Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : Russel Cepriano V151622 MOA Feb 2021
Uploaded by
Yeasa DolleteOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : Russel Cepriano V151622 MOA Feb 2021
Uploaded by
Yeasa DolleteCopyright:
Available Formats
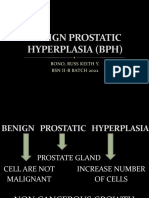
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) also called prostate gland enlargement is a common
condition as men get older. An enlarged prostate gland can cause uncomfortable urinary
symptoms, such as blocking the flow of urine out of the bladder. It can also cause bladder,
urinary tract or kidney problems. There are several effective treatments for prostate gland
enlargement, including medications, minimally invasive therapies and surgery. To choose the
best option, you and your doctor will consider your symptoms, the size of your prostate, other
health conditions you might have and your preferences.
The severity of symptoms in people who have prostate gland enlargement varies, but symptoms
tend to gradually worsen over time. Common signs and symptoms of BPH includes frequent or
urgent need to urinate, increased frequency of urination at night (nocturia), difficulty starting
urination, weak urine stream or a stream that stops and starts, dribbling at the end of urination
and inability to completely empty the bladder. The size of your prostate doesn't necessarily
determine the severity of your symptoms. Some men with only slightly enlarged prostates can
have significant symptoms, while other men with very enlarged prostates can have only minor
urinary symptoms. In some men, symptoms eventually stabilize and might even improve over
time. Other possible causes of urinary symptoms Conditions that can lead to symptoms similar to
those caused by enlarged prostate includes urinary tract infection, inflammation of the prostate
(prostatitis), narrowing of the urethra (urethral stricture), scarring in the bladder neck as a result
of previous surgery, bladder or kidney stones, problems with nerves that control the bladder and
cancer of the prostate or bladder.
Russel Cepriano V151622 MOA Feb 2021
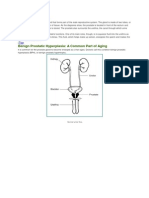
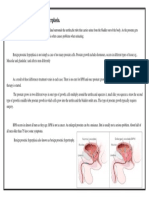
The prostate gland is located beneath your bladder. The tube that transports urine from the
bladder (urethra) passes through the center of the prostate. When the prostate enlarges, it begins
to block urine flow. In many men, this continued growth enlarges the prostate enough to cause
urinary symptoms or to significantly block urine flow. It isn't entirely clear what causes the
prostate to enlarge. However, it might be due to changes in the balance of sex hormones as men
grow older. Complications of an enlarged prostate can include sudden inability to urinate
(urinary retention), Urinary tract infections (UTIs), Bladder stones, Bladder damage and Kidney
damage.
In conclusion, most men with an enlarged prostate don't develop these benign prostatic
hyperplasia complications. However, acute urinary retention and kidney damage can be serious
health threats. Having an enlarged prostate is not believed to increase your risk of developing
prostate cancer. If you have mild symptoms, you may want to make some lifestyle changes to
help manage them. Try to limit the fluids you drink, especially before bedtime. Also try to avoid
fluids with caffeine (such as coffee or soda) and spicy foods.
Bibliography:
[ CITATION htt6 \l 1033 ]
[ CITATION htt7 \l 1033 ]
Russel Cepriano V151622 MOA Feb 2021
You might also like
- The Essential Guide For Good Prostate Health: in This Issue - .Document9 pagesThe Essential Guide For Good Prostate Health: in This Issue - .untarai100% (1)
- Prostatitis: Symptoms, Causes and TreatmentsDocument16 pagesProstatitis: Symptoms, Causes and TreatmentsjoserodrrNo ratings yet
- Proatate Enlargment & BPH TreatmentDocument12 pagesProatate Enlargment & BPH TreatmentprosmanNo ratings yet
- Enlarged Prostate Booklet PDFDocument52 pagesEnlarged Prostate Booklet PDFnabin hamalNo ratings yet
- Types, causes, symptoms and diagnosis of urinary incontinenceDocument12 pagesTypes, causes, symptoms and diagnosis of urinary incontinenceAmrit Preet KaurNo ratings yet
- Manual For Dental TechniciansDocument186 pagesManual For Dental Techniciansstabik96% (23)
- Benign Prostate HyperplasiaDocument49 pagesBenign Prostate HyperplasiaRohani TaminNo ratings yet
- Understanding the prostate gland and BPH symptomsDocument14 pagesUnderstanding the prostate gland and BPH symptomsRheena PadayNo ratings yet
- Medscape BPHDocument41 pagesMedscape BPHEugenia ShepanyNo ratings yet
- BPH Guide: Symptoms, Causes and Diagnostic TestsDocument57 pagesBPH Guide: Symptoms, Causes and Diagnostic TestsDiannetotz MoralesNo ratings yet
- 1 BPHDocument27 pages1 BPHVikrant GholapNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocument9 pagesBenign Prostatic HyperplasiaElizabeth Mapa100% (1)
- (Medical Masterclass) Coll.-Infectious Diseases and DermatologyDocument333 pages(Medical Masterclass) Coll.-Infectious Diseases and DermatologyVijay Mg100% (2)
- Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocument20 pagesBenign Prostatic HyperplasiaOepil Kirick100% (1)
- Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocument17 pagesBenign Prostatic HyperplasiaAyuNo ratings yet
- Microbiologist: 3.1.5 Isolation & Gram StainingDocument5 pagesMicrobiologist: 3.1.5 Isolation & Gram Stainingapi-534896073No ratings yet
- BPH and BOO Nursing CareDocument73 pagesBPH and BOO Nursing CareSwe Zin NaingNo ratings yet
- NP1 - ToprankDocument16 pagesNP1 - ToprankAllaiza Cristille100% (1)
- BPH Symptoms, Risk Factors, and TreatmentDocument15 pagesBPH Symptoms, Risk Factors, and TreatmentIrene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia BPHDocument14 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia BPHIrene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia BPHDocument14 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia BPHIrene Grace BalcuevaNo ratings yet
- Manage Urinary Tract Problems with BPH TreatmentDocument11 pagesManage Urinary Tract Problems with BPH TreatmentLovely DaroleNo ratings yet
- What Are Prostate Problems?Document2 pagesWhat Are Prostate Problems?Okki Masitah Syahfitri NasutionNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : Russel Cepriano V151622 MOA Feb 2021Document2 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : Russel Cepriano V151622 MOA Feb 2021Yeasa DolleteNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)Document5 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)Suneel Kumar PrajapatiNo ratings yet
- The Prostate GlandDocument8 pagesThe Prostate GlandRACHMAH KURNIASARINo ratings yet
- Education On Prostate HealthDocument4 pagesEducation On Prostate HealthAsobo-khan NkengNo ratings yet
- Everything You Need to Know About BPHDocument3 pagesEverything You Need to Know About BPHAIMNo ratings yet
- BPH InternetDocument72 pagesBPH InternetDesty ArianiNo ratings yet
- What Is The Prostate Gland?Document5 pagesWhat Is The Prostate Gland?Sienny AgustinNo ratings yet
- Types of Incontinence: Pertinent Negatives? Fever Chills Malaise Dysuria Perineal or Rectal PainDocument4 pagesTypes of Incontinence: Pertinent Negatives? Fever Chills Malaise Dysuria Perineal or Rectal PainDanekka TanNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Presented By: 2BSN2 - Group 6Document34 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia: Presented By: 2BSN2 - Group 6Hazel Ann MolinoNo ratings yet
- WONG Activity#9Document4 pagesWONG Activity#9Lecery Sophia WongNo ratings yet
- Enlarged Prostate (BPH) With Insignificant PVRDocument6 pagesEnlarged Prostate (BPH) With Insignificant PVRAshish KumarNo ratings yet
- PROSTATE - Press Release FINALDocument2 pagesPROSTATE - Press Release FINALParag DhurkeNo ratings yet
- Prostate & Homoeopathic ManagementDocument69 pagesProstate & Homoeopathic ManagementSasiikumar Vattiyoorkavu Sankaran NairNo ratings yet
- What Is Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocument3 pagesWhat Is Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaLeo CortinaNo ratings yet
- Prostate Enlargement (BPH) : What Is The Prostate?Document2 pagesProstate Enlargement (BPH) : What Is The Prostate?murti_fatiyaNo ratings yet
- Urogenital SystemDocument32 pagesUrogenital SystemLove & Humanity100% (1)
- Prostate Hyperplasia GuideDocument36 pagesProstate Hyperplasia GuideGerald FilomenoNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostate HypertrophyDocument26 pagesBenign Prostate Hypertrophybkbaljeet116131No ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia Treatment and SymptomsDocument9 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia Treatment and SymptomsSALOME PANTOJANo ratings yet
- Urinary Problems and Common CausesDocument6 pagesUrinary Problems and Common CausesHikari 光 ShidouNo ratings yet
- LBM 6syifaaaDocument29 pagesLBM 6syifaaasyifa dianNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)Document3 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)Shahmeer KhanNo ratings yet
- BPH GuideDocument7 pagesBPH GuideSomesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Jê Jê Jê JêDocument2 pagesJê Jê Jê JêRaymond Zamora HijaraNo ratings yet
- Urinary Tract Obstruction in Children: StudentDocument9 pagesUrinary Tract Obstruction in Children: StudentAmeer AlghazaliNo ratings yet
- امير ستار الاطفالDocument9 pagesامير ستار الاطفالAmeer AlghazaliNo ratings yet
- BPH - TextDocument7 pagesBPH - TextSomesh GuptaNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocument9 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasiaanju rachel joseNo ratings yet
- Prostate HealthDocument13 pagesProstate Healthapi-243453649No ratings yet
- Microsoft Office 2000Document3 pagesMicrosoft Office 2000Paillin EyeNo ratings yet
- LBM 6 SGD 7 UgDocument10 pagesLBM 6 SGD 7 UgngrhoNo ratings yet
- Benigna Hiperplasia ProstatDocument23 pagesBenigna Hiperplasia ProstatShanti ArianiNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : University of California, San FranciscoDocument1 pageBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : University of California, San FranciscoMaich ScdNo ratings yet
- Anatomy of Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocument1 pageAnatomy of Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaKeanno James O. GardeNo ratings yet
- Case 2 ReflectionDocument5 pagesCase 2 ReflectionAmaNo ratings yet
- Prostatectomy Procedures and Risks ExplainedDocument11 pagesProstatectomy Procedures and Risks ExplainedPhyan HyunNo ratings yet
- AssignmentLec12_RodriguezDocument2 pagesAssignmentLec12_RodriguezRAZELLE JOY CATIAN RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Bladder Stones: CausesDocument2 pagesBladder Stones: CausesDokter FransNo ratings yet
- Inkontenensia Urine MayoDocument4 pagesInkontenensia Urine MayoirvanagheNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic HyperplasiaDocument15 pagesBenign Prostatic HyperplasiaAilene GuzmanNo ratings yet
- Department of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesDocument3 pagesDepartment of Education: Republic of The PhilippinesYeasa DolleteNo ratings yet
- Statement of The ProblemDocument7 pagesStatement of The ProblemYeasa DolleteNo ratings yet
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : Russel Cepriano V151622 MOA Feb 2021Document2 pagesBenign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) : Russel Cepriano V151622 MOA Feb 2021Yeasa DolleteNo ratings yet
- Lesson-Plan-For For DemoDocument5 pagesLesson-Plan-For For DemoYeasa DolleteNo ratings yet
- Panitan National High School Class Program 2021-2022Document2 pagesPanitan National High School Class Program 2021-2022Yeasa DolleteNo ratings yet
- Schedule 2021 2022 Final EditedDocument2 pagesSchedule 2021 2022 Final EditedYeasa DolleteNo ratings yet
- Journal - A Bracket Positioning OverviewDocument5 pagesJournal - A Bracket Positioning OverviewRetta GabriellaNo ratings yet
- Specialized Group Homes For Persons With Severe or Profound Mental Retardation and Serious Problem Behaviour in EnglandDocument18 pagesSpecialized Group Homes For Persons With Severe or Profound Mental Retardation and Serious Problem Behaviour in EnglandDeborah RiskinNo ratings yet
- Khatib2017 PDFDocument14 pagesKhatib2017 PDFluxmansrikanthaNo ratings yet
- Clobazam As First Add On What Is The Evidence and Experience - Final Deck - 14 Feb 2023Document51 pagesClobazam As First Add On What Is The Evidence and Experience - Final Deck - 14 Feb 2023veerraju tvNo ratings yet
- Uts Advocacy PaperDocument11 pagesUts Advocacy PaperPlu AldiniNo ratings yet
- Skilled Birth Attendant (SBA) : State Institute of Health & Family Welfare JaipurDocument32 pagesSkilled Birth Attendant (SBA) : State Institute of Health & Family Welfare JaipurDurga NaikNo ratings yet
- Sia DH FinalDocument26 pagesSia DH FinalJennifer DixonNo ratings yet
- Pharma Laboratory ExperimentsDocument34 pagesPharma Laboratory Experimentsapi-3748748100% (4)
- Anti - HyperlipidemiaDocument18 pagesAnti - HyperlipidemiaZakarie Abdullahi Hussein100% (1)
- 2019b TK ManualDocument210 pages2019b TK ManualZvonko ŠuljakNo ratings yet
- Nauclea Latifolia: A Medicinal, Economic and Pharmacological ReviewDocument19 pagesNauclea Latifolia: A Medicinal, Economic and Pharmacological ReviewMichael Kwesi BaahNo ratings yet
- B1621 - V - Lisdexamfetamine For Patients Within Adult ServicesDocument27 pagesB1621 - V - Lisdexamfetamine For Patients Within Adult Servicesdimitros kristianopoulosNo ratings yet
- Design Requirements For Working Chairs of A Dental TherapistDocument10 pagesDesign Requirements For Working Chairs of A Dental TherapistShaaibNo ratings yet
- Prenatal Development and Birth: The Developing Person Through The Life Span Kathleen Stassen Berger - Tenth EditionDocument42 pagesPrenatal Development and Birth: The Developing Person Through The Life Span Kathleen Stassen Berger - Tenth EditionJoel PayneNo ratings yet
- Pityriasis VersicolorDocument6 pagesPityriasis Versicolorh8j5fnyh7dNo ratings yet
- Rebecca Sunseri: Developing A Nutrition PlanDocument7 pagesRebecca Sunseri: Developing A Nutrition PlanBecca SunseriNo ratings yet
- Kounis Syndrome A Pediatric PerspectiveDocument10 pagesKounis Syndrome A Pediatric PerspectiveAna Belén Artero CastañoNo ratings yet
- Info - PathophysiologyDocument6 pagesInfo - PathophysiologyRupert BassigNo ratings yet
- Rabbithematology PDFDocument12 pagesRabbithematology PDFHuda HudaNo ratings yet
- A Study of Stigma and Discrimination Towards People Living With Hiv/AidsDocument20 pagesA Study of Stigma and Discrimination Towards People Living With Hiv/Aidsmusamuwaga100% (1)
- Review On Contact Tracing With Machine LearningDocument4 pagesReview On Contact Tracing With Machine LearningInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- AVBS1003-2020-Lecture 3-Anthrozoology IDocument25 pagesAVBS1003-2020-Lecture 3-Anthrozoology IOttilia LaiNo ratings yet
- First Aid For BurnsDocument10 pagesFirst Aid For BurnsRalc Retsel AtadNo ratings yet
- Part B - Aditya BirlaDocument4 pagesPart B - Aditya BirlaRainbow Multispeciality HospitalNo ratings yet
- Discharge PlanDocument2 pagesDischarge PlanHannah ChiuNo ratings yet
- Pneumothoraks Jurnal RadiologiDocument9 pagesPneumothoraks Jurnal RadiologiRachmi MerrinaNo ratings yet