Professional Documents
Culture Documents
Ethernet Bits Per Second (BPS)
Uploaded by
Aditya MangleOriginal Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
Ethernet Bits Per Second (BPS)
Uploaded by
Aditya MangleCopyright:
Available Formats
BASIC NETWORK TERMS
A network address serves as a unique identifier for a computer on a network. (2 types
- IP address and MAC address)
A network adapter interfaces a computer to a network. The term "adapter" was
popularized originally by Ethernet add-in cards for PCs.
Bandwidth in computer networking refers to the data rate supported by a network
connection or interface. One most commonly expresses bandwidth in terms of bits per
second (bps).
bps (bits per second) Network performance has traditionally been measured in units of
bits per second (bps).
CAT5 is the 5th generation of twisted pair Ethernet cabling and the most popular of all
twisted pair cables in use today.
DHCP (Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol) allows a computer to join an IP-based
network without having a pre-configured IP address.
The DNS (Domain Name Service) translates Internet domain and host names to IP
addresses.
The term Denial of Service (DoS) refers to a form of attacking computer systems over a
network.
A network firewall protects a computer network from unauthorized access.
FTP (File Transfer Protocol) allows one to transfer files between computers on the
Internet. Technically, FTP is a simple network protocol based on IP, but many also use
the term "FTP" to refer to this type of file sharing service.
In computer networking, a hop represents one portion of the path between source and
destination.
HTTP (hypertext transfer protocol) is an application layer network protocol built on top
of TCP. HTTP allows Web browsers and Web servers to communicate.
A hub is a small, simple, inexpensive network device that joins multiple computers
together.
The term Internet today refers to the global network of public computers running Internet
Protocol
Intranet is the generic term for a collection of private computer networks within an
organization.
An IP address is the logical address of a network adapter. The IP address uniquely
identifies computers on a network. (example: 215.123.34.45)
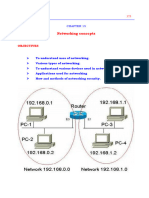
A local area network (LAN) supplies networking capability to a group of computers in
close proximity to each other such as in an office building, a school, or a home.
MAC (Media Access Control) technology provides unique identification and access
control for computers on an Internet Protocol (IP) network. (example: 48-3F-0A-91-00-
BC)
NIC (Network Interface Card) provides a hardware interface between a computer and a
network. The term NIC most commonly refers to network adapter hardware in the form
factor of an add-in card.
The OSI model defines internetworking in terms of a vertical stack of seven layers.
A packet is one unit of binary data capable of being routed through a computer network.
Ping is the name of a standard network utility packaged with popular network operating
systems. The utility can be used to determine if a remote device (such as Web or game
server) can be reached on the network and, if so, roughly how fast the current
connection is.
A port number represents an endpoint or "channel" for network communications. Port
numbers allow different applications on the same computer to utilize network resources
without interfering with each other.
A network protocol defines a "language" of rules and conventions for communication
between network devices.
Routers are physical devices that join multiple wired or wireless networks together.
Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and Internet Protocol (IP) are two distinct network
protocols, technically speaking. TCP and IP are so commonly used together, however,
that TCP/IP has become standard terminology to refer to either or both of the protocols.
UDP (User Datagram Protocol) is a lightweight transport built on top of IP.
You might also like
- Definition of A NetworkDocument5 pagesDefinition of A NetworkJefersonNo ratings yet
- Web Technology UNIT IDocument68 pagesWeb Technology UNIT IMeentchi.rNo ratings yet
- Networking 101: File Sharing, Topologies, Protocols & MoreDocument11 pagesNetworking 101: File Sharing, Topologies, Protocols & MoreanjilenajolieNo ratings yet
- Basic Networking ConceptsDocument30 pagesBasic Networking ConceptsQamar KhanNo ratings yet
- IEEE Standards and Network Protocols GuideDocument7 pagesIEEE Standards and Network Protocols GuideGray FullbusterNo ratings yet
- Interfaces: Medium Access ControlDocument6 pagesInterfaces: Medium Access ControlnaziaNo ratings yet
- Difference between intranet and internetDocument3 pagesDifference between intranet and internetNaveen YadavNo ratings yet
- Diploma in Engineering (Computer Science and Engineering)Document32 pagesDiploma in Engineering (Computer Science and Engineering)himanshu SHARMANo ratings yet
- Networking Computer UAF TTS TopicsDocument23 pagesNetworking Computer UAF TTS TopicsNaziaNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: WEB Essentials: Clients, Servers AND CommunicationDocument48 pagesUnit 1: WEB Essentials: Clients, Servers AND CommunicationAshokNo ratings yet
- TCP/IP Protocols: Ibrahim I. Banat, Computer Science, AL-Hussein Bin Talal University, Maan-JordanDocument10 pagesTCP/IP Protocols: Ibrahim I. Banat, Computer Science, AL-Hussein Bin Talal University, Maan-JordanDer1991ChefNo ratings yet
- Packet Switching Is The Dividing Of: MessagesDocument31 pagesPacket Switching Is The Dividing Of: MessagesShokin AliNo ratings yet
- Internet ProtocolDocument6 pagesInternet ProtocolDdyash DayaNo ratings yet
- TCP IpDocument36 pagesTCP IpMonisha MoniNo ratings yet
- IT Notes Unit 5Document14 pagesIT Notes Unit 5Deepankar Anil KumarNo ratings yet
- Introduction To TC PipDocument20 pagesIntroduction To TC PipJESUS JHOJANSON BERMEJO LLANOSNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: WEB Essentials: Clients, Servers AND CommunicationDocument60 pagesUnit 1: WEB Essentials: Clients, Servers AND Communicationlegy86No ratings yet
- Networking RefresherDocument2 pagesNetworking Refresherpkamal0111No ratings yet
- IP Addressing and Protocols ExplainedDocument22 pagesIP Addressing and Protocols Explainedmelkamu debasNo ratings yet
- Technical Interview Questions: OSI Model, TCP/IP, IP Address, Subnet, and MoreDocument9 pagesTechnical Interview Questions: OSI Model, TCP/IP, IP Address, Subnet, and MoreBadrinath KadamNo ratings yet
- SVCE Web Programming Lecture Notes Unit 1 Moore's Law & Internet EvolutionDocument14 pagesSVCE Web Programming Lecture Notes Unit 1 Moore's Law & Internet EvolutionkishorekumarNo ratings yet
- Unit 1: A Very Brief History of The InternetDocument39 pagesUnit 1: A Very Brief History of The InternetChandra Sekhar DNo ratings yet
- Computer Network.Document6 pagesComputer Network.sivakumarannam2001No ratings yet
- Computer NetworkingDocument7 pagesComputer NetworkingOcampo AmyNo ratings yet
- Networking Data Link Protocol Networking Nodes Authentication Encryption CompressionDocument9 pagesNetworking Data Link Protocol Networking Nodes Authentication Encryption CompressionAdit LalNo ratings yet
- Definition of TermsDocument2 pagesDefinition of TermsRaprap De OcampoNo ratings yet
- Chapter 11: Wide Area Networks and the InternetDocument12 pagesChapter 11: Wide Area Networks and the InternetDanny OxinaNo ratings yet
- Local Area NetworkDocument9 pagesLocal Area Networkapi-26989621No ratings yet
- Computer and Multimedia Networks: OSI Layers and TCP/IP ProtocolsDocument35 pagesComputer and Multimedia Networks: OSI Layers and TCP/IP ProtocolsAamir HiraniNo ratings yet
- What is Computer Networking Basics Components UsesDocument32 pagesWhat is Computer Networking Basics Components UsesLeo Walican AntonioNo ratings yet
- Networking ConceptsDocument40 pagesNetworking Conceptscalligraphy4instagramNo ratings yet
- Ludhiana College of Engineering and Technology Katani Kalan, Ludhiana 141113Document19 pagesLudhiana College of Engineering and Technology Katani Kalan, Ludhiana 141113Nishant GargNo ratings yet
- IPv4 vs IPv6, Intranet vs Internet, Routers, Subnet Mask, NAT, NIC, Private IP, MAC Addresses, DHCP, ARPDocument6 pagesIPv4 vs IPv6, Intranet vs Internet, Routers, Subnet Mask, NAT, NIC, Private IP, MAC Addresses, DHCP, ARPJatin SangwanNo ratings yet
- CN VivaDocument3 pagesCN VivaDhrumil DancerNo ratings yet
- UNIT II - Day 10 07.03.2024Document8 pagesUNIT II - Day 10 07.03.2024V VizNo ratings yet
- Data Communication Laboratory: Bicol State College of Applied Sciences and Technology Naga CityDocument7 pagesData Communication Laboratory: Bicol State College of Applied Sciences and Technology Naga CityRaprap Payte BaraquielNo ratings yet
- BASICS OF COMPUTER NETWORKINGDocument34 pagesBASICS OF COMPUTER NETWORKINGVashu TiwariNo ratings yet
- Installation of Inside Plant Network Intro NotesDocument28 pagesInstallation of Inside Plant Network Intro Notesonchiriemmanuel891No ratings yet
- Mc5303-Web-Programming-Essentials-All UnitsDocument75 pagesMc5303-Web-Programming-Essentials-All UnitsrathinadeviNo ratings yet
- Unit 4 NotesDocument37 pagesUnit 4 NotesAryan AgneyNo ratings yet
- Business in A Networked Env.22Document11 pagesBusiness in A Networked Env.22ashishgiri100% (2)
- Computer Communication & Networking AssignmentDocument3 pagesComputer Communication & Networking AssignmentSoni DellaNo ratings yet
- Client-Server Network: Local Area Networks (Lans) FTP DnsDocument8 pagesClient-Server Network: Local Area Networks (Lans) FTP DnsPopa AlinNo ratings yet
- Networking QuestionsDocument26 pagesNetworking QuestionsSahil ThakurNo ratings yet
- Lecture TwoDocument47 pagesLecture TwomikiNo ratings yet
- Computer NetworkDocument18 pagesComputer NetworkRaju LalNo ratings yet
- Networking Theory (Part 1)Document54 pagesNetworking Theory (Part 1)Irsan EhcNo ratings yet
- Assignment 1Document18 pagesAssignment 1Kushal BajracharyaNo ratings yet
- Lecture 8Document31 pagesLecture 8Alpengolden MoonderlandNo ratings yet
- Home PC Networking 101 Rev1 131229Document18 pagesHome PC Networking 101 Rev1 131229ΆνναΚατερίναΛουκίδουNo ratings yet
- Explain Layered Architecture of OSI Reference ModelDocument2 pagesExplain Layered Architecture of OSI Reference ModelVikas KhatriNo ratings yet
- Notes e CommerceDocument83 pagesNotes e CommerceSawmya ShanmuganathanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 - Network SecurityDocument48 pagesChapter 4 - Network SecuritygabrielgngrNo ratings yet
- Computer Networks TCP IpDocument15 pagesComputer Networks TCP IpSudarshan KrishnaNo ratings yet
- Networking Protocols: A Network ProtocolDocument2 pagesNetworking Protocols: A Network ProtocolHabib FaridoonNo ratings yet
- WT UNIT 1 Lecture 1.2 Protocols Governing The WebDocument20 pagesWT UNIT 1 Lecture 1.2 Protocols Governing The WebSACHIDANAND CHATURVEDINo ratings yet
- Netwrking Assingment April 2011 5 Semester: Computer Networking or Data Communications (Datacom) Is TheDocument4 pagesNetwrking Assingment April 2011 5 Semester: Computer Networking or Data Communications (Datacom) Is Thesunya2011No ratings yet
- Tcp/Ip: Types of LayersDocument5 pagesTcp/Ip: Types of LayersHamza Bin TahirNo ratings yet
- Introduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyFrom EverandIntroduction to Internet & Web Technology: Internet & Web TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Computer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1From EverandComputer Networking: An introductory guide for complete beginners: Computer Networking, #1Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (2)
- OSI Model (PDFDrive)Document111 pagesOSI Model (PDFDrive)FatimaNo ratings yet
- Answer Key: Case Study 1-1 Answer Key: ACMC Hospital Network Upgrade InformationDocument15 pagesAnswer Key: Case Study 1-1 Answer Key: ACMC Hospital Network Upgrade InformationSulayman Alwabel100% (1)
- Capsman MikrotikDocument37 pagesCapsman MikrotikMehdi GrimNo ratings yet
- ICMP MisbehaviourDocument34 pagesICMP Misbehavioural-amin shohag100% (1)
- Efficiency5 31Document4 pagesEfficiency5 31mahmoud166No ratings yet
- Mod - 7 Basic Router ConfigurationDocument44 pagesMod - 7 Basic Router ConfigurationIrfan Irawan CbnNo ratings yet
- Routers (Network Routing) : ResearchDocument13 pagesRouters (Network Routing) : ResearchMarin AndreiNo ratings yet
- SNMP Tutorial Explains Manager/Agent ModelDocument6 pagesSNMP Tutorial Explains Manager/Agent ModelcmohimacNo ratings yet
- CUCM Traces Analysis - CUCM ArchitectureDocument10 pagesCUCM Traces Analysis - CUCM ArchitecturesenthilNo ratings yet
- ALC EthDocument130 pagesALC EthtutenoNo ratings yet
- Understanding MPLS OAM Capabilities To Troubleshoot MPLS NetworksDocument70 pagesUnderstanding MPLS OAM Capabilities To Troubleshoot MPLS NetworksDushyantRavalNo ratings yet
- Windows Server 2008 R2 Certificate Enrollment Web ServicesDocument91 pagesWindows Server 2008 R2 Certificate Enrollment Web ServicesFebbin RajanNo ratings yet
- Competitive Access and SwitchingDocument94 pagesCompetitive Access and SwitchingcinzapaquetaNo ratings yet
- IP PBX Configuration IssabelDocument10 pagesIP PBX Configuration IssabelCoko Mirindi Musaza0% (1)
- Ip Touch 4008Document29 pagesIp Touch 4008Jose Alberto Redondo CampillosNo ratings yet
- Computer Network Fundamentals: Dr. Reda Elbarougy ىجورابلا اضر د م أDocument7 pagesComputer Network Fundamentals: Dr. Reda Elbarougy ىجورابلا اضر د م أreda elbarougyNo ratings yet
- CCNA V2 Cheet SheetDocument71 pagesCCNA V2 Cheet SheetgurgrewalNo ratings yet
- EE511-Homework 2: You Get A Wrong Answer, You Can Get Partial Credit If You Show Your Work. If You Make ADocument5 pagesEE511-Homework 2: You Get A Wrong Answer, You Can Get Partial Credit If You Show Your Work. If You Make ARao Arslan RajputNo ratings yet
- SMG Administration GuideDocument913 pagesSMG Administration GuideNguyễn Đình ThànhNo ratings yet
- SIP IntroductionDocument7 pagesSIP IntroductionkflimNo ratings yet
- PrplMesh An Open Source Implementation of The Wi Fi Alliance® Multi AP Specification Arnout Vandecappelle EssensiumMind PDFDocument37 pagesPrplMesh An Open Source Implementation of The Wi Fi Alliance® Multi AP Specification Arnout Vandecappelle EssensiumMind PDFIcaro PosdataNo ratings yet
- Harris Truepoint Keypad MenusDocument3 pagesHarris Truepoint Keypad MenusWashburn61No ratings yet
- LAN-520 LAN Port Application Note PDFDocument33 pagesLAN-520 LAN Port Application Note PDFGuillermo Guerra IbarraNo ratings yet
- Check Point Sandblast PoC Guide v84Document92 pagesCheck Point Sandblast PoC Guide v84Kirill0% (1)
- 2.1.2.10 Lab - Building A Switched Network With Redundant Links ListoDocument9 pages2.1.2.10 Lab - Building A Switched Network With Redundant Links ListoMartin SaldañaNo ratings yet
- Nexthop Vmware NetworkingDocument36 pagesNexthop Vmware NetworkingDavIdFernsNo ratings yet
- Product Data Sheet: Modicon Managed Switch - 8 Ports For Copper + 4 Gigabit SFPDocument4 pagesProduct Data Sheet: Modicon Managed Switch - 8 Ports For Copper + 4 Gigabit SFPPedro PicoloNo ratings yet
- Advanced ConfigurationDocument9 pagesAdvanced Configurationsomanet64No ratings yet
- Newtec MDM2510-ip-satellite-modem DatasheetDocument2 pagesNewtec MDM2510-ip-satellite-modem DatasheetAlfredo SetiadiNo ratings yet
- Cisco IP Phone IntegrationDocument215 pagesCisco IP Phone IntegrationNaveenNo ratings yet