Professional Documents
Culture Documents
DRUG-STUDY To Share
Uploaded by
John CincoOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
DRUG-STUDY To Share
Uploaded by
John CincoCopyright:
Available Formats
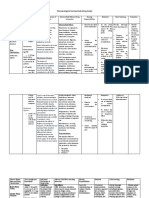
Date Specific Action Indications Contraindications Side/Adverse Effects Nsg.
Responsibilities
Generic name: Mechanism of action is Partial seizures (adjunct Contraindicated in: CNS: SUICIDAL THOUGHTS, ▹ Monitor closely for notable changes
Gabapentin not known. May affect treatment) (immediate- Hypersensitivity confusion, depression, in behavior that could indicate the
transport release only). dizziness, drowsiness, emergence or worsening of suicidal
Brand name: of amino acids across Postherpetic neuralgia. Use Cautiously in: sedation, anxiety, thoughts or behavior or depression.
Gralise, Horizant, and stabilize neuronal Restless legs syndrome All patients (may risk concentration difficulties ▹ Instruct patient to take medication
Neurontin membranes. (Horizant only). of suicidal (children), emotional lability exactly as directed. Do not double
thoughts/behaviors); (children), hostility, dose. Do not discontinue abruptly;
Dose: Therapeutic Effects: Unlabeled Use: Renal insufficiency hyperkinesia (children), may cause increase in frequency of
100 mg/tab ▹ Decreased Neuropathic pain. (dose and/or dosing malaise, vertigo, seizures.
incidence of Prevention of migraine interval if CCr ≤ 60 weakness. ▹ Advise patient not to take gabapentin
seizures. Decreased headache. Bipolar mL/min); OB: EENT: abnormal vision, within 2 hr of
Frequency: postherpetic pain. disorder. Anxiety. Pregnancy; nystagmus. an antacid.
OD Decreased leg Diabetic peripheral Pedi: Children < 18 yr CV: hypertension. ▹ May be administered without regard
restlessness. neuropathy. (sustained-/extended- GI: weight gain, anorexia, to meals.
Route: release) flatulence,
▹ Gabapentin may cause dizziness and
Oral Source: Davis’s Drug or < 3 yr (immediate- gingivitis.
drowsiness. Caution patient to avoid
Guide for Nurses, release) (safety not MS: RHABDOMYOLYSIS,
driving or activities requiring
Drug Classification: p601 established); arthralgia,qcreatine
alertness until response to
analgesic adjuncts, Lactation: kinase.
medication is known.
therapeutic, Discontinue drug or Neuro: ataxia, altered
▹ Advise patient and family to notify
anticonvulsants, bottle-feed; reflexes, hyperkinesia,
health care professional if thoughts
mood stabilizers Geri: May be more paresthesia.
about suicide or dying, attempts to
susceptible to toxicity Misc: MULTIORGAN
commit suicide; new or worse
due to age-related in HYPERSENSITIVITY
depression; new or worse anxiety;
renal function. REACTIONS,
feeling very agitated or restless; panic
facial edema.
attacks; trouble sleeping; new or
worse irritability; acting aggressive;
being angry or violent; acting on
dangerous impulses; an extreme
increase in activity and talking; or
other unusual changes in behavior or
mood occur.
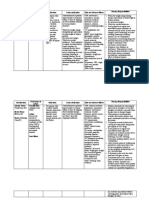
Date Specific Action Indications Contraindications Side/Adverse Effects Nsg. Responsibilities
Generic name: Bind to bacterial cell Treatment of the Contraindicated in: CNS: SEIZURES (high doses). ▹ Assess for infection (vital signs;
Cefuroxime wall membrane, causing following infections Hypersensitivity to GI: CLOSTRIDIUM DIFFICILE- appearance of wound, sputum, urine,
cell death. caused by susceptible cephalosporins ASSOCIATED DIARRHEA and stool; WBC) at beginning and
Brand name: organisms: Skin and skin Serious (CDAD), diarrhea, cramps, during therapy.
Ceftin, Zinacef Source: Davis’s Drug structure infections, Bone hypersensitivity to nausea, vomiting. ▹ Before initiating therapy, obtain a
Guide for Nurses, p289 and joint infections penicillins. Derm: rashes, urticaria. history to determine previous use of
Dose: Hemat: agranulocytosis, and reactions to penicillins or
750 mg bleeding ( with cefotetan and cephalosporins. Persons with a
cefoxitin), eosinophilia, negative history of penicillin
hemolytic anemia, sensitivity may still have an allergic
Frequency: neutropenia, response.
q 8h thrombocytopenia ▹ Obtain specimens for culture and
Local: pain at IM site, phlebitis sensitivity before initiating therapy.
Route: at IV site. First dose may be given before
IVTT Misc: allergic reactions receiving results.
including ANAPHYLAXIS ▹ Observe patient for signs and
Drug Classification: and SERUM SICKNESS, symptoms of anaphylaxis (rash,
- second-generation superinfection. pruritus, laryngeal edema, wheezing).
cephalosporins Discontinue the drug immediately if
- anti-infectives these symptoms occur. Keep
epinephrine, an antihistamine, and
resuscitation equipment close by in
the event of an anaphylactic reaction.
▹ Monitor bowel function. Diarrhea,
abdominal cramping, fever, and
bloody stools should be reported to
health care professional promptly as
a sign of Clostridium difficile-
associated diarrhea (CDAD). May
begin up to several weeks following
cessation of therapy.
▹ Instruct patient to take medication
around the clock at evenly spaced
times and to finish the medication
completely, even if feeling better.
Take missed doses as soon as
possible unless almost time for next
dose; do not double doses. Use
calibrated measuring device with
liquid preparations.
▹ Advise patient that sharing of this
medication may be dangerous.
▹ Advise patient to report signs of
superinfection (furry overgrowth on
the tongue, vaginal itching or
discharge, loose or foul-smelling
stools) and allergy.
▹ Instruct patient to notify health care
professional if fever and diarrhea
develop, especially if stool contains
blood, pus, or mucus. Advise patient
not to treat diarrhea without
consulting health care professional.
Date Specific Action Indications Contraindications Side/Adverse Effects Nsg. Responsibilities
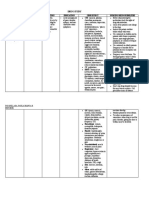
Generic name: Inhibits synthesis of Mild to moderate pain, Previous CNS: agitation ( in children) ▹ Assess overall health status and
Acetaminophen prostaglandins that may Moderate to severe pain hypersensitivity (IV), anxiety (IV), alcohol usage before administering
serve as mediators of with opioid analgesics Products containing headache (IV), fatigue (IV), acetaminophen. Patients who are
Brand name: pain and fever, primarily Fever. alcohol, aspartame, insomnia (IV). malnourished or chronically abuse
Paracetamol in the CNS. Has no saccharin, sugar, or Resp: atelectasis ( in children) alcohol are at higher risk of
significant anti- tartrazine (FDC yellow (IV), dyspnea (IV). developing hepatotoxicity with
Dose: inflammatory properties dye #5) should be CV: hypertension chronic use of usual doses of this
250 mg or GI toxicity. avoided in patients (IV), hypotension (IV). drug.
who have GI: HEPATOTOXICITY ▹ Assess amount, frequency, and type
Source: Davis’s Drug hypersensitivity or (DOSES), constipation (in of drugs taken in patients self-
Frequency: Guide for Nurses, p100 intolerance to these children) (IV), liver enzymes, medicating, especially with OTC
q 4h now then for compounds nausea (IV), vomiting (IV). drugs. Prolonged use of
T>38C° Severe hepatic F and E: hypokalemia (IV). acetaminophen increases risk of
impairment/ active GU: renal failure (high adverse hepatic and renal effects. For
Route: liver disease. doses/chronic use). short-term use, combined doses of
IVTT Hemat: neutropenia, acetaminophen and salicylates
pancytopenia. should not exceed the recommended
Drug Classification: MS: muscle dose of either drug given alone. Do
- Antipyretics spasms (IV), trismus (IV). not exceed maximum daily dose of
- NSAIDs Derm: ACUTE GENERALIZED acetaminophen when considering all
EXANTHEMATOUS routes of administration and all
PUSTULOSIS, STEVENS- combination products containing
JOHNSON SYNDROME, acetaminophen.
TOXIC EPIDERMAL ▹ Advise patient to take medication
NECROLYSIS, rash, urticaria. exactly as directed and not to take
more than the recommended
amount.
▹ Advise patient to discontinue
acetaminophen and notify health
care professional if rash occurs.
▹ Advise patient to consult health care
professional if discomfort or fever is
not relieved by routine doses of this
drug or if fever is greater than 39.5°C
(103°F) or lasts longer than 3 days.
Date Specific Action Indications Contraindications Side/Adverse Effects Nsg. Responsibilities
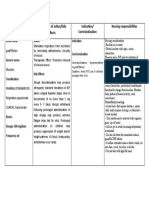
Generic name: Appears to inhibit DNA- Active tuberculosis (with Hypersensitivity CNS: ataxia, confusion, ▹ Perform mycobacterial studies and
Rifampicin dependent RNA other agents). Concurrent use of drowsiness, fatigue, susceptibility tests prior to and
polymerase in
Brand name: susceptible organisms. atazanavir, darunavir, headache, periodically during therapy to detect
Famtricin Forte fosamprenavir, weakness. possible resistance.
Source: Davis’s Drug saquinavir, tipranavir, Derm: rash, pruritus. ▹ Monitor hepatic function at least
Dose: Guide for Nurses, p1087 or ritonavir-boosted EENT: red discoloration monthly during therapy. May cause
200 mg/5 ml saquinavir. BUN, AST, ALT, and serum alkaline
of tears.
phosphatase, bilirubin, and uric acid
GI: abdominal pain,
concentrations.
diarrhea, flatulence,
Frequency: ▹ Administer medication on an empty
OD, 30 mins before heartburn, nausea,
stomach at least 1 hr before or 2 hr
meals vomiting,qliver enzymes, after meals with a full glass (240 mL)
red discoloration of water. If GI irritation becomes a
Route: of saliva. problem, may be administered with
Oral GU: red discoloration of food
urine. ▹ Advise patient to take medication
Drug Classification: Hemat: hemolytic anemia, once daily, as directed, and not to
- Anti-tuberculosis thrombocytopenia. skip doses or double up on missed
MS: arthralgia, muscle doses.
weakness, myalgia.
Misc: flu-like syndrome.
Date Specific Action Indications Contraindications Side/Adverse Effects Nsg. Responsibilities
Generic name: Inhibits mycobacterial First-line therapy of Hypersensitivity CNS: psychosis, seizures. ▹ May be administered with food or
Isoniazid cell wall synthesis and active tuberculosis, in Acute liver disease EENT: visual disturbances. antacids if GI irritation occurs,
interferes combination with other History of hepatitis GI: DRUG-INDUCED although antacids containing
Brand name: with metabolism. agents from previous use. HEPATITIS, nausea, aluminum should not be taken within
INH vomiting. 1 hr of administration.
Isotamine Source: Davis’s Drug Derm: rashes. ▹ Advise patient to notify health care
Guide for Nurses, p719 Endo: gynecomastia. professional promptly if signs and
Dose: symptoms of hepatitis (yellow eyes
Hemat: blood dyscrasias.
200mg/20mg/5ml and skin, nausea, vomiting, anorexia,
Neuro: peripheral
dark urine, unusual tiredness, or
Frequency: neuropathy.
weakness) or peripheral neuritis
OD, 30 mins before Misc: fever. (numbness, tingling, paresthesia)
meals occur.
▹ Advise patient to take medication as
Route: directed. Take missed doses as soon
Oral as possible unless almost time for
next dose; do not double up on
Drug Classification: missed doses. Emphasize the
- Anti-tuberculosis importance of continuing therapy
even after symptoms have subsided.
▹ Emphasize the importance of regular
follow-up physical and
ophthalmologic exams to monitor
progress and to check for side effects
Date Specific Action Indications Contraindications Side/Adverse Effects Nsg. Responsibilities
Generic name: Converted to pyrazinoic Used in combination with Hypersensitivity GI: HEPATOTOXICITY, ▹ Advise patient to take medication as
Pyrazinamide acid in susceptible other agents in the Cross-sensitivity with anorexia, diarrhea, nausea, directed and not to skip doses or
strains of treatment of active ethionamide, double up on missed doses. Take
Brand name: Mycobacterium which tuberculosis. isoniazid, niacin, or vomiting. missed doses as soon as remembered
Pyramin lowers the pH of the nicotinic acid may GU: dysuria. unless almost time for next dose.
environment. exist Derm: acne, itching, Emphasize the importance of
Dose: Severe liver photosensitivity, continuing therapy even after
250 mg/5 ml Source: Davis’s Drug impairment symptoms have subsided. Length of
rash.
Guide for Nurses, p1057 therapy depends on regimen being
Hemat: anemia,
used and underlying disease states.
thrombocytopenia.
Frequency: ▹ Advise patients to notify health care
TID, 30 mins before Metab: professional if no improvement is
meals hyperuricemia. noticed after 2–3 wk of therapy or if
MS: arthralgia, gouty fever, anorexia, malaise, nausea,
Route: arthritis vomiting, darkened urine, yellowish
IVTT discoloration of the skin and eyes,
pain, or swelling of the joints occurs.
Drug Classification: ▹ Advise patients to use sunscreen and
- Anti-tuberculosis protective clothing to prevent
photosensitivity reactions.
▹ Emphasize the importance of regular
follow-up exams to monitor progress
and check for side effects
Date Specific Action Indications Contraindications Side/Adverse Effects Nsg. Responsibilities
Generic name: Inhibits the growth of Active tuberculosis or Hypersensitivity CNS: confusion, dizziness, ▹ Assessments of visual function should
Ethambutol mycobacteria. other mycobacterial Optic neuritis. hallucinations, headache, be made frequently during therapy.
diseases (with at least malaise. Advise patient to report blurring of
Brand name: Source: Davis’s Drug one other drug). vision, constriction of visual fields, or
Hambutol Guide for Nurses, p530 EENT: optic neuritis. changes in color perception
GI: HEPATITIS, abdominal immediately. Visual impairment,
Dose: pain, anorexia, nausea, if not identified early, may lead to
400mg/tab vomiting. permanent sight impairment.
Metab: hyperuricemia. ▹ Instruct patient to take medication as
directed. Take missed doses as soon
MS: joint pain.
Frequency: as possible unless almost time for
OD, before meals Neuro: peripheral neuritis.
next dose; do not double up on
Resp: pulmonary infiltrates. missed doses. A full course of therapy
Route: Misc: anaphylactoid may take mo to yr. Do not
Oral reactions, fever. discontinue without consulting health
care professional, even though
Drug Classification: symptoms may disappear.
- Anti-tuberculosis ▹ Instruct patient to notify health care
professional if no improvement is
seen in 2–3 wk. Health care
professional should also be notified if
unexpected weight gain or decreased
urine output occurs.
▹ Emphasize the importance of routine
exams to evaluate progress and
ophthalmic examinations if signs of
optic neuritis occur.
Date Specific Action Indications Contraindications Side/Adverse Effects Nsg. Responsibilities
Generic name: Inhibits synthesis of Mild to moderate pain, Previous CNS: agitation ( in children) ▹ Assess overall health status and
Prednisone prostaglandins that may Moderate to severe pain hypersensitivity (IV), anxiety (IV), alcohol usage before administering
serve as mediators of with opioid analgesics Products containing headache (IV), fatigue (IV), acetaminophen. Patients who are
Brand name: pain and fever, primarily Fever. alcohol, aspartame, insomnia (IV). malnourished or chronically abuse
Biopred in the CNS. Has no saccharin, sugar, or Resp: atelectasis ( in children) alcohol are at higher risk of
significant anti- tartrazine (FDC yellow (IV), dyspnea (IV). developing hepatotoxicity with
Dose: inflammatory properties dye #5) should be CV: hypertension chronic use of usual doses of this
20mg/tab (1 tab) or GI toxicity. avoided in patients (IV), hypotension (IV). drug.
who have GI: HEPATOTOXICITY ▹ Assess amount, frequency, and type
Source: Davis’s Drug hypersensitivity or (DOSES), constipation (in of drugs taken in patients self-
Frequency: Guide for Nurses, p100 intolerance to these children) (IV), liver enzymes, medicating, especially with OTC
OD after meals for 2 compounds nausea (IV), vomiting (IV). drugs. Prolonged use of
weeks Severe hepatic F and E: hypokalemia (IV). acetaminophen increases risk of
impairment/ active GU: renal failure (high adverse hepatic and renal effects. For
Route: liver disease. doses/chronic use). short-term use, combined doses of
Oral Hemat: neutropenia, acetaminophen and salicylates
pancytopenia. should not exceed the recommended
Drug Classification: MS: muscle dose of either drug given alone. Do
- Corticosteroids spasms (IV), trismus (IV). not exceed maximum daily dose of
- Antiasthmatics Derm: ACUTE GENERALIZED acetaminophen when considering all
EXANTHEMATOUS routes of administration and all
PUSTULOSIS, STEVENS- combination products containing
JOHNSON SYNDROME, acetaminophen.
TOXIC EPIDERMAL ▹ Advise patient to take medication
NECROLYSIS, rash, urticaria. exactly as directed and not to take
more than the recommended
amount.
▹ Advise patient to discontinue
acetaminophen and notify health
care professional if rash occurs.
▹ Advise patient to consult health care
professional if discomfort or fever is
not relieved by routine doses of this
drug or if fever is greater than 39.5°C
(103°F) or lasts longer than 3 days.
Date Specific Action Indications Contraindications Side/Adverse Effects Nsg. Responsibilities
Generic name: Hyoscine Butylbromide relief of smooth muscle Previous dryness of the mouth, ▹ Be alert for adverse reactions and
Hyoscine butylbromide is a quaternary spasm of the hypersensitivity with difficulty in drug interactions.
ammonium gastrointestinal and Products containing swallowing
Brand name: antimuscarinic agent. genitourinary system alcohol, aspartame, thirst ▹ Assess for eye pain
Paracetamol Hyoscine butyl bromide
does not readily pass saccharin, sugar, or dilation of the pupils with
Dose: the blood-brain barrier. tartrazine (FDC yellow loss of accommodation ▹ Assess for urinary hesitancy
250 mg It’s a competitive dye #5) should be and photophobia
antagonist of the avoided in patients increased intra-ocular ▹ Assess for constipation
actions of acetylcholine who have pressure
Frequency: and other muscarinic hypersensitivity or flushing and dryness of ▹ Monitor urine output
q 4h agonists. The receptors intolerance to these the skin
affected are those of compounds bradycardia followed by ▹ Encourage patient to void.
Route: peripheral structures Severe hepatic tachycardia, with
IVTT that are either impairment/ active palpitations and ▹ Monitor BP for possible
stimulated or inhibited liver disease. arrhythmias hypertension.
Drug Classification: by muscarine, ie. urinary urgency with the
- Antispasmodic exocrine glands, smooth inability to do so, as well
and cardiac muscle. as reduction in the tone
and motility of the gastro-
Source: Davis’s Drug intestinal tract, leading to
Guide for Nurses, p100 constipation
occasionally
vomiting, giddiness
and staggering may
occur
restrosternal pain may
occur due to
increasedgastric reflux.
Date Specific Action Indications Contraindications Side/Adverse Effects Nsg. Responsibilities
Generic name: A coenzyme that Secondarily infected Contraindicated with Headache ▹ Monitor vital signs
Multivitamins + Vitamin stimulate metabolic traumatic skin lesions hypersensitivity to Paresthesia
B complex function and is needed caused by Staphylococcus Vit. B1, Vit. B2, Vit. B3 Blurred vision ▹ Give the drug with meals.
for cell replication, aureus and Streptococcus or any component of Rashes
Dose: hematopoiesis, and pyogenes theformulation. Wheezing ▹ Administer liquid preparations in
250 mg nucleoprotein and Active peptic ulcer Diarrhea water or juice to mask the taste and
myelin synthesis Severe hypotension Flatulence prevent staining of teeth.
Nausea andvomiting
Frequency: Source: Nursing Drug Irritation ▹ Warn the patient that stool may be
q 4h Guide 2016, Wolters Agitation dark or green
Kluwer, p1577 Slightly drop of blood
Route: pressure. ▹ Be alert for adverse reactions and
IVTT drug interactions.
Drug Classification:
- Vitamins and Minerals
Date Specific Action Indications Contraindications Side/Adverse Effects Nsg. Responsibilities
Generic name: Inhibits bacterial Secondarily infected Hypersensitivity to CNS: headache ▹ Assess lesions before and daily during
Mupirocin protein synthesis traumatic skin lesions mupirocin or EENT: cough, itching, therapy.
caused by Staphylococcus polyethylene glycol. GI: nausea; altered taste. ▹ Wash affected area with soap and
Dose: Source: Nursing Drug aureus and Streptococcus Derm: burning, itching, water and dry thoroughly. Apply a
250 mg Guide 2016, Wolters pyogenes small amount of mupirocin to the
pain, stinging.
Kluwer, p1577 affected area 3 times daily and rub in
gently. Treated area may be covered
Frequency: with gauze if desired.
q 4h ▹ Instruct patient on the correct
application of mupirocin.Advise
Route: patient to apply medication exactly as
Topical directed for the full course of
therapy. If a dose is missed, apply as
Drug Classification: soon as possible unless almost time
- Anti-infectives for next dose. Avoid contact with
eyes.
▹ Patient should consult health care
professional if
symptoms have not improved in 3–5
days.
You might also like
- APA - DSM5 - Level 2 Inattention Parent of Child Age 6 To 17 PDFDocument3 pagesAPA - DSM5 - Level 2 Inattention Parent of Child Age 6 To 17 PDFLiana Storm0% (1)
- A Guide To Clinical Case Study and Its PresentationDocument13 pagesA Guide To Clinical Case Study and Its PresentationVince Troy AquinoNo ratings yet
- PromethazineDocument3 pagesPromethazineGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Drug Study PDFDocument3 pagesTramadol Drug Study PDFMa. Eloisa YrogirogNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY LamotrigineDocument1 pageDRUG STUDY LamotrigineP B0% (2)
- Evidence Based Assessment of OCDDocument17 pagesEvidence Based Assessment of OCDDanitza YhovannaNo ratings yet
- Pharmacologic Class: Therapeutic Class: Atypical: Dibenzothiazepine Derivative AntipsychoticDocument2 pagesPharmacologic Class: Therapeutic Class: Atypical: Dibenzothiazepine Derivative AntipsychoticBianca Nicole Gacad Fernandez100% (1)
- DRUGSDocument5 pagesDRUGSDanica EspejoNo ratings yet
- Vision Ans MissionDocument11 pagesVision Ans MissionValarmathiNo ratings yet
- Nursing Theorists (W/ Their Theory/model) : Faye Glenn Abdellah Dorothy Johnson Imogene KingDocument3 pagesNursing Theorists (W/ Their Theory/model) : Faye Glenn Abdellah Dorothy Johnson Imogene KingRodel P. Elep IIINo ratings yet
- OlanzapineDocument3 pagesOlanzapineLeris Luigi VictorioNo ratings yet
- Nursing 110 FinalDocument36 pagesNursing 110 FinalAngel Lopez100% (1)
- ValiumDocument1 pageValiumJess MatiasNo ratings yet
- Reading Test-02 Part - B - CDocument15 pagesReading Test-02 Part - B - Cbinu mathai100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument4 pagesDrug StudyYasminGianneDeOcampoBarizoNo ratings yet
- Nursing Responsibilities Adverse Effect Indication / Contraindication Mechanism of Action Drug Name IndicationDocument1 pageNursing Responsibilities Adverse Effect Indication / Contraindication Mechanism of Action Drug Name IndicationOmar IzzoNo ratings yet
- Quetiapine Drug StudyDocument3 pagesQuetiapine Drug StudyEula Angelica Oco100% (1)
- Pregabalin LYricaDocument2 pagesPregabalin LYricaKristine Young100% (3)
- Demerol DrugDocument2 pagesDemerol DrugMsOrange100% (1)
- Final Drug Study.Document20 pagesFinal Drug Study.Bobbie Sison67% (3)
- Therapeutic Sheet: Date Specific Action Indications Contraindications Side/Adverse Effects Nsg. ResponsibilitiesDocument11 pagesTherapeutic Sheet: Date Specific Action Indications Contraindications Side/Adverse Effects Nsg. Responsibilitiesclydell joyce masiarNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Tramadol)Document1 pageDrug Study (Tramadol)Baji ۦۦNo ratings yet
- Clorazepate 3.75 MG Classification Action Indications Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument3 pagesClorazepate 3.75 MG Classification Action Indications Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesAirah Ramos PacquingNo ratings yet
- Drug Study GabapentinDocument3 pagesDrug Study Gabapentinbridget.badiang001No ratings yet
- Drowsiness, Sedation, LightDocument2 pagesDrowsiness, Sedation, LightGrape JuiceNo ratings yet
- Final Drug StudyDocument4 pagesFinal Drug StudyBasema HashhashNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY LevetiracetamDocument3 pagesDRUG STUDY LevetiracetamMaria Althea NajorraNo ratings yet
- Alprazolam BiperidinDocument6 pagesAlprazolam BiperidinFionah RetuyaNo ratings yet
- In Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in NCM 116-RLE Case StudyDocument7 pagesIn Partial Fulfillment of The Requirements in NCM 116-RLE Case Studynur aisa hamjaNo ratings yet
- DS Debie18 20Document6 pagesDS Debie18 20Irene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NameDocument2 pagesDrug Name Mecahnism of Action Indication Side Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic NamehahahaNo ratings yet
- Valproic Acid: Pharmacologic Class: CarboxylicDocument2 pagesValproic Acid: Pharmacologic Class: CarboxylicBianca Nicole Gacad FernandezNo ratings yet
- Fluphenazine Drug Study - DoxDocument3 pagesFluphenazine Drug Study - Doxan naNo ratings yet
- NCM 112 - Drug StudyDocument35 pagesNCM 112 - Drug StudyZoe WsetNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument5 pagesDrug StudyMAE RACHELLE LAMOSTENo ratings yet
- Brand Name: Chemical Effect: CNS: DizzinessDocument2 pagesBrand Name: Chemical Effect: CNS: DizzinessGwww BabababaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Sedation, Dizziness/vertigo, Headache, Hypotension Sweating, Nausea, VomitingDocument1 pageDrug Study: Sedation, Dizziness/vertigo, Headache, Hypotension Sweating, Nausea, VomitingJoshua DavantesNo ratings yet
- Mechanism of Action Prozac Anti-DepressantsDocument13 pagesMechanism of Action Prozac Anti-DepressantsJose Luis HernandezNo ratings yet
- FluoxetineDocument2 pagesFluoxetineSherena NicolasNo ratings yet
- Drug Study CCMHDocument35 pagesDrug Study CCMHJose Mari F. EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Drug Study: Davao Doctors College Nursing ProgramDocument4 pagesDrug Study: Davao Doctors College Nursing ProgramJiezl Abellano AfinidadNo ratings yet
- DS DR RodasDocument7 pagesDS DR RodasChristian MarquezNo ratings yet
- Classification Mechanism of Action Indication Contra-Indication Side and Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: ClassificationDocument3 pagesClassification Mechanism of Action Indication Contra-Indication Side and Adverse Effects Nursing Responsibilities Generic Name: ClassificationAngela NeriNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument3 pagesDrug StudyPang ProjectNo ratings yet
- Drug Therapeutic Record No. 1 (ANIMA BSN 2C)Document2 pagesDrug Therapeutic Record No. 1 (ANIMA BSN 2C)Rhea Mae S. AnimaNo ratings yet
- Mefenamic AcidDocument2 pagesMefenamic AcidHanz Abbigail RocoNo ratings yet
- DRUG STUDY ClonazepamDocument2 pagesDRUG STUDY ClonazepamP BNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Ni BobotDocument2 pagesDrug Study Ni BobotMaui LopezNo ratings yet
- Risperidone: Generic Name: ClassificationsDocument9 pagesRisperidone: Generic Name: ClassificationsColeen Mae CamaristaNo ratings yet
- Drug Study Module 4Document6 pagesDrug Study Module 4Hannah Angelu CabadingNo ratings yet
- Tramadol NestDocument9 pagesTramadol NestAbegail PolicarpioNo ratings yet
- Drug Study-AkinetonDocument2 pagesDrug Study-AkinetonKrizia KrizhNo ratings yet
- Tramadol Drug-StudyDocument3 pagesTramadol Drug-StudyPang ProjectNo ratings yet
- Drug StudyDocument2 pagesDrug StudyNorjana Hadji WahabNo ratings yet
- Print Drug StudDocument12 pagesPrint Drug StudGabriel HinolanNo ratings yet
- Drug Mechanism of Action/side Effects Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument1 pageDrug Mechanism of Action/side Effects Indication/ Contraindication Nursing ResponsibilitiesSheryhan Tahir BayleNo ratings yet
- Phenergin DrugDocument2 pagesPhenergin DrugMsOrangeNo ratings yet
- College of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDocument3 pagesCollege of Health Sciences: Urdaneta City UniversityDan Dan ManaoisNo ratings yet
- Drug Name Classification Dosage/ Indication Mechanism of Action Contraindication Side Effect/ Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument2 pagesDrug Name Classification Dosage/ Indication Mechanism of Action Contraindication Side Effect/ Adverse Effect Nursing ResponsibilitiesEula Angelica OcoNo ratings yet
- Drug Study OrthoDocument12 pagesDrug Study OrthoSienaNo ratings yet
- Case Presentation Station 3B Drug Study TramadolDocument3 pagesCase Presentation Station 3B Drug Study TramadolhahahahaaaaaaaNo ratings yet
- LevetiracetamDocument4 pagesLevetiracetamGwyn RosalesNo ratings yet
- THPDocument3 pagesTHPtonmoyNo ratings yet
- Drug Study (Acetaminophen)Document1 pageDrug Study (Acetaminophen)Kian HerreraNo ratings yet
- Course Task - Week 7Document34 pagesCourse Task - Week 7JoelynMacalintalNo ratings yet
- Abnormal Illness BehaviorDocument7 pagesAbnormal Illness Behavioransha2011p0% (1)
- The Following Resources Related To This Article Are Available Online atDocument8 pagesThe Following Resources Related To This Article Are Available Online atFerdina NidyasariNo ratings yet
- Revitears Study 2Document16 pagesRevitears Study 2office.hospimedNo ratings yet
- Community Health Nursing VocabDocument2 pagesCommunity Health Nursing VocabMaureen Beldorin0% (1)
- Priyanka Sen Final Practice School Internship ReportDocument35 pagesPriyanka Sen Final Practice School Internship ReportThakur Aditya PratapNo ratings yet
- 5,600 Residents Tested: Case SummaryDocument3 pages5,600 Residents Tested: Case SummaryPeterborough ExaminerNo ratings yet
- Nursing DiagnosisDocument3 pagesNursing DiagnosislesternNo ratings yet
- News Story 3Document2 pagesNews Story 3api-558280939No ratings yet
- Perioperative Nursing: Lecturer: Mr. Renato D. Lacanilao, RN, MANDocument27 pagesPerioperative Nursing: Lecturer: Mr. Renato D. Lacanilao, RN, MANJmarie Brillantes PopiocoNo ratings yet
- Secondary Amenorrhea Therapy With Accupu 2c484cf6Document5 pagesSecondary Amenorrhea Therapy With Accupu 2c484cf6NurNo ratings yet
- LeukocoriaDocument5 pagesLeukocoriabahaashakirNo ratings yet
- CraniomaDocument7 pagesCraniomaSophia BeecherNo ratings yet
- Allen Part Pedia CaseDocument3 pagesAllen Part Pedia CasePaul Michael Baguhin0% (1)
- Animal Care QP U1Document12 pagesAnimal Care QP U1boho14No ratings yet
- COPD Vs RLDDocument64 pagesCOPD Vs RLDXine DeeNo ratings yet
- CS 5 - Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy - EditedDocument3 pagesCS 5 - Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy - EditedKarishmaK.Dhanani100% (1)
- APAC Comarision of Registration Guidelines 2014 PDFDocument54 pagesAPAC Comarision of Registration Guidelines 2014 PDFAnu PariyarathNo ratings yet
- Pga R3Document71 pagesPga R3Samruddhi PataitNo ratings yet
- Biomedical Equipment Technology Bet1Document1 pageBiomedical Equipment Technology Bet1Rufaida HussainNo ratings yet
- Hypernatremia PediatricsDocument7 pagesHypernatremia PediatricsJOHANNESKIFENDINo ratings yet
- Int Endodontic J - 2022 - Shah - Outcomes Reporting in Systematic Reviews On Surgical Endodontics A Scoping Review For TheDocument22 pagesInt Endodontic J - 2022 - Shah - Outcomes Reporting in Systematic Reviews On Surgical Endodontics A Scoping Review For TheDhiaa AloweadatNo ratings yet
- Primary Lesion: Abdul Rashid Bin Tharek Group 90Document27 pagesPrimary Lesion: Abdul Rashid Bin Tharek Group 90rashidNo ratings yet
- Patient Record BookDocument1 pagePatient Record BooksumarumNo ratings yet