Professional Documents
Culture Documents
MCN Trans
Uploaded by
Marc BantilanOriginal Description:
Copyright
Available Formats
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentCopyright:
Available Formats
MCN Trans
Uploaded by
Marc BantilanCopyright:
Available Formats
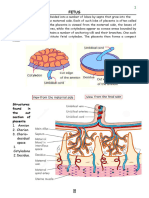
Fetal Circulation 2.
Ductus arteriosus-when the baby is
termed (38-42 weeks), become the
ligamentus arteriosum that would hold
the heart in place. If it does not close, it
will become patent ductus arteriosus
3. Foramen ovale-found in between the
right and left atrium, a pint hole that
would allow the blood from right atrium
toleft atrium to shunt. Normally, it is
closed. After immediately after delivery,
it will close. If not, it will make baby
FETAL CIRCULATION cyanotic, Tetralogy of Fallot (blue baby)
PLACENTA The blood from the placenta goes to the
umbilical vein, some of the blood goes to
UMBILICAL VEIN the liver, some to the ductus venosus, all
DUCTUS VENOSUS 40% LIVER go the inferior vena cava.
INFERIOR VENA CAVA
FOCUS OF FETAL DEVELOPMENT
First Trimester
o Organogenesis- Organogenesis
is the formation of organs
from the germ layers.
o -phase of embryonic
development that will start until
the birth of the baby
o -major body organs and systems
are formed
o -mother should not be exposed
• Fetal life- lungs do not function, but to communicable diseases such
through umbilical cord (the one that will as German measles, chicken
provide the oxygen as well as the pox, because organs will not
nutrients into the fetus and removes the completely form
waste from the fetus going to the placenta o Germ Layers-Endoderm,
going to the mother) and placenta (fetal mesoderm, ectoderm
lungs, oxygenated blood passes through Second Trimester
the umbilical vein (red) which enters the
I. Period of continued growth and
liver (40% of the blood) Umbilical
development- will take on new
arteries, responsible for carrying
meanings for the fetus. Time
unoxygenated blood from the fetus to the
placenta. where you want to know the
• Three mechanisms sex of the fetus. Where
1. Ductus venosus movement of fetus is felt- can
hear (best time to talk)
1. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
o -eyes gradually open, can hear progesterone hormone, cervical
any voice, weight and size softening
increases about 21 inches, 6-9 o Hegar’s sign (8th week)-
pounds, lungs start to mature softening of the lower uterine
Third Trimester segments causefd by pelvic
congestion due to enlarging fetus
o eriod of most rapid growth and
development- slow movement
and will position on the area
where he would descend
o Trying to position the head
down
o Hyperplasia happens- increase
cell, uterus enlarge to
o Hypertrophy- incerase size of
cells
o Post term 42 above o Chadwick’s sign (8th to 10th
o 38-42 full term week)-earliest sign, bluish
o Pre term 28-37 weeks purple discoloration/hue,
o Below 28 is abortion increased estrogen by increasing
o First cry of the baby= lungs are blood flow and engorgement that
functioning, by 38 weeks, the causes discoloration
placenta started to regress its
function, considered as the foreign
body
Hegers sign- pelvic congestion due to
enlarging fetus
NORMAL ADAPTATION IN PREGNANCY
REPRODUCTIVE SYSTEM o Cervix- earliest sign of
pregnancy which is having
o Uterus- uterine growth and discoloration
enlargement (under the influence of o Ovaries- (no ovulation, do not
estrogen with the myometrial cells in produce egg/ova, but produces
the muscle fibers to undergo progesterone)
hyperplasia-cells and hypertrophy- o Vagina- more acidic (pH 3.5 to 6 to
fibers to accommodate growing help control the number of pathogens
fetus) in the vaginal canal)
o Braxton Hicks contractions-irregular o Leukorrhea-increase white
and painless contractions begins in 4 discharges, causes the smell of
months or 16 weeks of gestation pregnant mothers, not
o Becomes globular (4th month = encouraged pantyliners, but
16 weeks) clean now and then
o Goodell’s sign (4th week)- o Breast- enlarged– melanotropin
stimulation during the course of (secreted by pituitary gland that
pregnancy in the estrogen and causes nipple to be tender) colostrum
2. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
(milk containing antibodies to protect o Corticosteroids-contribute to moon-
the body)-areola is darkened, nipple face and pregnancy-induced
is enlarged hypertension (ECLAM)
o Spinnbarkeit test- to test is fertile or o Best position-left lateral position,
reproduce, if it will not be cut off in aside from decompressing,right
10 cm atrium will receive the blood from
• Musculoskeletal System IVC and SVC, If RLP, Mother’s RA
o Waddling walk is also compressed
o Symphysis pubis may separate • Integumentary System
lightly o Increased pigmentation
• Circulatory System o chloasma/ melasma-increased
o Increased blood volume 40% to 50% pigmentation on the face, mask of
(to supply metabolic demand) pregnancy
o Physiologic anemia/pseudoanemia- o Striae gravidarum -streches
decreased RBC in the plasma o Linea negra lining going up to the
(normal) sternum
o Supplemented by ferrous sulface o Increased
o Heart is displaced upward (left side, perspiration
if diaphragm is pushed below the
sternum)
o Increases cardiac output to 30%
o Palmar erythema- discoloration in
the palmar surface of the mother
• Gastrointestinal system
o Morning sickness (not a positive
indication, abnormal growth in the
o Supine hypotension/Vena-caval cervix, Hmole (Hydatidiform mole
syndrome (inferior vena cava is (HM), caused by increased secretion
compressed leading to decreased of the Human chorionic
cardiac output and cardiac venous gonadotropin
return ) o Increased salivation-ptyalin enzyme
o Increased WBC that would decrease appetite
o CR and RR increased to 10-15 bpm (ptyalism)
o Varicosities and edema (retention of o Heartburn/pyrosis/dyspepsia (due to
water found in lower extremities relaxed sphincter between the
normal on 3rd trimester) stomach and esophagus during
pregnancy, and relaxed gastric
content)
3. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
o Decreased motility because of • Endocrine System
increased progesterone leading o Increased metabolism of CHON
constipation (protein) and CHO (carbohydrates)
o Constipation o Increased insulin production by
• Respiratory system pancreas
o Increases RR o Slight enlargement of the anterior
o Dyspnea (diaphragm is displaced pituitary gland of mother, as well as
about 2 cm upward by enlarging the thyroid gland, because of
fetus) uncreased circulation of
o Increased tidal volume (estrogen- progesterone-induced effects
pump hypertrophy and o Thyroxine (T4) hormones increase
hyperplasia,progesterone-decreased and attaches into the globulin
airway resistance by causing the o If mother has thyroidism. Mother is
relaxation of the smooth muscles of discouraged to be pregnant
the bronchus, bronchioles and o Lactogen-hormone found in the
alveoli) placenta that causes diminished
o Increased vital lung capacity- effectiveness of the insulin
(maximum amount of air moved in o 2nd trimester- most number of CHO
and out of the lungs with force leading to increase of insulin
during respiration) production
o Decreased residual volume • Weight Gain -not ideal to gain weight in
• Urinary the first trimester and trimester, not
o Urinary frequency (uterus is lying on abrupt
the bladder, as the fetus grows, it o Weight distribution
compresses the bladder, and leading ▪ Fetus- 7lbs
to frequency of urination-1st ▪ Placenta- 1 lb
trimester) (increased progesterone- ▪ Amniotic fluid- 1.5lb
relaxation of the urethra and ▪ Uterus- 2lb
sphincter relaxation ▪ Blood volume-1lb
o Increases GFR (Glomerular filtration ▪ Breast 1.5-3lbs
rate) or the Glycosuria-2nd trimester, ▪ Fluid 2 lbs
increase in renal tubular reabsorption ▪ Fats 4-6 lbs
present because of kidney’s inability, ▪ total 20-25lbs
indication of gestational diabetes ▪
mellitus) SIGNS OF PREGNANCY
o UTI is common of preganncy • First Trimester
because of the relaxation of the o Presumptive sign- least indicative of
smooth muscles of the mother and pregnancy taken as simple entity
urinary sphincter, movement of ▪ Amenorrhea, morning sickness,
kidney in the urine is reduced breast changes, fatigue, urinary
o asymptomatic bacteriuria refers to frequency, enlarging of uterus
isolation of bacteria in an (myoma)
appropriately collected urine o Probable signs (can be documented
specimen from an individual without by the examiner, not true diagnosis)
symptoms of urinary tract infection
(UTI)
4. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
▪ Chadwick’s sign, Goodells, ▪ By weeks- based on LMP
Hegars, (+) HCG,-if present si ▪ MC Donald’s method
myoma (FH/4=no. In mos.) (32
o Positive sign cm/4=8 months)
▪ Ultrasound result ▪ Barthonlomew’s rule-
▪ Indication that individual is through the examination
pregnant estimated AOG by the
• Second Trimester relative position of the
o Presumptive signs uterus in the abdominal
▪ Quickening, skin pigmentation, cavity through IE
chloasma, linea negra, striae
gravidarum
a. TPAL Scoring
o Probable signs
▪ Enlarged abdomen, Braxton
(term+preterm+abortion+living)
Hicks, Ballotement (examining b. EDC (expected date of confinement)
response) Nagele’s rule (-3+7+1)
o Positive sign c. EFW (Estimated fetal weight)-
▪ FHT, fetal movements, fetal x- Johnson’s rule FH-N x K (constant
ray 155)
• Third Trimester N-represents if it is enagaged or not
o Presumptive signs N= 11 not engaged, N=12 if
▪ Quickening, skin pigmentation, engaged
chloasma, linea negra, striae Example: 32 fundic height -11 (not
gravidarum engaged) x 155
o Probable signs (constant)=3100grams to kg 3.1 to
▪ Enlarged abdomen, fetal outline, lb=6.82 lb
Ballotement (examining d. GPA- Gravidity, Parity, Abortion in
response) pregnancy
o Positive sign
Gravidity-Number of pregnancies a
▪ FHT, fetal movements,
woman have regardless of the
visualization of fetus by USD
number of months
-Include present pregnancy
PRENATAL CARE Parity- number of pregnancies who
reached age of viability (28 weeks)
DATA GATHERING Abortion-termination of pregnancy
before age of viability (below 28
o Demographic data (Name, age,
weeks or 660 grams)
address, marital status and
e. TPAL- Term-38-42 weeks AOG
complaint)-during delivery, mother
will follow the family name of the Preterm-28-37 weeks
father Post term-42 weeks above
o Obstetrical data Living number of children alive
o LMP (last Menstrual Period)- 1st f. Past Pregnancies- Methods of
day of LMP (kanus a ang unang delivery
adlaw sa katapusang regla) -Place of delivery (home, hospital or
o AOG (age of Gestation) health center)
5. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
g. Present Pregnancy (C/S section, B. 21 4/7
NSVD, NSVD assisted by vacuum, C. G9PsA3
assisted by forceps D. T3P4A3L7
-any complications by mother,
diabetic, hyperthyroidism A. 10 16 09
Medical Data- illness before -3 +7 +1
(hypertensive, asthmatic, during 7
pregnancy) B. Oct. 15
-because there are mothers who only Nov. 30
experience illness during the course of Dec. 31
pregnancy like diabetes mellitus (GDM) Jan. 31
-contour of the abdomen during the Feb. 28
course of pregnancy Mar. 16
151/7 - 21weeks and 4 days/7
Calculate the estimated date delivery
using Naegele’s rule
Lynne is a 28 year-old woman who
comes to the clinic with a history of
amenorrhea and a positive pregnancy test
result. Her last menstrual period began on
May 31,2021. She bleeds for the usual
amount of time and reports that the amount
of blood loss was normal assuming that
Lynne had a 28 days cycle. Use the naegele’s
rule to calculate her estimated date of birth.
Sample Computation
COMPUTATION
1. Mrs. K, a mother of 7 children, visits a The mother has 4 living children and she is
health center for prenatal checkup. 38 weeks pregnant. The mother delivered the 1st
History is taken she had her LMP on child at 36 weeks, the 2nd at 37 weeks, the rest
October 16, 2009. She abortion in 1996, at 40 weeks and 39 weeks. She had two
1999, 2001. She had a couple of abortions at 20 weeks. She had also a twin
identical twins whom she delivered gestation at 38 weeks but died after delivery.
prematurely in the year 2000 and 2004. A. G8 P5 A2
• (use March 16, 2010 as the date B. T4 P2 A2 L4
of visit) Assessment
• A. EDC 1. Physical Exam
• B. AOG in weeks -check for gpa and tpal
• C. GPA -cephalocaudal assessment
• D. TPAL -pay attention to teeth
-during pregnancy, there is an increased
Answers: hormone that causes the gums to be edematous,
A. 7-23-10 which leads to bleeding during brushing, lesions
6. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
and dental problems that gives a pathway for the stage 3- extend to pelvic wall
pathogens to enter the bloodstream stage 4- beyond pelvic floor to the
-meticulous dental examination and dental care organs (especially in the breast)
is important for pregnant mothers to prevent f. Pelvic Measurement- Pelvimetry- to check if
infections and other infections the pelvis of the mother is appropriate for the
2. Pelvic Exam-inform the mother to empty shoulder as well as the head of the fetus, to
bladder first determine if it is appropriate for normal delivery
a. internal examination (IE)-to determine signs of or caesarian section or any like vacuum or
pregnancy like Chadwick, Hegar’s and Goodell’s forceps
Sign
-responsibility of nurse to have jot down
notebook to have different areas to check during
IE
-Time is determined on the wall clock of the
hospital
Dilatation (size of cervical opening, expressed in
cm and maximum opening of the cervix is up to
10 cms
Effacement-rugae in the vaginal canal,
expressed in percentage, part where the doctor
will palpate, maximum effacement is 100%
Bag of Water-if it is leaking or intact
Station-how the baby is engaged in the pelvic
cavity, expressed in positive or negative
Negative-baby is still floating, not engaged in the
pelvic cavity
Positive-engaged
Presentation-cephalic (head-common),
shoulder (transverse), back (breech), common
Breech-in caesarian section
b. vaginal Speculum-instrument that is inserted
In the vagina of the mother to visually see what
is the alterations in the vagina
-to see signs
c. transvaginal ultrasound-to check the
presentation as well as the total health status of
the fetus
d. ballottement-through IE done
e. Papanicolaou test (PAP Smear)-examination to
determine the presence of malignancies
staging of malignant cells:
stage 1- confined to the cervix
stage 2- extend beyond the cervix-might
be in the rectum
7. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
FUNDAL GRIP
Determine presentation.
Stand beside the woman facing her. Place back
of the hands on the uterine fundus and palpate
the contents of the fundus. If the buttocks are in
the fundus, indicating a vertex presentation
(which is true 96% of the time), you will feel a
soft, irregular object that does not move easily.
However, if the head in the fundus, indicating a
breech presentation, you will palpate a smooth,
hard, round, mobile object.
UMBILICAL GRIP
2. Determine position.
Place both hands on the maternal
abdomen, one on each side. Use one hand to
support the abdomen while you palpate the
opposite side with the other hand. Repeat the
procedure.
g. Leopold’s Maneuver-noninvasive method of
assessing fetal presentation, position and
attitude. This method is also used to locate the
fetal back before applying the fetal monitor. PELVIC GRIP
1. Fundal grip- fetal position-when the 3. Confirm Presentation
nurse towards the head, hands in is the Place one hand over the symphysis pubis
abdomen and and attempt to grasp the part that is
2. Umbilical grip- fetal back & extremities presenting to the pelvis between your
3. Pawlik’s grip- engagement, you cannot thumb and fingers of one hand. In the
move the head of the baby vast majority of cases you will feel a
4. Pelvic grip- fetal attitude-bent or hard, round fetal head. If the part moves
extended head easily, it is unengaged. If the part is not
movable, engagement probably has
occurred. If the breech is presenting, you
will feel a soft irregular object.
8. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
-It is also important to know the blood type of
the mother
5. Urine Exam-pregnancy test after 6 weeks
-used to check the presence of protein and
albumin which is an indication
-urine dipstick test
-albumin- if the patient is hypertensive or
PAWLICK’S GRIP eclamptic
4. Determine the attitude. -If benedict test is done to determine the glucose
Begin the last step by turning to face the in urine, which could be indication of GDM
woman’s feet. Use finger pads of the first three -also important to know presence of infection
fingers of each hand. Palpate in a downward DANGERS OF PREGNANCY
motion in the direction of the symphysis pubis. If Complications may arise in the course of
a hard bony prominence is felt on the side pregnancy. It is important to report
opposite the fetal back, you have located the immediately, so it can be dealt before if
fetal brow, and the fetus is in an attitude of something happens to the patient.
flexion. If the bony prominence is found on the A. Vaginal bleeding
same side as the fetal back, you are palpating the -No matter how slight the bleeding is,
occiput, and the fetus in in an attitude of report because it might lead to
extension. complications.
- Placenta previa- low implantation of
placenta that would cause painless
bleeding as the baby will push against
the cervical opening (minute rupture of
blood vessels)
- Abruptio placenta- premature
separation of placenta, presented with
vaginal bleeding but painful
2. Vital Signs - Premature labor- does not reach age of
Increase in RR-add 5-10 if it is a pregnant viability (28 weeks below)
mother - Threatened abortion (nothing done to
Increase in BP-Ask mother regarding the pregnancy but there is already
past BP, IF 130/90-Normal because of bleeding that occurs naturally):
the demand of the fetus for oxygenation • Spontaneous abortion- aborted w/o
-If there is an increase of 30 mmHg things done or miscarriage
systolic, and 15 mmHg diastolic, that • Septic abortion-something is done
would give an alarm because it is could to remove the baby, like quack
be (pregnancy-induced hypertension or doctors
Eclampsia) • Induced abortion- caused by
4. Blood studies-mother is subject to CBC to artificial or mechanical means to
check for hemoglobin level as well as the stop pregnancy and remove the
hematocrit in preparation to delivery, normally it baby
is 500 cc loss, the mother can still manage, if
caesarian- 1000cc- it would cause hemodilation
to the mother
9. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
• Therapeutic abortion- performed -If swelling in the face and fingers is present,
by licensed physicians as a form of hypertension is present.
treatment. G. Rapid weight gain
• If mother is having cancer and Weight should be gradual. Weight
having chemotherapy, therapeutic pattern is more important
abortion is given. H. Flashes of lights or dots before the
B. Persistent vomiting-1 or 2 times a eyes (hypertension in pregnancy)
day is normal I. Dimness or blurring of vision
Hyperemesis gravidarum- due to (hypertension in pregnancy)
systemic infection. This will deplete J. Severe headache cannot be relieved
nutritional supply to the fetus that will with medication (hypertension in
cause dehydration pregnancy)
• Admit to hospital and IV Fluid to K. Decreased urine output (oliguria)
infuse
C. Chills and fever- due to infection/
dehydration/ benign gastroenteritis DISCOMFORTS IN PREGNANCY
(MEDICATIONS) FIRST TRIMESTER
D. Sudden escape of fluid from vagina 1. NAUSEA AND VOMITING-due to increased
- PROM- Premature rupture of HCG level that would lead to changes in
Membrane (may indicate preterm carbohydrate metabolism
labor) The uterine cavity is no longer a. Eat dry crackers-it should be before arising,
sealed against the infection (amniotic let mother in upright position
fluid will prevent infection) b. Small frequent feeding-during the day
- If the fetus is too small, when the Bag of c. low fat meals-oily foods will stimulate
water rupture, the cord will descend vomiting
first causing interruption of d. Avoid fried foods
oxygenation, or it might cause umbilical e. Avoid antiemetics-medications that would
prolapse decrease the incidence of vomiting
- The head does not fit snugly into the 2. SYNCOPE-fainting caused by increase in
cervix so the umbilical cord will come blood volume or anemia or fatigue or sudden
first which may lead to prolapse position changes
- What doctors do is to push the baby’s a. Sit with feet elevated
presenting part and cord b. Change position slowly
E. Abdominal or chest pain c. Left lateral position-to relieve pressure of the
- May be due to Ectopic pregnancy, as uterus and inferior vena cava
fetus enlarges, the fallopian tube
cannot extend its size FIRST THROUGH THIRD TRIMESTER
- Abruptio placenta or the premature 3. BREAST TENDERNESS-due to increased
separation of the placenta estrogen and progesterone
- Uterine rupture a. Use supportive bra with elastic strap- breast
- Pulmonary embolism-caused by blood is engorged so it is heavy
or air causing blockage b. Avoid soap in the nipples and areola-this can
F. Swelling of face and fingers cause some dryness and minute cracks
(pregnancy-induced hypertension)
10. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
4. INCREASED VAGINAL DISCHARGES-cause of SECOND AND THIRD TRIMESTER
the lavagement increased estrogen level and 8. HEARTBURN or dyspepsia-increased
blood supply in the vaginal epithelium as well as progesterone level that maintain the pregnancy
the cervix of the mother causes decreased GI motility and
a. Proper cleaning and hygiene esophageal reflux, displacement of the stomach
b. Wear cotton underwear-absorb discharges or by enlarging fetus
use pantyliners without scent and changed a. Small frequent feeding
every 4 hours b. Sit upright for 30 minutes after meal
c. Avoid douching-fluid could be forced into the c. Drink milk between meals
uterine cervix d. Avoid fatty and spicy foods
d. Consult physician if infection is suspected-if e. Avoid antacids (one that would help coat the
the smell is accompanied by foul smell abdominal wall to prevent heartburn) unless
e. Full bath daily to wash accumulated prescribed by physician
secretions in the body 9. ANKLE EDEMA-observe if it is also occurring
5. NASAL STUFFINESS-1st to 3rd trimester due in the face, proteinuria-lead to hypertension
to estrogen, which causes swelling in the nasal causing relaxation of the blood vessels, causing
tissues as well as dryness in the tissues vasodilation, venostasis, increasing pressure to
a. Use humidifier-boiling water the ankle of the mother due to increasing
b. Avoid nasal sprays and antihistamines weight of the fetus
(medication that would help to humidify the a. Elevate legs at least twice a day
nasal portion of the mother) b. Wear support stockings-not be narrow as it
6. FATIGUE-due to increased metabolic will constrict blood vessels and impede
requirement which can be relieved by rest and circulation
sleep c. Avoid one position for long periods of time-
a. Frequent rest periods-do not sleep in the should be on the left side lying position to
morning, after lunch is recommended, rest increase glomerular filtration rate (which will
periods should be arranged within the day give good venous return)
-avoid stimulants d. Avoid diuretics- medications that would help
b. Regular exercise-fitted in the number of eliminate the urine
months, be encouraged by walking 30 minutes 10. VARICOSE VEINS-due to the weight of the
c. Avoid stimulants distended uterus that will puts pressure on the
7. URINARY FREQUENCY AND URGENCY-the vein returning blood in the lower extremities.
normal occurrence due to the pressure of the As a result, there will weakening of the walls of
growing fetus or anterior bladder, increased the vein and venous congestion occurs
progesterone, it will relax the muscle in the a. Wear support stockings
urethra b. Elevate feet when sitting
a. Increase oral fluid intake- c. Lying with feet and hips elevated-supported
b. Limit fluid intake in the evening with pillow
c. Void at regular intervals-have urination every d. Move out while standing
2 hours e. Avoid pressure on lower legs
d. Sleep on the side at night-left lateral; f. Avoid leg crossing-sole attached on the floor
e. Wear perineal pads if necessary-non-scented g. Avoid standing or sitting in long period of
pantyliners every 4 hours. time
h. Avoid constricting clothing
11. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
11. HEADACHES-occur as a result in changes in 16. LEG CRAMPS-as a result of altered calcium
the blood volume and vascular tone and phosphorus content and pressure in the
a. Change position slowly nerves due to prolonged sitting
b. Apply cool cloth at forehead-in a lying a. Exercise
position b. Elevate and dorsiflex the feet while resting
c. Eat small snack c. Increase calcium intake
d. Use pain relievers when prescribed or
acetaminophen RECOMMENDED EXERCISE
12. HEMORRHOIDS-due to increased venous Safety precautions for exercises during
pressure or caused by constipation, blood pregnancy should be observed. Never exercise
vessels that protrude to the point of fatigue. Always rise from the
Mothers are given ferrous sulfate-this will cause floor to prevent orthostatic hypotension. To rise
constipation on the floor, roll on the side first to prevent
a. Warm sitz bath-ordered by the doctor strain in the abdominal muscles.
b. High fiber diet (apple causes constipation) 1. Tailor sitting-with the legs parallel so
c. Increase oral fluid intake-2 liters per hour that one does not compress, this will
d. Exercise-walking, a person who is sitting in strengthen the thighs and the structure
one position will lead to constipation of the perineal muscles
e. Apply ointments/suppositories as prescribed- 2. Squatting-done third trimester to have
need doctor’s order, given in SPH is to relieve her EDC and tighten the structure of the
constipation is medications muscles, balance, help to balance
3. Pelvic Floor contraction (Kegel’s
13. CONSTIPATION-due to decreased intestinal Exercise)-to help the uterine muscles to
motility that would cause displacement in the strengthen, squeeze surrounding the
intestine and as well as taking iron vagina
a. High fiber diet 4. Abdominal Muscle contraction-tighten
b. Increase oral fluid intake abdominal muscles and help to relax
c. Exercise like blowing a candle
d. Avoid laxatives-suppositories 5. Pelvic Rocking-makes the lumbar spine
14. SHORTNESS OF BREATH- more flexible and help to lengthen or
a. Rest periods stretch the spine of the mother, during
b. Elevate head while sleeping-45 degrees bed deliver mother is extended in her
or moderate high back rest lithotomy position, to facilitate proper
c. Avoid overexertion- delivery of the fetus
15. BACKACHE-waddling walk, as the pregnancy
progresses, due to exaggerated lumbosacral
growth
a. Encourage rest
b. Use body mechanics
c. Wear Low-heeled shoes
d. Exercises
e. Sleep on firm mattress
12. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
LABOR
⮚ A series of events when the product
of conception is expelled out from
the woman’s body.
⮚ Regular uterine contractions cause
progressive dilatation of the cervix
and sufficient muscular force to
allow the baby to be pushed outside.
⮚ Usually begins when the fetus is
sufficiently mature.
⮚ series of event which the uterus
contraction expel the placenta???
13. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
THEORIES OF LABOR below ischial spine-positive (ex. +2),
1. Uterine stretch theory crowning
- contraction of the uterus would (-2) taas pa sa ischial spine
indicate labor begins. -the size of the fetus will fit in the
- any hollow organ, when stretched pelvis of the mother done through
to maximum, will contract or explode pelvimetry
2. Oxytocin and prostaglandin diagonal conjugate-AP diameter
theory transverse diameter-inlet of the
- works together to inhibit calcium pelvis
binding in muscle cells, raising gynecoid-appropirate for childbirth
intracellular calcium thus activating 2. Passenger- fetus and placenta
contractions. -composes placenta and the fetus
- the pressure on the cervix, 3. Power- uterine contraction, uterine
stimulates the pituitary gland, which muscles, and mother’s ability to
works with prostaglandin push during contraction
3. Progesterone deprivation theory a. once there is contraction-
- a decrease in progesterone causes mother will start pushing
uterine changes 4. Psyche- mother’s psychological
- labor pain occurs. condition
- when there is a decrease of -Emotional condition of the mother
progesterone, the uterine contracts 5. Position, maternal position-
4. Prostaglandin theory London(standing) the gravity push
- prostaglandin stimulates the baby
myometrium thus labor onset to Philippines (lithotomy position)
contract.
- initiation of labor contraction is THE PELVIS
caused by the interplay of the
adrenal gland of the fetus
5. Placental aging theory
- insufficient nutrients to reach the
fetus, no longer produce estrogen
and progesterone. Thus, labor
begins.
-when it reaches the full term, the
placenta will be considered a foreign
body
-one of the mechanisms is to expel
the placenta
-placenta will decrease in fxn
COMPONENTS OF LABOR (5 P’s)
1. Passageway- mother’s pelvis,
cervix and vagina
a. during labor, coccyx bone would
move to allow the baby to pass
ischial spine-where you will imagine
14. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
9
Gynecoid
- most appropriate for normal spontaneous
vaginal delivery (NSVD)
Platypeloid
- broad and flat
- transvers, not allowed for NSVD,; bears no
resemblance
Antropoid
- resembling the pelvis, posterior
presentation
Android
- inlet is a little bit triangular
- shaped as heart
- natrow lateral view
15. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
AREAS OF CONCERN: Station- relationship of the fetal
Internal Os presenting part to the level of the ischial
External Os spine
Thinning of Vaginal Canal
expressed by centimeters, max is 10cm
iF THIN, THIS AS A PAPER
Durine IE, if the doctor will tell about
effacement, expressed in percentage.
halfway-shaving
Retractor is used
Engagement- settling of the fetal
presenting part into the ischial spine
-if not reached in the ischial spine, not
engaged,
-expressed in positive or negative (not
engaged)
- -3,-4,-5 is floating -If it is in 7-8 cm already, the mother is
placed in the delivery table
-0 is in the level of Ischial spine -ADMISSION DIRECT DR: mother is
-+3, +4, +5-the baby is crowning placed directly to the delivery table,
-IE is done once ideally in the shift, it will skipping the Emergency room
contract further the myometrium
-MULTIPARA: multiple pregnancies; Figure: VERTEX CEPHALIC
thus may not be engaged PRESENTATION
-PRIMIPARA: non-engaged of the head
in the beginning of the labor; thus
indicating complications (abnormal
presentation, abnormal position,
abnormal presentation of the fetal head
like Anencephaly)
16. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
-lying inn is not allowed to handle first
delivery
-first baby- in the hospital (because
complications from first baby cannot be
detected and treated in the lying inn)
a. 1st degree- skin is lacerated
b. 2nd degree- skin and muscles
c. 3rd degree- external sphincter of rectum
together with skin and muscles
d. 4th degree- mucus membrane of rectum
- suturing is done
- In lying inn, the owner will allow nurses to
do the suturing and IE
DILATION PERINEUM
- opening of the cervical os Episiorrhaphy-repair of the surgical cut
- from 1 cm-10 cms (fully dilated cervix) site of episiotomy:
- due to uterine contraction and a. Median episiotomy
amniotic fluid b. Right mediolateral
- if there will be rupture of the bag of water c. Left mediolateral
you expect for faster effect of uterine
contraction Equipment in DR:
Gravida 1-okay ra -Ward notebook
Gravida 10-good luck, fast stretching of -Jot down notebook exclusive for or and dr
uterus because of Multipara Number of -Information from the case/patient should be
pregnancy, will not abot sa table signed by CI and Head NURSES and
written in log notebook (if not, you have to
EFFACEMENT repeat a case)
- thinning of the cervical canal -3 cases of cord care
-rogue kay mawala
- expressed in % (100% is a fully dilated PASSENGER- FETUS AND PLACENTA
cervix) • fetal skull of the fetus is the largest part of
Primipara-there is none engagement of the the body
head in the beginning of labor> some • the least compressible of all parts (fetal
complications like abnormal presentation skull)
or the abnormality of the feral heal • the most frequent presenting part
Anencephaly-baby has no skull -to allow the fetus to come out, it should be
Multipara-multiple pregnancy under go in the process of molding
(overlapping)
-Suture lines help in the process of
VAGINAL CANAL delivery> This undergoes overlapping/
- one of the passageway of the fetus molding> Facilitates in the delivery> Goes
- has rugae and capable of stretching but back to its original form
can be lacerated: (inside, not in the Anterior fontanel- diamond-
perineum) -6 months to heal
17. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
-affects delivery if its too long
Posterior fontanel- closes right after delivery -Vertex: usual presenting part of the fetus
-sometimes it closes after 3 months (rare
cases)
Vertex Presentation
-the most appropriate
Military Presentation
-body is not flexed
Full extension
-the baby may have taken some of the
water from the bag of water; may cause
aspiration when the baby is out; will cause
Anterior fontanel obstruction of the respiratory system of the
-aka bregma baby
-Diamond-shaped fontanel
-close at 18 months
Anteroposterior Diameter of the head
18. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
Fetal Lie
-relation of the long axis of the fetus to the
long axis of the mother
19. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
-Needed to be CS
Single Footling breech
-if the doctor is experienced, this may be
delivered normally
The skull is capable of molding to effectively
deliver fetus outside delivery
Umbilical prolapse
-delikado
Twin pregnancy
-There must be 2 FHT
-confirmed in ultrasound
20. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
Position-position of the fetal presenting part
to he specific quadrant of the mother
Quadrants:
Upper quadrant (right and left)
Lower quadrant (right and left)
normal FHT (fetal heart tone) 120-160
-indicate which quadrant you have taken the
FHT
21. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
-Ex: RUQ 120 • Auscultation of FHT
- through stethoscope
FETAL LANDMARKS -Leopold’s maneuver should be done before
Occiput - vertex/cephalic presentation (O) this
Mentum- chin/ face presentation (M) • Sonography (USD)
Sacrum - in breech presentation (Sa)
Acromion - scapula/shoulder presentation
(A)
FETAL POSITION -represented by 3-letter
abbreviation.
1ST letter - L (left) or R (right) quadrant
2ND - fetal landmarks (OMSaA)
3RD - A (anterior), P (posterior) T
(transverse) Left Occiput Anterior
presentation
Right Occiput Anterior
-Ex: LOA (Left occiput anterior)
METHODS TO DETERMINE FETAL
POSITION
• Leopold's manuever
- Helps in locating the position of fetus
-noninvasive method of assessing fetal
presentation, position and attitude. This
method is also used to locate the fetal back
before applying the fetal monitor.
• IE/Vaginal exam
- done by physician only Left Occiput Transverse
22. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
Right Occiput Transverse Direct Occiput Posterior
Direct Occiput Anterior
Left Occiput Posterior
Right Sacrum Posterior
Right Occiput Posterior
23. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
PRELIMINARY SIGNS OF LABOR
1. Lightening
2. Braxton Hick's contraction
- irregular and painless contractions
begins in 4 months or 16 weeks of
gestation
3. Cervical changes
- accompanied by cervical effacement
No contraction = no pushing
as well as dilatation
-only blow with air
- There are clear secretions with
-pushing should only start when the dilation
blood streaks
is in 8cm
4. Bloody Show
-stop the pushing after the count of 10
- Cervical changes with blood
5. Loss of weight
UTERINE CONTRACTION
- during expected date of
Duration-referring to the beginning of
confinement, mother’s appetite is
contraction up to the end of the same
lost
contraction
6. Increase in activity level
-To check: Palms should be over the
abdomen of the mother
SIGNS OF TRUE LABOR
-”Ma’am, check lang nako ug nagkusog
na imong tiyan?” ⮚ Uterine Contractions
-should be timed ⮚ Effacement- shortening and thinning
of the cervical canal expressed in %
Frequency- beginning of contraction to the (fully dilated cervix is 100%)
beginning of another contraction ⮚ Dilation- opening of the cervical os
-should be time from 1 cm- 10 cms (fully dilated
cervix)
⮚ Uterine changes-
Intensity- start of the contraction up to the - Upper uterine segment
peak of contraction becomes thick and active to expel
-maindent pa ang fingers, out the fetus
-kasing tigas ng agtang - Lower uterine segment
increment-increase in contraction becomes thin and because of the
-ACME-: peak of contraction pressure, it will help the fetus push
- DECREMENT: decreasing in contraction; out
the contraction subsided
-time-an ang kamot sa abdomen; in ⮚ Physiological retraction ring
seconds - is formed the boundary between
the lower and upper uterine
(SEQUENCE:INCREMENT>ACME>DECR segment
EMENT)
DIFFERENCE BETWEEN FALSE AND
Contraction- surest sign that labor is TRUE LABOR
already starting FALSE LABOR
-monitor intensity, duration, and frequency
24. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
• Irregular interval contractions - rapid increase of duration
• Pain in the abdomen - Frequency take 3-5 seconds
• Intensity remains the same - duration is about 30 seconds and of
• Intervals remain long moderate intensity
• Walking gives relief - mother is losing control of herself
• No bloody show (eg. shouting and crying mother)
• No cervical changes -oa era of the mother (!!!)
• Contractions stops with sedation -never give health teachings (pt is
not interested)
TRUE LABOR -monitor vital signs (don’t take bp if
• Regular interval of contraction nagbusog ang tiyan ng mother-increased
• Starts at the back to abdomen pressure in the peripheral ___
• Contractions are intensified -do not take fht (if there is
• Intervals gradually shorten contraction of the uterus, the fht will lower
• Intensified by walking down) because of the vagus nerve which
• With bloody show will stimulate bradycardia
• Cervical dilatation and effacement - fetal heart tone (N: 120-160)
• Does not stop with sedation -fht every 30 min monitoring
- Take fht and other vital signs EVERY 30
STAGES OF LABOR MINUTES
First stage - Dilatation/Dilation stage
-expect rupture of bag of water Transitional Phase
- Beginning of true labor contractions - 8-10 cm
and ends with the full dilatation of - PA and IE is done
cervix - get all info of pt
- rupture of amniotic fluid - Take fht and other vital signs
different phases: - EVERY 15 MINUTES
Latent Phase - this is the time, the baby is about to
-mild intensity of the abdomen expel
- early time of labor
- 2-3 cm dilatation Fetal Heart Tone
- contractions are of regular short - If fht is abnormal, advice the mother
duration to change position (LEFT side lying
- excited mother position, left lateral position, sim’s
- 15-30 seconds tapart position, left recumbent position);
- Takes about 8-12 hours Not on the right because the right
- Implement health teachings Ma’am, artery may be compressed
during sa active phase mo, pwede - Through FHT, we will know that
ka mag blow. Push like murag there is fetal distress
nalibang ug tubol; labor must be
consistent para di magbalik-balik Fetal Distress
ang ulo ni baby -thrashing
- Take fht and other vital signs -fetal tachycardia
EVERY HOUR -fetal bradycardia
-poop (???)
Active Phase (accelerated phase) -giving emotional support
- cervix is 4-7 cm
25. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
Second Stage- Fetal expulsion stage -lowspinal injected in 5th lumbar space
-announce that the baby is out (Ex. •Epidural
BABY OUT, at 2:13pm) •
-declare also the gender Side effect- post anesthesia headache,
-give emotional support to the mother hypotension
Third Stage- Placental Stage Elevate legs- to induce venous return on the
- brain, we d not deprive the brian from
oxygen
Fourth Stage- Recovery Fast drip-full, label lalagyan ng plaster, sa
- level ng 300 ilagay, resume previous drip,,
regulate the regulator into 120 cc/hr
FIRST STAGE OF LABOR Let patient lie for 12 hours and IOFI
14. Start IVF as ordered
15. Assist in amniotomy (artificial rupture of
membranes)
16. Watch out for SUBIRBA
17. Emotional support
WHEN TO POSITION PATIENT FOR
DELIVERY?
S - Severe uterine contraction
-complete dilation of the cervix
U - Urge to defecate
-because of the pressure of the
presenting part
B - Bearing down sensation
-increasing but we have to inform when
NURSING CARE DURING THE 1ST STAGE to do the pushing
1. Admission care I - Increase bloody show
2. Data gathering -vaginal discharges is becoming
3. Assisting IE increased
4. Leopold’s manuever R - Ruptured Bag of Water
5. Fetal Heart Tone (FHT) Monitoring B - Bulging of the perineum
6. Uterine Contraction Monitoring -you cannot identify where is the minora
7. Promote change in position and majora
8. Empty the bladder A - Anal dilation
9. Hygiene -pwet ng manok
10. Enema administration - depends if there
is an order Spontaneously ruptured- no need
11. Perineal preparation artificial rupture
12. Analgesic administration as ordered
13. Assist in the administration of regional
anesthesia- (sedation)
-
-pudendal-sacrospinous ligament
-paracervical
26. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
INTERNAL ROTATION
CARDINAL MOVEMENTS -allow the vertex
OR -extension begging the rotation
MECHANISMS OF LABOR
-passage of the fetus through te birth
canal that involves number of different
position changes to keep the smallest
diameter of the fetal head always
presenting to the smallest diameter of
the fetal head
THE DESCENT
-downward movement of the biparietal
diameter of the fetal heal with the pelvic
inlet
-inlet is already engaged during the
pushing of the mother
Stations of presentation- Fetal Head
positions during descent
INTERNAL ROTATION
.
FLEXION
-as the descent occurs, the fetal head
reaches the pelvic floor
Extension Beginning (rotation complete)
27. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
EXTENSION External Rotation (Shoulder rotation)
EXPULSION
-right hand, slide sa likod hanggang sa
extremities ng bata
-maslide tungod sa vernix caseosa
Extension Complete
Expulsion
EXTERNAL ROTATION
HEAD IS VISIBLE
External Rotation (Restitution)
-plus 3
-after the two shoulder, the whole body
follows
External Rotation (Restitution)
EXTERNAL ROTATION
28. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
CROWNING ASSIST IN THE EXTERNAL ROTATION
-plus 4 -once the baby is already out you have to
wipe the face to avoid aspiration
-labia is already pedamatus
EASING THE HEAD OUT INITIAL AUCTIONING OF MOUTH AND
NOSE
-the nurse should push the labia to help
the mother to eas
DELIVER THE SHOULDER
-once the cord is coiled, ease first the
cord
29. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
DELIVER THE BODY
CLAMPING AND CUTTING THE
THOROUGH SUCTIONING OF THE
UMBILICAL CORD
NEWBORN
-fold the chord, and check the pulsation
-once the baby is out, you need to do the
declaration - the clamp should be 2 inches from the
base of placenta
-Suction while the baby’s body is still in.
-2 inches from the clamp, place the
-Wipe the face when the body is fully out
forceps
then facilitate the Unang Yakap
-before you close the clamp, check 1st
-Upon expulsion of the baby, declare the
the pulsation. If there’s no pulsation,
time and its sex (Ex. Baby out at 2:32,
clamp it.
baby is a girl)
-The baby will stay in the mother’s chest
for 90 minutes. But if the baby’s Apgar
Score is not good, then 90 minutes is not
applicable
NURSING CARE ON SECOND STAGE
1. Lithotomy position
2. Perineal flushing
3. Drape aseptically
30. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
4. Teach breathing technique during uterine uniform from getting splashed by
relaxation blood
- When the cord is already separated
5. Teach pushing technique during uterine
form the baby, it gets longer. Thus,
contraction
you have to coil it until the perineum
6. Assist episiotomy of the mother (hold the tip of the
scissor to serve as stopper)
7. Do ritgen’s maneuver
- The doctor puts pressure using OS 2. Placental delivery
to the lacerated part of perineum Schultz delivery- fetal, shiny
until the baby goes out Duncan delivery- maternal, dirty,
rough
8. Ease head out, wipe face and do initial
suctioning Detachment and Delivery of 1st Placenta
9. Wait for external rotation - If placenta is not complete, the
doctor will clean it manually or
10. Pull head downward and upward to through the use of an instrument
deliver the shoulders - If this is not thoroughly removed, the
mother will continue to bleed
11. Deliver the body
12. Take note of time of delivery and sex of
the baby
13. Place baby on mother’s abdomen
14. Palpate for the pulsation of the cord
15. Clamp the cord near the vulva
16. Milk the cord towards the baby
17. Clamp 1 inch apart from initial clamping
18 Cut the cord.
THIRDSTAGE OF LABOR
(PLACENTAL STAGE)
1. Placental separation
a. Calkin’s sign-uterus becomes
globular and firm
b. Uterus rises above the abdomen
c. Sudden gush of blood
d. Lengthening of the cord
- While waiting for the baby to come
out, stay in the middle or in front of
the perineum. But during placental
separation, move aside to avoid
31. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
9. Promote uterine contraction:
- massage the hypogastric area
- Apply ice pack on the hypogastric
area
- Administer medication:
Oxytocin/Maleate (usually the IV has
oxytocin already)
- Empty the bladder
10. Inspect perineum for lacerations
11. Assist in episiorrhaphy
12. Do perineal care
DELIVER THE PLACENTA
13. Apply contoured brief/adult diaper
- the mother can’t be placed in the
stretcher if bleeding is seen in the
diaper
14. Make patient comfortable
- when covering the lower extremities,
seal or tuck in the end part of the
blanket
NEONATAL PERIOD
1. Airway
NURSING CARE ON THIRD STAGE
- wipe mouth and nose
1. Wait for signs of placental separation - suction
2. Do Brandt Andrew’s Maneuver - stimulate to cry (by massaging the
back)
- While coiling the cord, you are - oxygen administration (Attach a
massaging it cone-shape paper to serve as the
baby’s breathing mask)
3. Do Crede’s Maneuver
- hook to respiratory machine
- The coiling of the cord -
-
4. Gently pull the placenta downward 1. Temperature
5. Take not for the time of placental delivery - dry the baby
- wrap with towel
6. Check for type of placental delivery: - gooseneck lamp; or placing plastic in
the crib before the lamp (to maintain
7. Take BP once the placenta is out
the heat in the nursery)
8. Check for completeness of cotyledons - avoid unnecessary exposure
- place inside incubator
32. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
2. Proper identification abdominal circumference= 28-30
- name bond (Ex. Baby Girl Atillo and cms
the date of delivery) 8. Vital signs
- foot prints Heart rate= 120-160 bpm
3. Care of the cord Respiratory'= 40-60 bpm
- milking the cord Temp(rectal)- 36-37.6
- cord dress aseptically (not done to
pre-term unless the doctor orders
which is also dependent on the
baby’s weight; also because it is
where the IV is injected)
4. Care of the eyes
Crede's prophylaxis (prevents
ophthalmia
neonatorum) - terramycin
5. Vitamin K injection -if the legs are bending, just follow its
contour when measuring
-Head circumference: make sure to not
include fingers
-Chest circumference: basis is the nipple
of the baby ( should be inline with the
6. Newborn assessment nipple, and make sure to check if its
APGAR scoring- done on the first 1 parallel with the back of the baby)
and 5 mins of life
9. Head to toe assessment
a. Head- biggest part of the body of
the baby
moldings
fontanels
- will close at 18 months
(anterior), and after delivery
or at 3 months (posterior)
Score interpretation caput succedaneum
- this is a condition of the head
0-4= Poor of the newborn cause by
in serious danger and needs edema
resuscitation - Birth-related trauma due to
5-6= condition is guarded pressure
may need airway clearing and - Subsides for a couple of
oxygen days
Baby needs to be monitored closely - No treatment is needed
7-10= good - But the baby may experience
newborn is doing well discomfort
7. Anthropometric measurements cephalhematoma
Birth weight= 2.5-3.5 kgs - blood clot, pressure caused
Length= 45-55 cms by vacuum or forceps
Head circumference= 32-35.5 cms
Chest circumference= 30-33 cms
33. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
- caused by rupture of the
blood vessels in the
periosteum
- - no treatment CAPUT SUCCEDANEUM
- serous anguinosa
- we just need to put the head
cup of the newborn to
subside
suture lines
anencephaly
- When the brain of fetus is not
protected by a skull
- Brain is seen (only the
membrane covers it)
- Caused by Vitamin A
deficiency
b. Face CEPHALHEMATOMA
blink reflex
- Present til death -composed of blood in between scalp due to
strabismus pressure exerted during vacuum extraction
- Usually babies experience or forceps (that is usually done to ease the
strabismus delivery of the mother)
ears should be even or above
outer eye canthus
MOLDINGS
Anterior Fontanel
-sunkens if baby is having discomfort
-suture lines undergoes molding para lumiit
c. Chest= witch milk- normal upon
delivery to both sex of babies
d. Abdomen= check the umbilical
cord
= gastroschisis-
absence of abdominal
wall
- one of the neural
defect
e. Genitals
= should void within the 1st 24
hours
34. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
“if naka wiwi ang baby you = vernix caseosa
should inform the staff nurse, kay - this is the white cheese
if dili naka ihi there's a problem” substance but it is not be
=pseudomenses- Labia is removed
prominent and with blood, but - helps the adjustment of the
this is normal and will just baby in external temperature
eradicate - -helps regulate the
=testes should be descended temperature
(cryptorchidism- undescended - it melts and remove
testes which lead to infertility)
=preterm male has less rugae in = lanugo
the scrotum - fine hair that can be found in
= labia minora is prominent the shoulder
- it is due to unpigmented first
f. Extremities hair but it will be disappear
=flexed
=creases on the palm (Simean
= Milia
crease- only one crease)
polydactyl- extra toes or fingers - White spots like pimples,
(usually often asked by the found in the face of the
mother) newborn but prominent on
syndactyly — webbing of fingers the nose
=amelia- absence of upper - Do not prick and remove
extremities because it will just disappear
-needs further assessment after weeks
=tocophilia- absence of lower - Due to the sweat glands of
extremities the baby that is being
-usually causes by teratogens blocked
=clubfoot - needs no treatment
- If persists for 2-3 months,
g. Skin seek medical consultation
= color
- through Apgar Score MILIA
=Mongolian spots
- Marking of the skin after
birth, that will eventually
disappear
- Found in the back, at the
buttocks, spine, and should
- Present because of
melanocytes or the cell that
produces melanin, that
remains in the deeper layer
- Congenital-normal
melanocytosis
MONGOLIAN SPOTS
35. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
- bluish discoloration Puerperium/ postpartum period/ 4th
trimester/ recovery stage
- 6-8 weeks period after childbirth
during this time, the mother when admitted
has short stay, allowed to go home after 24
hrs, cesarean 3 days
-Post partum hemorrhage occurs mostly at
home
Involution- reproductive organs return to its
non-pregnant state
—-diri ra kutob madi—---------- -The uterus is expected to contract
immediately because if not, it may cause
hemorrhage
Subinvolution- failure of the reproductive
organ to return to its non-pregnant state
-checking of the substances left inside
Exfoliation- placental site heals by scaling
off dead tissues
-When the placenta detaches from the
endometrium
Atony- uterus does not have good muscle
tone and consequently relaxes
-if the uterus relax it leads also postpartum
hemorrhage
PRINCIPLES OF PUERPERIUM
• Promotion of healing and prevention of
illness
-One of the responsibility of the nurse is the
prevent the occurrence of illness
-We have to promote the wellness of the
client, continuously monitor the uterine
status of the mother, monitor vital signs to
know if there are alterations inside the body
o the mother, and CV
-We do not expect constipation
4TH stage- Puerperium / PP
36. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
-assess religiously different areas of the Temperature
mother to check if there are some risk that
may happen - increase on the 1st 24 hrs-
dehydration/effort in labor
• Prevent postpartal complications after 24 hours - infection
• establish successful lactation after 3-4 day- milk production
Expanded Breastfeeding Promotion Act -check the milk coming out from the
..RA 10028 nipples
Pituitary gland-produce oxytocin for -VS q15 if Post Partum
lactation
500ml of blood lost including
• Motivate use of family planning method electrolytes
• Provide emotional and psychological Pulse
support
- decrease due to decrease cardiac
-this is where the mother usually are output
neglected, check the wife mga goy,
postpartum blues will occur Blood pressure
- slightly decrease
- -peripheral bradycardia 50-70 bpm
- first 6-10 days which is normal
POSTPARTUM ASSESSMENT Tachycardia- occurs less frequent-r/t
to increased blood loss and
(AV BUBBLEHER) prolonged labor and birth
A = Appearance (when you check the color -base to the previous blood pressure
of the skin, lips and all)
-+30 is systolic/ +30 in
V = Vital Signs diastolic=postpartum hypertension
B = Breasts -it should remain constant
U = Uterus
B = Bladder Respiratory rate
B = Bowel - no changes
L = Lochia - expect 16-24 (without illness)
E = Episiotomy/Episiorrhaphy - slight elevation
H = Homan’s sign BREASTS
E = Emotion - drop in estrogen and
progesterone
R = Rhogam
you will also, note that there will be
VITAL SIGNS engorging (until the clavicle) of the
37. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
breast and will undergo physiological
changes
-check nipples if it is not inverted
- lactating
- you have to health teaching, warm
compress to increase breast milk
colostrum is present
Let-down reflex
- When the breasts starts to relax
- warm and tender
- engorged
- milk is produced by the 3rd – 4th
day
- veins are apparent
- Especially when engorging
UTERUS
6-12 hours
-Undergoes drastic changes during
postpartum Immediately after birth
- size is reduce: -put ice the hypogastric area
immediately after delivery- 1000 gms BLADDER
after end of 1s week -500gms
after 6 weeks - 50 gms Voiding should occur 4-6 hours postpartum
(6-8 hrs)
- placental site is sealed off
In C/S, we can monitor in the urobag
- cervical os are narrowed
-Apply cold water in the mons pubis
- painful during contraction (the after
pain that doesn’t need any pain medication BOWEL
only anti-inflammatory combined with
-Chromic 2O-leave it in the perineum
analgesic)
area
- let the uterus be contracted
• becomes more active soon after birth
• peptide hormone relaxin,-high
FUNDAL HEIGHT POST PARTUM circulating levels during pregnancy,
depresses bowel motility
• continued effects of of progesterone on the
smooth muscles
-decreased bowel motility
38. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
• bowel movement typically delayed until Assessment REEDA-redness, edema ,
2nd or 3rd puerperal date ecchymosis, discharges and approximation
• bowel tone is slowed -Redness: Betadine is not used in DR
because it may mask the redness of the site
• during labor, restriction of food (NPO)
-Ecchymosis: referring to discoloration. The
• fear of tearing the stiches
may turn to blue aside from res
LOCHIA
-Discharges: Not foul smelling
- discharges of the uterus after -Approximation of suture lines: take note of
delivery the number of stitches
- -also present in cesarean section or HOMAN’S SIGN
NSVD
- Refers to the deep tendon
Lochia rubra -1-3 days bloody red in reflexes
color - Assessed through dorsiflexion of
Lochia serosa-4-10 days, pink or lower extremities
brown color • used in assessment of deep venous
Lochia alba- 10-14 dyas creamy, thrombosis (DVT) in the leg
yeIIowish color • varicosities and signs of thrombophlebitis
If it is red after 10 days, refer (THROMBUS FORMATION)
because it might be postpartum hemorrhage inflammatory process that causes blood clot
- pattern should not reverse to form and block one or more veins
- increase in activity pedal pulses may be obstructed by
thrombophlebitis and should be
- decrease in breastfeeding
palpated with each assessment
(the discharges of the mother is few)
- not offensive in odor
EMOTIONAL STATUS
- without large clots
• sense of elation immediately after birth.
- present in CS
-the postpartum will occur
EPISIOTOMY
• mother wanted to talk about her labor and
• midline or mediolateral delivery
• lacerations -1st degree-skin , mucus • exhausted, need rest and sleep to restore
membrane her body to health
2nd degree-skin,mucus membrane,fascia • normally during the 1st 24 hours - passive,
3rd degree- skin , mucus membrane, preoccupied with own needs, talkative if
muscles, rectal sphincter unable to sleep
4th degree- involve all these structures plus • 1-2 days beginning to assume
anal wall responsibility
39. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
- NPO
Rh INCOMPATIBILITY
-Epektib sa 2nd, 3rd and 4th pregnancy Weight Loss
• possible when two specific circumstances - Diuresis
exist:
- Diaphoresis
-mother is Rh negative
- return to prepregnant weight at 6th week
-fetus is Rh positive -the father is
PROGRESSIVE CHANGES
Rh positive causes no harm to the mother,
but affects the fetus Lactation
*Inside the mother’s womb is the
Positive
-During 1st pregnancy, the Rh
negative of the mother cannot detect that
there is Rh positive na present
-But during the succeeding
pregnancies, the Rh negative will engulf the
Rh positive and will affect the fetus
Rhogam- Rh immune globulin, unsensitized
-28/7AOG,72 hrs PP-IM Icterus Gravis-RBC
are destroyed, fetal bilirubin increases=
-helps to immunize the Rh negative of the
mother so that when the Rh positive enters,
it will not be destroyed by the Rh negative
kernicterus-bilirubin encephalopathy
Erythroblastosis fetalis
-causing death to the fetus
Coomb’s test
Retrogressive changes
Exhaustion
- sleeplessness
- fetal movements
- after pains
- energy expenditures
40. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
THE CLUTCH OR FOOTBALL HOLD
SIDELYING OR RECLINING POSITION
HEALTH TEACHINGS FOR BREAST
FEEDING
1. Hand washing before and after
2. Clean nipple with water
3. Expose nipple to air
4. Feed the baby in short frequent intervals
and lengthen gradually
5. Alternate the breasts
6. Proper positioning
7. Adequate maternal nutrition and increase
OFI
8. Wear well-fitted bra THE CRADDLE
PROPER ATTACHMENT
Chin of the baby touches mother’s breast
Baby grasp not only the nipple but also the
areola Lower lip turned outward
Mouth wide open
PROPER POSITIONING
a. Head and lower body part must be
aligned
b. Baby is facing the mother
THE CROSS-OVER HOLD
c. Tummy to tummy
41. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
- woman is passive and dependent
- prefers talking about pregnancy,
labor and delivery
- uncertain in caring for newborn
- energies are focused on bodily
concerns
- uninterrupted sleep is important
- additional nourishment is necessary
- happens 1-2 days after delivery
2. Talking-hold Phase
- woman begin to initiate action
- interested in taking care of newborn
BREASTFEEDING - asserts independence
- mother focuses on regaining control
B - Best for baby, also best for mommy over her bodily functions — bowel
R - Reduces the incidence of allergies and bladder; strength and
endurance
E - Economical - no waste - happens 2 to 4 days after delivery
3. Letting-go Phase
A - Antibodies to protect baby against
- gives up old role
infection
- ready for her new role
S - Sterile and pure; stool inoffensive - postpartum depression most
commonly occurs
T - Temperature is always ideal
NURSING DIAGNOSES:
F - Fresh milk never goes off
• Actual/potential Fluid volume deficit
E - Easy once establish related to excessive bleeding of
E - Eradicates feeding difficulties birthing process/postpartum atony
D - digested easily • Pain related to uterine cramping
I - Immediately available (afterpains) or perineal sutures or
tissue damage related to childbirth
N - Nutritionally optimal; No mixing
required • Potential for impaired urinary
elimination related to perineal edema
G - Gastroenteritis greatly reduced
• Urinary retention related to bladder
DIFFERENT BURPING TECHNIQUE edema secondary to trauma during
• Over the lap delivery
• Tummy to tummy • Altered Pattern of Urinary
Elimination related to postpartum
• Over the shoulder Diure5is
• Holding the baby supported with one hand • Risk for Constipation related to loss
of bowel sensation after childbirth
EMOTIONAL PHASE OF PUEPERIUM
1. Talking-in Phase
42. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
• Acute pain / Alteration in comfort 7. Initiate breastfeeding
related to tissue damage secondary to
8. Monitor VS and watch for indications
birthing process
of hypovolemic shock
COMMON POST PARTUM
9. Prepare and assist for repair of
COMPLICATIONS
laceration, removal of fragments or
I. Hemorrhage blood loss more evacuation of hematoma
than 500 cc
10. Emotional support
a. Early post partum hemorrhage
II. Post Partum infection
» lacerations
a. Infection of the perineum
- cervix
> pain, heat, feeling of pressure in the
- vagina perineum, inflammation, redness, 1-2
sutures slough off, febrile
- labia
> remove the suture, drain and
- perineum
resuture
> hot sitz or warm compress
> atony — relaxed or boggy uterus
> perilight
causes: large babies
cesarean birth
b. Endometritis — infection of the
augmentation of labor
uterine endometrium
placental accidents
> abdominal tenderness
dystocia
> uterine atony
b. Late postpartum hemorrhage
> dark brown foul smelling lochia
> retained placental fragments > You -
> Management: oxytocin and fowler’s
pulled too hard on the cord-inversion of
position
uterus
> ruptured uterus
c. Mastitis
NURSING INTERVENTIONS
SOURCE OF INFECTION
1. Monitor fundus frequently
1. Endogenous (primary)
2. Massage the uterus
- Normal flora
3. Apply ice pack in the abdomen 2. Exogenous source
- Hospital personnel
4. Empty the bladder - Excessive obstetric manipulation
5. Regulate IVF as ordered - Break in aseptic technique
- Coitus in late pregnancy
6. Administer oxytocic agents - PROM
(Oxytocin/Maleate)
43. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
III. Thromboplebitis Concentrate on Antepartal (changes during
pregnancy), Intrapartum (when mother is
⮚ Signs and symptoms: already having the labor)
pain, stiffness, redness
swelling Not so much with the Postpartum (after
fever and chills delivery of the mother and placenta)
(+) Homan’s sign
⮚ Management
bed rest
elevate affected part analgesics
anticoagulant
elastic support to the affected part
⮚ Avoid:
frequent mobilization
thrombolytic agents
massage
POSTPARTUM DEPRESSION
• ” Many mothers experience a
“let down“ feeling after giving birth
related to the magnitude of the birth
experience and doubts about the
ability to cope effectively with the
demands of childbearing.
• ”This depression is mild and
transient, beginning 2 to 3 days after
delivery and resolving 1 to 2 weeks
HEALTH TEACHING
⮚ Self -Care
⮚ Infant care
⮚ Resumption of intercourse
⮚ PP exercises
⮚ Danger signs to be reported
COVERAGE FOR THE EXAM:
From the beginning to end.
44. by: Reynaldo Sumalinog, &
Sid Rian Frederick V. Laurente
You might also like
- Lexus - GS300 - GS430 - Service - Manual 1Document615 pagesLexus - GS300 - GS430 - Service - Manual 1seregap84100% (12)
- Maternal and Child Health NursingDocument22 pagesMaternal and Child Health NursingRam Van MunsterNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy Care of Dev FetusDocument5 pagesNursing Care During Normal Pregnancy Care of Dev FetusLuna Sang-anNo ratings yet
- Why Is This Happening To Me AgainDocument151 pagesWhy Is This Happening To Me Againochaynes11631100% (1)
- True HealthDocument112 pagesTrue Healthmarianaluca100% (2)
- Reproductive SystemDocument39 pagesReproductive SystemCenando Bodanio100% (1)
- MCN LectureDocument8 pagesMCN LectureEmily BernatNo ratings yet
- Fertilization To Conception: Maternal and Child Health Nursing PregnancyDocument8 pagesFertilization To Conception: Maternal and Child Health Nursing PregnancyNikki M. Arapol100% (1)
- Stages of Fetal DevelopmentDocument6 pagesStages of Fetal DevelopmentMark ElbenNo ratings yet
- Buscopan Drug StudyDocument3 pagesBuscopan Drug StudyMarc BantilanNo ratings yet
- Presented By-Ms. Nidhi Shukla M.Sc. Nursing 1 YearDocument43 pagesPresented By-Ms. Nidhi Shukla M.Sc. Nursing 1 YearFajar Islam SitanggangNo ratings yet
- RA 9231 (Special Protection For Children)Document5 pagesRA 9231 (Special Protection For Children)Lutchel Albis TanjayNo ratings yet
- RevkeDocument11 pagesRevkeLowellyn Grezen VillaflorNo ratings yet
- Origin and Development Organ System: MCN ARL: 11619Document5 pagesOrigin and Development Organ System: MCN ARL: 11619JacobNo ratings yet
- NCM 101Document8 pagesNCM 101Bing58No ratings yet
- Foetal DevelopmentDocument50 pagesFoetal Developmentdipendrakumarkushawaha44No ratings yet
- Prenatal CareDocument19 pagesPrenatal CareElla Mae MallorcaNo ratings yet
- Soft Mound of Fatty Tissue in Front ofDocument6 pagesSoft Mound of Fatty Tissue in Front ofKhristin Joy GamponiaNo ratings yet
- Presentation 1Document25 pagesPresentation 1vinuarunNo ratings yet
- DR - Sumeya: Normal Fetal Development and GrowthDocument42 pagesDR - Sumeya: Normal Fetal Development and Growthhussain AltaherNo ratings yet
- Kehamilan MuDocument65 pagesKehamilan MuKhalizaziaFaisalNo ratings yet
- Reproduction AnfismanDocument43 pagesReproduction AnfismanSyahirahNo ratings yet
- D.Fetal CirculationDocument5 pagesD.Fetal CirculationJulio NazarethNo ratings yet
- Juanpablo Miguel ZAVALETA RODRIGUEZ - Human ReproductionDocument23 pagesJuanpablo Miguel ZAVALETA RODRIGUEZ - Human ReproductionJuanpablo Miguel ZAVALETA RODRIGUEZNo ratings yet
- Reproduction in HumansDocument4 pagesReproduction in HumansIsra OmerNo ratings yet
- Week 2 Sex and FertDocument17 pagesWeek 2 Sex and FertAbmil Ching TinggalongNo ratings yet
- Pregnancy PowerPointDocument59 pagesPregnancy PowerPointHervis FantiniNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child (Family Concepts)Document22 pagesMaternal and Child (Family Concepts)Lenny SucalditoNo ratings yet
- Science 3rd QuarterDocument22 pagesScience 3rd QuarterBethel AquinoNo ratings yet
- The Growing Fetus For CPDocument19 pagesThe Growing Fetus For CPyzaNo ratings yet
- Module 1..lesson 1,2&3Document26 pagesModule 1..lesson 1,2&3Carlyn100% (1)
- CMCA Study Set 1 by MangloDocument6 pagesCMCA Study Set 1 by MangloYesha LouiseNo ratings yet
- Educ 11 Unit 2 ActivityDocument15 pagesEduc 11 Unit 2 ActivityQueen DaguroNo ratings yet
- Nursing Care During Normal Pregnancy & Care of Developing FetusDocument15 pagesNursing Care During Normal Pregnancy & Care of Developing FetusLuna Sang-an100% (1)
- Reproductive SystemDocument33 pagesReproductive Systemjheannegabriellea.ylaganNo ratings yet
- Conception and Fetal DevelopmentDocument69 pagesConception and Fetal Developmentbemina jaNo ratings yet
- The Reproductive SystemDocument18 pagesThe Reproductive Systemcmillica1176No ratings yet
- 8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesDocument13 pages8.7.10 REPRODUCTION IN HUMANS My CS NotesAndre KachigambaNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing (NCM 101 Lect) Part 1Document4 pagesMaternal and Child Health Nursing (NCM 101 Lect) Part 1yunjung0518100% (7)
- 107 Lec Prelim TopicsDocument22 pages107 Lec Prelim TopicsMary Ann SacramentoNo ratings yet
- Reproductive System Power Point AckroydDocument19 pagesReproductive System Power Point AckroydTrung Ngô Lê BảoNo ratings yet
- Obstetrics Day 1Document26 pagesObstetrics Day 1maggan donnaNo ratings yet
- Sexual Reproduction NotesDocument35 pagesSexual Reproduction NotesZelNo ratings yet
- Embryology IDocument94 pagesEmbryology Imasemola koketsoNo ratings yet
- REPRODUCTIONDocument78 pagesREPRODUCTIONglaizaNo ratings yet
- B.5 Care of The Pregnant Woman Going Through The Various Stages of PregnancyDocument11 pagesB.5 Care of The Pregnant Woman Going Through The Various Stages of PregnancySOLEIL LOUISE LACSON MARBASNo ratings yet
- NCM 101 LectureDocument6 pagesNCM 101 LectureGrace Sabater CAragayNo ratings yet
- Nur 214 HandoutsDocument6 pagesNur 214 HandoutsCharlz ZipaganNo ratings yet
- HAMILDocument82 pagesHAMILNandya CarolineNo ratings yet
- Lecture 3. FertilizationDocument52 pagesLecture 3. FertilizationBabbu YadavNo ratings yet
- Maternal and Child (Healthy Pregnancy)Document37 pagesMaternal and Child (Healthy Pregnancy)Lenny SucalditoNo ratings yet
- PlacentaDocument32 pagesPlacentaAbedur RahmanNo ratings yet
- Endocrine and Reproductive SystemsDocument53 pagesEndocrine and Reproductive Systemsapi-287032631No ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument58 pagesHuman ReproductionFelix HorseradaNo ratings yet
- The Growing Fetus FertilizationDocument6 pagesThe Growing Fetus FertilizationJustJ ThingsNo ratings yet
- Module 1.1 Reproductive SystemDocument12 pagesModule 1.1 Reproductive SystemPrincess Dela CruzNo ratings yet
- Stages of Human Development Before BirthDocument3 pagesStages of Human Development Before BirthAaronotix GamingNo ratings yet
- Group 2 Science-ReportDocument16 pagesGroup 2 Science-ReportIgnacio FelicityNo ratings yet
- 2776NEETZoologyReproductiveSystemTheory - Unlocked Opt PDFDocument21 pages2776NEETZoologyReproductiveSystemTheory - Unlocked Opt PDFMd Rizwan AhmadNo ratings yet
- PEDIA-REVIEWER EditedDocument7 pagesPEDIA-REVIEWER EditedTO THE MOONNo ratings yet
- Human ReproductionDocument42 pagesHuman ReproductionangelynNo ratings yet
- MCN Lec Antepartal To Ob ClassificationDocument11 pagesMCN Lec Antepartal To Ob ClassificationJay EstrellaNo ratings yet
- Placenta and Placental Hormones Lecture+PPT PDFDocument29 pagesPlacenta and Placental Hormones Lecture+PPT PDFPamela Marie Cope100% (1)
- NCM 208 Bioethics MIDTERMDocument2 pagesNCM 208 Bioethics MIDTERMMarc BantilanNo ratings yet
- FNCP Group 1 FinalDocument14 pagesFNCP Group 1 FinalMarc BantilanNo ratings yet
- Almazar Ritualistic-BehaviorDocument12 pagesAlmazar Ritualistic-BehaviorMarc BantilanNo ratings yet
- Urinary System SPC MLS1 Histo LabDocument10 pagesUrinary System SPC MLS1 Histo LabMarc BantilanNo ratings yet
- Phonic PA450 PDFDocument16 pagesPhonic PA450 PDFhplzNo ratings yet
- Thermo Plus 230 Thermo Plus 300 Thermo Plus 350: Heating SystemsDocument63 pagesThermo Plus 230 Thermo Plus 300 Thermo Plus 350: Heating SystemsДмитро ПоловнякNo ratings yet
- Catl Exp 2018 LR PDFDocument276 pagesCatl Exp 2018 LR PDFChera IlieNo ratings yet
- LD Flow ChartDocument1 pageLD Flow Chartapi-222173654No ratings yet
- 419E1BDocument3 pages419E1Bvidhyapmgrpsy2020No ratings yet
- Mineral Resources and Food ResourcesDocument31 pagesMineral Resources and Food Resourcesvaishali TMU studentNo ratings yet
- Hazardous Wastes Management Handling and Transboundary Movement Rules 2008Document40 pagesHazardous Wastes Management Handling and Transboundary Movement Rules 2008Shashank BhardwajNo ratings yet
- Suzuki 2017 Genuine Rigging Parts and AccessoriesDocument29 pagesSuzuki 2017 Genuine Rigging Parts and AccessoriesJose Luis HuilaNo ratings yet
- Prevention of Infection in The Hospital SettingDocument100 pagesPrevention of Infection in The Hospital SettingShantie Harun Al RosyidNo ratings yet
- MC HosvitDocument16 pagesMC Hosvitmarsha dechastraNo ratings yet
- Cylinder Head, Pressure Test (First), D7CDocument4 pagesCylinder Head, Pressure Test (First), D7CAl BimaNo ratings yet
- December IssueDocument104 pagesDecember Issuemiltonwcraft100% (1)
- Taxi ReceiptDocument17 pagesTaxi ReceiptPraveen KumarNo ratings yet
- Battery Fuses Megane 2Document18 pagesBattery Fuses Megane 2osdasoNo ratings yet
- Aerosoft Airbus X Extended - Normal ProceduresDocument26 pagesAerosoft Airbus X Extended - Normal Proceduresluka40No ratings yet
- The Nervous System Answer KeyDocument1 pageThe Nervous System Answer KeymichelleNo ratings yet
- Botulism Is A Serious Illness Caused by The Botulinum ToxinDocument10 pagesBotulism Is A Serious Illness Caused by The Botulinum ToxinReyNo ratings yet
- ANT341 Presentation 7Document2 pagesANT341 Presentation 7Dan Gideon CariagaNo ratings yet
- Fall 08 MC Newsletter Research Microscopy & Histology CoreDocument4 pagesFall 08 MC Newsletter Research Microscopy & Histology CoreslusompedsNo ratings yet
- Unit 6-Develop and Implement Proactive Monitoring Systems For Health and Safety RGDocument13 pagesUnit 6-Develop and Implement Proactive Monitoring Systems For Health and Safety RGAshraf EL WardajiNo ratings yet
- AmbergrisDocument4 pagesAmbergriskaram deolNo ratings yet
- Geriatric Nursing Oral Revalida and Skills Demonstration Case ScenarioDocument6 pagesGeriatric Nursing Oral Revalida and Skills Demonstration Case ScenarioGaea AngelaNo ratings yet
- Postpartum Clinical Prep SheetDocument3 pagesPostpartum Clinical Prep SheetKurata432No ratings yet
- The Persons With Disabilities 1995Document27 pagesThe Persons With Disabilities 1995siva ramanNo ratings yet
- Different Aspects of MindfulnessDocument38 pagesDifferent Aspects of MindfulnessShan BooksNo ratings yet
- Sympathetic Vs para SympatheticDocument2 pagesSympathetic Vs para SympatheticLesther Alba Dela CruzNo ratings yet