Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Biochem Lec Reviewer
Uploaded by
ZULFHIKAR KAPUSANOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Biochem Lec Reviewer
Uploaded by
ZULFHIKAR KAPUSANCopyright:
Available Formats
PROTEINS 6.
Phenylalanine
7. Threonine
Most abundant substance in cell next to
8. Tryptophan
water (15% of cell mass).
9. Valine
Typical human cell (9,000) and human
body (100,000) proteins. 4 CATEGORIES ACCORDING TO SIDE CHAIN
All proteins contain Carbon, Hydrogen, POLARITY
Oxygen, Nitrogen and Sulfur.
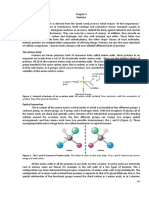
1. NON POLAR AMINO ACID- one (-NH2) &
Protein is unbranched polymer,
(-COOH) group + nonpolar side chain.
monomer unit= Amino Acid.
(Glycine, Alanine, Valine, Leucine,
Synthesis of enzymes, hormones, tissue
Isoleucine, Proline, Phenylalanine,
repair & energy.
Methionine,Tryptophan)
Presence of nitrogen (15.4%) sets them
apart from lipids & carbohydrates. -Hydrophobic when in protein, found
Casein- phosphorus (important for interior of proteins (less contact w/ H2O)
infants); Hemoglobin-iron (O2
-Nine non polar amino acid; Tryptophan
transport).
(water could H bond with NH ring).
AMINO ACIDS- Building Blocks of Protein.
-3 TYPES OF POLAR AMINO ACIDS, varying
Amino acids contain both Amino degrees for water affinity.
group(-H2N) and Carboxyl Group (-
-Hydrophilic within protein, often on
COOH)
protein surface.
a- amino acid= amino and carboxyl
group attached to a-carbon. 2. POLAR NEUTRAL AMINO ACID- one (-
R group =Side chains(distinguishes a- NH2) & (-COOH) group + polar but neutral
amino acids from each other). side chain. Ph neither basic or acidic. 6
Vary in size, charge, functional group, amino acids. (Serine, Cysteine, Threonine,
hydrogen bonding & chemical Asparagine, Glutamine, Tyrosine)
reactivity.
-more soluble in water R group can H bond
PROTEINS- is a chain of amino acids bond to one to H2O.
another by peptide bonds.
3. POLAR ACIDIC AMINO ACID- one (-NH2)
NON ESSENTIAL AMINO ACIDS- can get and two (-COOH) group 2nd (-COOH) group
from foods and can make ourselves. part of side chain. (Aspartic acid & Glutamic
acid).
1. Alanine
2. Asparagine 4. POLAR BASIC AMINO ACID- two (-NH2) &
3. Aspartic acid One (-COOH) group. (Histidine, Lysine,
4. Glutamic acid Arginine).
5. Serine
CONDITIONALLY ESSENTIAL AMINO ACIDS
-Healthy bodies can make them.
–Can’t make in starvation or inborn error of
metabolism.
1. Arginine
2. Cysteine
3. Glutamine
4. Glycine
5. Proline
6. Tyrosine
ESSENTIAL AMINO ACIDS- Can ONLY get from
food.
1. Histidine
2. Isoleucine
3. Leucine
4. Lysine
5. Methionine
You might also like
- Diesel Engines For Vehicles D2066 D2676Document6 pagesDiesel Engines For Vehicles D2066 D2676Branislava Savic63% (16)
- The DIRKS Methodology: A User GuideDocument285 pagesThe DIRKS Methodology: A User GuideJesus Frontera100% (2)
- Method Statement FINALDocument61 pagesMethod Statement FINALshareyhou67% (3)
- Assignment November11 KylaAccountingDocument2 pagesAssignment November11 KylaAccountingADRIANO, Glecy C.No ratings yet
- Post Renaissance Architecture in EuropeDocument10 pagesPost Renaissance Architecture in Europekali_007No ratings yet
- Biochem MidtermsDocument3 pagesBiochem MidtermsJhayneNo ratings yet
- PROTEINSDocument12 pagesPROTEINSSheena Liegh EntredichoNo ratings yet
- Characteristics of Proteins-SemifinalDocument3 pagesCharacteristics of Proteins-SemifinalKazylle TestaNo ratings yet
- الحموض الامينية معدل PDFDocument34 pagesالحموض الامينية معدل PDFleo kadehjianNo ratings yet
- Part 1 Proteins BiomoleculesDocument8 pagesPart 1 Proteins BiomoleculessamanthaNo ratings yet
- PROTEINS p1Document5 pagesPROTEINS p1Biang AbdullahNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry: Department of Physical Sciences College of ScienceDocument11 pagesBiochemistry: Department of Physical Sciences College of ScienceArianne ManaloNo ratings yet
- Biochem MidtermsDocument4 pagesBiochem MidtermschristinejeancenabreNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids: PropertiesDocument6 pagesAmino Acids: Propertiesmarie daitolNo ratings yet
- 12.protein - Rista Ajeng Mitasari - 18030194066 - PKU2018Document31 pages12.protein - Rista Ajeng Mitasari - 18030194066 - PKU2018Rista AjengNo ratings yet
- RayeDocument21 pagesRayeAngeline Raye RamosNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids: Associate Professor Ljiljana Andrijević Department of BiochemistryDocument41 pagesAmino Acids: Associate Professor Ljiljana Andrijević Department of BiochemistryVanja PlavšićNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Notes MidtermDocument13 pagesBiochemistry Notes MidtermCeline Ricci AbrahamNo ratings yet
- ProteinsDocument6 pagesProteinsAlliyah Gail LoraniaNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and Polypeptides NotesDocument4 pagesAmino Acids and Polypeptides Notesferdinand padillaNo ratings yet
- Module 5 Amino Acids, Proteins and Nucleic AcidsDocument25 pagesModule 5 Amino Acids, Proteins and Nucleic AcidsBig BrotherNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid 1Document30 pagesAmino Acid 1Siddharth RajamohananNo ratings yet
- 6 Prelims Proteins 1.0Document38 pages6 Prelims Proteins 1.0jdairoNo ratings yet
- Proteins 1Document15 pagesProteins 1Joanna Marie TulioNo ratings yet
- 3 Amino AcidsDocument45 pages3 Amino AcidsBereket Agumas KegneNo ratings yet
- Krislyn Diane Paradero Maano - BIO 024 - SESSION 5Document9 pagesKrislyn Diane Paradero Maano - BIO 024 - SESSION 5Krislyn MaanoNo ratings yet
- Amino AcidsDocument25 pagesAmino AcidsHeddy Myoi100% (1)
- 1 Aminoacids Protein 1Document51 pages1 Aminoacids Protein 1leylaNo ratings yet
- 3 Amino AcidsDocument47 pages3 Amino AcidsBereket Agumas KegneNo ratings yet
- Biochem Lesson 1Document2 pagesBiochem Lesson 1hello baiNo ratings yet
- Protein 2021Document29 pagesProtein 2021Dr. Mohamed ShamsNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid PDFDocument3 pagesAmino Acid PDFGio RiveraNo ratings yet
- ProteinDocument6 pagesProteinAbdullah Al MamunNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids - Properties, Structure, Classification, FunctionsDocument6 pagesAmino Acids - Properties, Structure, Classification, Functionssattyadev95No ratings yet
- Amino Acids & Proteins PDFDocument135 pagesAmino Acids & Proteins PDFJoelle AwarNo ratings yet
- Lec Amino Acid MBBSDocument28 pagesLec Amino Acid MBBSsanayaNo ratings yet
- Anupam Kumari AMINO ACID STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATIONDocument11 pagesAnupam Kumari AMINO ACID STRUCTURE AND CLASSIFICATIONAbhishek BarnwalNo ratings yet
- Proteinsoct 2016Document28 pagesProteinsoct 2016Abhimanyu BalyanNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and Peptides HoDocument17 pagesAmino Acids and Peptides Hochristian redotaNo ratings yet
- Activity 3 - Amino Acids and PeptidesDocument7 pagesActivity 3 - Amino Acids and PeptidesKate MendozaNo ratings yet
- Proteins TransesDocument10 pagesProteins TransesGwyn CaigoyNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids: Prepared By: KEYAM NIEL B. RACEDocument19 pagesAmino Acids: Prepared By: KEYAM NIEL B. RACEAizelle Taratara FaderoNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids: M. Sc. Ist SemDocument17 pagesAmino Acids: M. Sc. Ist SemGaming StuffNo ratings yet
- Shaha, Tal. Sinnar, Dist. Nashik: S.D.Jadhav English Medium SchoolDocument178 pagesShaha, Tal. Sinnar, Dist. Nashik: S.D.Jadhav English Medium SchoolGanesh PatilNo ratings yet
- Post Lab Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument85 pagesPost Lab Amino Acids and ProteinsELAINE MARIEJOY MANGAOILNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter 4Document16 pagesBiochemistry Chapter 4Jayson AguilarNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Week 7 - ProteinsDocument6 pagesBiochemistry Week 7 - ProteinsMicah JadeNo ratings yet
- CHY 47 Topic 4 2nd Sem 2018-2019 Protein Amino Acid PDFDocument129 pagesCHY 47 Topic 4 2nd Sem 2018-2019 Protein Amino Acid PDFHA RENo ratings yet
- Proteins: Biochemistry Handout - Proteins Prepared By: Cynthia Claire Guinto, RPH, CPH Sac (Sept 2021)Document9 pagesProteins: Biochemistry Handout - Proteins Prepared By: Cynthia Claire Guinto, RPH, CPH Sac (Sept 2021)Mark Jade Llena BernilNo ratings yet
- ch2 .ST - Medical - Protein1-MedDocument50 pagesch2 .ST - Medical - Protein1-Medsultan khabeebNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid1Document24 pagesAmino Acid1eshaanihsNo ratings yet
- Amino Acid NotesDocument4 pagesAmino Acid NotesCZARINA TUAZONNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and ProteinDocument44 pagesAmino Acids and ProteinAliyu MohammedNo ratings yet
- Proteins Proteins: DefinitionDocument5 pagesProteins Proteins: DefinitionPaula EdanoNo ratings yet
- 2 MTCHM3 LEC ProteinsDocument6 pages2 MTCHM3 LEC ProteinsMahal BarrosoNo ratings yet
- Amino Acids and ProteinsDocument62 pagesAmino Acids and Proteinsabaynehadisu53No ratings yet
- 3 - Biochemistry - 3rd Year Chem - Protein Structure and Function - Chapter-3Document21 pages3 - Biochemistry - 3rd Year Chem - Protein Structure and Function - Chapter-3MD. SAJID GHUFRANNo ratings yet
- Foods and Nutrition Paper OneDocument119 pagesFoods and Nutrition Paper OneNaduku EridadiNo ratings yet
- C4 ProteinsDocument34 pagesC4 ProteinsSoraya Al-obinayNo ratings yet
- Biochemistry Chapter 4Document17 pagesBiochemistry Chapter 4Jayson AguilarNo ratings yet
- Lecture 1 - Aminoacids. Peptides. ProteinsDocument33 pagesLecture 1 - Aminoacids. Peptides. ProteinsEiad SamyNo ratings yet
- AminoacidDocument28 pagesAminoacidapi-267795899No ratings yet
- Protein and Amino Acid Chemistry By: Dr. Hena Alcantara: BiochemistryDocument7 pagesProtein and Amino Acid Chemistry By: Dr. Hena Alcantara: BiochemistryRay Emmanuel Enriquez DomingoNo ratings yet
- Presentase A Amino AcidDocument23 pagesPresentase A Amino AcidMustopa TurmudziNo ratings yet
- The Peptides: Volume II Synthesis, Occurrence, and Action of Biologically Active PolypeptidesFrom EverandThe Peptides: Volume II Synthesis, Occurrence, and Action of Biologically Active PolypeptidesNo ratings yet
- 2022 AMR Dashboard Funding Opportunity Announcement 11.18.2022Document16 pages2022 AMR Dashboard Funding Opportunity Announcement 11.18.2022Tuhin DeyNo ratings yet
- Written Report SampleDocument16 pagesWritten Report Sampleallanposo3No ratings yet
- Current Harmonics: Electric Power System Power QualityDocument3 pagesCurrent Harmonics: Electric Power System Power QualityAlliver SapitulaNo ratings yet
- Agrinome For Breeding - Glossary List For Mutual Understandings v0.3 - 040319Document7 pagesAgrinome For Breeding - Glossary List For Mutual Understandings v0.3 - 040319mustakim mohamadNo ratings yet
- OBOE GougerDocument2 pagesOBOE GougerCarlos GaldámezNo ratings yet
- QAU TTS Form Annual AssessmentDocument6 pagesQAU TTS Form Annual AssessmentsohaibtarikNo ratings yet
- BSRM Ultima BrochureDocument2 pagesBSRM Ultima BrochuresaifuzzamanNo ratings yet
- Ppap - 2556 PDFDocument7 pagesPpap - 2556 PDFMohamed ElmakkyNo ratings yet
- SHS G11 Reading and Writing Q3 Week 1 2 V1Document15 pagesSHS G11 Reading and Writing Q3 Week 1 2 V1Romeo Espinosa Carmona JrNo ratings yet
- Measuring Road Roughness by Static Level Method: Standard Test Method ForDocument6 pagesMeasuring Road Roughness by Static Level Method: Standard Test Method ForDannyChaconNo ratings yet
- Wordbank 15 Coffee1Document2 pagesWordbank 15 Coffee1akbal13No ratings yet
- Makalah Bahasa Inggris TranslateDocument14 pagesMakalah Bahasa Inggris TranslatevikaseptideyaniNo ratings yet
- 16 - Ocean Currents & Salinity Interactive NotebookDocument23 pages16 - Ocean Currents & Salinity Interactive NotebookRaven BraymanNo ratings yet
- DBM Uv W ChartDocument2 pagesDBM Uv W ChartEddie FastNo ratings yet
- Bichelle HarrisonDocument2 pagesBichelle HarrisonShahbaz KhanNo ratings yet
- Microsoft Powerpoint BasicsDocument20 pagesMicrosoft Powerpoint BasicsJonathan LocsinNo ratings yet
- APJ Abdul Kalam Success StoryDocument1 pageAPJ Abdul Kalam Success StorySanjaiNo ratings yet
- CV Ashish PDFDocument3 pagesCV Ashish PDFRoshan KejariwalNo ratings yet
- The Phases of The Moon Station Activity Worksheet Pa2Document3 pagesThe Phases of The Moon Station Activity Worksheet Pa2api-284353863100% (1)
- WSD M1a283 B50Document9 pagesWSD M1a283 B50'Lampa'No ratings yet
- Communication Skill - Time ManagementDocument18 pagesCommunication Skill - Time ManagementChấn NguyễnNo ratings yet
- Chapter1 Intro To Basic FinanceDocument28 pagesChapter1 Intro To Basic FinanceRazel GopezNo ratings yet
- Level of Organisation of Protein StructureDocument18 pagesLevel of Organisation of Protein Structureyinghui94No ratings yet
- Sheetal PatilDocument4 pagesSheetal PatilsheetalNo ratings yet
- Study and Interpretation of The ScoreDocument10 pagesStudy and Interpretation of The ScoreDwightPile-GrayNo ratings yet