Professional Documents
Culture Documents
NCP Hyperthermia Related To Underlying Infection
Uploaded by
NIKKI CARYL ZAFRAOriginal Description:
Original Title
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
NCP Hyperthermia Related To Underlying Infection
Uploaded by
NIKKI CARYL ZAFRACopyright:
Available Formats
NURSING CARE PLAN
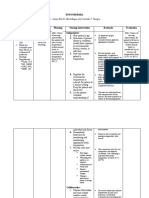
CUES DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTIONS EVALUATIONS
Subjective: Hyperthermia Within 4hrs of nursing 1. Assess the patient’s vital signs to After 4hrs of
Objective: related to intervention the patient will be determine if there still a progress nursing
-Left facial swelling and redness underlying infection able to maintains body of his condition. intervention the
noted (sepsis) temperature below 39° C. 2. Monitor fluid intake and urine patient was able to
-limited range of motion as output. If the patient is maintains body
observed unconscious, central venous temperature below
-febrile (39.1 C) Within 3 days of nursing pressure or pulmonary artery 39° C as evidence
-tachycardia to 120 interventions the patient will be pressure should be measured to by 37.6 C.
-chills noted able prevent from complications monitor fluid status because fluid Goal met.
such as neurological damage. resuscitation may be required to
correct dehydration.
3. As indicated, adjust and monitor
environmental variables such as
room temperature and bed sheets After 3 days of
to regulate temperature of the nursing
patient. interventions the
4. Prepare and ready oxygen therapy patient was able
for extreme cases since prevent from
hyperthermia increases the complications such
metabolic demand for oxygen. as neurological
5. Provide cooling mechanisms such damage as
as cooling mattress, cold packs evidence by the
applied to major blood vessels to patient follows
promote cooling and lower core order of the nurse
temperature. such as moving his
6. Perform tepid sponge bath sponge feet, hand and
bath helps to reduce opening his mouth.
hyperthermia. Take note, using
alcohol and iced water which may N.ZAFRA FSUU/SN
even produce chills and increase 8-30-21
client’s temperature.
7. Raise the side rails at all times to
ensure patient’s safety even
NURSING CARE PLAN
without the presence of seizure
activity.
Dependent interventions:
8. Give antipyretic medications as
prescribed to lower body
temperature by blocking the
synthesis of prostaglandins that act
in the hypothalamus.
9. Provide chlorpromazine
(Thorazine) and diazepam (Valium)
when excessive shivering occurs.
Shivering increases the metabolic
rate and body temperature.
Collaboration
10. Educate patient and family
members about the signs and
symptoms of hyperthermia and
help in identifying factors related
to occurrence of fever.
You might also like
- Hypothermia: By: James Rod D. Marinduque and Jeanette T. DungcaDocument2 pagesHypothermia: By: James Rod D. Marinduque and Jeanette T. DungcaJAMES ROD MARINDUQUENo ratings yet
- NCP No. 2Document2 pagesNCP No. 2Lorraine Tuesday BuenviajeNo ratings yet
- Living Systems Information Therapy LSIT: Introduction to Quantum MedicineFrom EverandLiving Systems Information Therapy LSIT: Introduction to Quantum MedicineNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationWinnie AriolaNo ratings yet
- Selected Topics in Environmental Biology: Based on the Sessions on Environmental Biology Held at the XXVI International Congress of Physiological Sciences, New Delhi, October 20-26, 1974From EverandSelected Topics in Environmental Biology: Based on the Sessions on Environmental Biology Held at the XXVI International Congress of Physiological Sciences, New Delhi, October 20-26, 1974Balraj BhatiaNo ratings yet
- Ncpdrug StudyDocument4 pagesNcpdrug StudyMicaela CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- The Healing Power of Fever: Your Body's Natural Defense against DiseaseFrom EverandThe Healing Power of Fever: Your Body's Natural Defense against DiseaseNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia Drug StudyDocument2 pagesHyperthermia Drug StudyTipey SegismundoNo ratings yet
- Therapeutic Hypothermia - Principles, Indications, Practical ApplicationFrom EverandTherapeutic Hypothermia - Principles, Indications, Practical ApplicationNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan - FeverDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan - FeverRhelina MinNo ratings yet
- Family Nursing Care Plan For FeverDocument2 pagesFamily Nursing Care Plan For Feverbharat singhNo ratings yet
- TASk 2 DS NCPDocument3 pagesTASk 2 DS NCPCHRISTIAN CALAMBANo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Inference Planning Intervention Rationale EvaluationMichelle Dona MirallesNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument2 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Nursing Analysis Planning Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationChristian ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- Activity 1 - Case Agent RookieDocument2 pagesActivity 1 - Case Agent RookieChristian ConcepcionNo ratings yet
- NCPDocument7 pagesNCPTroy MirandaNo ratings yet
- Sample Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Document2 pagesSample Nursing Care Plan (NCP)Darwin Sang-an100% (1)
- Hyperthermia HIV NURSING CARE PLAN FLODocument4 pagesHyperthermia HIV NURSING CARE PLAN FLOMicaela CrisostomoNo ratings yet
- NCP Sample 1Document9 pagesNCP Sample 1Vincent BarcenillaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument1 pageNursing Care Plan: Cues Objectives Interventions Rationale EvaluationAkiraMamoNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Short Term IndependentDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Nursing Intervention Rationale Subjective Short Term IndependentMoi Valdoz100% (1)
- Seizure NCP Tinoy 1Document2 pagesSeizure NCP Tinoy 1Jobelyn MalisaNo ratings yet
- Gender: FemaleDocument9 pagesGender: FemaleNicole Villanueva, BSN - Level 3ANo ratings yet
- Assessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Explanation of The Problem Objectives Nursing Interventions Rationale EvaluationAlyssa Moutrie Dulay Arabe100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan: Subjective: Short Term IndependentDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan: Subjective: Short Term IndependentKristine Young50% (2)
- NCP For Swine FluDocument3 pagesNCP For Swine FluGiana CalloNo ratings yet
- Assessment NCM 101Document1 pageAssessment NCM 101Lorainne Angel U. MolinaNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care PlanDocument3 pagesNursing Care PlanAnnahNo ratings yet
- Nursing InterventionsDocument37 pagesNursing InterventionsRajalakshmi100% (1)
- NCP FeverDocument3 pagesNCP FeverJenner NatividadNo ratings yet
- Ody Temperature As Evidenced by Temperature of 38.5Document1 pageOdy Temperature As Evidenced by Temperature of 38.5Jordz PlaciNo ratings yet
- Vital SignsDocument7 pagesVital SignsEmeroot RootNo ratings yet
- Nilo, Klarenz Medical Surgical Ward BSN Iv-B2 Nursing Care PlanDocument2 pagesNilo, Klarenz Medical Surgical Ward BSN Iv-B2 Nursing Care PlanAce FabrigasNo ratings yet
- Assessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesAssessment Nursing Diagnosis Planning Implementation Rationale EvaluationChloie Marie RosalejosNo ratings yet
- VI. Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationDocument3 pagesVI. Nursing Care Plan Cues Nursing Diagnosis Analysis Goals and Objectives Intervention Rationale EvaluationJenny AjocNo ratings yet
- Cues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument6 pagesCues Nursing Diagnosis Scientific Rationale Objectives Intervention Rationale Evaluation IndependentKasandra Dawn Moquia Beriso100% (1)
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation IndependentDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Interventions Rationale Evaluation IndependentFau Fau DheoboNo ratings yet
- NCM 101B - NCP - Miguel, Roenth Rhene D - BSN 1DDocument2 pagesNCM 101B - NCP - Miguel, Roenth Rhene D - BSN 1DRiri MiguelNo ratings yet
- Assessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evauation IndependentDocument2 pagesAssessment Diagnosis Planning Intervention Evauation IndependentCHRISTIAN CALAMBANo ratings yet
- NCP Fever FinalDocument3 pagesNCP Fever FinalAllyssa Jane PragadosNo ratings yet
- NCP HyperthermiaDocument6 pagesNCP HyperthermiavonjasonbuenafeNo ratings yet
- Dnrle Influenza NCPDocument3 pagesDnrle Influenza NCPEna RodasNo ratings yet
- Hyperthermia NCPDocument2 pagesHyperthermia NCPmahangin85% (20)
- NCP Sit. 2Document3 pagesNCP Sit. 2Jay Debby RuizoNo ratings yet
- HyperthermiaDocument5 pagesHyperthermiaRapunzel Leanne100% (1)
- Hyperthermia NCPDocument3 pagesHyperthermia NCPkaylejordan_29100% (2)
- Nursing Care Plan: Assessment: Nursing Diagnosis: Nursing Goal: Nursing Intervention: Rationale: EvaluationDocument6 pagesNursing Care Plan: Assessment: Nursing Diagnosis: Nursing Goal: Nursing Intervention: Rationale: Evaluationeliza luisNo ratings yet
- Case Study Ii Nursing Assessment of Patients and FamiliesDocument3 pagesCase Study Ii Nursing Assessment of Patients and FamiliesEti JuniaNo ratings yet
- FeverDocument2 pagesFevernymphaaugustusNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan 1: Soure: Marilyn E. Doenges, Mary Frances Moorhouse, Alice C. Murr "Nursespocket Guide."14th Ed.p.784Document30 pagesNursing Care Plan 1: Soure: Marilyn E. Doenges, Mary Frances Moorhouse, Alice C. Murr "Nursespocket Guide."14th Ed.p.784Jesil MarolinaNo ratings yet
- NCP Dengue Fever-MalariaDocument2 pagesNCP Dengue Fever-Malariachristian quiaoit25% (4)
- NCP LeptospirosisDocument2 pagesNCP LeptospirosisLouise Anne Asuncion OclimaNo ratings yet
- Date, Shift & Time Assessment Need Nursing Diagnosis Plan Intervention EvaluationDocument6 pagesDate, Shift & Time Assessment Need Nursing Diagnosis Plan Intervention EvaluationAubrey Unique EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Date, Shift & Time Assessment Need Nursing Diagnosis Plan Intervention EvaluationDocument6 pagesDate, Shift & Time Assessment Need Nursing Diagnosis Plan Intervention EvaluationAubrey Unique EvangelistaNo ratings yet
- Kawasaki Disease FinalDocument5 pagesKawasaki Disease FinalMarie Ashley Casia100% (1)
- Chicken Pox N C P BY BHERU LALDocument2 pagesChicken Pox N C P BY BHERU LALBheru Lal100% (1)
- NCP For HyperthermiaDocument3 pagesNCP For HyperthermiaNikael Patun-ogNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care Plan PediaDocument2 pagesNursing Care Plan PediaNat B. AntipoloNo ratings yet
- NCP Post OpDocument4 pagesNCP Post OpNIKKI CARYL ZAFRANo ratings yet
- What Are The 6 Code Blue Roles During The Code and Explain Their TaskDocument2 pagesWhat Are The 6 Code Blue Roles During The Code and Explain Their TaskNIKKI CARYL ZAFRANo ratings yet
- Drug Study AMIODARONE & PROPOFOLDocument3 pagesDrug Study AMIODARONE & PROPOFOLNIKKI CARYL ZAFRANo ratings yet
- Nursing Homes: Special Care UnitsDocument3 pagesNursing Homes: Special Care UnitsNIKKI CARYL ZAFRANo ratings yet
- Under Stochastic Theories: Wear and Tear TheoryDocument2 pagesUnder Stochastic Theories: Wear and Tear TheoryNIKKI CARYL ZAFRANo ratings yet
- TransModeler BrochureDocument12 pagesTransModeler BrochureedgarabrahamNo ratings yet
- Comparative Analysis of Severe Pediatric and Adult Leptospirosis in Sa o Paulo, BrazilDocument3 pagesComparative Analysis of Severe Pediatric and Adult Leptospirosis in Sa o Paulo, BrazilShofura AzizahNo ratings yet
- Average and Instantaneous AccelerationDocument35 pagesAverage and Instantaneous AccelerationaraneyaNo ratings yet
- Sponsorship Details - IIT DelhiDocument4 pagesSponsorship Details - IIT DelhiRohit KumarNo ratings yet
- Teresa of Avila - The Life of ST Teresa, A Carmelite Nun Reprint 1912Document674 pagesTeresa of Avila - The Life of ST Teresa, A Carmelite Nun Reprint 1912WaterwindNo ratings yet
- Στέργος Νεκτάριος-Μικκιος-CVDocument4 pagesΣτέργος Νεκτάριος-Μικκιος-CVNektarios MikkiosNo ratings yet
- 17373.selected Works in Bioinformatics by Xuhua Xia PDFDocument190 pages17373.selected Works in Bioinformatics by Xuhua Xia PDFJesus M. RuizNo ratings yet
- "Article Critique" Walden University Methods For Evidence-Based Practice, Nursing 8200 January 28, 2019Document5 pages"Article Critique" Walden University Methods For Evidence-Based Practice, Nursing 8200 January 28, 2019Elonna AnneNo ratings yet
- HDLSS Numerical Assignments - DOC FormatDocument3 pagesHDLSS Numerical Assignments - DOC FormatNikhil UpadhyayNo ratings yet
- Renal CalculiDocument12 pagesRenal CalculiArieNo ratings yet
- Medication Instructions Prior To SurgeryDocument11 pagesMedication Instructions Prior To Surgeryhohj100% (1)
- Skills For Developing Yourself As A LeaderDocument26 pagesSkills For Developing Yourself As A LeaderhIgh QuaLIty SVTNo ratings yet
- Sequences and Series Integral Topic AssessmentDocument6 pagesSequences and Series Integral Topic AssessmentOrion BlaqueNo ratings yet
- Pdf-To-Word EditedDocument48 pagesPdf-To-Word EditedJames Genesis Ignacio LolaNo ratings yet
- Brief Orientation To Counseling 1st Edition Neukrug Test BankDocument25 pagesBrief Orientation To Counseling 1st Edition Neukrug Test BankStevenAdkinsyjmd100% (55)
- Selvanathan-7e 17Document92 pagesSelvanathan-7e 17Linh ChiNo ratings yet
- A0 Unit1 Lesson3A PP GB AmbDocument9 pagesA0 Unit1 Lesson3A PP GB AmbMasterkolo KamisNo ratings yet
- Gordon College: Lived Experiences of Family Caregivers of Patients With SchizophreniaDocument128 pagesGordon College: Lived Experiences of Family Caregivers of Patients With Schizophreniaellton john pilarNo ratings yet
- Final Exam1-Afternoon SessionDocument40 pagesFinal Exam1-Afternoon SessionJoshua Wright0% (1)
- IndexDocument3 pagesIndexBrunaJ.MellerNo ratings yet
- Vocabulary ListDocument2 pagesVocabulary List謝明浩No ratings yet
- Heirs of Candelaria V RomeroDocument2 pagesHeirs of Candelaria V Romeromoniquehadjirul100% (1)
- DSP Setting Fundamentals PDFDocument14 pagesDSP Setting Fundamentals PDFsamuel mezaNo ratings yet
- N Advocates Act 1961 Ankita218074 Nujsedu 20221008 230429 1 107Document107 pagesN Advocates Act 1961 Ankita218074 Nujsedu 20221008 230429 1 107ANKITA BISWASNo ratings yet
- Smith Vs CaDocument11 pagesSmith Vs CaIrene QuimsonNo ratings yet
- HaDocument15 pagesHaNicole Easther GabilangosoNo ratings yet
- Hindu Dharma Parichayam - Swami Parameswarananda SaraswatiDocument376 pagesHindu Dharma Parichayam - Swami Parameswarananda SaraswatiSudarsana Kumar VadasserikkaraNo ratings yet
- Ucharistic Doration: Eucharistic Adoration During MassDocument2 pagesUcharistic Doration: Eucharistic Adoration During Masstojo116732No ratings yet
- Scottish Gaelic 2nd EditionDocument117 pagesScottish Gaelic 2nd EditionMila Akimova-LeeNo ratings yet
- 9300 Servo Inverter TRDocument10 pages9300 Servo Inverter TRIhsan CanakogluNo ratings yet