Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Assignment 02: 1 What Is Meant by Mathematical Modelling of A Control System
Uploaded by
Syed AfzalOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Assignment 02: 1 What Is Meant by Mathematical Modelling of A Control System
Uploaded by
Syed AfzalCopyright:
Available Formats
Syed M.
Afzal, 180401046
Assignment 02
1 What is meant by mathematical modelling of a control system.
The method of drawing block diagrams for structures in order to evaluate their output and transition
functions is known as mathematical modelling of a control system.
State-space representations are useful in optimal control problems. The transfer function representation, on
the other hand, could be more convenient than any other for transient-response or frequency-response
analysis of SISO, linear, time-invariant structures.
Various analytical and computational approaches for interpretation and synthesis can be utilized after
creating a mathematical model of a structure. The equations are normally differential equations since the
systems under consideration are complex. The Laplace transform will be used to simplify the solution
process if these equations can be linearized.
1.1 Types of Mathematical Models:
Differential Equation
Transfer Function
State Space Model
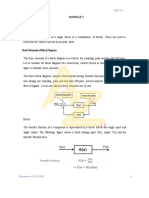
2 What does a block diagram represents? Explain it in detail.
A block diagram is a graphical depiction of a system that demonstrates how it operates. Block diagrams aid
in visualizing a shape’s capabilities and building hyperlinks within it. A block diagram's name comes from
the rectangular additives that make up the layout. They may be used to design hardware and software
program packages as well as to depict techniques. Block diagrams are defined and recognized in terms of
their cause and structure and their interconnections with different blocks.
A block diagram is a commonplace device for developing and documenting hardware and software
architecture, in addition to illustrating workflows and tactics. Block diagrams are used in electronics to
describe systems and their moving components which include within the trucking industry's mechatronic
systems.
Block diagrams are usually hired when it's crucial to depict information or control flows – or when systems
are involved. In this way, we may also constitute sophisticated algorithms, statistics flows, and verbal
exchange among diverse additives interior a big gadget, together with within a facility designed for mass
production. In certain instances, a graphical depiction is simpler to apprehend than a written description.
3 Enlist various rules of block diagram algebra.
The rules of block diagram algebra are as follows:
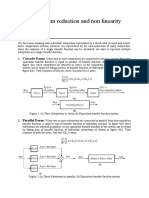
3.1 Rule 1
When blocks are connected in series. Their transfer function multiply with each other.
If two blocks are connected in series with transfer functions of G1 (block1) and G2 (block 2)
So their combine transfer function becomes G1G2.
Syed M.Afzal, 180401046
3.2 Rule 2
When blocks are connected in parallel. Their transfer function add with each other.
If two blocks are connected in parallel with transfer functions of G1 (block1) and G2 (block 2)
So their combine transfer function becomes G1+G2.
3.3 Rule 3
Moving the branch point ahead of a block.
It is done by taking reciprocal of a block function.
As we need to transfer the branch point at output without disturbing the output.
3.4 Rule 4
Moving the branch point before of a block.
It is done using the same block as we need same two outputs.
3.5 Rule 5
Moving summing ahead of block.
Using the comulative property add inputs first and then multiply it with the block is equal to multiply each
input with a block and then add both outputs.
So for simplification we convert it in this way.
3.6 Rule 6
Moving summing before a block.
It is done by multiplying a reciprocal of block so that when it further multiplies with the block after
addition then we get it as 1.
3.7 Rule 7
Interchanging summing point.
Suppose if we have three inputs A B and C. first two inputs A and B are adding with each other then the
input C will add. So we can interchange the summing point as by first adding A with C and then add B
with them or with another way by adding B and C and then add A.
3.8 Rule 8
Spliting of summing points.
Suppose three inputs are adding at one point so we break the summer into two so we add two inputs at a
time.
3.9 Rule 9
Elimination of a feedback.
It is done by making a transfer function depending upon positive and negative feedback and the used it as a
one block.
You might also like
- Transfer FunctionDocument11 pagesTransfer FunctionNagmani KumarNo ratings yet
- MSD2Document47 pagesMSD2moeNo ratings yet
- Control System LP 3Document13 pagesControl System LP 3Neans PlanterasNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram Reduction NotesDocument6 pagesBlock Diagram Reduction NotesMaMa BalochNo ratings yet
- BlockDiagram and Signal Flow GraphsDocument29 pagesBlockDiagram and Signal Flow GraphsDienies TorresNo ratings yet
- Feedback and Control System Module - 19Document28 pagesFeedback and Control System Module - 19AkiHiro San CarcedoNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram Algebra in Control Systems - GATE Study Material in PDFDocument6 pagesBlock Diagram Algebra in Control Systems - GATE Study Material in PDFPraveen AgrawalNo ratings yet
- Slides 3: Reduction of Multiple SystemsDocument25 pagesSlides 3: Reduction of Multiple SystemsAhmad AbunassarNo ratings yet
- Dynamic Topology Processing in A Radial Distribution SystemDocument9 pagesDynamic Topology Processing in A Radial Distribution Systemtoni andrianNo ratings yet
- Reduction of Multiple SubsystemsDocument38 pagesReduction of Multiple SubsystemsattayyabkhanNo ratings yet
- Study, Analysis and Evaluation of Block Diagram Reduction Name: University of Polytechnic/college ofDocument10 pagesStudy, Analysis and Evaluation of Block Diagram Reduction Name: University of Polytechnic/college ofTana AzeezNo ratings yet
- Coverage Analysis For Model Based Design Tools: William Aldrich The Mathworks, Inc. 3 Apple Hill Dr. Natick, Ma 02478Document17 pagesCoverage Analysis For Model Based Design Tools: William Aldrich The Mathworks, Inc. 3 Apple Hill Dr. Natick, Ma 02478Lindung SiswantoNo ratings yet
- Experiment 3Document7 pagesExperiment 3Usama NadeemNo ratings yet
- Objectives : Transfer Function +Document5 pagesObjectives : Transfer Function +Ehab SagaNo ratings yet
- Lecturer Two Summary Transfer Function of Physical SystemDocument5 pagesLecturer Two Summary Transfer Function of Physical SystemLiezel HenwoodNo ratings yet
- Signal Flow Graph and Block DiagramDocument23 pagesSignal Flow Graph and Block DiagramSolayao, Jan Marvin J.No ratings yet
- FeedCon (Unit 4)Document32 pagesFeedCon (Unit 4)Dovie MayNo ratings yet
- Controls Finals ResearchDocument15 pagesControls Finals ResearchRenz Xynor Liotib CadizNo ratings yet
- Unidad 2 Sistema Sec Uac I OnesDocument15 pagesUnidad 2 Sistema Sec Uac I OnesRAUL OSORIO RAMOSNo ratings yet
- Lab Report 05 56Document8 pagesLab Report 05 56MEEN201101056 KFUEITNo ratings yet
- Eee 336 L3Document24 pagesEee 336 L3Rezwan ZakariaNo ratings yet
- Modeling 101Document15 pagesModeling 101สหายดิว ลูกพระอาทิตย์No ratings yet
- Lab # 8 Control SystemDocument10 pagesLab # 8 Control SystemZabeehullahmiakhailNo ratings yet
- EEE 441 - Note IIDocument4 pagesEEE 441 - Note IIAlex Peter OnojaNo ratings yet
- Reduction of Multiple SubsystemsDocument40 pagesReduction of Multiple Subsystemsramisa rizwanNo ratings yet
- Multibody System Simulation With SimmechanicsDocument24 pagesMultibody System Simulation With SimmechanicsSonny Jason ANo ratings yet
- Block DiagramsDocument5 pagesBlock DiagramsumairelectNo ratings yet
- CSEXP2Document15 pagesCSEXP2Kavita DhamalNo ratings yet
- Fuzzy Flux EstimatorDocument9 pagesFuzzy Flux EstimatorMuhammad Ali Masood CheemaNo ratings yet
- Modeling and Digital Simulation Case Studies: 3.1 Pre-Lab AssignmentDocument13 pagesModeling and Digital Simulation Case Studies: 3.1 Pre-Lab AssignmentLittle_skipNo ratings yet
- DDLab ManualsDocument36 pagesDDLab Manualskelsiu1No ratings yet
- Lab Experiment # 03: ObjectiveDocument7 pagesLab Experiment # 03: ObjectiveMuhammad Samee baigNo ratings yet
- Efficient Simulation of Component-Based Hybrid Models Represented As Hybrid Bond GraphsDocument16 pagesEfficient Simulation of Component-Based Hybrid Models Represented As Hybrid Bond GraphsIbrahima GueyeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3: Block Diagram ModelsDocument4 pagesChapter 3: Block Diagram ModelsMuhammed IfkazNo ratings yet
- HLS AllocationDocument19 pagesHLS AllocationmohanraomamdikarNo ratings yet
- DC Motor Control 2017Document43 pagesDC Motor Control 2017Rasheed ShahNo ratings yet
- Mec500 Chapter 2 - AtmaDocument31 pagesMec500 Chapter 2 - AtmaFaez FeakryNo ratings yet
- Block DiagramDocument20 pagesBlock DiagramabcdeNo ratings yet
- ICOV MA-Mechanism-Design-Volume-I Erdman Sandors-164-188Document25 pagesICOV MA-Mechanism-Design-Volume-I Erdman Sandors-164-188Adit andriiNo ratings yet
- Control Systems Theory: Introduction To Block DiagramDocument47 pagesControl Systems Theory: Introduction To Block DiagramFadly ShafiqNo ratings yet
- FME 326 - Module 5 - Signal Flow and Block Diagram ModelsDocument47 pagesFME 326 - Module 5 - Signal Flow and Block Diagram ModelsJesse Jon FerolinoNo ratings yet
- Se ImpDocument5 pagesSe Impamyth89No ratings yet
- CS Mod2@AzDOCUMENTS - inDocument26 pagesCS Mod2@AzDOCUMENTS - insssNo ratings yet
- Lab # 8 SolvedDocument10 pagesLab # 8 SolvedZabeehullahmiakhailNo ratings yet
- Modern Control SystemDocument72 pagesModern Control SystemBewnet GetachewNo ratings yet
- Control Engineering Instructional Module LecturesDocument13 pagesControl Engineering Instructional Module LecturesJohn Kenneth Santiago PaulinoNo ratings yet
- Module 004 - Block Diagram of Control Systems: System ModelingDocument22 pagesModule 004 - Block Diagram of Control Systems: System ModelingDiane GutierrezNo ratings yet
- Antenna Azimuth Position Control System VerificationDocument4 pagesAntenna Azimuth Position Control System VerificationmsbajoriNo ratings yet
- Block Diagram and Signal Flow GraphDocument28 pagesBlock Diagram and Signal Flow GraphHarshaNo ratings yet
- Zahra AbdulHameed ShukrDocument11 pagesZahra AbdulHameed ShukrTana AzeezNo ratings yet
- Chapter 3 - Reduction of Multiple Subsystems PDFDocument28 pagesChapter 3 - Reduction of Multiple Subsystems PDFvisionNo ratings yet
- FeedConunit 2Document51 pagesFeedConunit 2Jerc ZajNo ratings yet
- ME340 Lab03 Handout Simulink IntroDocument8 pagesME340 Lab03 Handout Simulink IntroIbrahim MoamenNo ratings yet
- CS LabReport 2Document8 pagesCS LabReport 2Muhammad AfzaalNo ratings yet
- Lab #2: PI Controller Design and Second Order SystemsDocument4 pagesLab #2: PI Controller Design and Second Order SystemssamielmadssiaNo ratings yet
- Report 1 - Week 1 - Group 5Document10 pagesReport 1 - Week 1 - Group 5Bảo ThiênNo ratings yet
- Rabino Lineth B Activity-10 ConsyslabDocument10 pagesRabino Lineth B Activity-10 ConsyslabLineth RabinoNo ratings yet
- Automatic Control Systems I e LearningDocument9 pagesAutomatic Control Systems I e LearningAlfred K ChilufyaNo ratings yet
- Planar Linkage Synthesis: A modern CAD based approachFrom EverandPlanar Linkage Synthesis: A modern CAD based approachNo ratings yet
- 1 IntroductioDocument16 pages1 IntroductioSyed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Be Less Than The DC Term (Average Value)Document28 pagesBe Less Than The DC Term (Average Value)Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Document25 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- 7.13 Power Supply Control Input Voltage and Duty Ratio.: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Document12 pages7.13 Power Supply Control Input Voltage and Duty Ratio.: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Document25 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
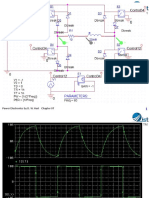
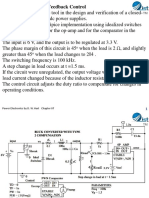
- Pspice Simulation of Feedback Control: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Document19 pagesPspice Simulation of Feedback Control: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- 2 PerceptionGDocument37 pages2 PerceptionGSyed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Chapter 2 SignalsDocument53 pagesChapter 2 SignalsSyed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Document20 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 04Document4 pagesPower Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 04Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pe 36 Ee17Document21 pagesPe 36 Ee17Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 06Document10 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 06Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Document18 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pe 38 Ee17Document22 pagesPe 38 Ee17Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 06Document19 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 06Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pe 27 Ee17Document11 pagesPe 27 Ee17Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pe 23 Ee17Document18 pagesPe 23 Ee17Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Assignment #02 - 15 Oct To 22 Oct 2021Document21 pagesAssignment #02 - 15 Oct To 22 Oct 2021Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 05Document20 pagesPower Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 05Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Document13 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 07Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Creating A DC Voltage From An AC Source: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Document41 pagesCreating A DC Voltage From An AC Source: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- For Different Values of ALPHA: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Document16 pagesFor Different Values of ALPHA: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Continuous-Current Case: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 06Document20 pagesContinuous-Current Case: Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 06Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Full-Wave Rectifier With RL-Source Load-Continuous Current: Power Electronics by D.W.Hart Chapter 04Document20 pagesFull-Wave Rectifier With RL-Source Load-Continuous Current: Power Electronics by D.W.Hart Chapter 04Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D.W.Hart Chapter 04Document12 pagesPower Electronics by D.W.Hart Chapter 04Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 01Document19 pagesPower Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 01Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Pe 26 Ee17Document23 pagesPe 26 Ee17Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Document15 pagesPower Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 03Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Fourier Series For A Periodic Function F (T) : Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02Document43 pagesFourier Series For A Periodic Function F (T) : Power Electronics by D. W. Hart Chapter 02Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Power Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 04Document13 pagesPower Electronics by Daniel W. Hart Chapter 04Syed AfzalNo ratings yet
- Sociology Internal AssessmentDocument21 pagesSociology Internal AssessmentjavoughnNo ratings yet
- BarDocument1 pageBarJoannalyn Libo-onNo ratings yet
- SAP Group Reporting 1909Document28 pagesSAP Group Reporting 1909SUDIPTADATTARAY86% (7)
- DSP UPG CU EngDocument1 pageDSP UPG CU EngArtur KwiatkowskiNo ratings yet
- ADCD LowDocument8 pagesADCD LowrahulmultivisionNo ratings yet
- Discovering JerusalemDocument134 pagesDiscovering JerusalemDzhel DezjayNo ratings yet
- The Light BulbDocument6 pagesThe Light Bulbapi-244765407No ratings yet
- معالجات ستاذ يزنDocument11 pagesمعالجات ستاذ يزنammerNo ratings yet
- CanagliflozinDocument7 pagesCanagliflozin13201940No ratings yet
- Richard Feynman - The Hierarchy of ComplexityDocument3 pagesRichard Feynman - The Hierarchy of ComplexityjacquesyvescaruanaNo ratings yet
- Tata Steel LTD.: Elements Unit Min Max RemarksDocument2 pagesTata Steel LTD.: Elements Unit Min Max RemarksPavan KumarNo ratings yet
- James Bruce, One of Russian Tsar Peter The Great's Key Advisors (1669-1735)Document2 pagesJames Bruce, One of Russian Tsar Peter The Great's Key Advisors (1669-1735)Johanna Granville100% (1)
- Affidavit of Insurance ClaimsDocument2 pagesAffidavit of Insurance Claimsشزغتحزع ىطشفم لشجخبهNo ratings yet
- Screen 2014 Uricchio 119 27Document9 pagesScreen 2014 Uricchio 119 27NazishTazeemNo ratings yet
- Hermes - GodDocument19 pagesHermes - GodAvocadoraNo ratings yet
- Walkie Talkie - 10 Codes - CommUSADocument1 pageWalkie Talkie - 10 Codes - CommUSASakthi VasuNo ratings yet
- Detailed Lesson Plan in English 2Document9 pagesDetailed Lesson Plan in English 2RENELYN PANSIPANSI100% (1)
- Syracuse University Dissertation FormatDocument4 pagesSyracuse University Dissertation FormatWritingContentNewYork100% (1)
- Review Problems Chapter 6Document8 pagesReview Problems Chapter 6Yue FeiNo ratings yet
- Aurora National High School: Report On AttendanceDocument2 pagesAurora National High School: Report On AttendanceLimuel CaringalNo ratings yet
- Wind Turbine Power Plant Seminar ReportDocument32 pagesWind Turbine Power Plant Seminar ReportShafieul mohammadNo ratings yet
- Activate My Win 7 Pro Product KeyDocument4 pagesActivate My Win 7 Pro Product KeydoktauNo ratings yet
- A Christmas Memory. Lesson - AnthologyDocument24 pagesA Christmas Memory. Lesson - AnthologySherry CallisonNo ratings yet
- Bubbles in Transformer Oil Dynamic Behavior Internal Discharge and Triggered Liquid BreakdownDocument9 pagesBubbles in Transformer Oil Dynamic Behavior Internal Discharge and Triggered Liquid BreakdownMuhammad Irfan NazhmiNo ratings yet
- HLSS 310 Critical Infrastructure ProtectionDocument12 pagesHLSS 310 Critical Infrastructure ProtectionMoffat HarounNo ratings yet
- Wooden Buildings: exposed to tiếp xúc với dramatic renewal sự làm mới đáng kểDocument6 pagesWooden Buildings: exposed to tiếp xúc với dramatic renewal sự làm mới đáng kểNguyễn Phạm Thảo NguyênNo ratings yet
- Pasir Ex UD - Am Tes 2024Document8 pagesPasir Ex UD - Am Tes 2024Achmad MaulanaNo ratings yet
- Spsi 622 Page Quattlebaum-Severecommunicationdisorders W Ecolog Inventory ExDocument25 pagesSpsi 622 Page Quattlebaum-Severecommunicationdisorders W Ecolog Inventory Exapi-270949898No ratings yet
- Table of Contents and Company Profile of JPCOM CARES STAC5Document4 pagesTable of Contents and Company Profile of JPCOM CARES STAC5Ch Ma100% (1)
- Pertemuan Ke 12 - The Passive VoiceDocument5 pagesPertemuan Ke 12 - The Passive VoiceZarNo ratings yet