Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Targeting the Audience: Tips for Academic Writing Styles
Uploaded by
TESL10620 Muhammad Luqmanhakim Bin Ramli0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageInfographic TSLB3023 ENGLISH FOR ACADEMIC PURPOSE
Original Title
AUDIENCE AND STYLE w13
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentInfographic TSLB3023 ENGLISH FOR ACADEMIC PURPOSE
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
12 views1 pageTargeting the Audience: Tips for Academic Writing Styles
Uploaded by
TESL10620 Muhammad Luqmanhakim Bin RamliInfographic TSLB3023 ENGLISH FOR ACADEMIC PURPOSE
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
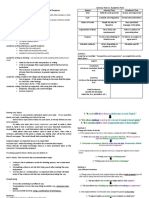
AUDIENCE AND STYLE
IN ACADEMIC WRITING
SKILLS
What are the audience and target audience? S
It is formal and uses particular language
norms.
Audience can be defined as the individual or group T Consistent and suitable both in terms of
whom the writer intends to address.
audience and messages
Y
More than just a writing convention
Target audience is the intended audience by the
helps audience to think more logically
writer; it is also the group of readers that the writer L
want to read his/her document or expect will read the and clearly
document. E
Four main key features of
The target audience should understand everything
written in the writer's document because they are the academic style
people the writer is designing his/her document for. 1. Objectivity
2. Formally
Types of Audience In Writing 3. Precision
The experts - has a substantial amount of
4. Hedging
knowledge on the subject matter the writer is
CTIV
writing about. O
B
JE IT
Y
1. Presents and evaluates issues and arrives at
The laypeople - This audience has virtually no
an objective position; focuses on research and
knowledge about the topic the writer is writing
reasoning.
about.
2. Personal pronouns are usually avoided as it is
The Manager - someone who has decision-making often associated with subjectives views that
powers that are greater than the writer's from a influenced by personal preferences or biases
professional standpoint. 3. Writer's own evaluation is important however
the writer must use evidence and logical
The Technicians - wants to see the technical argumentation
details make logical sense.
use topic as subject
The Hybrids - know a lot about what you’re writing How to
and they have high levels of decision-making power.
use passive verb
establish
use 'it' as an empty
objectivity subject
Why audience important?
Helps the writer to make decisions about what FORMALITY
information you should include, how the writer
should arrange that information, and what kind of Without notation of relaxed and friendly
supporting details will be necessary for the reader language
to understand what you are presenting. Helps in evading misinterpretation and
ambiguity
Influences the tone and structure of the document. Provides understandable information
To develop and present a better and effective How to make writing more
argument. formal
How to identify and find the audience?
Know your most likely book audience - Think about Use formal vocabulary
who would be interested in the content of your Avoid rhetorical question
writing. Visualize who they are, and what they look Avoid colloquail words and expression ( stuff,
like. things)
It is important because writing for an audience Avoid abbreviated forms ( can't, shouldn't)
will help guide how you structure your work, Avoid two word verbs (first-class, put off
what kind of language you use, what information bring up)
you include, and how you approach each topic.
For example, if you are writing a blog for small
Include a sufficient high level of P
business owners that may need digital
marketing or website help, you should make
detail and specificity R
sure to explain web-related topics and The amount of details depends on
E
keywords thoroughly. the purpose of writing
C
Avoid ambiguity
Identify writing works that are similar to yours - I
Take the time to research other books that would Choose verbs that express concepts
S
be in the same category, genre, or niche. It may be succintly
easier for you to pinpoint your potential readers Certain verbs considered too I
because chances are, you share the same target imprecise for academic writing; do O
audience. not provide exact meaning we require
N
Use single verb expression for more
Look at Social Media - Keep an eye out for the
precise writing
demographics, trends, and other habits that might
not be obvious, but can provide a tremendous Example: do, make, put, keep, have,
amount of useful information. get
Ask Your Help - If you’re having trouble identifying Hedging
Its function to soften claims in
your target audience, ask other authors or industry
professionals for help.
Academic writing
Used to express caution and avoid
strong unqualified statements
How to reach and deal the audience? that may easily disproven
Contruct a persona - To better understand your
audience, you can build a fictional consumer to hedging language
represent your target.
Create a connection - After you’ve established who
Adverbs or clearly, definitely, certainly,
adverbial phrases often, sometimes, usually
your audience is, you need to dive into what your
audience is looking for. Modal verbs will, must, may, might, could
Be helpful -Your content should provide useful and
beneficial information. You want it to stick with and seems, like, appear to be,
Introductory verbs doubt, indicate, think
influence your reader.
Be informative - Provide facts and not just opinions. Certain lexical Verbs believe, assume, suggest
Remember, practice makes perfect.
You might also like
- Elements Technical Writing or On-The-Job Writing Academic or Expository Writing Literature or Fictional WritingDocument2 pagesElements Technical Writing or On-The-Job Writing Academic or Expository Writing Literature or Fictional WritingangelicaNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing Essentials for 1st Quarter LessonsDocument7 pagesAcademic Writing Essentials for 1st Quarter LessonsGeraldine SarmientoNo ratings yet
- Academic and Professional Writing Style and The Rhetorical SituationDocument3 pagesAcademic and Professional Writing Style and The Rhetorical SituationHyrum MilanNo ratings yet
- Reading Critically and Avoiding PlagiarismDocument7 pagesReading Critically and Avoiding PlagiarismSheena CansonNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 Academic vs. Non-Academic TextDocument1 pageActivity 1 Academic vs. Non-Academic TextNeil GaleonNo ratings yet
- Eapp ReviewerDocument12 pagesEapp ReviewerGweneth WajeNo ratings yet
- Introduction To Academic WritingDocument3 pagesIntroduction To Academic WritingHari TharanNo ratings yet
- Myp Unit Plan 1Document6 pagesMyp Unit Plan 1api-524845185100% (4)
- Reading Academic TextDocument7 pagesReading Academic TextCheena Francesca LucianoNo ratings yet
- English Writing To InformNewspaper Report Writing Skills Educational Presentation in Blue and Yellow Illustrative StyleDocument25 pagesEnglish Writing To InformNewspaper Report Writing Skills Educational Presentation in Blue and Yellow Illustrative StyleNathän P. CorletNo ratings yet
- Eapp Reviewer Q3, Jess Anch.Document6 pagesEapp Reviewer Q3, Jess Anch.JessicaNo ratings yet
- Lesson 1eappDocument2 pagesLesson 1eappMonique DanielleNo ratings yet
- Crwt111 Reviewer PrelimDocument8 pagesCrwt111 Reviewer PrelimDENNIS BELGIRA JR.No ratings yet
- Reading and Writing PDFDocument12 pagesReading and Writing PDFRashier AquinoNo ratings yet
- ENG 21 - Chapter 4Document25 pagesENG 21 - Chapter 4jinscollantesNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 FinalDocument13 pagesChapter 7 FinalLiezel Constantino100% (1)
- Critical Reading Involves Using Logical and Rhetorical Skills. Identifying The Author PDFDocument5 pagesCritical Reading Involves Using Logical and Rhetorical Skills. Identifying The Author PDFemysamehNo ratings yet
- EAPP Notes Lesson 1 8Document13 pagesEAPP Notes Lesson 1 8dwyquishNo ratings yet
- LECTURES IN READING AND WRITING SKILLS CompleteDocument10 pagesLECTURES IN READING AND WRITING SKILLS CompleteAdrian BulawanNo ratings yet
- WEEK 2 LECTURE NOTES Part 1Document5 pagesWEEK 2 LECTURE NOTES Part 1Harold Saldy CasalemNo ratings yet
- ASSH2005 - Fundamental Considerations on Text Production and ConsumptionDocument4 pagesASSH2005 - Fundamental Considerations on Text Production and ConsumptionKrishaNo ratings yet
- CRWT PrelimDocument10 pagesCRWT Prelimseolux13No ratings yet
- MARTYRS MEER NATHAN What Have I Learned So FarDocument3 pagesMARTYRS MEER NATHAN What Have I Learned So FarNathan Peter MeerNo ratings yet
- Differentiating Language Used in Academic Texts From Various DisciplinesDocument38 pagesDifferentiating Language Used in Academic Texts From Various DisciplinesDiane SantosNo ratings yet
- English For Academic and Professional Purposes PPT MIDTERMDocument59 pagesEnglish For Academic and Professional Purposes PPT MIDTERMMelprin CorreaNo ratings yet
- Compre RWDocument5 pagesCompre RWKaycee ValenzuelaNo ratings yet
- Critical Reading PresentationDocument16 pagesCritical Reading PresentationJulie Pearl SimanNo ratings yet
- Figure 10.3 How The Writing Traits May Be Intergrated Into A Writing ProcessDocument7 pagesFigure 10.3 How The Writing Traits May Be Intergrated Into A Writing ProcessPutriNo ratings yet
- LecturesDocument14 pagesLecturesLei Yunice NorberteNo ratings yet
- Academic vs Non-Academic TextDocument12 pagesAcademic vs Non-Academic TextJuan CruzNo ratings yet
- CS8 - Reading and Writing: Module 6/7Document67 pagesCS8 - Reading and Writing: Module 6/7Patrick BaleNo ratings yet
- Module FinalsDocument24 pagesModule FinalsJosh PinedaNo ratings yet
- 11 - Integrity - Abendan & Macasaet (Assignment #1)Document4 pages11 - Integrity - Abendan & Macasaet (Assignment #1)Sophia AbendanNo ratings yet
- EAPP-Q1 Module1 Lesson-1Document9 pagesEAPP-Q1 Module1 Lesson-1Johnpatrick CiaNo ratings yet
- Nonfiction Lesson Plan Example: With BIG Ideas and BIG QuestionsDocument3 pagesNonfiction Lesson Plan Example: With BIG Ideas and BIG QuestionsTasneem Al-tawilNo ratings yet
- English RebyuDocument14 pagesEnglish Rebyushua.all4seul100% (1)
- English For Academic and Professional PurposesDocument2 pagesEnglish For Academic and Professional PurposesAnonymousNo ratings yet
- Notes On Good Legal Writing (JCL)Document3 pagesNotes On Good Legal Writing (JCL)Jor LonzagaNo ratings yet
- Communication Skills Focus On WritingDocument3 pagesCommunication Skills Focus On WritingPhe MenghourNo ratings yet
- Analyze Expository TextsDocument15 pagesAnalyze Expository TextsTibetan FoxNo ratings yet
- LP Format EFDT English 10Document9 pagesLP Format EFDT English 10Chamile BrionesNo ratings yet
- G10 Language and Literature Unit 2: " Purpose and Structure Are Key Components To Effective Communication "Document5 pagesG10 Language and Literature Unit 2: " Purpose and Structure Are Key Components To Effective Communication "api-429499161No ratings yet
- Article Writing Made EasyDocument23 pagesArticle Writing Made EasySulaimanNo ratings yet
- Eapp ReviewerDocument8 pagesEapp Reviewer107919120099No ratings yet
- MYP Programme: Criteria Level Level Descriptors (Ib Myp Published: Year 1) Task IndicatorsDocument2 pagesMYP Programme: Criteria Level Level Descriptors (Ib Myp Published: Year 1) Task Indicatorsapi-360153065No ratings yet
- Nature of Academic Text PDFDocument5 pagesNature of Academic Text PDFMia Dyle MagallanesNo ratings yet
- GE 5 Module 3 - L1, L2, & L3Document13 pagesGE 5 Module 3 - L1, L2, & L3Rash Mia LabaoNo ratings yet
- Unit 1 LOTF Summative Exam PaperDocument6 pagesUnit 1 LOTF Summative Exam PapersophieNo ratings yet
- Engl 1010 Project 2 Literacy Profile Assignment SheetDocument2 pagesEngl 1010 Project 2 Literacy Profile Assignment Sheetapi-336004351No ratings yet
- Distinguishing Academic and Non-Academic WritingDocument14 pagesDistinguishing Academic and Non-Academic WritingJudith Tero MuñezNo ratings yet
- Academic Writing Style: How is it Different from OthersDocument5 pagesAcademic Writing Style: How is it Different from OthersShayne Herrera IINo ratings yet
- Creative Writing q2!18!20 PDF FreeDocument4 pagesCreative Writing q2!18!20 PDF FreeWelfredo Jr YuNo ratings yet
- UntitledDocument5 pagesUntitledpiyawan sunasuanNo ratings yet
- Communicating with Friends Around the WorldDocument14 pagesCommunicating with Friends Around the Worldsolany perezNo ratings yet
- Technical Writing Overview and Style GuideDocument10 pagesTechnical Writing Overview and Style GuideAzucena HayaNo ratings yet
- Enhanced Hybrid English 10 q1 m6Document12 pagesEnhanced Hybrid English 10 q1 m6Rica Irish AbejuroNo ratings yet
- Celebratory Oral TASK SHEET Stage 1 English 2019Document2 pagesCelebratory Oral TASK SHEET Stage 1 English 2019Andrew EwersNo ratings yet
- Essay Plan Comparative StudyDocument4 pagesEssay Plan Comparative StudySilivia MarawaNo ratings yet
- Effect of Classical Music on Grade 11 Students’ Math AnxietyDocument3 pagesEffect of Classical Music on Grade 11 Students’ Math AnxietyJoshua AngelesNo ratings yet
- Active Listening Skills, The Bug Activity (08-09)Document8 pagesActive Listening Skills, The Bug Activity (08-09)Scholar WinterflameNo ratings yet
- Lesson Plan 1Document6 pagesLesson Plan 1api-301250503No ratings yet
- Methodology of Literature PDFDocument56 pagesMethodology of Literature PDFroshani Vasudev BhootraNo ratings yet
- 7 Steps of Moral Reasoning ModelDocument5 pages7 Steps of Moral Reasoning ModelTricha Mae PotencianoNo ratings yet
- Personal DevelopmentDocument2 pagesPersonal DevelopmentAngelica Sanchez de VeraNo ratings yet
- Outdoor Recreation IntroductionDocument5 pagesOutdoor Recreation IntroductionAngei NiledefNo ratings yet
- Life of EpictetusDocument17 pagesLife of EpictetusYvonne BascoNo ratings yet
- PG Diploma in Psychotherapy Course InfoDocument1 pagePG Diploma in Psychotherapy Course InfoSabitri SanyalNo ratings yet
- Introduction - Grade 11 English-Language Arts: Released Test QuestionsDocument57 pagesIntroduction - Grade 11 English-Language Arts: Released Test QuestionsEamon BarkhordarianNo ratings yet
- HOG Program 2019 v26Document66 pagesHOG Program 2019 v26Ngaire TaylorNo ratings yet
- HR Questions & AnswersDocument2 pagesHR Questions & AnswersHari HaranNo ratings yet
- MODULE 4 CognitiveDocument4 pagesMODULE 4 Cognitive20138874 PANKHURI SAWHNEYNo ratings yet
- Exercise for CPTDocument3 pagesExercise for CPTFariska Zata AmaniNo ratings yet
- Hurd Science LiteracyDocument10 pagesHurd Science LiteracydedewNo ratings yet
- Epigrams and ConsolationDocument32 pagesEpigrams and ConsolationJohn MazoNo ratings yet
- Phineas Gage Scavenger HuntDocument5 pagesPhineas Gage Scavenger Huntapi-275566629No ratings yet
- Ge 05 - Purposive Communication: Camiguin Polytechnic State CollegeDocument4 pagesGe 05 - Purposive Communication: Camiguin Polytechnic State CollegeAron Matthew CagampangNo ratings yet
- Mitchell, Wesley C - The Role of Money in Economic History (JEH4 1944)Document8 pagesMitchell, Wesley C - The Role of Money in Economic History (JEH4 1944)Joohyoung100% (1)
- Rorty - PragmatisimDocument22 pagesRorty - PragmatisimTisan AramNo ratings yet
- Jayla Carr ResumeDocument2 pagesJayla Carr ResumeJayla CarrNo ratings yet
- G4 PD - CL On Filipino's Understandings of Leadership, Relations and Social InfluenceDocument12 pagesG4 PD - CL On Filipino's Understandings of Leadership, Relations and Social InfluenceRyan CorditaNo ratings yet
- Assignment On People Management Fiasco in Honda Motorcycles and Scooters India LTDDocument6 pagesAssignment On People Management Fiasco in Honda Motorcycles and Scooters India LTDJaidev NairNo ratings yet
- Teaching 7 Principles For Public Health EthicsDocument10 pagesTeaching 7 Principles For Public Health Ethicsapi-491280545No ratings yet
- Employee Coping With Organizational Change in The Face of A PandemicDocument11 pagesEmployee Coping With Organizational Change in The Face of A PandemicDadi Bangun WismantoroNo ratings yet
- Joreskog Sorbom LISREL 8 Structural Equation Modeling With Simplis Command Language 1998Document12 pagesJoreskog Sorbom LISREL 8 Structural Equation Modeling With Simplis Command Language 1998varunvijay89No ratings yet
- Theme of RootsDocument2 pagesTheme of RootsParv sharmaNo ratings yet
- Chemistry Project ON Determine Caffine in Different Tea SamplesDocument16 pagesChemistry Project ON Determine Caffine in Different Tea SamplesAbhishek Tiwari100% (1)
- Ukff2013 Assignment 201805Document4 pagesUkff2013 Assignment 201805EZern KongNo ratings yet