave produced by moving electric charges, Electromagnetic waves are
the combination of waves in electric and magnetic fields produced by
moving charges.
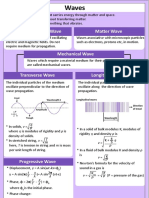
2. What are the parameters in an electromagnetic wave? Describe them with
your words.
Electromagnetic waves are characterized by three fundamental
parameters: Wavelength, Frequency and Energy:
Wavelength (λ): It is the distance between the crests of two
consecutive waves, and is measured in units of length (m). The
amplitude of the wave depends on the radiant power of the emitting
source.
Frequency (ν or f): It is the number of times a wave oscillates in one
second and is measured in cycles / second or Hertz (Hz).
Energy (E): The energy transported by electromagnetic radiation can be
measured in Joules (J), although it is more frequently measured in
electron volts (eV). The electron volt represents the kinetic energy that
an electron acquires when it is accelerated by a potential difference of 1
volt. Equivalent to 1.602176462 × 10-19 J.
3. What is electrical permittivity ε and magnetic permeability μ of a medium?
Permeability
In physics, magnetic permeability is called the ability of a substance or
medium to attract and make magnetic fields pass through it, which is given by
the relationship between the existing magnetic induction and the intensity of
the magnetic field that appears inside. of said material.
Permittivity
The permittivity (also called the dielectric constant) is a physical constant that
describes how an electric field affects and is affected by a medium. The
permittivity of vacuum [epsilon] 0 is 8.8541878176x10-12 C2 / Nm2.
The permittivity is determined by the tendency of a material to polarize before
the application of an electric field and in this way to partially annul the internal
field of the material.
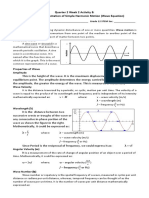
4. From the following wave equation:
2π ^
(
E y ( x , t )= A sen ( wt−kx ) ^j = A sen 2 πft−
λ )
x j=C1 sen ( C2 t−C3 x ) ^j
where C 1 , C2 and C 3correspond to the last 3 digits of your identification.
Notice that in the equation:1049628455
2π
A=C1 (4) w=2 πf =C 2(5) k= =C 3 (5)
λ
Complete:
Parameter Variables and unit Description
Example : A=c 1=4 V /m It is the highest
a. Amplitude A . [V/m] value of the wave
oscillations
Times a cycle is
Example: if 𝐶2 = 5,
then repeated in a unit
b. Frequency f =w/2 π [ Hz]
w 5 rad /s
f= = =0.636 Hz of time s.
2 π 2 π rad
It is the distance in
m, between the
2 πrad
c. Wavelength λ = 𝟐𝜋/𝑘 [m] λ= =1.256 m peak of one wave
5 rad /m
and another
Distance traveled
2 πrad 5 rad
∗ by a wave in a
d. Propagation speed V p 𝒇 𝝀 5 rad s
[m/s] V p=
m
=1 m/s time interval
2 πrad
Is the number of
times a wave
e. Wave number k 5rad/m vibrates in a unit
of distance.
Is the number of
oscillations or
turns per second
f. Angular frequency w 5 rad/s that are made in
proportion to the
change in angle
Is the axis through
Propagates on the which the wave
g. Travel direction ( x , y or z )
axis x propagates
The loads were
It is the oscillation
moved in the
h. Polarization direction (i^ , ^j or k^ ) direction of the
direction of the
wave
component ^j
References
Reference 1:
Relación entre la velocidad angular, el periodo y la frecuencia
18 dic. 2017
Khan Academy en español
Relación entre la velocidad angular, el periodo y la frecuencia | Khan Academy
en Español - YouTube
Velocidad de propagación de una onda
1 mar. 2017
Jorge Alejandro Guerra
Velocidad de propagación de una onda - YouTube
Unidad de medida Hertz
EcuRed-Fuente
Artículo wordreference.Disponible en “www.wordreference.com”.
Consultado el 5 de octubre del 2011.
Artículo duiops.Disponible en “www.duiops.net”. Consultado el 5 de
octubre del 2011.
Artículo fisica.Disponible en “www.fisica.netii.net”. Consultado el 5 de
octubre del 2011.
Hertz - EcuRed
You might also like
- Jhon Ramirez - G 40Document4 pagesJhon Ramirez - G 40duvan garciaNo ratings yet
- Trabajo Teoria ElectromagneticaDocument5 pagesTrabajo Teoria Electromagneticaoswaldo perciaNo ratings yet
- Pre Task - Diego CardonaDocument4 pagesPre Task - Diego CardonaDiego Alejandro Cardona GiraldoNo ratings yet
- Annex 0 - Delivery Format - Pre TaskDocument4 pagesAnnex 0 - Delivery Format - Pre TaskMelanny MenesesNo ratings yet
- Pre TaskDocument6 pagesPre Taskedgar armando marinNo ratings yet
- Pre Task RecognitionDocument6 pagesPre Task RecognitionDaVid CaNoNo ratings yet
- Annex 0 - Delivery Format - Pre TaskDocument4 pagesAnnex 0 - Delivery Format - Pre TaskMateo CiroNo ratings yet
- Pre Task - Group63 - William LoperaDocument5 pagesPre Task - Group63 - William LoperaelianaNo ratings yet
- Solution of The QuestionsDocument5 pagesSolution of The QuestionsMilton RojasNo ratings yet
- Pre Task - Rafael DominguezDocument5 pagesPre Task - Rafael DominguezelianaNo ratings yet
- Pre Task - Fraiber ZambranoDocument5 pagesPre Task - Fraiber ZambranoLugar De La Mancha MuñozNo ratings yet
- Annex 0 - Delivery Format - Pre TaskDocument3 pagesAnnex 0 - Delivery Format - Pre Taskoswaldo perciaNo ratings yet
- Annex 0 - Delivery Format - Pre TaskDocument5 pagesAnnex 0 - Delivery Format - Pre TaskMemilio DE Las TorresNo ratings yet
- Pre Task (1) - Brayan Devia - 203058 - 74 - Teoría Electromagnética y OndasDocument3 pagesPre Task (1) - Brayan Devia - 203058 - 74 - Teoría Electromagnética y OndasBrayan Andres Devia HerreraNo ratings yet
- Samuel Madero - Pre TaskDocument4 pagesSamuel Madero - Pre TaskelianaNo ratings yet
- Gen Physics 1 Q2 W8Document3 pagesGen Physics 1 Q2 W8J-heart Basabas MalpalNo ratings yet
- (L2) - Waves - 24th Dec. PDFDocument49 pages(L2) - Waves - 24th Dec. PDFharishNo ratings yet
- Annex 0 - Delivery Format - Pre TaskDocument5 pagesAnnex 0 - Delivery Format - Pre TaskUnadista880No ratings yet
- Annex 0 - Delivery Format - Pre TaskDocument3 pagesAnnex 0 - Delivery Format - Pre TaskFabian TorresNo ratings yet
- Pre TaskDocument5 pagesPre Taskkevin narvaez henriquezNo ratings yet
- Module 1 - Introduction To WavesDocument20 pagesModule 1 - Introduction To WavesMahek KhushalaniNo ratings yet
- Waves - Notes For A Revised)Document16 pagesWaves - Notes For A Revised)Dave100% (1)
- Chapter 16 Waves IDocument27 pagesChapter 16 Waves IWardaNo ratings yet
- Chap 10 P1-1Document15 pagesChap 10 P1-1Andrew BederNo ratings yet
- Progressive Waves - The One: in Which The Wave Profile PropagatesDocument1 pageProgressive Waves - The One: in Which The Wave Profile PropagatesDash ShaaNo ratings yet
- Pre Task - FABIAN EDUARDO BARONDocument4 pagesPre Task - FABIAN EDUARDO BARONleidyNo ratings yet
- WAVES NOTES Progressive WavesDocument2 pagesWAVES NOTES Progressive WavesTerrenceNo ratings yet
- Chapter11 WavesDocument10 pagesChapter11 WavesRahayu CamscanNo ratings yet
- 3.3 Waves AnswersDocument66 pages3.3 Waves Answersmarkmattesz06No ratings yet
- The Nature of Light Unit - 02Document117 pagesThe Nature of Light Unit - 02TEBATSONo ratings yet
- WavesDocument32 pagesWavesrachna chhabraNo ratings yet
- ElegmaDocument40 pagesElegmaNoriel_James_B_7906No ratings yet
- We Will See The Difference of That Two WaveDocument3 pagesWe Will See The Difference of That Two WaveM Ramadhan ANo ratings yet
- Electromagne C Wave Ma Er WaveDocument1 pageElectromagne C Wave Ma Er WaveRekha BhasinNo ratings yet
- Waves and SuperpositionsDocument19 pagesWaves and SuperpositionsTazrin BibortonNo ratings yet
- 15 Lesson 2 Wave Properties v23Document9 pages15 Lesson 2 Wave Properties v23Fati VillarrealNo ratings yet
- New Microsoft Office Word DocumentDocument39 pagesNew Microsoft Office Word DocumentUadNo ratings yet
- Phys2 Week5 Transverse Mechanical WavesDocument4 pagesPhys2 Week5 Transverse Mechanical WavesSahirNo ratings yet
- PhysDocument16 pagesPhysDerrick RamosNo ratings yet
- Interactions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsFrom EverandInteractions between Electromagnetic Fields and Matter: Vieweg Tracts in Pure and Applied PhysicsNo ratings yet
- Chapter 18Document63 pagesChapter 18Arthur ParizNo ratings yet
- The Nature of Waves HWDocument8 pagesThe Nature of Waves HW2144639220No ratings yet
- EMII2013 Chap 10 P1 PDFDocument49 pagesEMII2013 Chap 10 P1 PDFFabian ZambranoNo ratings yet
- Waves: Krauss Chapter NineDocument17 pagesWaves: Krauss Chapter NineFoda KodaNo ratings yet
- Waves: Krauss Chapter NineDocument17 pagesWaves: Krauss Chapter NineIulia AntonNo ratings yet
- Waves: Krauss Chapter NineDocument17 pagesWaves: Krauss Chapter Ninemega maurinaNo ratings yet
- Pre Task Recognition Heidy CastañedaDocument4 pagesPre Task Recognition Heidy CastañedahjcastanedamNo ratings yet
- 4 1 Oscillations-3 PDFDocument11 pages4 1 Oscillations-3 PDFHeng LiNo ratings yet
- Coursebook Answers Chapter 12 Asal PhysicsDocument3 pagesCoursebook Answers Chapter 12 Asal Physicssalaudeenaliyah9No ratings yet
- Tutorial 1 c10Document14 pagesTutorial 1 c10Priyaa JayasankarNo ratings yet
- Physics Module - IIDocument219 pagesPhysics Module - IIAnwesh SahaNo ratings yet
- Derivation and Analysis of Some Wave EquationsDocument19 pagesDerivation and Analysis of Some Wave EquationsAxad Ali ChaudharyNo ratings yet
- WavesDocument18 pagesWavesMbrn AliNo ratings yet
- Weekly Learning Activity Sheets General Physics 1 Grade 12, Quarter 2, Week 4Document4 pagesWeekly Learning Activity Sheets General Physics 1 Grade 12, Quarter 2, Week 4Shekaina Faith Cuizon Lozada100% (2)
- TJD WaveNotesDocument82 pagesTJD WaveNotesTheodore Bouras-SoulimasNo ratings yet
- Waves: Any Picture You Think It Can Represent This ChapterDocument27 pagesWaves: Any Picture You Think It Can Represent This Chapterيزيد الزهرانيNo ratings yet
- Interference of Light by Mr. Charis Israel AnchaDocument11 pagesInterference of Light by Mr. Charis Israel AnchaCharis Israel Ancha100% (1)
- Calculation of Slowly Varying Drift ForcesDocument4 pagesCalculation of Slowly Varying Drift Forcesmohdsolihat1No ratings yet
- CH 15Document25 pagesCH 15MohammedNo ratings yet
- Advances in Structure Research by Diffraction Methods: Fortschritte der Strukturforschung mit BeugungsmethodenFrom EverandAdvances in Structure Research by Diffraction Methods: Fortschritte der Strukturforschung mit BeugungsmethodenR. BrillNo ratings yet
- Elements: Camera Natural Light Source White Card / ReflectorDocument3 pagesElements: Camera Natural Light Source White Card / ReflectorОлександр Царенко100% (1)
- Kuliah 5.1 - Indicatrix PDFDocument27 pagesKuliah 5.1 - Indicatrix PDFBERNARDUS ANGGIT WINAHYUNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 1 CHM 260Document9 pagesLab Report 1 CHM 260Hazwan HamimNo ratings yet
- Excitation of Plasmons and Interband Transitions by Electrons PDFDocument2 pagesExcitation of Plasmons and Interband Transitions by Electrons PDFRobNo ratings yet
- LPSR Based Paper - Optik JournalDocument12 pagesLPSR Based Paper - Optik JournalSK ChaulyaNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful WorldDocument8 pagesChapter 11 Human Eye and Colourful Worldapi-246793885No ratings yet
- Yag Comparison ChartDocument2 pagesYag Comparison ChartAbiNo ratings yet
- Heine XHL Xenon Halogen Bulbs: For Optimum Performance and Cost-EffectivenessDocument7 pagesHeine XHL Xenon Halogen Bulbs: For Optimum Performance and Cost-EffectivenessGunwant SinghNo ratings yet
- The Physics of Water Drops and Lift-OffDocument3 pagesThe Physics of Water Drops and Lift-OffBobapatatasNo ratings yet
- Kodak Easyshare Dx7590 Zoom Digital Camera: User'S GuideDocument82 pagesKodak Easyshare Dx7590 Zoom Digital Camera: User'S GuideDaryl Spindler SrNo ratings yet
- V-Ray DMC SamplerDocument13 pagesV-Ray DMC SamplerJayson Jedidiah UdangNo ratings yet
- JEE Main 2019 Paper Answer Physics 09-01-2019 1stDocument7 pagesJEE Main 2019 Paper Answer Physics 09-01-2019 1stDeepak SainiNo ratings yet
- Thickness and Surface Measurement of Transparent Thin-Film Layers Using White Light Scanning Interferometry Combined With ReflectometryDocument8 pagesThickness and Surface Measurement of Transparent Thin-Film Layers Using White Light Scanning Interferometry Combined With ReflectometryChang MingNo ratings yet
- Z730 ManualDocument79 pagesZ730 ManualJohn TaramasNo ratings yet
- Spectrophotometry ExperimentDocument8 pagesSpectrophotometry ExperimentDan ZhengNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2Document23 pagesChapter 2Patrick LenguajeNo ratings yet
- Grade 8 Science 1st Quarter ExamDocument5 pagesGrade 8 Science 1st Quarter ExamMjoyTibay100% (28)
- Laser PropertiesDocument13 pagesLaser PropertieszxcvuiopNo ratings yet
- Infrared Spectroscopy of Organic Compounds: College of Science, University of Santo Tomas, Manila, PhilippinesDocument3 pagesInfrared Spectroscopy of Organic Compounds: College of Science, University of Santo Tomas, Manila, PhilippinesJOHN JERALD VILLAMANCANo ratings yet
- Work Energy Power - 1Document10 pagesWork Energy Power - 1rahimuddinNo ratings yet
- ArtLantis Tutorial External LightingDocument3 pagesArtLantis Tutorial External LightingAndra PopaNo ratings yet
- FiO Final Program 2011Document132 pagesFiO Final Program 2011Sathish KumarNo ratings yet
- Physics (Specification A) PHA5/W Unit 5 Nuclear Instability: Astrophysics OptionDocument12 pagesPhysics (Specification A) PHA5/W Unit 5 Nuclear Instability: Astrophysics OptionAli WanNo ratings yet
- Topic 6 ALL Answers Pagenumber 1Document38 pagesTopic 6 ALL Answers Pagenumber 1Kevin OktaNo ratings yet
- The Real Biefeld Brown EffectDocument3 pagesThe Real Biefeld Brown EffectaxtimeNo ratings yet
- Contact LensesDocument28 pagesContact LensesDaniel IlievNo ratings yet
- Tutorial 1Document3 pagesTutorial 1doldolzzNo ratings yet
- Ifm TW7000 Infrared Temperature Sensor GB 2014Document5 pagesIfm TW7000 Infrared Temperature Sensor GB 2014ifm electronicNo ratings yet
- To Determine Radius of Curvature of A Given Spherical Surface by A SpherometerDocument3 pagesTo Determine Radius of Curvature of A Given Spherical Surface by A SpherometerYash TandonNo ratings yet
- Marks 23 Time: 30 Min: Advanced Institution of PhysicsDocument4 pagesMarks 23 Time: 30 Min: Advanced Institution of PhysicssdasdasNo ratings yet