Professional Documents
Culture Documents
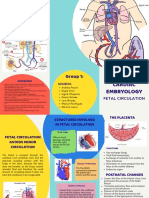
5 NCM207 Fetal Circulation
Uploaded by
Vhiance Czaramae LahuranCopyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
5 NCM207 Fetal Circulation
Uploaded by
Vhiance Czaramae LahuranCopyright:
Available Formats
5.
Ductus Arteriosus
FET AL CIRCULATION Is between the Pulmonary artery and the
Aorta
OUTLINE In some cases, after delivery it will close
after 3 months, but in other cases, it will not
I. FETAL CIRCULATION close leading to Patent ductus arteriosus
II. FOCUS OF FETAL DEVELOPMENT (PDA) = abnormal connection between the
III. NORMAL ADAPTATION OF PREGNANCY aorta and the pulmonary artery in the heart
Additional notes:
Foramen Ovale, Ductus Venosus, Ductus
Arteriosus = will close before delivery but in
some cases it will not close (like foramen ovale)
it will lead to disorder of a baby
Blue baby syndrome = mix of oxygenated and
unoxygenated blood
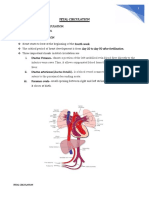
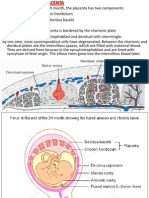
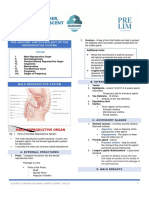
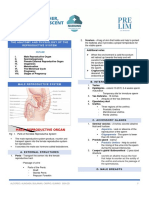
FET AL CIRCULATION FLOW CHART
Refer to the fig_
Oxygenated blood from the placenta returns via the
umbilical vein
The umbilical vein distributes
Fig 1: Fetal Circulation o 40% of its flow to the liver
Inferior vena cava drains into the right atrium
FEATURES IN FETAL CIRCULATION From the right atrium, the flow splits into right
ventricle and left atrium via foramen ovale
1. Umbilical Artery From the left ventricle, into the aorta
Transport the blood from the baby to the o From the aorta, upper body blood flow
placenta going back to the mother (brain and arms) is purely from the left
circulation ventricle, whereas lower body blood flow is
2. Umbilical Vein the combined output of the left ventricle and
Transports the blood and nutrients from the right ventricle via the ductus arteriosus
mother to the placenta going to the fetus From the common iliac arteries, via the umbilical
Collection between the mother and fetus arteries to the placenta
3. Foramen Ovale
Septum between the right atrium and the FOCUS OF FET AL DEVELOPMENT
left atrium
Like prick of a needle but it will allow the FIRST TRIMESTER
shunting of the blood from right to left
4. Ductus Venosus Organogenesis
Is the one that carries the blood
between the umbilical vein and the inferior SECOND TRIMESTER
vena cava that allows the blood bypassing
the liver Period of continued growth and development
ALCORDO, ALINGASA, BULAWAN, CARPIO, QUIMNO BSN 2D 20
THIRD TRIMESTER o Increase blood flow in cervix or the vagina that
causes engorgement of the vagina or the cervix
Period of most rapid growth and development as well, and vulva that produces discoloration
Hegar’s sign (8th week)
NORM AL ADAPT ATION OF PREGNANCY o Cause by an increase of secretion of
estrogen and progesterone that produces a
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM cervical softening of cervix
o Softening of the lower uterine segment that
Undergoes greatest changes in size as well in its is caused by of pelvic congestion
function Chadwick’s sign (8th to 10th week)
Uterus o One of the earliest signs of pregnancy that
o Uterine growth and enlargement the discoloration bluish-purple hue that
o Length – 6.5 cms to 32 cms appears on the cervix, vaginal, and vulva
o Width – 4 cms to 24 cms o estrogen and progesterone
o Depth – 2.5 cms to 22 cms Ovaries = no ovulation, during pregnancy, the ovary
o Weight – 50 gms to 1000 gms stops to produce ova but continues to produce
o Volume – 1-2 ml to 1000 ml hormone progesterone
Vagina = more acidic (ph 3.5 to 6) help control the
Additional notes: growth of pathogens in the vaginal canal to prevent
ascending infections like UTI, Leukorrhea = whitish,
Uterus increases as the baby grows: it can yellowish discharge
accommodate Breasts = as the fetus enlarges in the uterus,
Uterus is under the influence of estrogen and estrogen and progesterone produces number of
myometrial cells as well as the muscle fibers, changes to the mammary glands
undergoes changes: Hypertrophy, with the
process that allows the uterus to enlarge and
Additional notes:
stretch as the fetus enlarges also
Estrogen = cause hypertrophy of uterus and Melanotropin = a hormone that is secreted
enhance the uterus contractility, prepares the by the pituitary gland that causes the nipple
muscles during pregnancy; myometrium contracts become tender and darkening of areola
Progesterone = enables the pregnancy to thrive Colostrum = whitish, appeared in 3rd
the effect by relaxation on a smooth muscle, trimester, it is creamy whitish yellow liquid
prevent the labor if the baby is not on full term, help that have antibodies that help create natural
in the contractility to expel the baby outside, immunity of the baby; encourages baby to
decrease of progesterone - the baby will be
Braxton Hicks Contraction suck the breast of mother to get colostrum
expelled
o Irregular and painless contraction or fetal
movement felt by the mother during the 16
weeks or for 4 months
Becomes globular (4th month) MUSCULOSKELET AL SYST EM
o Abdomen, as the baby increase in its size and
This involves the pelvic joint. The pelvis of the mother
growth the uterus of the mother becomes
during pregnancy normally relaxes causing a waddling
globular in shape and seen physically
walk (walking like a duck).
Goodell’s sign (4th week)
- Waddling walk
o Cervix/cervical softening is caused by the
- Symphysis pubis may separate slightly
stimulation from the hormone estrogen and
progesterone
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
ALCORDO, ALINGASA, BULAWAN, CARPIO, QUIMNO BSN 2D 21
Increased blood volume 40% to 50% - because there - Darkening of neck, under arms, and color changes
is a need to increase this amount due to metabolic of the palm which termed as Palmar Erythema.
demands of the new tissues of the growing fetus - The breast also darkens especially the areola.
Physiologic anemia- occurs due to hemodilution of the - Abdomen also have a line which is termed as
hemoglobin content of the blood volume. There is Linea Negra is the dark streak down midline in the
decrease RBC during pregnancy which is term as abdomen
PSEUDOANEMIA. Chloasma/ Melasma
Heart is displaced upward – to the left because of the - darkening of skin especially on the face.
growing fetus. - term as “MASK OF PREGNANCY”
Increased cardiac output to 30 % - that is why we ask Stria Gravidarum – this the stretch mark found the
the mother to position to left lateral. abdomen sometimes due to the scratching of the
Supine hypotension mother
- if the CO increase to 30 %. Linea Negra- dark streak down midline in the abdomen
- It also causes the mother to have difficulty in Increased Perspiration- during pregnancy causes the
breathing. mother to take bath several times a day.
- They experienced due to the enlarging fetus and the
location of the inferior vena cava. G ASTROINTESTINAL SYSTEM
- The mother has difficulty to lie on supine position
because of compression. Morning Sickness
- If the mother is in flat position, it compresses inferior - vomiting in the morning
vena cava that causes Cardiac Venous Return that - Caused by the hormone HCG (Human
decreases cardiac output and that would lead to chorionic gonadotropin)
Supine Hypotension or Vena Cava Syndrome. - An increased salivary secretion because of
Increased WBC enzyme Ptyalin that helps in mastication but also
CR & PR increased to 10 -15 beats/min causes morning sickness due to increase level
of HCG, Estrogen, and progesterone
Heartburn
- due to the relaxation of the sphincter between
the stomach and the esophagus that causing a
reflux of the gastric content
- Medical term for heartburn is Pyrosis
Constipation
- caused by the decrease motility of the
gastrointestinal tract which is brought about by
increased progesterone.
- additional Ferrous sulfate(sulphate) to
increase the RBC content of the body and one
of the side effects of this constipation.
Fig.2 Growth of baby and enlargement of the uterus.
INTEGUMENT ARY SYSTEM
Increased pigmentation
ALCORDO, ALINGASA, BULAWAN, CARPIO, QUIMNO BSN 2D 22
RESPIRATORY SYSTEM
Increased RR: up to 23 RR
-Normal: 12-16 RR
-Other Factors: Chest Contractions
Dyspnea – Difficulty in breathing
-diaphragm is being displaced about 2 cm upward.
Increased tidal volume – amount of air breathe of
the mother per minute
-Caused by the increase of estrogen and
progesterone
*Estrogen increase – causes hypertrophy
(increased muscle cells) and hyperplasia (increase
of cells) of the lung tissue
*Progesterone increase – causes relaxation of
Fig. 3 Mask of Pregnancy (Melasma or Chloasma) smooth muscle of the bronchi, bronchioles, and
alveoli.
Increase vital lung capacity – force of respiration is
increased.
Decreased residual volume
URINARY SYSTEM
Urinary frequency – compress bladder
Increased GFR (Glomerular Filtration Rate)
-Caused by increased progesterone:
-Mothers are advised to increase fluid intake during
the day
-includes relaxation of the sphincter
-causes asymptomatic bacteriuria and UTI (urinary
tract infection)
*Careful during this time if there is glycosuria result.
It is the inability of the kidney to reabsorb glucose.
ENDOCRINE SYSTEM
Increase metabolism of CHON and ChO
-Caused by the pancreas
-Pancreas increase insulin during pregnancy
Increased insulin production
WEIGHT G AIN
Weight distribution:
Fetus - 7lbs
Placenta - 1lbs
Amniotic fluid - 1.5lbs
Uterus - 2lbs
Blood Volume - 1lbs
ALCORDO, ALINGASA, BULAWAN, CARPIO, QUIMNO BSN 2D 23
Breast - 1.5 – 3lbs
Fluid - 2lbs REFERENCE:
Fats - 4 – 6lbs
I. Power Point Presentation
Total: - 20 – 25lbs
II. Notes From Discusion
FLOWCHART OF FET AL CIRCULATION
Placenta
Umbilical vein
(oxygenated Blood)
Liver (40% Blood)
Ductus Venosus Hepatic Vein
Inferior Vena
cava
Right Atrium
Foramen Ovale Tricuspid Valve
Ductus Arteriosus
Right Ventricle
Left Atrium
Mitral Valve
Left Ventricle Pulmonary Circulation
Aortic Valve
Ascending Aorta Descending Aorta
Brain and Upper Body Parts Lower Body Parts
Common Iliac Artery
Superior Vena Cava
Umbilical Artery
Umbilical Cord
ALCORDO, ALINGASA, BULAWAN, CARPIO, QUIMNO BSN 2D 24
You might also like
- Observations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itFrom EverandObservations on Abortion: Containing an account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes which produced it, and the method of preventing or treating itNo ratings yet
- Fet Al Circul Ation: 5. Ductus ArteriosusDocument5 pagesFet Al Circul Ation: 5. Ductus ArteriosusVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- Observations on Abortion: An account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes, and the method of preventing itFrom EverandObservations on Abortion: An account of the manner in which it is accomplished, the causes, and the method of preventing itNo ratings yet
- NCM 107 - Fetal Circulation Final PDFDocument4 pagesNCM 107 - Fetal Circulation Final PDFAngelica Rose VillegasNo ratings yet
- D.Fetal CirculationDocument5 pagesD.Fetal CirculationJulio NazarethNo ratings yet
- Cardio Day 1 TemplateDocument18 pagesCardio Day 1 TemplateMikeNo ratings yet
- Fetus Circulation LectureDocument28 pagesFetus Circulation LecturecandrastefannNo ratings yet
- Handsout Module 2 A PrelimDocument25 pagesHandsout Module 2 A PrelimErin SaavedraNo ratings yet
- MCN TransDocument44 pagesMCN TransMarc BantilanNo ratings yet
- FetalcirculationDocument32 pagesFetalcirculationannu panchalNo ratings yet
- Conginetal Heart Defects Cafe Baridji Bantasan 1Document19 pagesConginetal Heart Defects Cafe Baridji Bantasan 1Kyrajane EsguerraNo ratings yet
- Case 3Document7 pagesCase 3Edilyn BalicaoNo ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument20 pagesFetal CirculationMuhyeeSalaIdjadNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaeDocument4 pagesAbruptio Placentaeeugeniamaranan.06No ratings yet
- DR - Sumeya: Normal Fetal Development and GrowthDocument42 pagesDR - Sumeya: Normal Fetal Development and Growthhussain AltaherNo ratings yet
- Fetal Circulation ORIGINALDocument13 pagesFetal Circulation ORIGINALombir007No ratings yet
- CVS Embryology Questions and Study Guide - Quizlet Flashcards by Hugo - OxfordDocument5 pagesCVS Embryology Questions and Study Guide - Quizlet Flashcards by Hugo - OxfordAzizNo ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument28 pagesFetal CirculationNelai GoNo ratings yet
- RJI - Fetal CirculationDocument10 pagesRJI - Fetal CirculationgalaetiNo ratings yet
- Midwife Care Plan AbruptioDocument6 pagesMidwife Care Plan AbruptioDivina Gracia Vibal CieloNo ratings yet
- AnaPhy Cardiovascular SystemDocument3 pagesAnaPhy Cardiovascular SystemKiara Catelyn RetretaNo ratings yet
- Neonatal ResuscitationDocument7 pagesNeonatal Resuscitation2012100% (3)
- Fetal CirculationDocument5 pagesFetal CirculationChandu RajNo ratings yet
- 0419 Hospi LabDocument11 pages0419 Hospi LabbiancaNo ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument13 pagesFetal CirculationPraveen YadavNo ratings yet
- PlacentaDocument32 pagesPlacentaAbedur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Update Fetal Circulation - MDM AmyDocument10 pagesUpdate Fetal Circulation - MDM AmyNana Yunus100% (1)
- RevkeDocument11 pagesRevkeLowellyn Grezen VillaflorNo ratings yet
- HisterectomíaDocument2 pagesHisterectomíaTamara PricilaNo ratings yet
- COURSE UNIT WEEK 4 MaternalDocument9 pagesCOURSE UNIT WEEK 4 Maternalesmactal8408antNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy Care of Dev FetusDocument5 pagesNursing Care During Normal Pregnancy Care of Dev FetusLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy & Care of Developing FetusDocument15 pagesNursing Care During Normal Pregnancy & Care of Developing FetusLuna Sang-an100% (1)
- Fetal Circulation FinalDocument21 pagesFetal Circulation FinalpriyaNo ratings yet
- 11th Lecture Amnion& Amniotic FluidDocument35 pages11th Lecture Amnion& Amniotic FluidHussein Al Saedi100% (1)
- Exceptional Fetal Malformation Acardiac Headless TwinDocument2 pagesExceptional Fetal Malformation Acardiac Headless TwinInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyNo ratings yet
- Chapter 120. Septation of Ventricles, Truncus Arteriosus, and Conus Cordis - Review of Medical Embryology Book - LifeMap DiscoveDocument1 pageChapter 120. Septation of Ventricles, Truncus Arteriosus, and Conus Cordis - Review of Medical Embryology Book - LifeMap DiscoveMatthew GiscombeNo ratings yet
- Fetal Circulation 67406422Document21 pagesFetal Circulation 67406422Dexter BagarinaoNo ratings yet
- Physiologic Adaptation of The Newborn and Nursing AssessmentDocument108 pagesPhysiologic Adaptation of The Newborn and Nursing AssessmentRevathi DadamNo ratings yet
- Fertilization: Glora P. de Leon, RN, RM, ManDocument103 pagesFertilization: Glora P. de Leon, RN, RM, ManJoan VillafrancaNo ratings yet
- Female Pelvis and MeasurementsDocument21 pagesFemale Pelvis and MeasurementsBia KhanNo ratings yet
- Q4 Week 2 Female Reproductive Stem 11Document19 pagesQ4 Week 2 Female Reproductive Stem 11Arcyn CuramengNo ratings yet
- 1 Fetal CirculationDocument21 pages1 Fetal Circulationdr_mohanad100% (1)
- Terms and DefinitionsDocument5 pagesTerms and DefinitionskbNo ratings yet
- Umbilical Cord EOR - 163162 - 284 - 18220 - v1Document16 pagesUmbilical Cord EOR - 163162 - 284 - 18220 - v1Secret ImamNo ratings yet
- Gynecology - Pelvic AnatomyDocument2 pagesGynecology - Pelvic AnatomyEugen MNo ratings yet
- (OB) 1.03 Maternal Physiology - Dr. QuilangDocument6 pages(OB) 1.03 Maternal Physiology - Dr. QuilangMarlon BauagNo ratings yet
- Maternal Midterm TransesDocument24 pagesMaternal Midterm TransesTaegyu IS SAILING Periodt.No ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument22 pagesFetal CirculationJSeasharkNo ratings yet
- Abruptio PlacentaeDocument4 pagesAbruptio Placentaeeugeniamaranan.06No ratings yet
- Fetal and Placental Development - FETAL Sac, Umbilical Cord .Abnormalities of PlacentaDocument150 pagesFetal and Placental Development - FETAL Sac, Umbilical Cord .Abnormalities of PlacentaKripa SusanNo ratings yet
- Placenta: DR Nimco A Hassan Obstetrics and GynaecologyDocument62 pagesPlacenta: DR Nimco A Hassan Obstetrics and GynaecologyMahad Maxamed AxmedNo ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument2 pagesFetal Circulationapi-593562519No ratings yet
- Umblical CordDocument5 pagesUmblical CordprembarnabasNo ratings yet
- Obexam Anat PhysioDocument2 pagesObexam Anat PhysioChoy SavillaNo ratings yet
- (OBa) 1.4 Plcental GRWTH and Maturation (Marinas) - PacisDocument6 pages(OBa) 1.4 Plcental GRWTH and Maturation (Marinas) - PacisClyde Yuchengco Cu-unjiengNo ratings yet
- Fetal CirculationDocument13 pagesFetal CirculationHarish Kumar Kumawat100% (2)
- Anatomy and Embryology of Umbilicus in Newborns: A Review and Clinical CorrelationsDocument7 pagesAnatomy and Embryology of Umbilicus in Newborns: A Review and Clinical Correlationsbayu pamungkasNo ratings yet
- FETALDocument9 pagesFETALGunaNo ratings yet
- Enumerate The Parts and Discuss Its Function For The Following Organs/system of Farm AnimalsDocument27 pagesEnumerate The Parts and Discuss Its Function For The Following Organs/system of Farm AnimalsJaryll Vhasti P LagumbayNo ratings yet
- Umblical Cord AbnormalitiesDocument54 pagesUmblical Cord AbnormalitiesKeerti Patel100% (5)
- 2 NCM207-Sexuality PregnancyDocument4 pages2 NCM207-Sexuality PregnancyVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- 1 - NCM207 Maternity GoalsDocument2 pages1 - NCM207 Maternity GoalsVhiance Czaramae Lahuran100% (1)
- 4 - NCM207 - Fetal DevelopmentDocument4 pages4 - NCM207 - Fetal DevelopmentVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- 2 NCM207-Sexuality PregnancyDocument4 pages2 NCM207-Sexuality PregnancyVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- 3 - NCM207 - The Anatomy and Physiology of The Reproductive SystemDocument9 pages3 - NCM207 - The Anatomy and Physiology of The Reproductive SystemVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- 1 - NCM207 Maternity GoalsDocument2 pages1 - NCM207 Maternity GoalsVhiance Czaramae Lahuran100% (1)
- 4 - NCM207 - Fetal DevelopmentDocument4 pages4 - NCM207 - Fetal DevelopmentVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- 1 - NCM207 Maternity GoalsDocument2 pages1 - NCM207 Maternity GoalsVhiance Czaramae Lahuran100% (1)
- 3 - NCM207 - The Anatomy and Physiology of The Reproductive SystemDocument9 pages3 - NCM207 - The Anatomy and Physiology of The Reproductive SystemVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- 2 NCM207-Sexuality PregnancyDocument4 pages2 NCM207-Sexuality PregnancyVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- 1 NCM207 Maternity GoalsDocument2 pages1 NCM207 Maternity GoalsVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- 4 - NCM207 - Fetal DevelopmentDocument4 pages4 - NCM207 - Fetal DevelopmentVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- 3 - NCM207 - The Anatomy and Physiology of The Reproductive SystemDocument9 pages3 - NCM207 - The Anatomy and Physiology of The Reproductive SystemVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- 1 - NCM207 Maternity GoalsDocument2 pages1 - NCM207 Maternity GoalsVhiance Czaramae Lahuran100% (1)
- 2 NCM207-Sexuality PregnancyDocument4 pages2 NCM207-Sexuality PregnancyVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- 4 - NCM207 - Fetal DevelopmentDocument4 pages4 - NCM207 - Fetal DevelopmentVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- 3 - NCM207 - The Anatomy and Physiology of The Reproductive SystemDocument9 pages3 - NCM207 - The Anatomy and Physiology of The Reproductive SystemVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- 2 NCM207-Sexuality PregnancyDocument4 pages2 NCM207-Sexuality PregnancyVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- 3 - NCM207 - The Anatomy and Physiology of The Reproductive SystemDocument9 pages3 - NCM207 - The Anatomy and Physiology of The Reproductive SystemVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- 4 - NCM207 - Fetal DevelopmentDocument4 pages4 - NCM207 - Fetal DevelopmentVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- 4 - NCM207 - Fetal DevelopmentDocument4 pages4 - NCM207 - Fetal DevelopmentVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- 1 - NCM207 Maternity GoalsDocument2 pages1 - NCM207 Maternity GoalsVhiance Czaramae Lahuran100% (1)
- 2 NCM207-Sexuality PregnancyDocument4 pages2 NCM207-Sexuality PregnancyVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- 3 - NCM207 - The Anatomy and Physiology of The Reproductive SystemDocument9 pages3 - NCM207 - The Anatomy and Physiology of The Reproductive SystemVhiance Czaramae LahuranNo ratings yet
- MOV'SDocument5 pagesMOV'SRoderick CristobalNo ratings yet
- 2q Summative Exam Mapeh 8Document2 pages2q Summative Exam Mapeh 8Kristel Mariz OriaNo ratings yet
- Ncert Solutions For Class 8 March 31 Science Chapter 10 Reaching The Age of AdolescenceDocument6 pagesNcert Solutions For Class 8 March 31 Science Chapter 10 Reaching The Age of Adolescencekanchansharma7840No ratings yet
- CK PracticeDocument9 pagesCK PracticeAppu ayyala100% (1)
- Ayushman Bharat YojanaDocument28 pagesAyushman Bharat YojanaParth VasaveNo ratings yet
- ALL Pediatrics End-Block MCQsDocument18 pagesALL Pediatrics End-Block MCQsSarwar Sarkawt100% (1)
- 4.b. Bogin Et Al - 2007 PDFDocument12 pages4.b. Bogin Et Al - 2007 PDFGabriela EspinosaNo ratings yet
- Case BookDocument1 pageCase Bookedrinsne100% (2)
- Maternal Lec CompreDocument5 pagesMaternal Lec Compreshai espejoNo ratings yet
- Unit 14 ReviewDocument14 pagesUnit 14 Reviewfrisma aulia ANo ratings yet
- Professional CV Rasha Abu BakerDocument4 pagesProfessional CV Rasha Abu BakerHamed NazariNo ratings yet
- Teenage PregnancyDocument49 pagesTeenage PregnancySam AlerozaNo ratings yet
- Reproduction Notes Biol1008 ANUDocument14 pagesReproduction Notes Biol1008 ANUAbby FaureNo ratings yet
- Chloe Weng/QW2669 NTR 338W Final ManuscriptDocument15 pagesChloe Weng/QW2669 NTR 338W Final Manuscriptapi-536652711No ratings yet
- Video 1: Ethico Legal Considerations: The Ethical Principles or Bio-Ethical PrinciplesDocument9 pagesVideo 1: Ethico Legal Considerations: The Ethical Principles or Bio-Ethical PrinciplesBianx Flores DosdosNo ratings yet
- Fetal DistressDocument3 pagesFetal DistressMaria Donabella OngueNo ratings yet
- Breech Presentation Delivery CareDocument12 pagesBreech Presentation Delivery CareFatmaNo ratings yet
- Semen Analysis and Preparation: Aysha ItaniDocument11 pagesSemen Analysis and Preparation: Aysha ItaniFarid NurdiansyahNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy Induced HypertensionDocument21 pagesPregnancy Induced HypertensionLorren Frances Marie CalsarinNo ratings yet
- Module 2Document14 pagesModule 2mark ivanNo ratings yet
- Normal Delivery Checklist 2020Document4 pagesNormal Delivery Checklist 2020Ever Seneca EscaLeraNo ratings yet
- Prenatal AssessmentDocument2 pagesPrenatal AssessmentPrincess Pilove GawongnaNo ratings yet
- Elementary Animal ReproductionDocument8 pagesElementary Animal ReproductionJibachha SahNo ratings yet
- Stockley's Drug Interaction 9th Ed (2010) Halaman 1176Document1 pageStockley's Drug Interaction 9th Ed (2010) Halaman 1176Kharisma Aprilita RosyidahNo ratings yet
- Pointers To Review NMC CBTDocument2 pagesPointers To Review NMC CBTLouie Rudolf Kim67% (9)
- Study of Estrus Cycle in BuffaloesDocument31 pagesStudy of Estrus Cycle in BuffaloesMUHAMMAD AWAISNo ratings yet
- Module 3 - Human Sexuality and MarriageDocument10 pagesModule 3 - Human Sexuality and MarriageKatie HolmesNo ratings yet
- Animal Reproduction: The Process by Which Offspring Are ReproducedDocument25 pagesAnimal Reproduction: The Process by Which Offspring Are ReproducedTshegofatsoNo ratings yet
- Nutrition Bulletin - 2006 - Williamson - Nutrition in PregnancyDocument32 pagesNutrition Bulletin - 2006 - Williamson - Nutrition in PregnancyShahazaman ShazuNo ratings yet
- PPH 130212083247 Phpapp01Document25 pagesPPH 130212083247 Phpapp01Dauda Lawal dareNo ratings yet
- The Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityFrom EverandThe Age of Magical Overthinking: Notes on Modern IrrationalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (28)
- ADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDFrom EverandADHD is Awesome: A Guide to (Mostly) Thriving with ADHDRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (2)
- By the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsFrom EverandBy the Time You Read This: The Space between Cheslie's Smile and Mental Illness—Her Story in Her Own WordsNo ratings yet
- LIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionFrom EverandLIT: Life Ignition Tools: Use Nature's Playbook to Energize Your Brain, Spark Ideas, and Ignite ActionRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (404)
- Summary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedFrom EverandSummary: The Psychology of Money: Timeless Lessons on Wealth, Greed, and Happiness by Morgan Housel: Key Takeaways, Summary & Analysis IncludedRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (81)
- The Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsFrom EverandThe Ritual Effect: From Habit to Ritual, Harness the Surprising Power of Everyday ActionsRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (3)
- Raising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsFrom EverandRaising Good Humans: A Mindful Guide to Breaking the Cycle of Reactive Parenting and Raising Kind, Confident KidsRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (170)
- Love Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)From EverandLove Life: How to Raise Your Standards, Find Your Person, and Live Happily (No Matter What)No ratings yet
- The Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossFrom EverandThe Obesity Code: Unlocking the Secrets of Weight LossRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (6)
- Raising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsFrom EverandRaising Mentally Strong Kids: How to Combine the Power of Neuroscience with Love and Logic to Grow Confident, Kind, Responsible, and Resilient Children and Young AdultsRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (1)
- Think This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeFrom EverandThink This, Not That: 12 Mindshifts to Breakthrough Limiting Beliefs and Become Who You Were Born to BeRating: 2 out of 5 stars2/5 (1)
- Summary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia MD, With Bill Gifford: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (42)
- Mindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessFrom EverandMindset by Carol S. Dweck - Book Summary: The New Psychology of SuccessRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (328)
- Outlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandOutlive: The Science and Art of Longevity by Peter Attia: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (1)
- Why We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityFrom EverandWhy We Die: The New Science of Aging and the Quest for ImmortalityRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (4)
- Dark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.From EverandDark Psychology & Manipulation: Discover How To Analyze People and Master Human Behaviour Using Emotional Influence Techniques, Body Language Secrets, Covert NLP, Speed Reading, and Hypnosis.Rating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (110)
- Summary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisFrom EverandSummary: Limitless: Upgrade Your Brain, Learn Anything Faster, and Unlock Your Exceptional Life By Jim Kwik: Key Takeaways, Summary and AnalysisRating: 5 out of 5 stars5/5 (8)
- To Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceFrom EverandTo Explain the World: The Discovery of Modern ScienceRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (51)
- When the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisFrom EverandWhen the Body Says No by Gabor Maté: Key Takeaways, Summary & AnalysisRating: 3.5 out of 5 stars3.5/5 (2)
- The Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaFrom EverandThe Body Keeps the Score by Bessel Van der Kolk, M.D. - Book Summary: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of TraumaRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (266)
- The Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlFrom EverandThe Marshmallow Test: Mastering Self-ControlRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (58)
- Cult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryFrom EverandCult, A Love Story: Ten Years Inside a Canadian Cult and the Subsequent Long Road of RecoveryRating: 4 out of 5 stars4/5 (45)
- The Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeFrom EverandThe Courage Habit: How to Accept Your Fears, Release the Past, and Live Your Courageous LifeRating: 4.5 out of 5 stars4.5/5 (253)